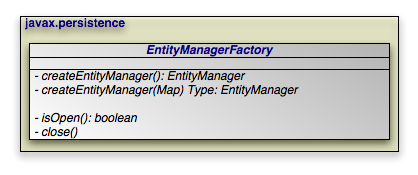
The EntityManagerFactory creates
EntityManager instances for application
use.
![[Note]](img/note.gif) | Note |
|---|---|
Kodo extends the standard |
Within a container, you will typically use injection
to access an EntityManagerFactory.
There are, however, alternative mechanisms for
EntityManagerFactory construction.
Some vendors may supply public constructors for their
EntityManagerFactory implementations, but
we recommend: using the Java Connector Architecture (JCA) in a managed
environment; using the Persistence class's
createEntityManagerFactory methods in an
unmanaged environment, as described in
Chapter 6, Persistence. These strategies allow
vendors to pool factories, cutting down on resource utilization.
JPA allows you to create and configure an
EntityManagerFactory, then store it in a
Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI) tree for later retrieval
and use.