11 Integration with Oracle Identity Management
This chapter describes how to integrate Oracle Enterprise Content Management Suite with Oracle Identity Management. It contains the following sections:
11.1 Credential and Policy Store Configuration
The following topics describe credential and policy store configuration in detail:
11.1.1 Overview of Credential and Policy Store Configuration
Oracle Fusion Middleware allows using different types of credential and policy stores in a WebLogic domain. Domains can use stores based on an XML file or on different types of LDAP providers. When a domain uses an LDAP store, all policy and credential data is kept and maintained in a centralized store. However, when using XML policy stores, the changes made on managed servers are not propagated to the Administration Server unless they use the same domain home. The enterprise deployment topology for Oracle Enterprise Content Management Suite uses different domain homes for the Administration Server and the managed servers, which means that Oracle requires the use of an LDAP store as policy and credential store for integrity and consistency. By default, Oracle WebLogic Server domains use an XML file for the policy store. The following sections describe the steps required to change the default store to Oracle Internet Directory LDAP for credentials or policies.
Note:
The backend repository for the policy store and the credential store must use the same kind of LDAP server. To preserve this coherence, note that reassociating one store implies reassociating the other one, that is, the reassociation of both the credential and the policy stores is accomplished as a unit using the Fusion Middleware Control or the WLST commandreassociateSecurityStore. For more information, see Section 11.1.4, "Reassociation of Credentials and Policies."11.1.2 Credential Store Configuration
A credential store is a repository of security data (credentials). A credential can hold user name and password combinations, tickets, or public key certificates. Credentials are used during authentication, when principals are populated in subjects, and, further, during authorization, when determining what actions the subject can perform. This section provides steps to configure Oracle Internet Directory LDAP as a credential store for the Oracle Enterprise Content Management Suite enterprise deployment topology. For more details on credential store configuration, refer to the "Configuring the Credential Store" chapter in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Security Guide.
The following section describe credential store configuration:
-
Section 11.1.2.2, "Moving the WebLogic Administrator to LDAP"
-
Section 11.1.2.3, "Reassociating the Domain Credential Store"
11.1.2.1 Creating the LDAP Authenticator
To be safe, before you create the LDAP authenticator, you should first back up the relevant configuration files:
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver/domain_name/config/config.xml ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver/domain_name/config/fmwconfig/jps-config.xml ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver/domain_name/config/fmwconfig/system-jazn-data.xml
Also back up the boot.properties file for the Administration Server.
To configure the credential store to use LDAP, set the proper authenticator using the WebLogic Server Console:
-
Log in to the WebLogic Server Console.
-
Click the Security Realms link on the left navigational bar.
-
Click the myrealm default realm entry to configure it.
-
Open the Providers tab within the realm.
-
Observe that there is a
DefaultAuthenticatorprovider configured for the realm. -
Click the New button to add a new provider.
-
Enter a name for the provider such as OIDAuthenticator or OVDAuthenticator depending on whether Oracle Internet Directory or Oracle Virtual Directory will be used.
-
Select the OracleInternetDirectoryAuthenticator or OracleVirtualDirectoryAuthenticator type from the list of authenticators depending on whether Oracle Internet Directory or Oracle Virtual Directory will be used.
-
Click OK.
-
In the Providers screen, click the newly created Authenticator.
-
Set the control flag to SUFFICIENT. This indicates that if a user can be authenticated successfully by this authenticator, then it should accept that authentication and should not continue to invoke any additional authenticators. If the authentication fails, it will fall through to the next authenticator in the chain. Make sure all subsequent authenticators also have their control flag set to SUFFICIENT; in particular, check the DefaultAuthenticator and set that to SUFFICIENT.
-
Click Save to save this setting.
-
Open the Provider Specific tab to enter the details for the LDAP server.
-
Enter the details specific to your LDAP server, as shown in the following table:
Parameter Value Value Description Host For example: oid.mycompany.comThe LDAP server's server ID. Port For example: 636The LDAP server's port number. Principal For example: cn=orcladminThe LDAP user DN used to connect to the LDAP server. Credential NA The password used to connect to the LDAP server. SSL Enabled Checked Specifies whether SSL protocol is used when connecting to LDAP server. User Base DN For example: cn=users,dc=us,dc=mycompany,dc=comSpecify the DN under which your Users start. Group Base DN For example: cn=groups,dc=us,dc=mycompany,dc=comSpecify the DN that points to your Groups node. Use Retrieved User Name as Principal Checked Must be turned on. Click Save when done.
-
Click Activate Changes to propagate the changes.
11.1.2.1.1 Setting the Order of Providers
Reorder the OID/OVD Authenticator and Default Authenticator and ensure that the control flag for each authenticator is set as follows:
-
OID LDAP Authenticator: SUFFICIENT
-
Default Authenticator: SUFFICIENT
Restart the Administration Server using the procedure in Section 5.5, "Starting the Administration Server on SOAHOST1."
11.1.2.2 Moving the WebLogic Administrator to LDAP
This section provides details for provisioning a new administrator user and group for managing Oracle Enterprise Content Management Suite's WebLogic domain in the enterprise deployment topology. This section describes the following tasks:
-
Section 11.1.2.2.1, "Provisioning Admin Users and Groups in an LDAP Directory"
-
Section 11.1.2.2.2, "Assigning the Admin Role to the Admin Group"
-
Section 11.1.2.2.3, "Updating the boot.properties File and Restarting the System"
11.1.2.2.1 Provisioning Admin Users and Groups in an LDAP Directory
As mentioned in the introduction to this section, users and groups from multiple WebLogic domains may be provisioned in a central LDAP user store. In such a case, there is a possibility that one WebLogic admin user may have access to all the domains within an enterprise. This is not a desirable situation. To avoid this, the users and groups provisioned must have a unique distinguished name within the directory tree. In this guide, the admin user and group for the ECM EDG WebLogic domain will be provisioned with the DNs below:
-
Admin User DN:
cn=weblogic_ecm,cn=Users,dc=us,dc=mycompany,dc=com
-
Admin Group DN:
cn=ECM Administrators,cn=Groups,dc=us,dc=mycompany,dc=com
Follow these steps to provision the admin user and admin group in Oracle Internet Directory:
-
Create an ldif file named
admin_user.ldifwith the contents shown below and then save the file:dn: cn=weblogic_ecm, cn=Users, dc=us, dc=mycompany, dc=com orclsamaccountname: weblogic_ecm givenname: weblogic_ecm sn: weblogic_ecm userpassword: Welcome1 obver: 10.1.4.0 mail: weblogic_ecm objectclass: top objectclass: person objectclass: organizationalPerson objectclass: inetorgperson objectclass: orcluser objectclass: orcluserV2 objectclass: oblixorgperson uid: weblogic_ecm cn: weblogic_ecm description: Admin User for the ECM Domain
-
Run the
ldapaddcommand located under the ORACLE_HOME/bin directory to provision the user in Oracle Internet Directory.Note:
The ORACLE_HOME used here is the ORACLE_HOME for the Identity Management installation where Oracle Internet Directory resides.For example (the command is shown as two lines in the example below for readability purposes, but you should enter the command on a single line):
OIDHOST1> ORACLE_HOME/bin/ldapadd -h oid.mycompany.com -p 389 -D cn="orcladmin" -w welcome1 -c -v -f admin_user.ldif -
Create an ldif file named
admin_group.ldifwith the contents shown below and then save the file:dn: cn=ECM Administrators, cn=Groups, dc=us, dc=mycompany, dc=com displayname: ECM Administrators objectclass: top objectclass: groupOfUniqueNames objectclass: orclGroup uniquemember: cn=weblogic_ecm cn=users,dc=us,dc=mycompany,dc=com cn: ECM Administrators description: Administrators Group for the ECM Domain
-
Run the
ldapaddcommand located under the ORACLE_HOME/bin directory to provision the group in Oracle Internet Directory (the command is shown as two lines in the example below for readability purposes, but you should enter the command on a single line):OIDHOST1> ORACLE_HOME/bin/ldapadd -h oid.mycompany.com -p 389 -D cn="orcladmin" -w welcome1 -c -v -f admin_group.ldif
11.1.2.2.2 Assigning the Admin Role to the Admin Group
After adding the users and groups to Oracle Internet Directory, the group must be assigned the Admin role within the WebLogic domain security realm. This enables all users that belong to the group to be administrators for that domain. Follow these steps to assign the Admin role to the Admin group:
-
Log in to the WebLogic Administration Server Console.
-
In the left pane of the console, click Security Realms.
-
On the Summary of Security Realms page, click myrealm under the Realms table.
-
On the Settings page for myrealm, click the Roles & Policies tab.
-
On the Realm Roles page, expand the Global Roles entry under the Roles table. This brings up the entry for Roles. Click on the Roles link to bring up the Global Roles page.
-
On the Global Roles page, click the Admin Role to bring up the Edit Global Role page:
-
On the Edit Global Roles page, under the Role Conditions table, click the Add Conditions button.
-
On the Choose a Predicate page, select Group from the drop down list for predicates and click Next.
-
On the Edit Arguments Page, specify ECM Administrators in the Group Argument field and click Add.
-
-
Click Finish to return to the Edit Global Rule page.
-
The Role Conditions table now shows the ECM Administrators Group as an entry.
-
Click Save to finish adding the Admin Role to the ECM Administrators Group.
-
Validate that the changes were successful by bringing up the WebLogic Administration Server Console using a web browser. Log in using the credentials for the weblogic_ecm user.
Note:
Each Oracle application in the Oracle ECM enterprise deployment topology may have its own predefined roles and groups defined for administration and monitoring purposes. By default, the "Administrator" group will allow these operations. However, this group may be too broad. For example, it may be undesirable that SOA administrators are also administrators for the Oracle WebLogic Server domain where Oracle SOA, I/PM and UCM are running. This is why it may be desirable, as suggested in this section, to create a more specific group such as "ECM Administrators." In order for the various applications to allow the ECM Administrators group to administer the different systems, you need to add the required roles to that group. For example, for SOA Worklistapp's administration, add the SOAAdmin role. Refer to each component's specific roles for the required roles in each case.11.1.2.2.3 Updating the boot.properties File and Restarting the System
The boot.properties file for the Administration Server should be updated with the WebLogic admin user created in Oracle Internet Directory. Follow the steps below to update the boot.properties file:
-
On SOAHOST1, go the following directory:
SOAHOST1>cd ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver/domain_name/servers/AdminServer/security
-
Rename the existing boot.properties file:
SOAHOST1> mv boot.properties boot.properties.backup
-
Use a text editor to create a file called boot.properties under the security directory. Enter the following lines in the file:
username=Admin_User password=Admin_User_Password
-
Save the file.
-
Stop the Administration Server:
SOAHOST1> cd ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver/domain_name/bin SOAHOST1> ./stopWebLogic.sh
-
Start the Administrator Server using the procedure in Section 5.5, "Starting the Administration Server on SOAHOST1."
11.1.2.3 Reassociating the Domain Credential Store
The reassociation of both the credential and the policy stores is accomplished as a unit using Fusion Middleware Control or the WLST command reassociateSecurityStore. See Section 11.1.4, "Reassociation of Credentials and Policies" for detailed steps.
11.1.3 Policy Store Configuration
The domain policy store is the repository of system and application-specific policies. In a given domain, there is one store that stores all policies that all applications deployed in the domain may use. This section provides the steps to configure Oracle Internet Directory LDAP as the policy store for the Oracle Enterprise Content Management Suite enterprise deployment topology. For more details on policy store configuration, refer to the "OPSS Authorization and the Policy Store" chapter in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Security Guide.
11.1.3.1 Prerequisites to Using an LDAP-Based Policy Store
In order to ensure the proper access to an LDAP server directory (Oracle Internet Directory) used as a policy store, you must set a node in the server directory.
An Oracle Internet Directory administrator must follow these steps to create the appropriate node in an Oracle Internet Directory Server:
-
Create an LDIF file (assumed to be
jpstestnode.ldifin this example) specifying the following DN and CN entries:dn: cn=jpsroot_ecm cn: jpsroot_ecm objectclass: top objectclass: OrclContainer
The distinguished name of the root node (illustrated by the string
jpsroot_ecmabove) must be distinct from any other distinguished name. One root node can be shared by multiple WebLogic domains. It is not required that this node be created at the top level, as long as read and write access to the subtree is granted to the Oracle Internet Directory administrator. -
Import this data into Oracle Internet Directory server using the
ldapaddcommand, as illustrated in the following example (the command is shown as two lines in the example below for readability purposes, but you should enter the command on a single line):OIDHOST1> ORACLE_HOME/bin/ldapadd -h ldap_host -p ldap_port -D cn=orcladmin -w password -c -v -f jpstestnode.ldif
-
Verify that the node has been successfully inserted using the
ldapsearchcommand, as illustrated in the following example (the command is shown as two lines in the example below for readability purposes, but you should enter the command on a single line):OIDHOST1> ORACLE_HOME/bin/ldapsearch -h ldap_host -p ldap_port -D cn=orcladmin -w password -b "cn=jpsroot_ecm" objectclass="orclContainer"
-
When using Oracle internet Directory as the LDAP-Based Policy Store run the
oidstats.sqlutility in the INFRADBHOST servers to generate database statistics for optimal database performance:OIDHOSTn> ORACLE_HOME/ldap/admin/oidstats.sql
The
oidstats.sqlutility must be run just once after the initial provisioning. For details about this utility, consult the Oracle Fusion Middleware User Reference for Oracle Identity Management.
11.1.3.2 Cataloging Oracle Internet Directory Attributes
An Oracle Internet Directory attribute used in a search filter must be indexed. The ldapmodify command, whose syntax is illustrated below, can also be used to index attributes specified in an LDIF file (the command is shown as two lines in the example below for readability purposes, but you should enter the command on a single line):
OIDHOST1> ORACLE_HOME/bin/ldapmodify -h host -p port -D bindDN -w bindPassword -v -f catalogue-modify-ldif-filename
For example, the above command can be used with the following sample LDIF file to catalog the createtimestamp and modifytimestamp attributes:
dn: cn=catalogs changetype: modify add: orclindexedattribute orclindexedattribute: modifytimestamp orclindexedattribute: createtimestamp
Each of the following Oracle Internet Directory attributes must be indexed:
orclrolescope orclassignedroles orclApplicationCommonName orclAppFullName orclCSFAlias orclCSFKey orclCSFName orclCSFDBUrl orclCSFDBPort orclCSFCredentialType orclCSFExpiryTime modifytimestamp createtimestamp orcljpsassignee
11.1.3.3 Reassociating the Domain Policy Store
Reassociating the policy store consists in migrating policy data from a file-based or LDAP-based repository to an LDAP-based repository; that is, reassociation changes the repository preserving the integrity of the data stored. For each policy in the source policy store, reassociation searches the target LDAP directory and, if it finds a match, it updates the matching policy as appropriate. If none is found, it simply migrates the policy as is.
At any time, after a domain policy store has been instantiated, a file-based or LDAP-based policy store can be reassociated into an LDAP-based policy store storing the same data. To support it, the domain has to be configured, as appropriate, to use an LDAP policy store.
The reassociation of both the credential and the policy stores is accomplished as a unit using Fusion Middleware Control or the WLST command reassociateSecurityStore. See Section 11.1.4, "Reassociation of Credentials and Policies" for detailed steps.
11.1.4 Reassociation of Credentials and Policies
To reassociate the policy and credential store with Oracle Internet Directory, use the WLST reassociateSecurityStore command. Follow these steps:
-
From SOAHOST1, start the
wlstshell:SOAHOST1>cd ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin SOAHOST1>./wlst.sh -
Connect to the WebLogic Administration Server using the
wlst connectcommand shown below:Syntax:
connect('Admin_User',"Admin_User_Password",t3://hostname:port)For example:
connect("weblogic","welcome1","t3://ADMINVHN:7001") -
Run the
reassociateSecurityStorecommand as shown below:Syntax:
reassociateSecurityStore(domain="domain_name",admin="cn=orcladmin", password="orclPassword",ldapurl="ldap://LDAP_HOST:LDAP_PORT",servertype="OID", jpsroot="cn=jpsroot_ecm")
For example:
wls:/ECMEDGDomain/serverConfig>reassociateSecurityStore(domain="ecmedg_domain", admin="cn=orcladmin",password="welcome1",ldapurl="ldap://oid.mycompany.com:389",servertype="OID",jpsroot="cn=jpsroot_ecm")
The output for the command is shown below:
{servertype=OID,jpsroot_ecm=cn=jpsroot_ecm_idm_idmhost1,admin=cn=orcladmin, domain=IDMDomain,ldapurl=ldap://oid.mycompany.com:389,password=welcome1} Location changed to domainRuntime tree. This is a read-only tree with DomainMBean as the root. For more help, use help(domainRuntime) Starting Policy Store reassociation. LDAP server and ServiceConfigurator setup done. Schema is seeded into LDAP server Data is migrated to LDAP server Service in LDAP server after migration has been tested to be available Update of jps configuration is done Policy Store reassociation done. Starting credential Store reassociation LDAP server and ServiceConfigurator setup done. Schema is seeded into LDAP server Data is migrated to LDAP server Service in LDAP server after migration has been tested to be available Update of jps configuration is done Credential Store reassociation done Jps Configuration has been changed. Please restart the server. -
Restart the Administration Server after the command completes successfully.
To restart the Administration Server, use the procedure in Section 5.5, "Starting the Administration Server on SOAHOST1."
Note:
For credential and policy changes to take effect, the servers in the domain must be restarted.
11.2 Oracle Access Manager Integration
This section describes how to set up Oracle Access Manager as the single sign-on solution for the Oracle Enterprise Content Management Suite enterprise deployment topology. It contains the following sections:
-
Section 11.2.1, "Overview of Oracle Access Manager Integration"
-
Section 11.2.5, "Configuring IP Validation for the EDG Webgate"
11.2.1 Overview of Oracle Access Manager Integration
Oracle Access Manager (OAM) is the recommended single sign-on (SSO) solution for Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g Release 1. For more information on installing and configuring an OAM installation, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Enterprise Deployment Guide for Oracle Identity Management. This chapter explains the procedure for configuring the Oracle ECM installation with an existing OAM installation and the underlying directory service. Oracle recommends using either Oracle Internet Directory (OID) or Oracle Virtual Directory (OVD) or both of these directory services.
Note:
The Oracle ECM enterprise deployment topology described in this book uses a single sign-on configuration where both the Oracle ECM system and the single sign-on system are in the same network domain (mycompany.com). For a multi-domain configuration, please refer to the required configuration steps in "Configuring Single Sign-On" of the Oracle Access Manager Access Administration Guide.11.2.2 Prerequisites for Oracle Access Manager
The setup for Oracle Access Manager (OAM) assumes an existing OAM installation complete with Access Managers and a policy protecting the Policy Manager. For more information on installing and configuring an OAM installation, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Enterprise Deployment Guide for Oracle Identity Management. This setup includes a directory service such as Oracle Internet Directory (OID) either as a stand-alone or as part of an Oracle Virtual Directory (OVD) configuration. This chapter provides the necessary steps for configuring your SOA installation with either OID or OVD.
In addition, the OAM installation should have its own Web server configured with WebGate. This section also provides the steps for using the OAM Web server as a delegated authentication server.
11.2.3 Using the OAM Configuration Tool
The OAM Configuration Tool (oamcfg) starts a series of scripts and sets up the required policies. It requires various parameters as inputs. Specifically, it creates the following:
-
A form authentication scheme in OAM
-
Policies to enable authentication in Oracle WebLogic Server
-
A WebGate entry in OAM to enable Oracle HTTP Server WebGates (from your Web Tier) to protect your configured application
-
A host identifier, depending on the scenario chosen (a default host identifier would be used, if not provided)
-
Policies to protect and unprotect application specific URLs.
This section covers the following topics:
-
Section 11.2.3.1, "Collecting the Information for the OAM Configuration Tool"
-
Section 11.2.3.3, "Verifying Successful Creation of the Policy Domain and AccessGate"
-
Section 11.2.3.7, "Configuring Delegated Form Authentication"
11.2.3.1 Collecting the Information for the OAM Configuration Tool
The following information should be collected or prepared prior to running the OAM Configuration tool:
-
Password: Create a secure password. This will be used as the password for the WebGate installation created later.
-
LDAP Host: host name of the directory server or load balancer address in the case of an HA/EDG configuration.
-
LDAP Port: port of the directory server.
-
LDAP USER DN: DN of the LDAP admin user. This will be a value such as "cn=orcladmin."
-
LDAP password: password of the LDAP admin user.
-
oam_aaa_host: host name of an Oracle Access Manager.
-
oam_aaa_port: port of the Oracle Access Manager.
11.2.3.2 Running the OAM Configuration Tool
The OAM Configuration tool resides in the MW_HOME/oracle_common/modules/oracle.oamprovider_11.1.1 directory. The tool can be run from any machine with the required installation files. In this case, we run it from ECMHOST1.
The OAM Configuration Tool should be run as follows (all on a single command line):
ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/jrockit_160_<version>/bin/java -jar oamcfgtool.jar mode=CREATE app_domain="ECM_EDG" protected_uris="/cs/idplg,/cs/groups,/imaging/faces,/em,/console,/DefaultToDoTaskFlow,/sdpmessaging/userprefs-ui" ldap_host=OID.MYCOMPANY.COM ldap_port=389 ldap_userdn="cn=orcladmin" ldap_userpassword=Password_of_LDAP_Admin_User oam_aaa_host=OAMHOST1 oam_aaa_port=OAMPORT1
You will be prompted for the app_agent_password. If your command ran successfully, you should see the following output:
Processed input parameters Enter app_agent_password: Initialized Global Configuration Successfully completed the Create operation. Operation Summary: Policy Domain : ECM_EDG Host Identifier: ECM_EDG Access Gate ID : ECM_EDG_AG
11.2.3.3 Verifying Successful Creation of the Policy Domain and AccessGate
Perform these steps to verify the policy domain:
-
Log in to Oracle Access Manager:
http://OAMADMINHOST:port/access/oblix/ -
Click Policy Manager.
-
Click the My Policy Domains link on the left panel. You will see a list of all policy domains, which includes the domain you just created. In the third column (URL prefixes), you will also see the URIs you specified during the creation of this domain).
-
Click the link to the policy domain you just created to go to the General area of this domain.
-
Click the Resources tab and you will see the URIs you specified. You can also click other tabs to view other settings.
Verifying the AccessGate Configuration
Perform these steps to verify the AccessGate configuration:
-
Click the Access System Console link on the top right-hand side (this acts like a toggle; after you click it, it becomes the Policy Manager link).
-
Click the Access System Configuration tab.
-
Click the AccessGate Configuration link on the left panel.
-
Enter 'ECM_EDG' as the search criterion (or any other substring you may have used as the
app_domainname in Section 11.2.3.2, "Running the OAM Configuration Tool"), and click Go. -
Once the access gate for the domain you just created shows up (this will have the suffix _AG (for example,
ECM_EDG_AG), click it, and you will see the details of the access gate you just created.
11.2.3.4 Updating the Host Identifier
The OAM Configuration Tool uses the value of the app_domain parameter to create a host identifier for the policy domain. This host identifier must be updated with all the host name variations for the host so that the configuration works correctly.
Perform these steps to update the host identifier created by the OAM Configuration Tool:
-
Navigate to the Access System Console by specifying the following URL in your web browser:
http://host_name:port/access/oblix
where
host_namerefers to the host where the WebPass Oracle HTTP Server instance is running andportrefers to the HTTP port of the Oracle HTTP Server instance. -
When prompted for a username and password, log in as an administrator. Click OK.
-
On the Access System main page, click the Access System Console link.
-
On the Access System Console page, open the Access System Configuration tab.
-
On the Access System Configuration page, click Host Identifiers at the bottom left.
-
On the List all host identifiers page, click on the host identifier created by the OAM Configuration Tool (for example, ECM_EDG).
-
On the Host Identifier Details page, click Modify.
-
On the Modifying host identifier page, add all the possible host name variations for the host. Click the plus and minus symbols to add or delete fields as necessary. The Preferred HTTP Host value used in the Access System Configuration must be added as one of the host name variations. For example:
ecmedg_wd,webhost1.mycompany.com:7777,admin.mycompany.com:7777. -
Select the check box next to Update Cache and then click Save.
A message box with the following message is displayed: "Updating the cache at this point will flush all the caches in the system. Are you sure?".
Click OK to finish saving the configuration changes.
-
Verify the changes on the Host Identifier Details page.
11.2.3.5 Updating the WebGate Profile
The OAM Configuration Tool populates the Preferred_HTTP_Host and hostname attributes for the WebGate profile that is created with the value of the app_domain parameter. Both these attributes must be updated with the proper values for the configuration to work correctly.
Perform these steps to update the WebGate profile created by the OAM Configuration Tool:
-
Navigate to the Access System Console by specifying the following URL in your web browser:
http://host_name:port/access/oblix
where
host_namerefers to the host where the WebPass Oracle HTTP Server instance is running andportrefers to the HTTP port of the Oracle HTTP Server instance. -
On the Access System main page, click the Access System Console link, then log in as an administrator.
-
On the Access System Console main page, click Access System Configuration, and then click the Access Gate Configuration Link in the left pane to display the AccessGates Search page.
-
Enter the proper search criteria and click Go to display a list of access gates.
-
Select the access gate created by the OAM Configuration Tool (for example, ECM_EDG_AG.
-
On the AccessGate Details page, select Modify to display the Modify AccessGate page.
-
On the Modify AccessGate page, update the following:
-
Hostname: Update the hostname with the name of the computer where WebGate is running, for example:
webhost1.mycompany.com. -
Preferred HTTP Host: Update the Preferred_HTTP_Host with one of the hostname variations specified in the previous section, for example:
admin.mycompany.com:7777. -
Primary HTTP Cookie Domain: Update the Primary HTTP Cookie Domain with the domain suffix of the host identifier, for example: mycompany.com
-
-
Click Save.
A message box with the "Are you sure you want to commit these changes?" message is displayed.
Click OK to finish updating the configuration.
-
Verify the values displayed on the Details for AccessGate page to confirm that the updates were successful.
11.2.3.6 Adding Additional Access Servers
Perform these steps to assign an access server to the WebGate:
-
Log in as the Administrator on the Access System Console.
-
Navigate to the Details for AccessGate page, if necessary. From the Access System Console, select Access System Configuration, then AccessGate Configuration, then the link for the WebGate (ECM_EDG_AG).
-
On the Details for AccessGate page, click List Access Servers.
-
A page appears showing the primary or secondary Access Servers currently configured for this WebGate.
Click Add.
-
On the Add a New Access Server page, select an Access Server from the Select Server list, specify Primary Server, and define two connections for the WebGate.
Click the Add button to complete the association.
-
A page appears, showing the association of the Access Server with the WebGate. Click the link to display a summary and print this page for later use.
-
Repeat steps 3 through 6 to associate more access servers to the WebGate.
11.2.3.7 Configuring Delegated Form Authentication
Perform these steps to configure the form authentication to redirect to the WebGate that was installed with the OAM installation:
-
Open the Access System Console.
-
In the Access System Configuration screen, select Authentication Management from the left-hand bar.
-
Select OraDefaultFormAuthNScheme.
-
Click Modify.
-
In the Challenge Redirect field, enter the host and port of the IDM installation; for example:
http://sso.mycompany.com.
A WebGate should already be installed in the IDM installation. Refer to Oracle Fusion Middleware Enterprise Deployment Guide for Oracle Identity Management for details.
11.2.4 Installing and Configuring WebGate
WebGate needs to be installed on each of the WEBHOSTn machines in order to secure the web tier:
-
Launch the WebGate installer (see Section 1.8, "What to Install" for information on where to obtain it) using the following command:
WEBHOSTn> ./Oracle_Access_Manager10_1_4_3_0_linux_OHS11g_WebGate –guiNote:
There is a known issue with the Oracle Access Manager installer that sometimes manifests as a hang at install time on Linux. This is a third-party issue caused by InstallShield. To work around this issue, follow these steps:-
Copy and paste the following in the shell where you start the installer:
cd /tmp mkdir bin.$$ cd bin.$$ cat > mount <<EOF #! /bin/sh exec /bin/true EOF chmod 755 mount export PATH=`pwd`:$PATH
-
Run the installation.
-
When the installer is finished running, clean the temporary directory using this command:
rm -r /tmp/bin.$$
-
-
The Welcome screen is displayed. Click Next.
-
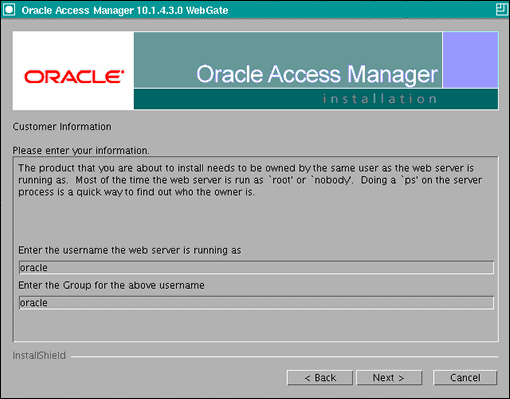
In the Customer Information screen (Figure 11-1), enter the user name and user group that the web server is running as. Click Next to continue.
-
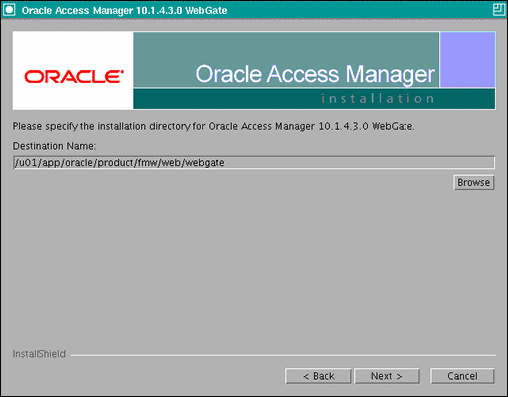
In the installation target screen (Figure 11-2), specify the directory where WebGate should be installed. Click Next to continue.
-
In the installation summary screen, click Next.
-
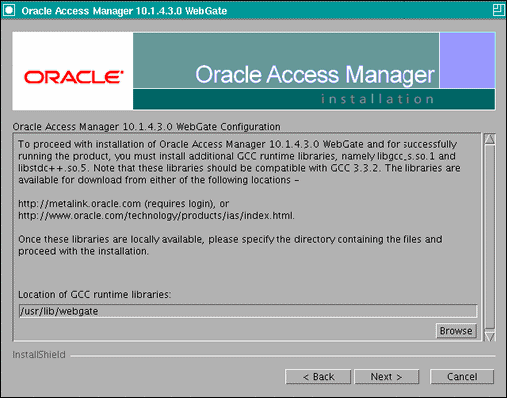
Download the required GCC runtime libraries for WebGate as instructed in the WebGate configuration screen (Figure 11-3), and use Browse to point to their location on the local computer. Click Next to continue.
-
The installer now creates the required artifacts. After that is completed, click Next to continue.
-
In the transport security mode screen (Figure 11-4), select "Open Mode: No Encryption" and click Next to continue.
Figure 11-4 Transport Security Mode Screen

Description of "Figure 11-4 Transport Security Mode Screen"
-
In the WebGate configuration screen, provide the details of the access server that will be used. You must provide the following information:
-
WebGate ID, as provided when the OAM configuration tool was executed
-
Password for WebGate
-
Access Server ID, as reported by the OAM Access Server configuration
-
Access Server host name, as reported by the OAM Access Server configuration
-
Access Server port number, as reported by the OAM Access Server configuration
Note:
The Access Server ID, host name, and port are all required.You can obtain these details from your Oracle Access Manager administrator. Click Next to continue.
Figure 11-5 Access Server Configuration Screen
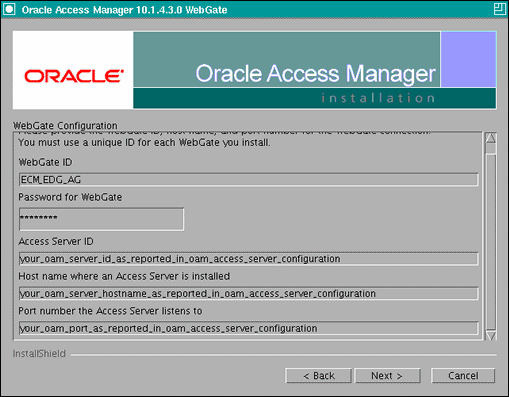
Description of "Figure 11-5 Access Server Configuration Screen"
-
-
In the Configure Web Server screen, click Yes to automatically update the web server. Click Next to continue.
-
In the next Configure Web Server screen, specify the full path of the directory containing the httpd.conf file. This file is located in the following directory:
ORACLE_BASE/admin/OHS_Instance/config/OHS/OHS_Component_Name
For example:
/u01/app/oracle/admin/ohs_instance2/config/OHS/ohs2/httpd.conf
Click Next to continue.
-
In the next Configure Web Server page, a message informs you that the Web server configuration has been modified for WebGate. Click Yes to confirm.
-
Stop and start your Web server for the configuration updates to take effect. Click Next to continue.
-
In the next Configure Web Server screen, the following message is displayed: "If the web server is set up in SSL mode, then the httpd.conf file needs to be configured with the SSL related parameters. To manually tune your SSL configuration, please follow the instructions that come up". Click Next to continue.
-
In the next Configure Web Server screen, a message with the location of the document that has information on the rest of the product setup and Web server configuration is displayed. Choose No and click Next to continue.
-
The final Configure Web Server screen appears with a message to manually launch a browser and open the HTML document for further information on configuring your Web server. Click Next to continue.
-
The Oracle COREid Readme screen appears. Review the information on the screen and click Next to continue.
-
A message appears (along with the details of the installation) informing you that the installation was successful.
11.2.5 Configuring IP Validation for the EDG Webgate
IP validation determines if a client's IP address is the same as the IP address stored in the ObSSOCookie cookie generated for single sign-on. IP validation can cause issues in systems using load balancer devices configured to perform IP termination or when the authenticating web gate is front-ended by a different load balancing router (LBR) or proxy than the one front-ending the EDG system.
Perform these steps to make sure your enterprise deployment's LBR or proxy are not validated in these cases:
-
Navigate to the Access System Console by specifying the following URL in your web browser:
http://host_name:port/access/oblix
where
host_namerefers to the host where the WebPass Oracle HTTP Server instance is running andportrefers to the HTTP port of the Oracle HTTP Server instance. -
On the Access System main page, click the Access System Console link and log in as an administrator.
-
On the Access System Console main page, click Access System Configuration, and then click the Access Gate Configuration link in the left pane to display the AccessGates Search page.
-
Enter the appropriate search criteria and click Go to display a list of access gates.
-
Select the access gate created by the Oracle Access Manager Configuration Tool.
-
Click Modify at the bottom of the page.
-
In the IPValidationException field, enter the IP address of the load balancer or proxy front-ending the EDG system.
-
Click Save at the bottom of the page.
11.2.6 Setting Up WebLogic Authenticators
This section assumes that you have already set up the LDAP authenticator by following the steps in Section 11.1.2.1, "Creating the LDAP Authenticator." If you have not already created the LDAP authenticator, do it before continuing with this section.
This section covers the following topics:
11.2.6.1 Back Up Configuration Files
To be safe, first back up the relevant configuration files:
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver/domain_name/config/config.xml ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver/i/config/fmwconfig/jps-config.xml ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver/domain_name/config/fmwconfig/system-jazn-data.xml
Also back up the boot.properties file for the Administration Server.
11.2.6.2 Setting Up the OAM ID Asserter
Perform these steps to set up the OAM ID Asserter:
-
Log in to Weblogic Console, if not already logged in.
-
Navigate to SecurityRealms, then the default realm name, and then Providers.
-
Click New and select 'OAM Identity Asserter' from the dropdown menu.
-
Name the asserter (for example, "OAM ID Asserter") and click Save.
-
Click the newly added asserter to see the configuration screen for OAM Identity Asserter.
-
Set the control flag to 'REQUIRED' and click Save.
-
Open the Provider Specific tab to configure the following required settings:
-
Primary Access Server: provide OAM server endpoint information in host:port format.
-
AccessGate Name: name of the AccessGate (for example,
ECM_EDG_AG). -
AccessGate Password: password for the AccessGate (optional).
-
-
Save the settings.
11.2.6.3 Setting the Order of Providers
Reorder the OAM Identity Asserter, OID Authenticator, and Default Authenticator by ensuring that the control flag for each authenticator is set as follows:
-
OAM Identity Asserter: REQUIRED
-
OID LDAP Authenticator (or OVD LDAP Authenticator): SUFFICIENT
-
Default Authenticator: SUFFICIENT
11.3 Backing Up the Installation
After you have verified that the extended domain is working, back up the installation. This is a quick backup for the express purpose of immediate restore in case of problems in the further steps. The backup destination is the local disk. This backup can be discarded once the enterprise deployment setup is complete. At that point, the regular deployment-specific backup and recovery process can be initiated. The Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide provides further details. For information on describing the Oracle HTTP Server data that must be backed up and restored, refer to the "Backup and Recovery Recommendations for Oracle HTTP Server" section in this guide. For information on how to recover components, see "Recovery of Components" and "Recovery After Loss of Component" sections in the guide. For recommendations specific to recovering from the loss of a host, see the "Recovering Oracle HTTP Server to a Different Host" in the guide. Also refer to the Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide for information on database backup.
Perform these steps to back up the installation at this point:
-
Back up the web tier:
-
Shut down the instance using
opmnctl.ORACLE_BASE/admin/instance_name/bin/opmnctl stopall -
Back up the Middleware Home on the web tier using the following command (as root):
tar -cvpf BACKUP_LOCATION/web.tar $MW_HOME
-
Back up the Instance Home on the web tier using the following command (as root):
tar -cvpf BACKUP_LOCATION/web_instance.tar $ORACLE_INSTANCE
-
Start the instance using
opmnctl:ORACLE_BASE/admin/instance_name/bin/opmnctl startall
-
-
Back up the AdminServer domain directory. Perform a backup to save your domain configuration. The configuration files all exist under the ORACLE_BASE/ admin/domain_name directory.
SOAHOST1> tar -cvpf edgdomainback.tar ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name