 Overview of Excise Tax
Overview of Excise Tax
This chapter provides overviews of:
Excise tax.
Process flow for excise tax.
Software solution for excise tax in the O2C cycle.
Software solution for excise tax in the P2P cycle.
Setup requirements for excise tax.
See Also
(IND) Setting Up Country-Specific Functionality for India
(IND) Working with Excise Tax for 100 Percent Export-Oriented Units
(IND) Working with Excise Registers
(IND) Processing Excise-Exempt Consignments
 Overview of Excise Tax
Overview of Excise Tax
An excise tax is a tax levied by the central government on goods manufactured in India. A buyer collects the excise tax or excise duty from the purchaser at the time of sale of a product. The excise duty is levied on all products specified in the Central Excise Tariff Act, 1985 (CETA).
The excise tax can be based on the value of goods or a fixed rate tax. Based on the notifications issued by the Central Government of India, some products are fully exempted from excise duty.
You can define one or more excise units for each company. Each company has one excise unit for each state and each excise unit is mapped to multiple business units. The transactions for excise tax occur at the business unit or excise unit level.
The system creates the transactions related to excise tax during the Procure-to-Pay (P2P) and Order-to-Cash (O2C) cycles. The P2P cycle comprises the period from the creation of a purchase order to when the payment is made to the supplier. When traders purchase goods on which excise tax is applicable, they must perform the tasks defined in the P2P cycle.
The O2C cycle comprises the period from the creation of a sales order to when the payment is received from the customer. When traders sell goods on which excise tax is applicable, they must perform the tasks defined in the O2C cycle.
The excise tax authorities have defined these requirements for different types of traders who work with the excise component of trade:
Manufacturers must pay excise duty when purchasing raw materials. This is a part of the P2P cycle. However, they must also pay excise duty when selling finished goods. This is a part of the O2C cycle. Manufacturers maintain all statutory records according to the excise rules defined by the excise authorities.
Dealers are not required to pay excise duty because they perform only a goods transfer.
Manufacturers who are exporters are not required to pay excise duty according to the excise rules. However, they must submit ARE 1 bonds or ARE 3 certificates, which are equivalent to the excise amount or excise quantity, to the excise authorities for a given period.
The manufacturers who send consignment of goods outside the company for work do not have to pay excise duty if they receive the consignment within 180 days. They must submit the consignment note to the tax authorities to declare the receipt of goods within the required time period.
Each excise unit has to maintain legal records to submit to the tax authorities. These include:
RG1 register. Excise units maintain this register. This register includes receipts, issues, and stock of furnished goods.
RG23D register. Dealers maintain this register to record the stock transfer at purchase price.
Personal ledger account (PLA). Excise units maintain this register by depositing the cash amount for the duty payment in the bank with the TR-6 challan.
RG23A-II. Manufacturers maintain this account for the purchase of raw materials. This account is also referred to as AII.
RG23C-II. Manufacturers maintain this account for the purchase of capital goods. This account is also referred to as CII.
 Process Flow for Excise Tax
Process Flow for Excise Tax
This process flow shows the tasks that a supplier performs to work with the excise tax component of sales:
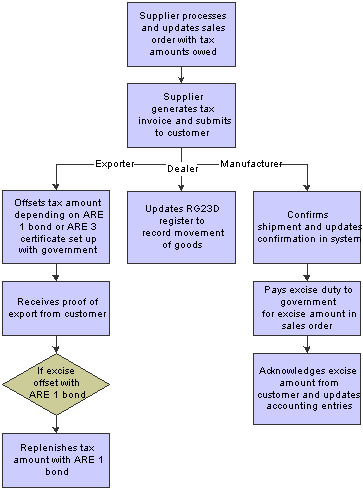
Excise process flow for the O2C cycle
This process flow shows the tasks that a manufacturer performs to work with the excise tax component of purchase:
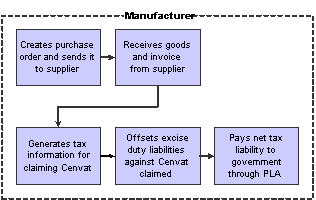
Excise process flow for the P2P cycle
 Software Solution for Excise Tax in the O2C Cycle
Software Solution for Excise Tax in the O2C Cycle
This section provides overviews of the software solution for excise tax in the O2C cycle for:
Manufacturer
Dealer
Exporter

 Manufacturer
Manufacturer
To meet the excise tax requirements specified by the tax authorities for a manufacturer in the O2C cycle, the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne programs enable you to:
Create a sales order for items that are eligible for excise duty.
Issue a tax invoice to charge excise duty to customers for goods purchased.
Confirm the shipment after receiving the shipment confirmation for the goods exported.
Update inventory and the RG1 register.
Update the accounts receivable.
Produce reports that show the revenue generated on a periodic basis.
Pay excise duty to the government by offsetting the excise duty amount and update the PLA.

 Dealer
Dealer
To meet the excise tax requirements specified by the tax authorities for a dealer in the O2C cycle, the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne programs enable you to:
Create a sales order for items that are eligible for excise duty.
Issue a dealer tax invoice.
Confirm the shipment after receiving the shipment confirmation for the goods dispatched.
Update the excise tax in the RG23D register.

 Exporter
Exporter
To meet the excise tax requirements specified by the tax authorities for an exporter in the O2C cycle, the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne programs enable you to:
Set up ARE 1 bonds and ARE 3 certificates.
Create a sales order with excise tax for items that you export.
Create an invoice.
Offset the amount or quantity of excise duty by the ARE 1 bond or ARE 3 certificate respectively.
Receive the proof of export.
Replenish the bond amount with ARE 1.
Print Annexure 19 periodically to submit to the government.
 Software Solution for Excise Tax in the P2P Cycle
Software Solution for Excise Tax in the P2P Cycle
To meet the excise tax requirements specified by the tax authorities for a manufacturer in the P2P cycle, the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne programs enable you to:
Create a purchase order for items that are eligible for excise duty.
Receive goods with tax component and a receipt note from the supplier.
Claim the excise duty on the purchase order.
Update credit balances for the AII, CII, or PLA register.
 Setup Requirements for Excise Tax
Setup Requirements for Excise Tax
This table lists the excise tax setup requirements for India:
|
Setup Requirement |
Cross-Reference |
|
Create address book records with search type EXU for excise units. |
|
|
Associate tax types to tax regimes. |
|
|
Map price adjustment names to the excise tax components. |
|
|
Set up tax registration details for excise units. |
|
|
Set up excise account details. |
|
|
Define periods and fiscal years for excise units. |
|
|
Create cross-references between excise units and business units. |
See Creating Cross-References Between Excise Units and Business Units. |
|
Map order and document types to excise units. |
|
|
Set up chapter numbers and descriptions. |
|
|
Map Landed Cost Components to Tax Types |
See Setting Up Level Costs for Combinations of Tax Types and Tax Regimes. |
|
Add lot numbers for all items for which you apply excise tax. |