 Understanding the Commodity Structure
Understanding the Commodity Structure
This chapter provides an overview of the commodity structure and discusses how to set up the commodity structure.
 Understanding the Commodity Structure
Understanding the Commodity Structure
The commodity structure enables you to categorize items, services, and supplier branch information in a hierarchical tree structure. After you set up the commodity structure, you create relationships for commodities. The system uses commodity relationships to provide default information for requisitions. Commodity relationship information is eventually passed to Enterprise Performance Management, where you can perform spend analysis.
When setting up the commodity structure, you must observe these guidelines:
Each commodity may have only one parent commodity.
You may not create duplicate commodities.
You may have only three commodity levels in the commodity hierarchy.
Each commodity may contain a maximum of 15 alphanumeric characters.
The description associated with the commodity may contain a maximum of 30 alphanumeric characters.
The first level of the commodity structure is level 0.
The Requisition Self Service system provides a default commodity, Unknown. The system uses this commodity if you do not set up a commodity structure or if the system cannot find a default commodity for a requisition. You can attach a buyer to the Unknown commodity so that the buyer is alerted when users enter requisitions for which they do not know the commodity. You cannot set up line types, G/L class codes, and item relationships for the Unknown commodity.
Note. Do not delete the Unknown commodity.
After you have created the initial commodity structure, you can add new items to the structure as needed. If you want to apply the commodities to purchase order records created before you set up the commodity structure, run the Populate F4311 Commodity/UNSPSC Program (R43910). This program assigns commodities and United Nations Standard Products and Services Codes (UNSPSC) to existing purchase order lines, based on data selection.
See Understanding the Populate F4311 Commodity/UNSPSC Program.
Note. If you do not want to set up the commodity structure, you can still perform spend analysis on account-driven requisition lines by setting up relationships between UNSPSC codes and general ledger account numbers. Use the UNSPSC to Account Relationship program (P40243) to set up these relationships, and then use the Enterprise Performance Management systems to create reports that include UNSPSC code information. This program does not create UNSPSC relationships for item-driven requisition lines.
 Setting Up the Commodity Structure
Setting Up the Commodity Structure
This section provides overviews of the Commodity Structure program, commodity relationships, and the Populate F4311 Commodity/UNSPSC program, and discusses how to:
Add a commodity.
Enter an item number.
Enter a UNSPSC code.
Enter a supplier relationship for the commodity.
Enter a supplier's commodity code.
Enter a G/L account number.
Set up a UNSPSC code for an account number.
Run the Populate F4311 Commodity/UNSPSC program (R43910).

 Understanding the Commodity Structure Program
Understanding the Commodity Structure Program
Use the Commodity Structure program (P40500) to create the commodity structure. When you add a commodity, you enter the commodity, a description, whether it is a product, service, or both, and the line type. You can also enter a buyer number and a G/L class code. You must enter this basic commodity data and save it before entering any relationship information.
After you add each commodity, you can cut and paste the commodities into the appropriate level of the hierarchy. You can create up to three levels in the structure.
You can also move nodes within the structure; however, you cannot move a node if moving the node would create more than three levels in the structure. When you move a node, the system moves any children that are associated with the node.
Note. The Commodity Structure program is enabled with record locking. Record locking prevents a user from making any changes to the commodity structure when another user is updating the structure, ensuring data integrity. If your business practices require that multiple users have access to the commodity structure at one time, you can disable the record locking feature for this program by removing the P40500 program from user-defined code table 00/RR. However, we recommend that you leave record locking enabled.
See Oracle JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tools 8.98: Development Tools: APIs and Business Functions

 Understanding Commodity Relationships
Understanding Commodity Relationships
You can set up relationships for each commodity. Relationships provide default information for the system to use when you enter a commodity on the requisition and throughout the requisition and purchase order process.
This graphic illustrates commodity relationships:
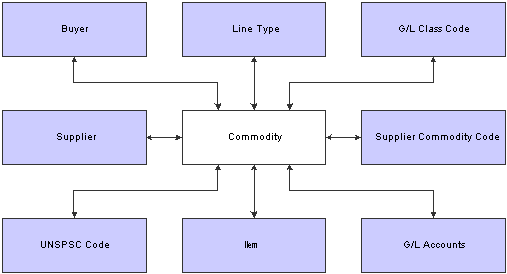
Commodity relationships
Item Number
Enter an item number for a commodity when you want to track commodity by item number. If you enter an item number for a commodity, you do not need to enter information such as G/L class code, because the system uses the information in the F4102 table. If you do enter any information for the commodity, the system overrides the information with the values specified in the F4102 table when you enter the requisition. The system stores item number relationship information in the F40540 table.
You can also enter the commodity directly into the Item Master program (P4101).
UNSPSC Code
If you want to track items by UNSPSC code separately or in addition to a commodity, you enter the UNSPSC code at the item master level. When you enter a requisition for a stock item, the system uses the UNSPSC code and the commodity associated with the item in the F4102 table.
However, you might want to enter a UNSPSC code for a commodity that does not have an item, such as a services commodity. To accomplish this, use the Commodity Structure program to associate the commodity with the UNSPSC code. When a user enters a requisition, the system retrieves the UNSPSC code from the associated commodity. The system stores UNSPSC code relationship information in the F40510 table.
Note. You can download a complete list of the UNSPSC codes from the UNSPSC website (www.UNSPSC.com). When you download the codes, the system stores them in the F40241 table. The visual assist for the UNSPSC field is attached to this table.
Suppliers
You usually attach supplier numbers to commodities for items that you do not normally stock, so that a user has a list of preferred suppliers for that particular item. When you create this relationship, the supplier name appears in the commodity structure under the designated commodity. If you implement the Direct Connect feature for one or more suppliers, the user can connect directly to the suppliers' website to shop for items. The system stores supplier relationship information in the F40520 table.
Note. When you enter a supplier for the commodity, you must also enter a branch/plant for that supplier. If you do not enter a branch/plant, the system assigns the value of ALL. You usually assign a branch/plant of ALL for national suppliers that are used by all regions of your organization. For services, such as electrical work, you usually enter the branch/plant that applies to each supplier, so that users can select a supplier that is located in their region.
Suppliers' Commodity Codes
Enter a supplier's commodity code to create a cross-reference between your commodity and that of the supplier. You generally enter suppliers' commodity codes only if you are using the Direct Connect feature. After you set up the relationship between your commodity and the supplier's commodity code, the supplier's website can pass the commodity code to the Shopping Cart application so that the system can cross-reference this code and then use the internal commodity as the default value for commodity on the requisition line. The system stores supplier commodity code cross-reference information in the F40530 table.
Note. You must set up a supplier and branch/plant relationship before attaching a supplier's commodity code to a commodity.
G/L Account Number
Enter a G/L account number commodity relationship if users at your organization most often enter an account number instead of a commodity on the requisition line. When the user enters an account number, the system searches the F40551 table for a related commodity for that account number. When searching for a commodity relationship, the system uses this hierarchy:
The system first searches the F40551 table to locate a related commodity for the business unit, object account, and subsidiary that the user entered.
If unsuccessful, the system then searches for a relationship for the object account and subsidiary that the user entered.
If unsuccessful, the system then searches for a relationship for the object account that the user entered.
When the system locates a commodity, it populates the Commodity field on the Requisition Entry form.
The system stores general ledger account number relationship information in the F40551 table.

 Understanding the Populate F4311 Commodity/UNSPSC Program
Understanding the Populate F4311 Commodity/UNSPSC Program
If you create the commodity structure after you have already entered requisitions and purchase orders into the system, run the Populate F4311 Commodity/UNSPSC program (R43910) to attach commodities and UNSPSC codes to existing transactions. Based on data selection that you specify, the system reviews existing records in the F4311 table and attempts to find a commodity and UNSPSC code to assign to the lines. For stock lines, the system uses the item number to find a commodity relationship using the F40540 table. If the system does not find a commodity, the system assigns the Unknown commodity. For account-based lines (services), the system uses the account number to search for a commodity relationship using the F40551 table. After the system finds a commodity for a line, it searches for a UNSPSC relationship for the commodity, by using the F40510 table.
Note. This program overwrites any existing values in the Commodity and UNSPSC Code fields, including blank and Unknown. Therefore, you should be certain that the data selection that you enter does not include requisition lines for which you do not want the values updated.
If you decide that the commodity structure provides too much or too little detail on spend information, you can change the commodity structure and run the Populate F4311 Commodity/UNSPSC program to update existing transactions with the new commodities and UNSPSC codes.

 Forms Used to Set Up the Commodity Structure
Forms Used to Set Up the Commodity Structure
|
Form Name |
FormID |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
W40500B |
Commodity Structure (2/G43E31), Commodity Structure |
Add base commodity information. Move a commodity from one tree node to another. |
|
|
W40500A |
Select Edit on the Item tab of the Set up Commodity Structure form. |
Enter an item number for the commodity. |
|
|
W40500F |
Select Edit on the UNSPSC tab of the Set up Commodity Structure form. |
Enter a default UNSPSC code for the commodity. |
|
|
W40500D |
Select Edit on the Supplier tab of the Set up Commodity Structure form. |
Enter a valid supplier number for the commodity. |
|
|
W40500E |
Select Edit on the Supplier Commodity Code tab of the Set up Commodity Structure form. |
Enter a supplier's commodity code. |
|
|
W40500H |
Select Edit on the G/L Account tab of the Set up Commodity Structure form. |
Enter a general ledger account number for the commodity code. |
|
|
W40500G |
Select Cut Tree Node on the Set up Commodity Structure form. |
Delete a node from the structure. |
|
|
W40510A |
Commodity Structure 2/(G43E31), UNSPSC and Commodity |
Set up a relationship for a UNSPSC code and a commodity. |
|
|
W40551A |
Commodity Structure (2/G43E31), G/L Account and Commodity |
Set up a relationship for a general ledger account and a commodity. |
|
|
W40521A |
Supplier Direct Connect menu (3/G43E31), Setup Supplier Information Select a supplier on the Work With Supplier form and then select Commodity Structure from the Row menu. |
Search for a branch/plant associated with the supplier. Click Set up Supplier Branch Plant. Click Set up Supplier Commodity Codes. |
|
|
W40520A |
Select Set Up Supplier Commodity Codes on the Search Branch Plant form. |
Set up a cross-reference between a supplier's commodity codes and your commodity structure. |
|
|
W40243A |
UNSPSC Definition (G43A412), UNSPSC to Account Relationship |
Review existing relationships. |
|
|
W40243B |
Click Add on the Work With Commodity Relationships form. |
Set up a UNSPSC relationship for an account number, if you do not want to set up the commodity structure. |

 Adding A Commodity
Adding A Commodity
Access the Set up Commodity Structure form.

 Entering an Item Number
Entering an Item Number
Access the Edit Item Relationship form.
|
Item Number |
Enter a value in this field if you want to filter on a particular item. For example, enter 42* if you want to view all items beginning with the number 42. |
|
2nd Item Number |
Enter the item number with which you want to associate the commodity. If you entered a commodity or UNSPSC code for an item in the F4102 table, these values appear when you inquire on the item. Each item can only be associated with one commodity. If you change the item on this form, the system only uses the new item on new transactions. The system does not update existing transactions with the new item for the commodity. |

 Entering a UNSPSC Code
Entering a UNSPSC Code
Access the Edit UNSPSC Code form.
|
Primary |
Select this option if you have related more than one UNSPSC code to a commodity. This option designates a primary UNSPSC code for the system to use as a default value for the requisition. |
|
UNSPSC Code |
Enter a UNSPSC code if you want to filter on a particular UNSPSC code for the field in the header. For the field in the detail, enter a UNSPSC code if you want to add a new commodity relationship. When you enter a commodity during requisition entry, the system uses this UNSPSC code as the default value. |
|
UNSPSC Code Description |
Enter a UNSPSC code description if you want to filter on a particular UNSPSC description for the field in the header. For the field in the detail, the system uses the description associated with the UNSPSC code in the F40241 table. |

 Entering a Supplier Relationship for the Commodity
Entering a Supplier Relationship for the Commodity
Access the Edit Supplier Relationship form.
|
Supplier Number |
Enter the address book number of the supplier or subcontractor that you want to associate with the commodity. |
|
Branch Plant |
Enter the branch/plant for the supplier. |

 Entering a Supplier's Commodity Code
Entering a Supplier's Commodity Code
Access the Edit Supplier Commodity Code Relationship form.
|
Supplier Commodity Code |
Enter the commodity code defined by the supplier. You obtain this information from the supplier, usually when you receive the information necessary for Direct Connect. |
|
Supplier Commodity Code Description |
Enter the description for the supplier's commodity code. You obtain this information from the supplier, usually when you receive the information necessary for Direct Connect. |

 Entering a G/L Account Number
Entering a G/L Account Number
Access the Edit G/L Account Relationship form.
|
Branch Plant |
Enter the branch/plant number of the account for which you want to set up a relationship for the commodity. This field is optional. |
|
Object Account |
Enter the object of the account number for which you want to set up a relationship for the commodity. This field is required. |
|
Subsidiary |
Enter the subsidiary of the account number for which you want to set up a relationship for the commodity. This field is optional. |

 Setting Up a UNSPSC Code for an Account Number
Setting Up a UNSPSC Code for an Account Number
Access the Commodity Relationship Revisions form.
|
Business Unit |
Enter the business unit of the account number for which you want to set up a UNSPSC code relationship. |
|
Object Account |
Enter the object account of the account number for which you want to set up a UNSPSC code relationship. |
|
Subsidiary |
Enter the subsidiary of the account number for which you want to set up a UNSPSC code relationship |
|
UNSPSC Code |
Select a valid UNSPSC code to relate to the general ledger account number that you specified. |

 Running the Populate F4311 Commodity/UNSPSC Program
Running the Populate F4311 Commodity/UNSPSC Program
Select Adv/Tech Operations (G43E31), Populate F4311 Commodity/UNSPSC.