4 Preparing Your Integrated Excel Workbook
This chapter describes preparatory tasks that must be performed in developing a Fusion web application so that you can integrate an Excel workbook with the finalized application. This chapter also describes how to configure an Excel workbook before you add Oracle ADF functionality, using the tools provided in the ADF Desktop Integration module.
This chapter includes the following sections:
-
Section 4.1, "About Preparing Your Integrated Excel Workbooks"
-
Section 4.2, "Adding an Integrated Excel Workbook to a Fusion Web Application"
-
Section 4.3, "Working with Page Definition Files for an Integrated Excel Workbook"
4.1 About Preparing Your Integrated Excel Workbooks
This chapter (and the guide as a whole) assumes that you have developed a functioning Fusion web application, as described in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
Having developed the Fusion web application, you perform the tasks described in this chapter to configure an integrated Excel workbook with the Fusion web application. The subsequent chapters of the guide enable you to configure the integrated workbook with advanced features, such as configuration with Oracle ADF functionality, and adding Oracle ADF components that provide the functionality you require at runtime.
Note:
Before you start, ensure that the Designer edition of ADF Desktop Integration is installed. For more information about the ADF Desktop Integration editions, see Section 3.5, "Installing ADF Desktop Integration."4.2 Adding an Integrated Excel Workbook to a Fusion Web Application
The Fusion web application is automatically enabled with ADF Desktop Integration when you add an integrated Excel workbook. An integrated Excel workbook enables you to add ADF components and ADF data bindings.
4.2.1 How to Add an Integrated Excel Workbook to a Fusion Web Application
To add an integrated Excel workbook, open the Fusion web application in JDeveloper and add an Excel workbook to the project from the New Gallery.
It may be helpful to have an understanding of adding ADF Desktop Integration to a Fusion web application. For more information, see Section 4.2, "Adding an Integrated Excel Workbook to a Fusion Web Application."
To add an integrated Excel workbook in JDeveloper:
-
Open the Fusion web application in JDeveloper.
-
In the Application Navigator, select the project, such as ViewController, to which you want to add the new integrated Excel workbook.
-
From the File menu, choose New.
-
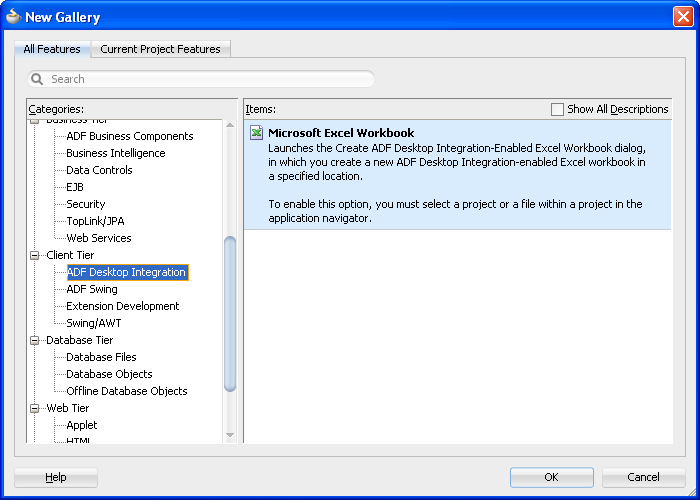
In the New Gallery, expand Client Tier, select ADF Desktop Integration and then Microsoft Excel Workbook, and click OK. Figure 4-1 shows the New Gallery with ADF Desktop Integration category and the Microsoft Excel Workbook option.
Click OK.
-
In the Create ADF Desktop Integration-Enabled Excel Workbook dialog, if required, edit the file name of the workbook and its location.
By default, the integrated Excel workbook is saved as
adfdi-workbook.xlsxin the\src\exceldirectory of the selected project. Although you can save the workbook anywhere you choose, it is recommended to save the workbook with the other files of the Fusion web application. -
Click OK.
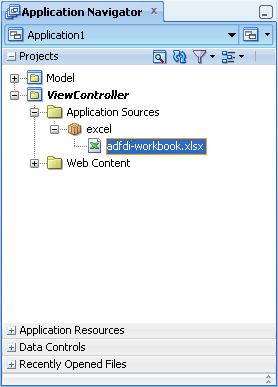
JDeveloper adds the integrated Excel workbook into the Fusion web application, and automatically enables the Fusion web application with ADF Desktop Integration. Figure 4-2 shows the integrated Excel workbook in the Application Navigator.
4.2.2 How to Configure a New Integrated Excel Workbook
After adding the integrated Excel workbook, you must configure it.
It may be helpful to have an understanding of adding an integrated Excel workbook to a Fusion web application. For more information, see Section 4.2, "Adding an Integrated Excel Workbook to a Fusion Web Application."
To configure a new integrated Excel workbook:
-
Open the integrated Excel workbook.
-
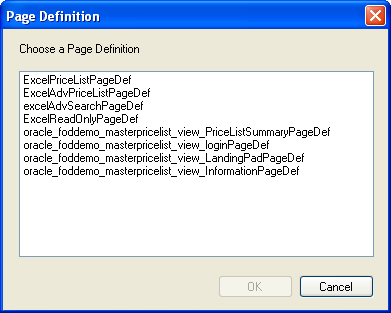
If you have saved the workbook with other files of the Fusion web application, the Page Definition dialog automatically appears, as illustrated in Figure 4-3.
Select the page definition file in the Page Definition dialog, and click OK.
-
If you have saved the workbook elsewhere, configure the workbook as described in Section 4.4.3, "How to Manually Configure a New Integrated Excel Workbook."
-
-
In the Workbook group of the Oracle ADF tab, click Workbook Properties.
-
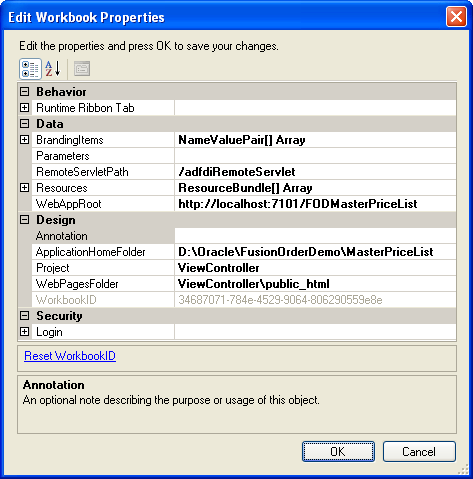
In the Edit Workbook Properties dialog, set or verify the values for the following properties so that you can switch between design mode and test mode as you configure the workbook:
-
ApplicationHomeFolderThe value for this property corresponds to the absolute path for the root directory of the JDeveloper application workspace (
.jws). If the workbook is located within the JDeveloper application workspace, the value of theApplicationHomeFolderworkbook property is assigned automatically.Note:
If you are opening the Excel file after moving the application directory, ensure that theApplicationHomeFolderproperty's value reflects the correct path. -
ProjectThe value for this property corresponds to the name of the JDeveloper project (
.jpr) in the JDeveloper application workspace. To change the project, click the ellipsis (...) button and choose the project from the Project dialog, which lists the projects defined in the JDeveloper application workspace.By default,
Projectis set to the name of the project that contains the Excel document. ADF Desktop Integration loads the names of the available projects from theapplication_name.jwsspecified as a value forApplicationHomeFolder. -
WebAppRootSet the value for this property to the fully qualified URL for the web context root that you want to integrate the Fusion web application with. The fully qualified URL has the following format:
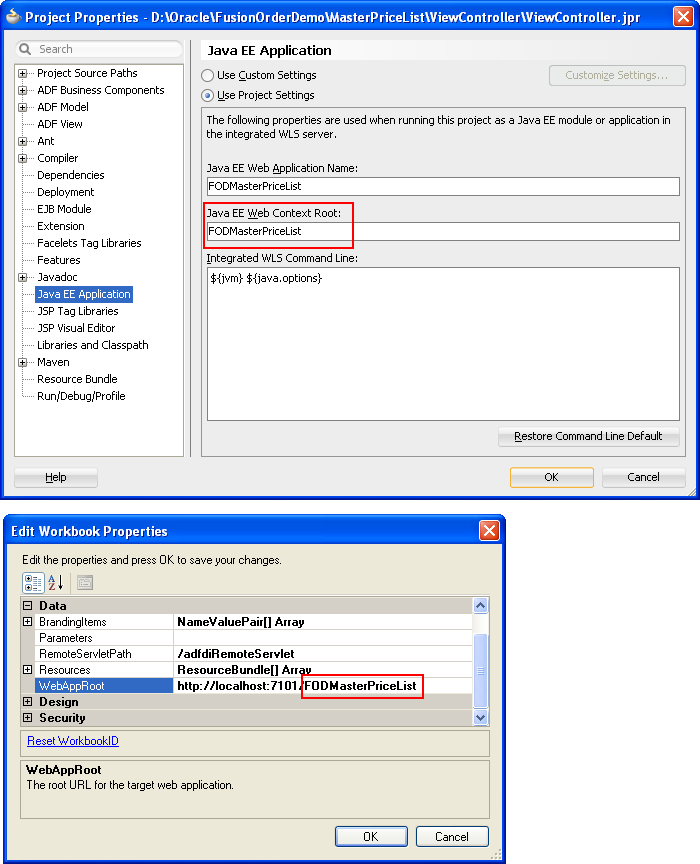
http://<hostname>:<portnumber>/context-rootIn JDeveloper, you specify the web context root (
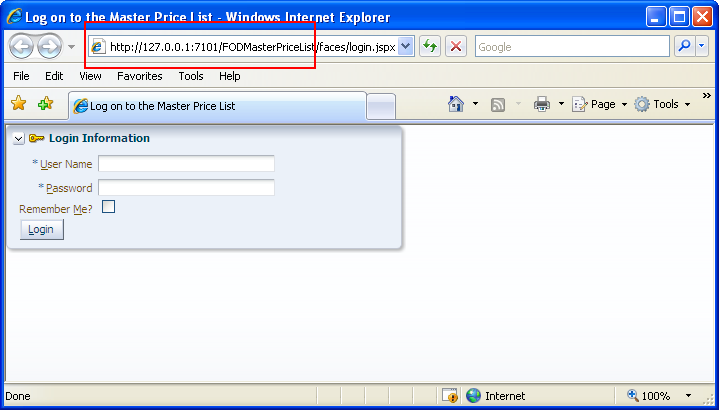
context-root) in the Java EE Application page of the Project Properties dialog. Figure 4-4 shows the web context root for the Master Price List module.Note that the fully qualified URL is similar to the following if you set up a test environment on the system using the Master Price List module, as shown in Figure 4-5.
http://127.0.0.1:7101/FODMasterPriceListFor information about how to verify that the Fusion web application is online and that it supports ADF Desktop Integration, see Section C.1, "Verifying That Your Fusion Web Application Supports ADF Desktop Integration."
If you are integrating an Excel file with a secure Fusion web application, it is recommended that you use the
httpsprotocol while entering the value forWebAppRoot. For more information about securing the Fusion web application, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Programming Security for Oracle WebLogic Server. -
WebPagesFolderSet the value for this property to the directory that contains web pages for the Fusion web application. The directory path should be relative to the value of
ApplicationHomeFolder. For example, in theEditPriceList-DT.xlsxworkbook,WebPagesFolderis set toViewController\public_html.
Figure 4-6 shows an example of workbook properties in the Edit Workbook Properties dialog of the Master Price List module's
EditPriceList-DT.xlsxworkbook. -
-
Click OK.
-
Save the Excel workbook.
4.2.3 How to Add Additional Worksheets to an Integrated Excel Workbook
To use Oracle ADF functionality, associate each worksheet with a page definition file. You associate a page definition file with a worksheet when you add a worksheet to the integrated Excel workbook. You can integrate multiple worksheets in an integrated Excel workbook with a Fusion web application. Use a different page definition file for each worksheet in the integrated Excel workbook.
It may be helpful to have an understanding of adding an integrated Excel workbook to a Fusion web application. For more information, see Section 4.2, "Adding an Integrated Excel Workbook to a Fusion Web Application."
To associate a page definition file with an Excel worksheet:
-
While the Excel workbook is in design mode, click the Home tab in the Excel ribbon, and then choose Insert > Insert Sheet in the Cells group.
-
In the Choose Page Definition dialog, select the page definition file.
This populates the bindings palette in the ADF Desktop Integration task pane with the bindings contained in the page definition file. You can now configure the worksheet with Oracle ADF functionality.
Note:
If you get an error message Programmatic access to Visual Basic Project is not trusted when you run an integrated Excel workbook after inserting a new worksheet, enable the Trust access to the VBA project object model checkbox in Excel Options. For more information, see Section 3.4, "Allowing ADF Desktop Integration to Access Microsoft Excel."4.2.4 What Happens When You Deploy an ADF Desktop Integration-Enabled Fusion Web Application from JDeveloper
When you deploy the ADF Desktop Integration-enabled Fusion web application from JDeveloper, references to the ADF Desktop Integration shared libraries are added to the appropriate descriptor files. For any Fusion web application that contains one or more projects referencing the ADF Desktop Integration Model API library or the ADF Desktop Integration Runtime library, a platform-dependent reference to the ADF Desktop Integration Model API shared library is added during deployment.
For any web application module (WAR) project that contains a reference to the ADF Desktop Integration Runtime library, a platform-dependent reference to the ADF Desktop Integration Runtime shared library is added during deployment.
4.2.4.1 Deploying the Fusion Web Application on Oracle WebLogic Server
When you deploy the Fusion Web application on Oracle WebLogic Server, the following happens:
-
The
META-INF/weblogic-application.xmlfile of the deployed application EAR contains a library reference tooracle.adf.desktopintegration.model.For example:
<library-ref> <library-name>oracle.adf.desktopintegration.model</library-name> </library-ref>
The shared library is delivered in
MW_HOME/oracle_common/modules/oracle.adf.desktopintegration.model_11.1.1, in theoracle.adf.desktopintegration.model.ear. -
The
WEB-INF/weblogic.xmlfile of the deployed web application WAR contains a library reference tooracle.adf.desktopintegration.For example:
<library-ref> <library-name>oracle.adf.desktopintegration</library-name> </library-ref>
The shared library is delivered in
MW_HOME/oracle_common/modules/oracle.adf.desktopintegration_11.1.1, in theoracle.adf.desktopintegration.war.
4.2.4.2 Deploying the Web Application on IBM WebSphere Application Server
When you deploy the web application on IBM WebSphere Application Server, the following happens:
-
For applications requiring the ADF Desktop Integration Model API library or the ADF Desktop Integration Runtime library, the deployment procedure inserts a reference to the
com/oracle/adfdimodelextension into theMETA-INF/MANIFEST.MFfile of the application EAR file.For example:
Manifest-Version: 1.0 Extension-List: adfm adfdimodel adfm-Extension-Name: com/oracle/adfm adfm-Specification-Version: 1.0 adfdimodel-Extension-Name: com/oracle/adfdimodel adfdimodel-Specification-Version: 1.0 UseWSFEP61ScanPolicy: false
-
The
deployment.xmlfile for web applications with projects that refer to the ADF Desktop Integration Runtime library contains a library reference inserted during deployment.For example:
<libraries xmi:id="LibraryRef_1274886542330_oracle.adf.desktopintegration_1.0_11.1.1.2.0" libraryName="oracle.adf.desktopintegration_1.0_11.1.1.2.0" sharedClassloader="true"/>
Note:
For more information about system administration tasks and the specifics about shared libraries for these platforms, refer to the Oracle WebLogic Server and IBM WebSphere Application Server documentation.4.3 Working with Page Definition Files for an Integrated Excel Workbook
Page definition files define the bindings that populate the data in the Oracle ADF components at runtime. Page definition files also reference the action bindings and method action bindings that define the operations or actions to use on this data. You must define a separate page definition file for each Excel worksheet that you are going to integrate with a Fusion web application. The integrated Excel workbook can include worksheets that do not reference page definition files.
The ADF Desktop Integration task pane displays only those bindings that ADF Desktop Integration supports in the bindings palette. If a page definition file references a binding that ADF Desktop Integration does not support (for example, a graph binding), it is not displayed.
Table 4-1 lists and describes the binding types that the ADF Desktop Integration module supports.
Table 4-1 Binding Requirements for ADF Desktop Integration Components
| ADF Desktop Integration component | Supported Binding | Additional comments |
|---|---|---|
|
ADF Input Text |
Attribute binding |
|
|
ADF Output Text |
Attribute binding |
|
|
ADF Label |
Attribute and list bindings |
This ADF Desktop Integration component uses the label property of a control binding. |
|
ADF List of Values |
List binding |
|
|
Tree Node List |
Tree binding attributes and list binding |
Tree binding attributes must be associated with a model-driven list. |
|
ADF Button |
Various |
The ADF Button component in ADF Desktop Integration can invoke action sets. Action sets can reference action bindings, method action bindings, or actions exposed by components in ADF Desktop Integration. For more information about action sets, see Section 8.2, "Using Action Sets." |
|
ADF Read-only Table |
Tree binding |
|
|
ADF Table |
Tree binding |
For information about the bindings that components in ADF Desktop Integration use, see Appendix A, "ADF Desktop Integration Component Properties and Actions."
For information about the elements and attributes in page definition files, see the "pageNamePageDef.xml" section of the Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
For information about ADF data binding and page definition files in a Fusion web application, see the "Using Oracle ADF Model in a Fusion Web Application" chapter of the Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
4.3.1 How to Create a Page Definition File for an Integrated Excel Workbook
You create and configure a page definition file that determines the Oracle ADF bindings to expose in the JDeveloper project.
It may be helpful to have an understanding of page definition files. For more information, see Section 4.3, "Working with Page Definition Files for an Integrated Excel Workbook."
To create a page definition file for an integrated Excel workbook:
-
In JDeveloper, add a new JSF page in the ADF Desktop Integration application's project.
Tip:
Add an ADF FacesTablecomponent to the JSF page. JDeveloper generates the tree bindings in the JSF page that the ADF Table-type components use in the page definition file.Note:
JDeveloper creates a page definition file's name based on the name of the JSF page you choose. If you want a page definition file's name to indicate an association with a particular workbook or worksheet, choose this name when creating the JSF page. -
In the Application Navigator, right-click the page and choose Go to Page Definition.
-
In the Confirm Create New Page Definition dialog, click Yes.
-
Add the bindings that you require for the integrated Excel workbook to the page definition file.
-
Save the page definition file.
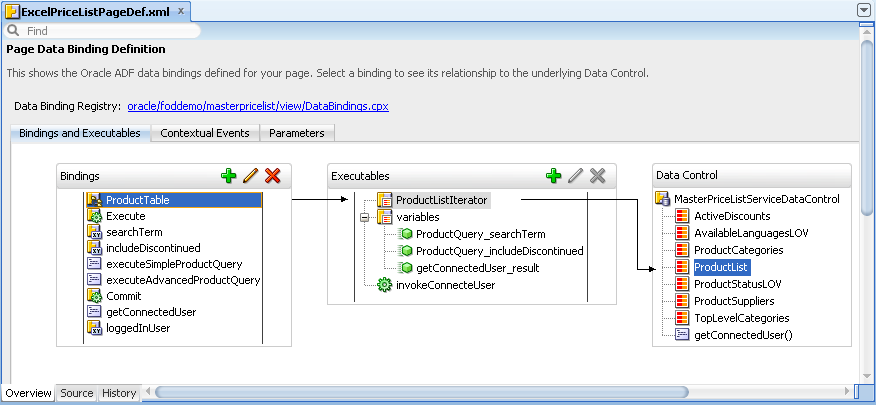
Figure 4-7 shows the
ExcelPriceListPageDef.xmlpage definition file that the Price List worksheet in theEditPriceList-DT.xlsxworkbook references.For information about working with page definition files, see the "Working with Page Definition Files" section in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
-
Make and run the Fusion web application if you plan to run the integrated Excel workbook in test mode or to publish it.
4.3.2 What Happens When You Create a Page Definition File
JDeveloper creates the DataBindings.cpx file the first time you add a page definition file in the JDeveloper project using the procedure described in Section 4.3.1, "How to Create a Page Definition File for an Integrated Excel Workbook."
The DataBindings.cpx file defines the binding context for the Fusion web application and provides the configuration from which the Oracle ADF bindings are created at runtime. Information about working with this file can be found in the "Working with the DataBindings.cpx File" section of the Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework. Information about the elements and attributes in the file can be found the "DataBindings.cpx" section of the same guide.
4.3.3 How to Reload a Page Definition File in an Excel Workbook
If you make changes in your JDeveloper desktop integration project to a page definition file that is associated with an Excel worksheet, rebuild the JDeveloper desktop integration project and reload the page definition file in the Excel worksheet to ensure that the changes appear in the ADF Desktop Integration task pane. You associate a page definition file with an Excel worksheet when you choose the page definition file, as described in Section 4.2.2, "How to Configure a New Integrated Excel Workbook."
The Oracle ADF tab provides a button that reloads all page definition files in an Excel workbook.
Errors may occur when you switch an integrated Excel workbook from design mode to runtime if you do not rebuild the JDeveloper desktop integration project and restart the application after making changes to a page definition file. For example, if you:
-
Remove an element in a page definition file
-
Do not rebuild and restart the Fusion web application
-
Or do not reload the page definition file in the integrated Excel workbook
an error message such as the following may appear when you attempt to switch a workbook to test mode:
[ADFDI-05530] unable to initialize worksheet: MyWorksheet [ADFDI-05517] unable to find control MyBindingThatWasRemoved
It may be helpful to have an understanding of page definition files. For more information, see Section 4.3, "Working with Page Definition Files for an Integrated Excel Workbook."
To reload page definition files in an Excel workbook:
-
Ensure that you have saved the updated page definition file in JDeveloper.
-
In the Excel workbook, click the Refresh Bindings button in the Components group of the Oracle ADF tab.
For information about the Refresh Bindings button, see Section 5.1, "About Development Tools."
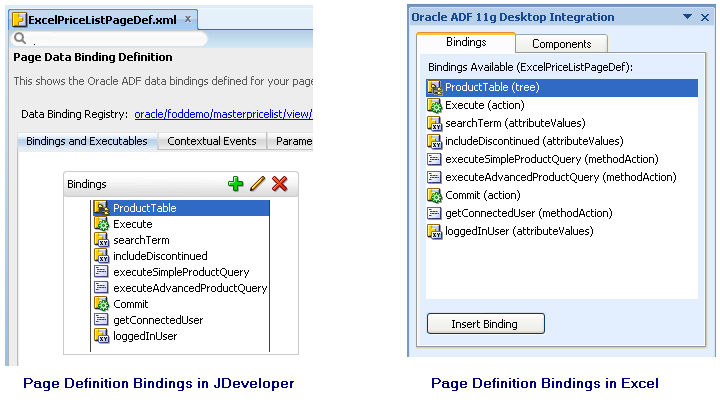
After reloading the page definition file, the ADF Desktop Integration task pane of the worksheet displays the same bindings that are available in its associated page of the Fusion web application. For example, Figure 4-8 shows the bindings in the ExcelPriceListPageDef.xml page definition file and the same bindings in the worksheet of the EditPriceList-DT.xlsx workbook.
4.3.4 What You May Need to Know About Page Definition Files in an Integrated Excel Workbook
Note the following points about page definition files in an ADF Desktop Integration project:
-
Integrating Multiple Excel Worksheets: You can integrate multiple worksheets in an Excel workbook with a Fusion web application. You associate a page definition file with each worksheet as described in Section 4.2.3, "How to Add Additional Worksheets to an Integrated Excel Workbook."
-
EL Expressions in a Page Definition File: Use the following syntax to write EL expressions in a page definition file:
Dynamic (${})Do not use the syntax
Deferred (#{})to write EL expressions. EL expressions using this syntax generate errors because they attempt to access the ADF Faces context, which is not available.Note:
EL expressions that you write for ADF Desktop Integration component in the integrated Excel workbook, such as the Input Text component, must use theDeferred (#{})syntax.
4.4 Enabling ADF Desktop Integration Manually
To enable ADF Desktop Integration in the Fusion web application without adding the integrated Excel workbook, you must add the ADF Desktop Integration feature manually.
4.4.1 How to Manually Add ADF Desktop Integration In Fusion Web Application
Use the Project Properties dialog in JDeveloper to add ADF Desktop Integration to the feature list of your project.
It may be helpful to have an understanding of adding ADF Desktop Integration to a Fusion web application. For more information, see Section 4.4, "Enabling ADF Desktop Integration Manually."
To manually add ADF Desktop Integration to your project:
-
Open the project in JDeveloper.
-
In the Application Navigator, right-click the project to which you want to add ADF Desktop Integration and choose Project Properties.
If the application uses the Fusion Web Application (ADF) application template, select the ViewController project. If the application uses another application template, select the project that corresponds to the web application.
-
In the Project Properties dialog, select Features to view the list of available features.
-
Click Add Features.
-
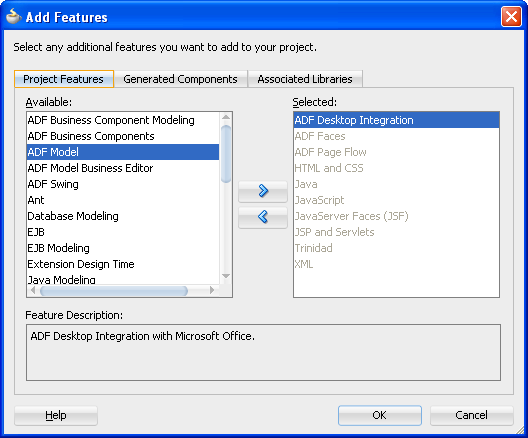
In the Add Features dialog, select the ADF Desktop Integration feature and add it to the Selected list, as shown in Figure 4-9.
-
Click OK to close the Add Features dialog.
-
Click OK to close the Project Properties dialog.
For more information about what happens when you add ADF Desktop Integration, see Section 4.4.4, "What Happens When You Add ADF Desktop Integration to Your JDeveloper Project."
Note:
If you plan to distribute integrated Excel workbooks by adding them to ADF library files through EAR and JAR files, add ADF Library Web Application Support to your project . For more information, see Section 4.4.5, "Adding ADF Library Web Application Support."4.4.2 How to Enable ADF Desktop Integration in an Existing Workbook
If you want to integrate an existing workbook with the ADF Desktop Integration enabled Fusion web application, you must manually enable ADF Desktop Integration for the workbook. For information about the file formats of Excel workbooks that you can convert for integration with a Fusion web application, see Section 3.2, "Required Oracle ADF Modules and Third-Party Software."
It may be helpful to have an understanding of adding integrated Excel workbook to a Fusion web application. For more information, see Section 4.4, "Enabling ADF Desktop Integration Manually."
To enable ADF Desktop Integration in an existing Excel workbook:
-
In Excel, open the workbook.
-
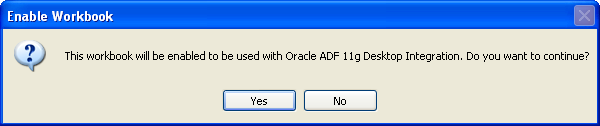
In the Workbook group of the Oracle ADF tab, click Workbook Properties.
-
In the Enable Workbook dialog, click Yes, as shown in Figure 4-10.
ADF Desktop Integration prepares your workbook, displays the ADF Desktop Integration Designer task pane, and opens the Browse For Folder dialog. For more information, see Section 4.4.3, "How to Manually Configure a New Integrated Excel Workbook."
-
Save the workbook.
Although you can store the Excel workbooks that you integrate with Fusion web applications anywhere you choose, there are several advantages to storing them with the other files of the Fusion web application. Some of these advantages are:
-
Source control of the workbooks
-
Facilitating the download of workbooks from web pages
-
The file system folder picker that appears the first time a workbook is opened defaults to the location where you store the workbook
For example, the Master Price List module of the Fusion Order Demo application stores the Excel workbooks it integrates in the following subdirectory:
FOD_HOME\MasterPriceList\ViewController\src\oracle\foddemo\masterpricelist\excel
where FOD_HOME is the root directory that stores the source files for the Fusion Order Demo application.
4.4.3 How to Manually Configure a New Integrated Excel Workbook
After enabling ADF Desktop Integration manually in a workbook, you would need to configure it.
It may be helpful to have an understanding of adding an integrated Excel workbook to a Fusion web application. For more information, see Section 4.4, "Enabling ADF Desktop Integration Manually."
To manually configure a new integrated Excel workbook:
-
Open the integrated Excel workbook.
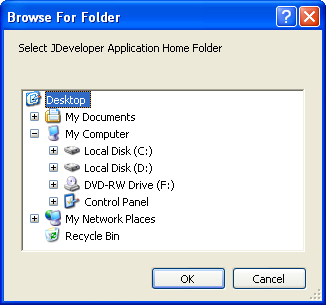
The Browse For Folder dialog automatically appears, as illustrated in Figure 4-11.
Use the Browse for Folder dialog to select the JDeveloper application home directory. In a typical JDeveloper project, the JDeveloper application home directory stores the
application_name.jwsfile. The value you select is assigned to theApplicationHomeFolderworkbook property.Note:
The Browse for Folder dialog does not appear if the workbook is located within the JDeveloper application workspace. In such a case, the value of theApplicationHomeFolderworkbook property is assigned automatically. -
In the Workbook group of the Oracle ADF tab, click Workbook Properties.
-
In the Edit Workbook Properties dialog, configure the properties as described in Step 3 of Section 4.2.2, "How to Configure a New Integrated Excel Workbook."
-
Click OK.
-
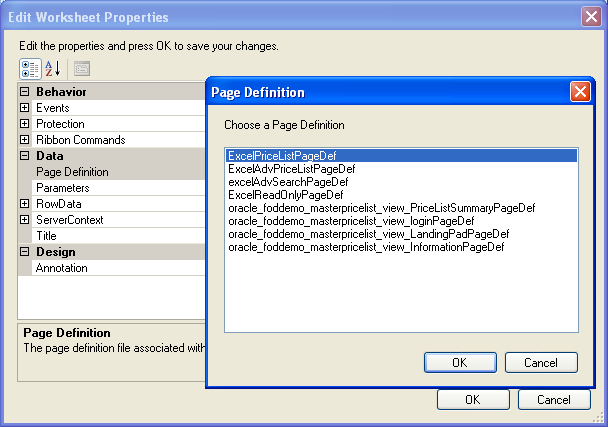
In the Workbook group of the Oracle ADF tab, click Worksheet Properties.
-
In the Edit Worksheet Properties dialog, click the ellipsis button (...) beside the Page Definition input field and select a page definition file from the Page Definition dialog, as shown in Figure 4-12.
-
Click OK.
The Excel worksheet appears with ADF Desktop Integration in the task pane. The bindings of the page definition file that you selected in Step 6, appear in the Bindings tab.
-
Save the Excel workbook.
By default, when you prepare a new Excel workbook with ADF Desktop Integration, it is assumed that the workbook will be integrated with an unsecure Fusion web application. If you want to integrate a workbook with a secure Fusion web application, see Chapter 11, "Securing Your Integrated Excel Workbook."
4.4.4 What Happens When You Add ADF Desktop Integration to Your JDeveloper Project
When you add the ADF Desktop Integration feature to a project, the following events occur:
-
The project adds the ADF Desktop Integration runtime library. This library references the following
.jarfiles in its class path:-
adf-desktop-integration.jar -
adf-desktop-integration-model-api.jar -
resourcebundle.jar
-
-
The project's deployment descriptor (
web.xml) is modified to include the following entries:-
An ADF bindings filter (
adfBindings) -
A servlet named
adfdiRemoteNote:
The value for theurl-patternattribute of theservlet-mappingelement foradfdiRemotemust match the value of theRemoteServletPathworkbook property described in Table A-18. -
A filter named
adfdiExcelDownload -
A MIME mapping for Excel files (
.xlsxand.xlsm)
The previous list is not exhaustive. Adding ADF Desktop Integration to a project makes other changes to
web.xml. Note that some entries inweb.xmlare added only if they do not already appear in the file. -
4.4.5 Adding ADF Library Web Application Support
If you want to distribute integrated workbooks by adding them to ADF library files, add ADF Library web application support to the Fusion web application. For more information, see the "Packaging a Reusable ADF Component into an ADF Library" section in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
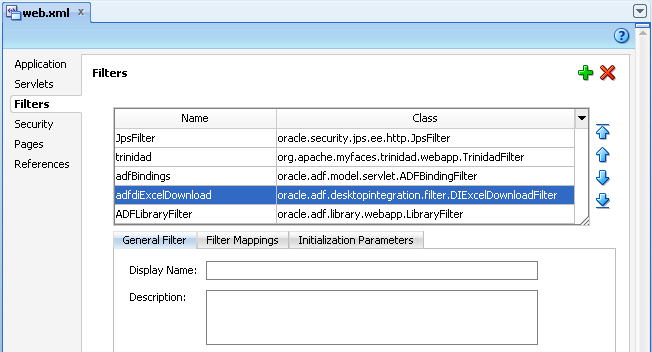
When updating filter and filter mapping information in the web.xml file, ensure that the filter for ADF Library Web Application Support (<filter-name>ADFLibraryFilter</filter-name>) appears below the adfdiExcelDownload filter entries, so that integrated Excel workbooks can be downloaded from the Fusion web application.
Figure 4-13 shows the Filters tab of the Overview Editor of the web.xml in JDeveloper.
For more information about web.xml, see Appendix E, "ADF Desktop Integration Settings in the Web Application Deployment Descriptor."