3 Setting Up Kanban Management
This chapter contains the following topics:
-
Section 3.3, "Setting Up a Kanban Size Calculation Definition"
-
Section 3.4, "Defining Values for Kanban Calculation Parameters"
3.1 Understanding Kanban Management Setup
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Kanban Management integrates with several other systems, and it is critical that you set up each system appropriately to support the business processes.
In the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Inventory Management system, branch/plant constants enable you to customize how you process daily transactions for each branch/plant in the distribution and manufacturing systems. You use the Branch/Plant Constants program (P41001) to set location control and warehouse control. By predefining locations to which material can be moved or completed through work order completions transactions, location and warehouse control can support backflush as an inventory-level improvement technique.
You must set up the bills of material and routings that support the work order and rate schedule for kanban-controlled items in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Product Data Management system. The bill of material associates each component item to a routing step which, in turn, identifies the consuming location of the item. If you are using work center locations for backflushing transactions, you should make sure that the business processes are accurately defined to do so.
In the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Shop Floor Management system, you set up manufacturing constants to define branch-specific information that affects processing throughout the manufacturing systems. You use the Manufacturing Constants program (P3009) to specify the value for backflush options on the Manufacturing Constants tab. On the Commitment Control tab, you specify when inventory is committed and backflushed.
When you finish producing items on the shop floor, you need to record the completions to inventory. The completion transactions that you enter in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Shop Floor Management system update the item quantity records in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Inventory Management system. You can record completions for discrete and process work orders, as well as rate schedules.
You use the Super Backflush (P31123) and Work Order Completions (P31114) programs to enter completions for work orders, and the Completions Workbench program (P3119) to enter completions to rate schedules.
The Super Backflush program, which is called by the check-In transaction (one-phase) or completion transaction (two-phase), completes the kanban-generated work orders and rate schedules. To use Super Backflush to complete manufacturing orders, you should:
-
Set up the bills of material and routings with the correct issue codes and pay point codes, respectively.
-
Define consuming locations in the item's routing that agree with the related kanbans.
When you create a manufacturing order using a kanban transaction, the system automatically updates the work order completion form with the finished goods location identifier. This location is the supplying location identifier of the related kanban.
Inventory kanbans are always only one-phase, even though you can technically define them as two-phase. When you check out an inventory (source type 2) kanban, the kanban is marked in the software as requiring replenishment, but no software transactions occur. When you check in the kanban, you initiate an inventory transfer to move the material from the supplying location to the consuming location.
Kanban-controlled items that are supplied by an outside source (supplier) can use blanket orders in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement system to facilitate order and replenishment of those items.
You can enter a blanket order when you have an agreement with a supplier to purchase a certain quantity or amount of goods over a period of time. Blanket purchase orders enable you to negotiate and control supplier prices over longer periods of time. When you create a blanket purchase order, you enter the total quantity for which you have negotiated with the supplier.
When you are ready to receive a portion of the goods or services on a blanket order, you must release the quantity or amount for which you want to create a purchase order. For example, if you have a blanket order for 1200 widgets, and you want to receive 100, you must locate the blanket order detail line and release 100 widgets. When you have a valid blanket order and the kanban is set up to release from blanket purchase orders, the system automatically debits the blanket order for the kanban quantity. When multiple blanket orders for the kanban item exist, a blanket release form appears so that you can select the blanket order from which you want to release materials.
The system creates transfer orders for kanbans that move from one branch/plant to another. You use sales orders and purchase orders during the check-out and check-in processes.
Integration with Oracle's JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Demand Flow® Manufacturing (DFM) provides support for DFM kanbans in base manufacturing. DFM kanbans include raw in-process (RIP) (source type 0) and dual card (source type 6) replenishment sources.
For JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Kanban Management, you must identify the items as kanban-controlled, create the kanban master, define the calculation method, define the parameter values, and then generate and print the kanban cards.
3.1.1 Kanban Items
As with all items, you must set up an item record in both the F4101 and F4102 tables for kanban-controlled items.
|
Note: All items that are part of a source type 4 kanban must have a stocking type of 9, including the parent item. Additionally, you must verify that stocking type 9 in the system is defined with O in the special handling code and either an M or P code in the Description 02 column. The stocking type user-defined code (UDC) table is 41/I.The parent item for the source type 4 kanban must have a corresponding bill of material structure. You use this bill of material to perform cost roll-ups and generate sales orders. |
On the Additional System Information form (Plant Manufacturing tab) of the item branch record, you must select the associated option to identify the item as kanban-specific to that branch. Within a branch/plant, an item that is kanban-controlled must be a kanban-controlled item throughout the entire branch/plant. This helps the planning system identify kanban-specific items.
Along with the item branch record that you create for a kanban item in the F4102 table, you must define a consuming location (the location to which the item is transferred for consumption) and a supplying location (the originating location, which could be a completion or receiving location, depending on whether the item is manufactured or purchased). The source, or supply, for a kanban can be an inventory location (common parts), a work center (a manufactured subassembly), or a receiving location (a purchased or transferred part).
The system validates that the consuming and supplying locations are set up, regardless of how the location control switch is set on branch/plant constants.
|
See Also: |
3.2 Setting Up Kanban Master Records
This section provides overviews of kanban master records, kanban processing, and kanban processing logic, lists a prerequisite, and discusses how to:
-
Set processing options for Kanban Master Revisions (P3016).
-
Set up kanban master records.
3.2.1 Understanding Kanban Master Records
Before you can initiate any kanban transactions, you must set up a kanban master record for the item. You set up kanban master records in the Kanban Master Revisions program (P3016). When you set up the kanban master record, you define the information that the system uses to generate the transaction when you initiate a kanban trigger.
Each record in the F3016 table has a unique kanban ID. Each of these kanban records can have multiple containers or cards. The records also appear in the F30161. When you define an item as kanban-controlled, you essentially define the relationship between a supplying location and consuming location. You define a kanban-controlled item by item number, consuming branch/plant, consuming location, supplying branch/plant, and supplying location. The system generates a unique kanban identifier for this specific relationship.
When you have multiple kanban records (kanban IDs) with the same item number, consuming branch/plant, consuming location, supplying branch/plant, and supplying location, the kanban size for each of these records should be the same.
When you set up the item as a kanban item, you define the source type in the kanban master record to indicate how the item is supplied. For example, if the source, or supply, is a manufacturing activity (the item is a subassembly part), the system can generate a work order when the last kanban card is checked out. You select the source type from the 31/RS Replenishment Source UDC table:
-
DFM Raw In-Process (RIP) - Source Type 0
Supports material movement in the RIP area. Valid locations are not required.
-
Work center - Source Type 1
-
Inventory - Source Type 2
-
Supplier - Source Type 3
-
Outside assembly - Source Type 4
-
Transfer Order - Source Type 5
-
DFM Dual Card - Source Type 6
You also define whether the system transfers a kanban item in a one-phase or two-phase process. When the transfer occurs in one phase, the completed work order or received purchase order quantity is directly transferred to the consuming location. When the kanban is set up as a two-phase kanban, the materials that are being facilitated through the processing of the kanban cards require an additional Complete transaction to make the materials ready for transfer to the consuming location, from the supplying location. For example, this option, enables you to test the materials before they move on to be consumed during subsequent manufacturing operations.
When you set up a kanban master record, you can enter the kanban size manually or define a calculation method. If you manually enter the kanban size on the Kanban Master Revisions form, ensure that the quantity that you enter is large enough to supply the material consumed, according to the replenishment lead time that is defined for the item. If you decide that the system should not override the user-specified kanban size, then you must set the override option in the kanban master record to 1.
If you decide to use a calculation method, you must first define the calculation method in the Kanban Size Calculation Definition program (P3017). You enter the calculation method identifier in the Calculation Method field of the kanban master record.
You then define parameter values in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program (P3018) and run the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450). The system updates the kanban master record with the kanban size, and either the number of cards or quantity per card that the batch program calculated. If more than one kanban master record has the same supplying branch, supplying location, consuming branch, consuming location, and item number, the system uses the calculation value of the first record to calculate the kanban size of the subsequent record.
It is recommended that the first kanban master record have the highest calculation values set up in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program (P3018) so that the requirements of the consuming location are met correctly.
When you leave the Calculation Method Identifier field blank, the system supplies the default value of Manual Entry.
When the kanban is a source type 1 (work center), and the item being produced when the kanban is checked out is a rate-scheduled item, you can indicate that you want the rate schedule to be assigned to a particular repetitive line. The line that you specify must be a valid work center in the F30006 table and have a valid line and item relationship.
|
Note: When a source type 2 kanban is slated to generate multi-tier kanban requests from the supplying location, the system maintains information about the secondary kanban and links to it using the Related Kanban ID. |
Given the relationship that you specify between the kanban size and the container size, the system calculates the number of containers. You define each kanban ID with the number of containers, and you can specify as many containers as needed.
For kanbans that are associated with JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Demand Flow® Manufacturing, the kanban sizes that are calculated in JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Demand Flow® Manufacturing populate the kanban size field in base manufacturing. The override flag in the F3016 table is set to 1 for kanban records that are imported from JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Demand Flow® Manufacturing. This prevents the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450) in Oracle's JD Edwards EnterpriseOne from recalculating the kanban size and overriding the kanban sizes that were calculated in JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Demand Flow® Manufacturing.
DFM kanbans in RIP (source type 0) function within a raw in-process area and require no check-in or check-out. Type 0 kanbans are optional since they perform no transactions. Inventory (source type 2) and Supplier (source type 3) kanbans are checked in to the first-in-RIP location. Once transactions are successfully completed, inventory balances are reflected in the first-in-RIP location. RIP kanbans pull inventory physically from the first-in-RIP location and item completions is performed which reduces the inventory balances in the first-in-RIP location.
Dual card kanbans (source type 6), specify the number of cards that require check-in before replenishment is performed. The transactions are supported by item completions.
Only internal users can maintain kanban records. When you change the kanban quantity, number of cards, or lead time, you can set up the system to initiate workflow to advise the supplier. All users can review kanban records. Each supplier can review only the procurement kanban master records for that supplier.
3.2.2 Understanding Kanban Processing
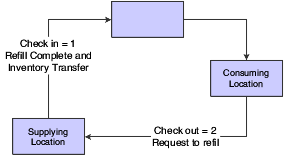
Kanbans can be used as part of a one-phase or two-phase process. The one-phase process assumes that the completion or receipt of quantity to the supplying location and transfer to the consuming location are performed in one step. With a one-phase kanban, the status of the kanban progresses as follows:
-
Check In to Check Out.
-
Check Out to Check In.
This diagram illustrates the one-phase kanban process:
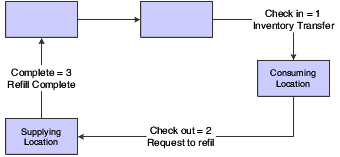
The two-phase approach assumes that the completion and transfer to the consuming location are reported separately. You complete or receive the quantity to the supplying location by using the Complete status, which is status 3. After the quantity has been physically received at the supplying location, you initiate an inventory transfer from the supplying location to the consuming location by checking in the kanban. The kanban status changes to Checked In (1). Using this method is helpful when you are working with items that require inspections or tests before they are moved to the consuming location. With a multiphase kanban, the status of the kanban progresses as follows:
-
Check In to Check Out.
-
Check Out to Complete.
-
Complete to Check In.
When you check in a kanban quantity from the supplier, the system can initiate a receipt transaction if you select the Receipts option in the kanban master.
This diagram illustrates the two-phase kanban process:
You can process kanbans for:
-
Inventoried items
-
Manufactured items (subassemblies)
-
Externally supplied items (supplier)
-
Interbranch items
When you check out an inventory kanban (source type 2), the system changes the kanban status. The supplying location replenishes the kanban quantity. You then check in the kanban, which results in an inventory transfer. Inventory kanbans only perform software transactions during the check-in process. All other statuses for this kanban type are informational only.
When you check out a work center kanban (source type 1), the program:
-
For discrete manufactured items, the software creates a new work order.
-
For rate scheduled items, which have an order policy code of 5 in the item branch record, the software looks for an existing open rate.
If no rate exists for the item and line combination that is specified in the kanban master record, then the software creates a new rate for the kanban quantity.
You should be aware that the software assumes that rate quantities that are generated from kanbans are due the same day that they are initiated. Therefore, no standard spreading of the subsequent rate quantity occurs in the Line Scheduling Workbench. You can set a processing option for the Enter/Change Rate Schedule program (P3109) so that the system automatically attaches the parts list and routing instructions when a new rate is created or changed.
When you check in a work center kanban, you complete the work order or rate, issue materials, enter hours and quantities, and transfer the parent item to the consuming location.
When you check out a kanban that a work center or production line supplies, and the item is a phantom, no transactions other than inventory transfers occur. When you have no work orders or rates to process; the producing line replenishes the item, and the system completes the kanban and checks it in. This results in a transaction for inventory transfer, from the supplying location to the consuming location.
An externally supplied kanban creates an open purchase order for the kanban item. This purchase order can be an existing one, or, optionally, one that is created during the check-out process. In addition, when you check out the kanban, the system might also initiate an electronic data interchange (EDI) transaction. When you check in kanbans from an external supplier, the system optionally creates a receipt for the purchase order. You can also use kanbans to release quantities from open blanket purchase orders.
A kanban that is supplied from a branch/plant requires you to create a transfer sales order when you check out the kanban. When you check in the kanban that is supplied by another branch/plant, the system creates a transfer purchase order and receipt.
For JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Demand Flow® Manufacturing, a raw in-process (RIP) (source type 0) kanban supports material movement within the RIP without requiring valid locations. The DFM dual card kanban (source type 6) triggers kanban replenishment from a machine cell. For a dual card kanban, the number of cards must be checked out from the consuming location for the replenishment to be triggered. A one-phase DFM kanban check-in triggers lean completions and an inventory transfer. A two-phase DFM kanban complete status triggers lean completions and check-in triggers an inventory transfer.
3.2.3 Understanding Kanban Processing Logic
This table outlines the kanban processing logic:
3.2.5 Forms Used to Set Up Kanban Master Records
3.2.6 Setting Processing Options for Kanban Master Revisions (P3016)
These processing options control default processing for the Kanban Master Revisions program.
3.2.6.1 Versions
This processing option controls which version the system uses when you call a program from the Kanban Master Revisions program.
- 1. Kanban Size Calculation (R40450)
-
Specify the version of the Kanban Size Calculation program. If you leave this processing option blank, the system uses the default version XJDE0001.
3.2.6.2 Process
This processing option controls the creation of ad hoc kanban cards.
- 1. Create an Ad Hoc Card
-
Enter 1 to enable the creation of ad hoc kanbans through the Kanban Master Revisions program. If you leave this processing option blank, you cannot create ad hoc kanbans.
3.2.7 Setting Up Kanban Master Records
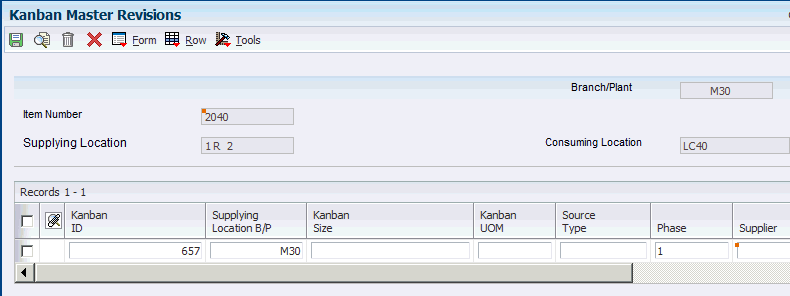
Access the Kanban Master Revisions form.
- Kanban Size
-
Enter the total size of the kanban. You can leave this field blank if the size is calculated using the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450).
- Source Type
-
Enter a code from user-defined code 31/RS that indicates the type of supplying location for a kanban. Values are:
0: DFM Raw and In Process (RIP)
1: Work center
2: Inventory
3: Supplier
4: Outside assembly
5: Transfer Order
6: DFM Dual Card
- Container Size
-
Displays the capacity of a container in a kanban-controlled environment. The value that appears in this field is set up in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program (P3018).
- Supplier
-
(Optional) Complete the supplier field if you use source type 3 (Supplier).
- Line/Cell Identifier
-
(Optional) Defines a production line or cell. You can define detailed work center operations inside the line or cell. If the item is a rate schedule item, this field identifies the line where the item is manufactured. For DFM items, the Line Design ID populates this field.
- Override
-
(Optional) Locks the kanban size and quantity to prevent changes by the kanban calculation program. Values are:
0: The system recalculates the size of the kanban.
1:The system does not recalculate the size of the kanban.
If you enable the override option, the system does not update the record when you run the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450).
- Receipts
-
(Optional) Indicates whether the system runs the receipts process at kanban check-in time. Values are:
0: The system does not run the receipt process.
1: The system runs the receipt process.
If you are setting up a supplier kanban (source type 3) and you want the purchase order receipt process to be initiated by a check-in transaction, you must activate this option.
- Number of Cards
-
Define the number of cards for a kanban. Each card represents a container. This number is determined by dividing the kanban size by the container size. For example, a kanban of 100 might be made up of four containers that each hold 25 components. Therefore, the kanban has four cards (1 of 4, 2 of 4, 3 of 4, and 4 of 4).
- Calculation Method
-
Specify the calculation method that you want the system to use for kanban calculations. The system provides four standard calculation methods to perform Kanban calculations.
- Related Kanban ID
-
(Optional) Identifies the second kanban that is assigned to an item in a specified branch/plant, consuming location, or supplying location. This field is used with multi-tier and reorder point.
- Ad Hoc Card Exists
-
Indicates the presence of an ad hoc kanban card. The card may be active or inactive. If you insert an ad hoc kanban card when an inactive ad hoc card exists, the inactive card is activated.
- Dual Cards
-
Enter the number of cards that are required to trigger the kanban check out transaction for a dual card kanban. For example, there might be five kanbans in use between the supplying and consuming locations, and the number of dual cards is three. Thus, three kanbans must be checked out to trigger replenishment.
3.3 Setting Up a Kanban Size Calculation Definition
This section provides an overview of kanban size calculations and standard kanban equations, and discusses how to set up a kanban size calculation definition.
3.3.1 Understanding Kanban Size Calculations
The Kanban Size Calculation Definition program (P3017) defines a kanban size calculation, also called a calculation method. You can enter a kanban size manually, or you can define a calculation method to be used by the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450).
The calculation method that determines kanban size, the number of kanban cards, and the quantity per card depends upon these attributes:
-
The methodologies that the inventory manager wants to adopt in reducing the work-in-process inventory levels (such as discrete versus rate-based, safety stock, multi-tier).
-
The physical dimensions of the product and the holding bin.
-
The demand profile of the product.
-
The lead time and shipment pattern of the product.
-
The cost of the product.
The goal of sizing an ideal kanban is to ensure that the system never runs out of inventory while the inventory level remains as low as possible.
Generally, you perform kanban calculations during periodic item planning cycles when the time periods are long. You should run the Kanban Size Calculation program after you run material requirements planning (MRP), which is generally once per month. When demand fluctuations are high, kanban calculations, particularly the number of kanban cards in process, should be calculated more frequently (for instance, on a weekly basis). You might also need to insert an ad hoc card to cover a short-term spike.
The Kanban Size Calculation Definition program enables you to use one of the default calculation methods that are provided by the system or to define a calculation method. A calculation identifier uniquely identifies each calculation method.
A calculation method consists of a description, business function, and defined set of parameters. The system provides four standard business functions. Each business function contains an equation that calculates the kanban size, and either the number of kanban cards or the quantity per card. The standard calculations that are provided by the system can be found in source module B3003960.
The system enables you to use custom programming to create custom equations, as well as the business functions that are required to implement the calculations. Some restrictions apply.
After you identify the business function for a specific calculation method, you must define which parameters to use. You can define 16 parameters; 13 are standard and three are custom. When you use a parameter in a calculation, you designate the parameter as either kanban-specific (specific to a kanban ID) or calculation-specific. The Kanban Parameter Usage UDC (30/KP) is hard-coded and designates how the system uses a parameter in the kanban size calculation:
-
0 - Parameter not used
-
1 - Kanban-specific parameter
-
2 - Calculation-specific parameter
If you want a kanban to use a specific calculation method, you must link that kanban master record to the calculation method using the Calculation Method field in Kanban Master Revisions program (P3016). It is recommended that you use the same calculation method to set up each kanban ID for the same kanban-controlled item, which eliminates any variance in kanban size.
3.3.1.1 Kanban Size Calculation Parameters
The Kanban Size Calculation Definition program (P3017) provides 16 parameters to define for a given calculation method. The program has 13 standard parameters and three custom parameters. When you use a parameter, you designate it as either kanban-specific (specific to a kanban ID) or calculation-specific. The Kanban Parameter Usage UDC (30/KP) is hard-coded and specifies how the system uses a parameter in the kanban size calculation.
3.3.2 Understanding Standard Kanban Equations
Software calculation methods that you use to determine the kanban size have associated business functions. The standard business functions contain one of the four standard size-calculation equations that the system provides.
You can customize the existing kanban sizing calculations or create different calculations using custom programming. You can also manually enter a kanban size instead of using a calculation method.
3.3.2.1 Kanban Equation 1: Fixed Container Size and High Demand
This equation calculates the number of cards when the kanban quantity is fixed to the container size. Use this equation when item demand fluctuates significantly:
(Kanban size) = (high daily demand) × [(lead time delivery (days)) + (scan delta days)] + (safety stock)
(High daily demand) = ( (Highest period demand in the Periods in MRP Window) x (vendor split percent) x (demand split percent for the consuming location)) ÷ (days built per period)
The system then calculates the number of kanban cards by dividing the kanban size by the container size.
3.3.2.2 Kanban Equation 2: Fixed Container Size and Average Demand
This equation calculates the number of cards when the kanban quantity is fixed to the container size and demand is based on the average daily demand.
(Kanban size) = (average daily demand) × [(leadtime delivery (days)) + (scan delta days)] + (safety stock)
(Average daily demand) = ( (average period demand in the Periods in MRP Window) × (vendor split percent) x (demand split percent for the consuming location)) ÷ (days built per period)
The system calculates the number of kanban cards by dividing the kanban size by the container size.
3.3.2.3 Kanban Equation 3: Fixed Number of Cards and High Demand
This equation calculates the kanban quantity for a fixed number of containers when an item has high demand.
(Kanban size) = (high daily demand) × [(lead time delivery (days)) + (scan delta days)] + (safety stock)
The quantity per container or container size is calculated by dividing the kanban size by the number of cards.
3.3.2.4 Kanban Equation 4: Fixed Number of Cards and Average Demand
This equation calculates the kanban quantity for a fixed number of containers with demand based on the average daily demand.
(Kanban size) = (average daily demand) × [(leadtime delivery (days)) + (scan delta days)] + (safety stock)
The system calculates the quantity per container or container size by dividing the kanban size by the number of cards.
3.3.2.5 Manual Entry of Kanban Sizes
The system enables you to manually enter the kanban quantity and number of containers. You enter this kanban information when you set up a kanban master record.
If you manually enter the kanban size on the Kanban Master Revisions form, ensure that the quantity that you enter is sufficiently large enough to supply the material that is consumed, according to the replenishment lead time that is defined for the item.
To prevent the system from overriding the user-specified kanban size, enter 1 in the Override field on the Kanban Master Revisions form.
When you use the manual entry method, the system performs no calculations.
3.3.3 Form Used to Set Up a Kanban Size Calculation Definition
3.3.4 Setting Up a Kanban Size Calculation Definition
Access the Kanban Size Calculation Revisions form.
Figure 3-4 Kanban Size Calculation Revisions form
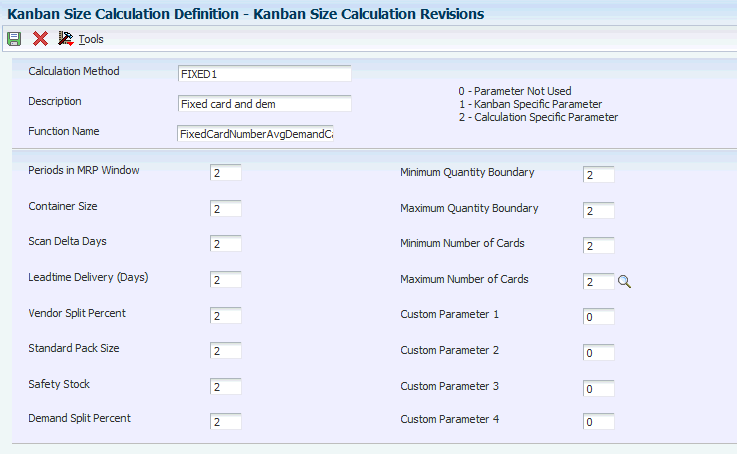
Description of "Figure 3-4 Kanban Size Calculation Revisions form"
- Function Name
-
Identify the actual name of the function. It must follow standard ANSI C naming conventions (for example, no space between words). Select the business function for this calculation method. The system verifies that the business function exists.
- Periods in MRP Window
-
Specify the usage level of the Periods in MRP Window parameter in the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450). Calculation-specific parameters have values that apply to all kanbans that use a specific size calculation method. Kanban-specific parameters have values that apply to a specific kanban using a particular size calculation method. Values are:
0: Parameter is not used.
1: Parameter is kanban-specific.
2: Parameter is calculation-specific.
This parameter defines the number of time buckets that the system uses to calculate the demand for kanban size.
The system counts the number of time buckets from a defined start date to arrive at the end of a time horizon. You enter the start date in a processing option for the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450). If you do not specify a date, the system uses the material requirements planning (MRP) generation date as the start date.
It is recommended that you set the MRP Planning Horizon periods in the MRP/MPS Requirements Planning program (R3482) to the same settings as the Periods in MRP Window in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program (P3018).
- Container Size
-
Specify the usage level of the Container Size parameter in the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450). This parameter defines the kanban movement quantity. For example, if the kanban is a physical container, the container size identifies how much the container can hold.
Calculation-specific parameters have values that apply to all kanbans that use a specific size calculation method. Kanban-specific parameters have values that apply to a specific kanban that uses a specific size calculation method. Values are:
0: Parameter is not used.
1: Parameter is kanban-specific.
2: Parameter is calculation-specific.
- Scan Delta Days
-
Specify the usage level of the Scan Delta Days parameter in the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450). This parameter defines the number of days between a kanban card checkout action and the day on which the supplier receives the notification of the checkout. For example, if a kanban card is scanned at 9:00 am one day, and the supplier receives an EDI 862 transaction the next day through a nightly batch program, the scan delta days parameter would be 1.
Calculation-specific parameters have values that apply to all kanbans that use a specific size calculation method. Kanban-specific parameters have values that apply to a specific kanban that uses a specific size calculation method. Values are:
0: Parameter is not used.
1: Parameter is kanban-specific.
2: Parameter is calculation-specific.
- Leadtime Delivery (Days)
-
Specify the usage level of the Leadtime Delivery (Days) parameter in the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450). This parameter is the time duration between when the goods leave the supplier and when they arrive at the work center. Calculation-specific parameters have values that apply to all kanbans that use a specific size calculation method. Kanban-specific parameters have values that apply to a specific kanban that uses a specific size calculation method. Values are:
0: Parameter is not used.
1: Parameter is kanban-specific.
2: Parameter is calculation-specific.
- Vendor Split Percent
-
Specify the usage level of the Vendor Split Percent parameter in the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450).
You specify the vendor in the kanban master record. When a feeder work center is the source of the kanban, then this number indicates the fraction of demand that the particular work center satisfies. The Kanban Size Calculation program multiplies this value by the calculated demand to determine the demand per supplier.
For a kanban master record with the same supplying branch, consuming branch, supplying location, consuming location, and item number, the vendor split percentage is the same for all of the records. The first record's vendor split percentage is applied to all of the records. You can have different vendors for different kanban IDs with the same supplying branch, consuming branch, supplying location, consuming location, and item number combinations. The first record's vendor split percentage should be the highest possible, as set up in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program. Thus, subsequent records are covered even if you have set up lower vendor split percentages in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program.
Calculation-specific parameters have values that apply to all kanbans that uses a specific size calculation method. Kanban-specific parameters have values that apply to a specific kanban using a particular size calculation method. Values are:
0: Parameter is not used.
1: Parameter is kanban-specific.
2: Parameter is calculation-specific.
This parameter is the percent of demand to which a particular vendor caters.
- Standard Pack Size
-
Specify the usage level of the Standard Pack Size parameter in the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450). This parameter is the standard shipment size for an item coming from a supplier. When you specify this value, the Kanban Size Calculation program rounds up the calculated kanban size to the closest multiple of this number.
Calculation-specific parameters have values that apply to all kanbans that use a specific size calculation method. Kanban-specific parameters have values that apply to a specific kanban that uses a specific size calculation method. Values are:
0: Parameter is not used.
1: Parameter is kanban-specific.
2: Parameter is calculation-specific.
- Safety Stock
-
Specify the usage level of the Safety Stock parameter in the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450). This parameter is the quantity kept on hand to cover fluctuations in demand. The Kanban Size Calculation program adds this value to the calculated demand.
Calculation-specific parameters have values that apply to all kanbans that use a specific size calculation method. Kanban-specific parameters have values that apply to a specific kanban that uses a specific size calculation method. Values are:
0: Parameter is not used.
1: Parameter is kanban-specific.
2: Parameter is calculation-specific.
- Demand Split Percent
-
Specify the usage level of the Demand Split Percent parameter in the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450).
This parameter defines the demand for a kanban item at its consuming location, expressed as a percentage of the total demand for the same item at all locations in the branch/plant over a period of time.
When the consuming location on the kanban is the only location in which the item is used, then the demand split percent is 100 percent.
When multiple consuming locations exist, this parameter identifies the percent of demand from one location. For instance, 40 percent of the demand is planned by this kanban, and 60 percent of the demand is planned by another kanban.
The Kanban Size Calculation program multiplies this value by the demand for the item to determine the demand at the consuming location. For a kanban master record with the same supplying branch, consuming branch, supplying location, consuming location, and item number, the demand split percentage is the same for all the records. The first record's demand split percentage is applied to all of the records.
You can have different demand split percentages for different kanban IDs for the same supplying branch, consuming branch, supplying location, consuming location, and item number. The first record's demand split percentage should be the highest possible, as set up in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program. Thus, subsequent records with the same supplying branch, consuming branch, supplying location, consuming location, and item number are covered, even if you have set up lower demand split percentages in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program.
Calculation-specific parameters have values that apply to all kanbans that use a specific size calculation method. Kanban-specific parameters have values that apply to a specific kanban that uses a specific size calculation method. Values are:
0: Parameter is not used.
1: Parameter is kanban-specific.
2: Parameter is calculation-specific.
- Minimum Quantity Boundary
-
Specify the usage level of the Minimum Quantity Boundary parameter in the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450). This parameter defines the minimum quantity that can be ordered by a single kanban trigger. When the Kanban Size Calculation program calculates the kanban size, and the calculated size is less than the minimum quantity, then the system uses the minimum quantity as the size of the kanban.
The system assumes the kanban is fixed-size, when the minimum quantity for an item is same as the maximum quantity defined for the item. The Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450) calculates the number of kanbans required based on the fixed-size.
Calculation-specific parameters have values that apply to all kanbans that use a specific size calculation method. Kanban-specific parameters have values that apply to a specific kanban using a particular size calculation method. Values are:
0: Parameter is not used.
1:Parameter is kanban-specific.
2: Parameter is calculation-specific.
- Maximum Quantity Boundary
-
Indicate the level of usage of the Maximum Quantity Boundary parameter in the Kanban Size Calculation program. This parameter defines the maximum quantity that a single kanban trigger can order. When the Kanban Size Calculation program calculates the kanban size, and the calculated size is greater than the maximum quantity, then the software uses the maximum quantity as the size of the kanban.
The system assumes the kanban is fixed-size, when the maximum quantity for an item is same as the minimum quantity defined for the item. The Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450) calculates the number of kanbans required based on the fixed-size.
Calculation specific parameters have values that apply to all kanbans using a particular size calculation method. Kanban-specific parameters have values that apply to a specific kanban using a particular size calculation method. Values are:
0: Parameter is not used.
1: Parameter is kanban-specific.
2: Parameter is calculation-specific.
- Minimum Number of Cards
-
Specify the usage level of the Minimum Number of Cards parameter in the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450). This parameter defines the minimum number of kanban cards in the cycle. Each kanban card represents a container. Each kanban should have at least one card. For fixed container size calculations, the Kanban Size Calculation program calculates the number of cards, and, if the calculated value is less than the specified minimum number of cards, the system uses the minimum number of cards.
For calculations that use a fixed number of cards, the minimum number of cards should equal the maximum number of cards.
Calculation-specific parameters have values that apply to all kanbans that use a specific size calculation method. Kanban-specific parameters have values that apply to a specific kanban that uses a specific size calculation method. Values are:
0: Parameter is not used.
1: Parameter is kanban-specific.
2: Parameter is calculation-specific.
- Maximum Number of Cards
-
Specify the usage level of the Maximum Number of Cards parameter in the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450). This parameter defines the maximum number of cards in the cycle. Each kanban card represents a container. Each kanban should have at least one card. For fixed container size calculations, the Kanban Size Calculation program calculates the number of cards, and, if the number of cards that the program calculates exceeds the maximum number of cards, then the system uses the value that represents the maximum number of cards. For calculations that use a fixed number of cards, the minimum number of cards should equal the maximum number of cards.
Calculation-specific parameters have values that apply to all kanbans that use a specific size calculation method. Kanban-specific parameters have values that apply to a specific kanban that uses a specific size calculation method. Values are:
0: Parameter is not used.
1: Parameter is kanban-specific.
2: Parameter is calculation-specific.
- Custom Parameter 1, 2, and 3
-
(Optional) Specify the usage level of Custom Parameter 1 in the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450). This custom parameter is user-defined. To use this parameter, you must modify or create the supporting business function.
Calculation-specific parameters have values that apply to all kanbans that use a specific size calculation method. Kanban-specific parameters have values that apply to a specific kanban that uses a specific size calculation method. Values are:
0: Parameter is not used.
1: Parameter is kanban-specific.
2: Parameter is calculation-specific.
- Custom Parameter 4
-
(Optional) A value that specifies the usage level of the Days Built Per Period parameter in the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450). Calculation-specific parameters have values that apply to all kanbans using a particular size calculation method. Kanban-specific parameters have values that apply to a specific kanban using a particular size calculation method. Values are:
0: Parameter is not used.
1: Parameter is kanban-specific.
2: Parameter is calculation-specific.
3.4 Defining Values for Kanban Calculation Parameters
This section provides an overview of kanban calculation parameters and discusses how to:
-
Define kanban-specific parameters.
-
Define calculation-specific parameters.
-
Define fixed-size kanban calculation parameters.
3.4.1 Understanding Kanban Calculation Parameters
Parameters are defined as kanban-specific or calculation-specific for each calculation method in the Kanban Size Calculation Definition program (P3017). After you define a calculation method, you use the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program (P3018) to define the specific value used by each parameter.
3.4.1.1 Kanban-Specific Parameters
Parameters are defined as kanban-specific or calculation-specific for each calculation method in the Kanban Size Calculation Definition program (P3017). After you define a calculation method, you use the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program (P3018) to define the specific value used by each parameter.
The system stores values for calculation method parameters that you defined as kanban-specific parameters (those that are specific to the kanban ID). When you use the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program (P3018) to enter default values, the system displays:
-
Calculation method.
-
Kanban ID.
-
Parameters that are identified as kanban-specific parameters for the calculation method.
The system enables you to enter or revise values for parameters designated as kanban-specific parameters for a calculation method.
The Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450) uses the value of each parameter from the kanban-specific record.
3.4.1.2 Calculation-Specific Parameters
The system stores values for calculation method parameters that are defined as calculation-specific parameters. When you use the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program (P3018) to enter default values, the system displays:
-
Calculation method.
-
Parameters that are identified as calculation-specific parameters for the calculation method.
The system enables you to enter or revise values for parameters that are designated as calculation-specific parameters for a calculation method.
The Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450) uses the value of each parameter from the calculation-specific record.
3.4.1.3 Fixed-size Kanban Calculation Parameters
In calculation, the system determines the number of kanbans depending on the size of the kanban. If you want to use fixed-size kanbans, you define a calculation parameter where the maximum and minimum quantities are the same. If you enter the same value for the maximum and minimum quantities, the system assumes that the size of kanban is fixed. The system calculates the number of required kanbans based on the size of the kanban.
In a bicycle manufacturing unit, for example, the production assistant might manage the painting station using kanbans. The painted frames are stacked in a rack which is moved to the shop floor for the next stage of production. Each rack is designed to hold a fixed number of frames. Here the rack serves as a kanban with fixed quantity or size. Based on the quantity of components required and the size of the kanban, the system calculates the required number of racks with painted frames.
3.4.2 Forms Used to Define Values for Kanban Calculation Parameters
3.4.3 Defining Kanban-Specific Parameters
Access the Kanban Parameter Revisions form.
Figure 3-5 Kanban Parameter Revisions form
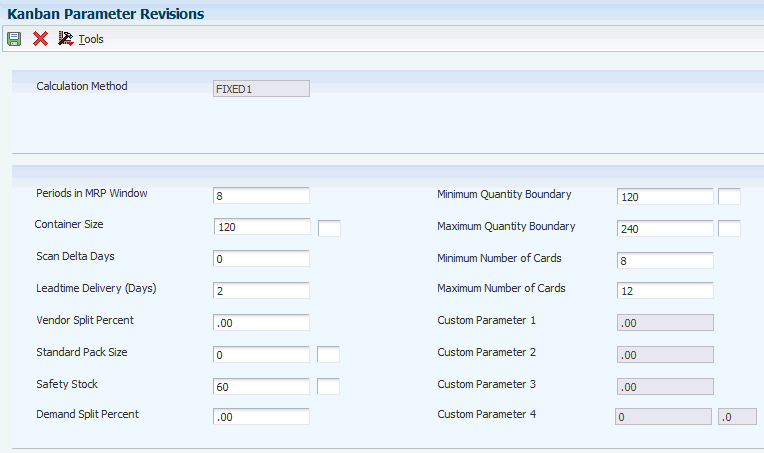
Description of "Figure 3-5 Kanban Parameter Revisions form"
Complete the value field for each parameter that is identified as a kanban-specific parameter. The value fields for parameters that were not defined as calculation-specific are disabled, so you cannot enter values in them.
3.4.4 Defining Calculation-Specific Parameters
Access the Kanban Parameter Revisions form.
Complete the value field for each parameter that is identified as a kanban-specific parameter. The value fields for parameters that were not defined as calculation-specific are disabled, so you cannot enter values in them. On the Kanban Parameter Revisions form, complete the value field for each parameter that is identified as a calculation-specific parameter.
3.5 Generating Kanbans
This section provides an overview of the kanban generation process and discusses how to:
-
Set processing options for Kanban Size Calculation (R30450).
-
Calculate kanban size using standard equations.
-
Calculate kanban size using processing options.
3.5.1 Understanding the Kanban Generation Process
After you set up the item in the Kanban Master Revisions program (P3016), define the calculation method in the Kanban Size Calculation Definition program (P3017) and define parameter values in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program (P3018), you can use the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450) to calculate the size of a kanban. If you already manually entered a kanban size, you can prevent the system from updating the information that you entered by entering 1 in the Override field on the Kanban Master Revisions form.
For kanbans that are associated with JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Demand Flow® Manufacturing, the kanban sizes that are calculated in JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Demand Flow® Manufacturing populate the kanban size field in base manufacturing. The override flag in the F3016 table is set to 1 for DFM imported kanban records. This prevents the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450) in JD Edwards EnterpriseOne from recalculating the kanban size and overriding the DFM calculated kanban sizes
When you generate kanbans, you define these processing options:
-
Specify whether the Kanban Size Calculation program runs in proof or final mode.
-
Print kanban cards.
-
Print an exception report for customization purposes.
-
Update the F3016 table if you are running the program in final mode.
-
Specify a range, expressed as a percentage, within which the system does not adjust the size of the kanban.
-
Specify the source of the demand (such as forecasts, sales orders, planned orders, firm orders, and rate schedules).
-
Specify the aggregation of demand.
-
Specify the start date to use for the demand calculation.
When you run the Kanban Size Calculation batch program, you use data selection criteria to select records from the Kanban Master table. When you have kanban records (kanban IDs) that have the same item number, consuming branch/plant, consuming location, supplying branch/plant, and supplying location, divide the demand by the number of similar kanban records so that the demand is distributed evenly among the records.
Kanban size is calculated using this formula:
(Kanban size) = [(demand) × ((scan delta days)+ (lead time delivery days))] + (safety stock)
After you run the Kanban Size Calculation program, the system updates the F30161 table with the new kanban size, container size, and number of cards, based on the calculation method that you specified.
The system calculates kanban size for the first record for which you defined kanban-specific values. For kanban-specific records, use the first record's calculation values for the kanban size calculation when subsequent records have the same item number, consuming branch/plant, consuming location, supplying branch/plant, and supplying location. Subsequent records that are similar have the same calculation values and kanban sizes. The kanban size is based on the calculation method that is specified in the Kanban Size Definition program.
After you run the Kanban Size Calculation program, a report displays the new calculated kanban size, container size, number of cards, and previous kanban size.
You can run the Kanban Size Calculation program in either proof mode or final mode. When you run the program in proof mode, it displays the calculated size and does not update the Kanban Card Detail table (F30161).
When you run the program in final mode, it displays the calculated size and updates the F30161 table.
The system assumes that the kanban size is fixed when the maximum and minimum quantities are set to be same for a kanban in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program (P3018). The Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450) calculates the number of kanbans required based on the specific size of a kanban.
For calculating the required number of fixed-size kanbans, the system uses following formula:
Number of kanbans = (demand) × (lead time delivery days + scan delta days) / (kanban size – safety stock)
The Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450) compares the number of required kanbans with the current number of kanbans. If the current number is less than the necessary number, the system automatically generates more kanbans. If the current number is larger than the necessary number, the system removes the excessive kanbans from the F3016 table.
The system will not perform any calculation if the kanban is defined with an override flag in Kanban master record.
You can run the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450) either in proof or final modes. For fixed-size kanbans, the report displays the details of the newly added kanban. In the proof mode, the report lists the new kanbans with sequence numbers and displays a warning message indicating that kanbans will be generated. In final mode the report assigns kanban Ids and displays a message that kanbans have been generated. In case of excess kanbans, the system in proof mode prints a warning message indicating the kanbans to be removed. In the final mode, the system removes the kanbans from the database and prints a message indicating the removal of kanbans.
There should be at least two kanbans for an item with a combination of consuming branch/plant, consuming location, supplying branch/plant, and supplying location. If there is only one kanban, then the Kanban Size Calculation program creates a second kanban with the same attributes as the first kanban. While deleting the excess kanbans, the system leaves two kanbans for an item.
3.5.2 Setting Processing Options for Kanban Size Calculation (R30450)
These processing options control default processing for the Kanban Size Calculation program.
3.5.2.1 Process
These processing options specify how the system performs processes and calculations when running the Kanban Size Calculation program.
- 1. Kanban Size
-
Specify whether to calculate kanban sizes. Values are:
Blank: Do not calculate kanban sizes.
1: Calculate kanban sizes.
- 2. Mode
-
Specify proof or final mode. Values are:
Blank: Proof mode
1: Final mode
- 3. Print Kanban Cards
-
Specify whether to print kanban cards. Values are:
Blank: Do not print kanban cards.
1: Print kanban cards.
- 4. Print Kanban Exception Report
-
Specify whether to print the kanban exception report. Values are:
Blank: Do not print the kanban exception report.
1: Print Kanban Exception Report.
- 5. Filter Control
-
Enter the range, expressed as a percentage, above or below which the kanban should not be changed. For example, a value of 15 means plus or minus 15 percent.
3.5.2.2 Demand
These processing options specify what demand to include in calculations when running the Kanban Size Calculation program.
- 6. Kanban Demand
-
Specify what value to use to calculate kanban demand. Values are:
Blank: Use planning time fence.
1: Use the sum of the included demands.
2: Use the highest value among the included demands.
- a. Forecasts
-
Specify whether to include forecasts. Values are:
Blank: Do not include
1: Include
- b. Sales Orders
-
Specify whether to include sales orders. Values are:
Blank: Do not include
1: Include
- c. Firm Work Orders
-
Specify whether to include firm work orders. Values are:
Blank: Do not include
1: Include
- d. Planned Orders
-
Specify whether to include planned orders. Values are:
Blank: Do not include
1: Include
- e. Rate Schedules
-
Specify whether to include rate schedules. Values are:
Blank: Do not include
1: Include
- 7. Start date for demand calculation
-
Specify a start date for demand calculation. If you leave this field blank, the system uses the MRP generation date.
3.5.3 Calculating Kanban Size Using Standard Equations
Select Kanban Management Setup (G30411), Kanban Size Calculation.
This example illustrates the calculation of each of the four standard kanban equations.
3.5.3.1 Prerequisite Setup
The demand profile for the item is:
| Date | Source | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| October 6 | FC | 100 |
| October 8 | FWO | 300 |
| October 15 | SO | 200 |
| October 17 | SO | 350 |
| November 6 | FC | 150 |
The MPS Regeneration program (R3482) ran for five days, four weeks, and three months. The resulting time series is:
| Date | Demand Type | Demand As Of Date | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| October 6 | FC | 100 | |
| October 7 | |||
| October 8 | FWO | 300 | |
| October 9 | |||
| October 10 | |||
| October 17 | SO | 550 | |
| October 24 | |||
| October 31 | 8 periods in MRP Window | ||
| November 7 | FC | 150 | |
| November 28 | |||
| December 31 | |||
| January 30 |
The calculation method has been set up using the Kanban Size Calculation Definition program (P3017). The calculation method has calculation-specific parameter values, as defined in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program (P3018).
| Parameter | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Periods in MRP Window | 8 |
| Days built per week | 5 |
| Days built per month | 20 |
| Scan delta days | 1 |
| lead time delivery (days) | 2 |
| Vendor split percent | 100 |
| Safety stock | 50 |
| Demand split percent | 100 |
| Container size | 25 |
3.5.3.2 Demand Calculation
Forecasts and sales orders are the demand types that are included in the demand calculation. The demand aggregation is the sum of individual demands.
So, because this item has a sales order, a forecast, and a planned order for a particular period, the demand at the end of that period is the sum of the sales order and forecast quantities.
3.5.3.3 High Daily Demand
Maximum demand occurs in the weekly period ending October 19.
Adjusted maximum demand = 550 units ÷ 5 days built per week = 110 units per day
Maximum demand is 550 units.
3.5.3.4 Average Daily Demand
Number of months in the chosen time horizon is 0.
Sum of all monthly demands is 0.
Number of weeks in the chosen time horizon is 3.
Sum of all weekly demands is 550 units.
Number of days in the chosen time horizon is 5.
Sum of all daily demands is 100 units.
(Total demand) = (number of months × sum of all monthly demands) + (number of weeks × sum of all weekly demands) + (number of days × sum of all daily demands)
(Total demand) = (0 × 0) + (3 × 550) + (5× 100) = 2150
(Total number of days) = (number of months × days build per month) + (number of weeks × days build per week) + (number of days)
(Total number of days) = (0 × 20) + (3 ×5) + (5) = 20
(Average daily demand) = (total demand) ÷ (total number of days) = 2150 ÷ 20 = 107.5 units per day
3.5.3.5 Kanban Equation 1: Fixed Container Size and High Demand
This equation calculates the number of cards when the kanban quantity is fixed to the container size. Use this equation when item demand fluctuates significantly.
(Kanban size) = (high daily demand) × [(lead time delivery (days)) + (scan delta days)] + (safety stock)
(Kanban size) = 110 × (2 + 1) + 50 = 380 units
(Number of cards) = (kanban size) ÷ (container size) = 380 ÷ 25 = 15.2 = 16 cards
(Quantity per container) = (container size) = 25 units
|
Note: To create a fewer number of cards, increase the container size in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program. |
3.5.3.6 Kanban Equation 2: Fixed Container Size and Average Demand
This equation calculates the number of cards when the kanban quantity is fixed to the container size and demand is based on the average daily demand.
(Kanban size) = (average daily demand) × [(leadtime delivery (days)) + (scan delta days)] + (safety stock)
(Number of cards) = (kanban size) ÷ (container size) = 373 ÷ 25 = 14.92 = 15 cards
(Quantity per container) = (container size) = 25 units
|
Note: To create a fewer number of cards, increase the container size in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program. |
3.5.3.7 Kanban Equation 3: Fixed Number of Cards and High Demand
This equation calculates the kanban quantity for a fixed number of containers when an item has high demand.
The number of cards is fixed at 10 in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program.
The maximum and minimum number of cards are the same in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program for the fixed number of cards.
(Kanban size) = (high daily demand) × [(lead time delivery (days)) + (scan delta days)] + (safety stock)
(Kanban size) = 110 × (2 + 1) + 50 = 380 units
(Container size) = (kanban size) ÷ (number of cards) = 380 ÷10 = 38 (quantity per card or container size)
|
Note: To create a larger container size, decrease the number of cards in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program. |
3.5.3.8 Kanban Equation 4: Fixed Number of Cards and Average Demand
This equation calculates the kanban quantity for a fixed number of containers with demand based on the average daily demand.
The number of cards is fixed at 10 in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program.
(Kanban size) = (average daily demand) × [(leadtime delivery (days)) + (scan delta days)] + (safety stock)
(Kanban size) = 107.5 ÷ (2 + 1) + 50 = 372.5 =373 units
(Container size) = (kanban size) ÷ (number of containers) = 373 ÷ 10 = 37.3 = 38 units
|
Note: To create a larger container size, decrease the number of cards in the kanban Size Calculation parameter Definition program. |
3.5.4 Calculating Kanban Size Using Processing Options
Select Kanban Management Setup (G30411), Kanban Size Calculation.
This example illustrates the calculation of kanban size using the processing option on the Demand tab of the Kanban Size Calculation program (R30450).
3.5.4.1 Sum of Included Demands
The processing option on the Demand tab in the Kanban Size Calculation program is set to 1 - Sum of Included Demands.
Use kanban standard equation 2, fixed container size and average demand to calculate the kanban size and number of kanban cards.
3.5.4.2 Prerequisite Setup
Forecasts and sales orders were entered for nine time periods. Verify that the MRP Time Periods processing option in the MPS Regeneration program (R3482) is set to 9 periods and the Periods in MRP Window field in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program (P3018) is set to 9.
The MRP Regeneration program ran for five days, three weeks, and one month. The resulting time series is:
| Date | FSCU Quantity | SOU Quantity | Sum of Included Demands |
|---|---|---|---|
| February 2 | 100 | 30 | 130 |
| February 3 | 200 | 40 | 240 |
| February 4 | 300 | 50 | 350 |
| February 5 | 300 | 50 | 350 |
| February 6 | 200 | 100 | 300 |
| February 13 | 200 | 100 | 300 |
| February 20 | 300 | 200 | 500 |
| February 27 | 250 | 200 | 450 |
| March 31 | 100 | 200 | 300 |
|
Note: FSCU Quantity is the unadjusted forecast quantity (gross) for a specific item from the detail forecast table. SOU Quantity is the actual sales orders from the sales order detail table. |
The calculation method has been set up using the Kanban Size Calculation Definition program (P3017). The calculation method has calculation-specific parameter values, as defined in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program:
| Parameter | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Periods in MRP window | 9 |
| Days built per week | 5 |
| Days built per month | 20 |
| Scan delta days | 1 |
| Lead time delivery (days) | 2 |
| Vendor split percent | 0 |
| Safety stock | 50 |
| Demand split percent | 100 |
| Container size | 50 |
| Minimum kanban size | 20 |
| Maximum kanban size | 60 |
3.5.4.3 Average Daily Demand
Number of months in the selected time horizon is 1.
Sum of all monthly demands is 300 units.
Number of weeks in the chosen time horizon is 3.
Sum of all weekly demands = 300 + 500 + 450 = 1250 units
Number of days in the chosen time horizon is 5.
Sum of all daily demands = 130 + 240 + 350 + 350 + 300 = 1370 units
(Total demand) = (number of months × sum of all monthly demands) + (number of weeks × sum of all weekly demands) + (number of days × sum of all daily demands)
(Total demand) = (1 × 300) + (3 × 1250) +(5 × 1370) = 10900
(Total number of days) = (number of months × days built per month) + (number of weeks × days build per week) + (number of days)
(Total number of days) = (1 × 20) + (3 ×5) + (5) = 40
(Average daily demand) = (total demand) ÷ (total number of days) = 10900 ÷ 40 = 272.5 units per day
3.5.4.4 Kanban Equation 2: Fixed Container Size and Average Demand
Because the demand split percentage is 100 percent, the average daily demand remains the same.
The F3016 table includes three kanban records for the same supplying branch, supplying location, consuming branch, consuming location, and item number. The demand has to be distributed evenly among the records.
(Average daily demand) = (average daily demand) ÷ (number of similar kanban records)
(Average daily demand) = 272.5 ÷ 3 = 91
(Kanban size) = (average daily demand) × [(leadtime delivery (days)) + (scan delta days)] + (safety stock)
(Kanban size) = 91 × (2 + 1) + 50 = 323 units
The maximum kanban size is defined as 60 in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program. Therefore, the kanban size is 60, because 323 is greater than 60.
(Number of cards) = (kanban size) ÷ (container size) = 60 ÷ 50 = 1.2 = 2 cards
3.5.4.5 Highest Value of Included Demands
The processing option on the Demand tab in the Kanban Size Calculation program is set to 2 - Highest Value of Included Demands.
Use kanban standard equation 2, fixed container size and average demand, to calculate the kanban size and number of kanban cards.
3.5.4.6 Prerequisite Setup
Forecasts and sales orders were entered for nine time periods. Verify that the MRP Time Periods processing option in the MPS Regeneration program (R3482) is set to 9 periods and that the Periods in MRP Window field in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program (P3018) is set to 9.
The MRP Regeneration program ran for five days, three weeks, and one month. The resulting time series is:
| Date | FSCU Quantity | SOU Quantity | Highest Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| February 2 | 100 | 30 | 100 |
| February 3 | 200 | 40 | 200 |
| February 4 | 300 | 50 | 300 |
| February 5 | 300 | 50 | 300 |
| February 6 | 200 | 100 | 200 |
| February 13 | 200 | 100 | 200 |
| February 20 | 300 | 200 | 300 |
| February 27 | 250 | 200 | 250 |
| March 31 | 100 | 200 | 200 |
The calculation method has been set up using the Kanban Size Calculation Definition program. The calculation method has calculation-specific parameter values, as defined in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program:
| Parameter | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Periods in MRP window | 9 |
| Days built per week | 5 |
| Days built per month | 20 |
| Scan delta days | 1 |
| Lead time delivery (days) | 2 |
| Vendor split percent | 0 |
| Safety stock | 50 |
| Demand split percent | 100 |
| Container size | 50 |
| Minimum kanban size | 20 |
| Maximum kanban size | 60 |
3.5.4.7 Average Daily Demand
Number of months in the selected time horizon is 1.
Sum of all monthly demands is 200 units.
Number of weeks in the chosen time horizon is 3.
Sum of all weekly demands = 200 + 300 + 250 = 750 units
Number of days in the selected time horizon is 5.
Sum of all daily demands = 100 + 200 + 300 + 300 + 200 = 1100 units
(Total demand) = (number of months × sum of all monthly demands) + (number of weeks × sum of all weekly demands) + (number of days × sum of all daily demands)
(Total demand) = (1 × 200) + (3 × 750) +(5 × 1100) = 7950
(Total number of days) = (number of months × days built per month) + (number of weeks × days built per week) + (number of days)
(Total number of days) = (1 × 20) + (3 ×5) + (5) = 40
(Average daily demand) = (total demand) ÷ (total number of days) = 7950 ÷ 40 = 198.75 units per day
3.5.4.8 Kanban Equation 2: Fixed Container Size and Average Demand
Because the demand split percentage is 100 percent, the average daily demand remains the same.
The Kanban Master table contains three kanban records for the same supplying branch, supplying location, consuming branch, consuming location, and item number. The demand must be distributed evenly among the records.
(Average daily demand) = (average daily demand) ÷(number of similar kanban records)
(Average daily demand) = 198.75 ÷ 3 = 67
(Kanban size) = (average daily demand) × [(leadtime delivery (days)) + (scan delta days)] + (safety stock)
(Kanban size) = 67 × (2 + 1) + 50 = 251 units
The maximum kanban size is defined as 60 in the Kanban Size Calculation Parameter Definition program. Therefore, the kanban size is 60, because 251 is greater than 60.
(Number of cards) = (kanban size) ÷ (container size) = 60 ÷ 50 = 1.2 = 2 cards