7 Planning Production Capacity
This chapter contains the following topics:
7.1 Understanding Capacity Planning
Use Capacity Planning to ensure that sufficient capacity is available to accomplish the planned production schedule that is generated by Master Production Schedule (MPS) or Material Requirements Planning (MRP). If sufficient capacity is not available, then you must alter the plan or the capacity.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Capacity Planning from Oracle comprises:
-
Resource Requirements Planning (RRP).
-
Rough Cut Capacity Planning (RCCP).
-
Capacity Requirements Planning (CRP).
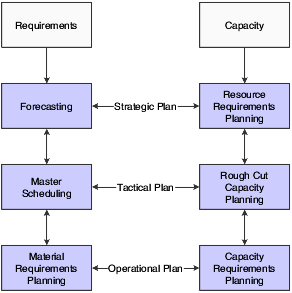
This flowchart illustrates the planning system process:
RCCP identifies capacity constraints at critical work centers.
CRP matches the available personnel and equipment resources to the resource requirements as generated by MRP. CRP indicates whether you need to revise the material requirements plan or increase resources.
Work center capacity is based on available hours to produce products within certain time frames. MPS, MRP, and JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Shop Floor Management provide the actual hours to produce products based on the quantity that is required.
Manufacturing must determine whether the production plan is supportable as is or whether additional future resources are needed, such as:
-
Additional skilled labor.
-
New machinery.
-
New facilities or additional real estate.
Demand forecasting is the logical starting point for developing a resource requirements plan. However, you must remember that the demand forecast is not the actual plan, but that it is used as input for the plan. RRP provides an estimate of the time and resources that you need to produce a product.
You generate a resource requirements plan after you generate the long-term forecast but before you run the Master Scheduling program. RRP uses the data from a forecast of future sales to estimate the time and resources that are required to meet the production plan.
RRP can help you resolve long-range planning issues such as:
-
Expanding existing facilities.
-
Acquiring new facilities.
-
Staffing loads.
-
Determining capital expenditures for equipment.
RRP enables you to support the company's strategic business plan with a realistic tactical plan that:
-
Is shorter in range than the strategic plan and has a planning horizon of 12 months to three years.
-
Enables planning at the product family level and has greater detail than the strategic plan.
-
Validates the monetary amounts that are allotted to the business plan.
The Resource Requirements Planning program (P3380) generates a capacity plan by critical work center. To answer long-range planning questions, you need to know the current capacity and the requirements to support the planned workload.
7.2 Generating Resource Requirements Plans
This section provides an overview of resource requirements planning, lists prerequisites, and discusses how to:
-
Run resource requirements planning.
-
Set processing options for Resource Requirements Planning (R3380).
7.2.1 Understanding Resource Requirements Planning
After you have entered resource units and resource profiles, you run the Resource Requirements Planning Regeneration program to generate the resource requirements plan. The plan contains long-range estimates of the capacity needs at the work centers. These needs might include:
-
The number of production staff that you need to hire to meet future production needs.
-
The number of additional machines that you will need for a new product line.
-
The real estate that you will need to buy for additional facilities.
Because you use the forecast in place of work orders for long-range planning, the data that this program creates is an estimate of capacity needs that is based on the forecast. The resource profile offsets required dates for capacity.
The types of data that you can create include:
-
Over-capacity or under-capacity messages.
-
Period summaries about work centers.
-
New load profile information based on the type of work center load:
-
Rated profile is the number of available units from the Work Center Resource Units table (F3007).
-
Loaded profile is the forecasted load that is derived from the master planned item's forecasts and their resource profiles.
-
Percent resource used is the loaded profile divided by the rated profile.
-
Resource available is the rated profile minus the loaded profile.
-
Accumulated resources available is a running total of the resources that are available.
-
When you set up the versions for planning the resource requirements, you need to determine the data selection for work centers, branch/plants, and dispatch groups that you want to process.
7.2.1.1 Work Centers to Process
You select one of these options:
-
N: Process only noncritical work centers.
-
1: Process critical work centers in calculating resource requirement plans only.
-
2: Process critical work centers in calculating capacity requirements plans only.
-
3: Process critical work centers in calculating resource requirements plans and capacity requirements plans.
-
4: Not a capacity work center (will not be processed in Capacity Requirements Planning).
7.2.1.2 Branch/plant and Dispatch Group
You can select the following specific information for planning facilities and dispatch groups:
-
A specific planning facility, the dispatch groups, or both.
-
A group of planning facilities, the dispatch groups that are using the RANGE or LIST values, or both.
7.2.2 Prerequisites
Before generating requirements plans, verify that:
-
Resource units exist for all of the work centers in the facility.
-
Resource profiles exist for all of the master-scheduled items.
-
A resource profile is set up with the appropriate units of measure.
You can use a maximum of five units of measure.
-
A detail forecast is created for the master-scheduled items using the Forecast Revisions program (P3460).
-
The forecast types that you want to use in the generation have been determined.
You can use a maximum of five.
-
A shop floor calendar is set up for all summary time periods for which you want to generate resource requirements plans.
7.2.3 Running Resource Requirements Planning
Select Periodic Resource/Capacity Planning (G3321), Resource Requirements Planning.
7.2.4 Setting Processing Options for Resource Requirements Planning (R3380)
Use these processing options to set planning parameters, specify forecast types used as input, and specify the output unit of measure.
7.2.4.1 Bucket Info
These processing options specify the regeneration start date, the planning horizon periods, and the past due periods in a planning process.
- 1. Regeneration Start Date
-
Specify the date that the program uses to start the planning process. This date is also the beginning of the planning horizon.
If you leave this option blank, the system uses the system date.
- 2. Planning Horizon Periods
-
Specify the number of weeks and months that the system creates in a planning period.
- Number of Planning Weeks
-
Specify the number of weeks that the system creates in a planning period. For example, when the system displays the Time Series program (P3413), the system also accesses data for the number of planning weeks.
- Number of Planning Months
-
Specify the number of months that the system creates in a planning period. For example, when the systems displays the Time Series program, the system also accesses monthly data for the number of planning months.
- 3. Past Due Periods
-
Specify the number of past due periods that the system generates for a loaded profile. These values represent the number of past due periods for the program's generation date. Values are:
0: Zero periods (default)
1: One past due period
2: Two past due periods
7.2.4.2 Process
These processing options enable you to specify the branch that a system uses for the CRP/RCCP Regeneration program (R3382) and the percentages for underrated and overrated capacity. Additionally, you determine whether you want work centers to be rolled up by dispatch group in the planning.
- 1. Branch
-
Specify the branch that the system uses for the CRP/RCCP Planning Regeneration program.
- 2. Under Rated Capacity Percent
-
Specify the tolerance percent under the rated capacity that the system uses to determine whether a work center is underloaded. The system displays messages with a status of U (under) for capacity loads that are less than the identified percentage under the rated value.
For example, if the rated capacity is 100 units and the underrated capacity is set to 5 percent, then the system still considers a capacity load of 95 units as a valid load at a work center. Similarly, the system would consider a capacity load of 94 units as an underload.
- 3. Over Rated Capacity Percent
-
Specify the tolerance percent over the rated capacity that the system uses to determine whether a work center is overloaded. The system displays messages with a status of O (over) for the capacity load that is greater than the identified percentage over the rated value.
For example, if the rated capacity is 100 units and the overrated capacity is set to 5 percent, then the system still considers a capacity load of 105 as a valid load at a work center. Similarly, the system would consider a capacity load of 106 units as an overload.
- 4. Roll Up To Dispatch Group
-
Specify whether multiple work centers within a dispatch group roll up to that dispatch group for review. Values are:
Blank: Do not roll up work centers to a dispatch group.
1: Roll up work centers to a dispatch group.
7.2.4.3 Forecast Types
These processing options enable you to specify the forecast type that the system processes when it runs the Resource Requirement Planning Regeneration program. You can enter up to five forecast types in the system. Forecast types are user defined and stored in the Forecast File (F3460) table.
- 1. Forecast Types Used (up to 5)
-
Specify up to five forecast types that the system processes when you run the Resource Requirements Planning program.
- Forecast Type 1 through Forecast Type 5
-
Specify the forecast type that the system processes when you run the Resource Requirements Planning program.
Forecast types are user defined and are stored in the F3460 table (Detail Forecast table).
7.2.4.4 UOM
This processing option enables you to specify the units of measure that the system processes when you run the Resource Requirements Planning Regeneration program. The system can process up to five units of measure at a time.
- 1. Units of Measure Used (up to 5)
-
Specify up to five units of measure that the system processes when you run the Resource Requirements Planning program.
- Unit of Measure 1 through Unit of Measure 5
-
Specify the unit of measure that the system processes when you run the Resource Requirements Planning program.
7.3 Validating Resource Requirements Plans
This section provides an overview of resource requirements plan validation and discusses how to:
-
Set processing options for Capacity Message Summary (P3301).
-
Review dispatch groups.
-
Set processing options for Capacity Load (P3313).
-
Review work center loads.
-
Set processing options for Period Summary (P3312).
-
Review period summaries.
-
Set processing options for Capacity Planning Message Revisions (P3311).
-
Review capacity planning message details.
7.3.1 Understanding Resource Requirements Plan Validation
Validating a resource requirements plan consists of identifying the overloaded work centers, adjusting the forecast or resources, and generating the plan again to see whether the adjustments distributed the loads among the work centers. Repeat the steps until all of the loads at each work center are appropriate.
7.3.1.1 Resource Requirements Plans
When you generate a resource requirements plan, the system creates a time series that displays the load during each planning period for a work center. If you organize several work centers as a dispatch group according to common functions, similar operations, or steps in a routing, you can view the group to see how the production plan affects the capacity of the work centers as a group.
You can review summaries of each period to determine the load that is placed on a work center by each item or order. You can also review messages for each work center and delete, clear, or the hold messages.
If the system encounters over-capacity or under-capacity conditions, you can review the plan and identify the periods or work centers in which the conditions occur. You might have to adjust the forecast or capacity, and then generate the resource requirements plan again.
7.3.1.2 Dispatch Groups for RRP
If several work centers are organized as a dispatch group, you can review the group to determine how capacity affects all of the work centers in the group. Dispatch groups enable you to organize work centers according to common functions, similar operations, or steps in a routing.
When you review dispatch groups, you can also review messages about all the work centers in the group and use that information to redistribute the load within the group.
7.3.1.3 Work Center Load for RRP
The Resource Requirements Planning Regeneration program provides a numerical breakdown, by planning period, of the capacity load that is placed on a work center. Use this information to determine whether to adjust capacity or the forecast.
The code in the Prime Load field on the Work Center Master Revisions form determines the type of load. For example, if you enter machine and setup hours as the prime load code, the numbers that appear differ from those that appear if you enter machine hours only.
This table describes the calculations for the types of load:
When the system calculates the demand, it is offset by the Resource Offset value from the Capacity Resource Profile table (F3303). The resource offset determines the number of days that the actual use of a work center resource should be offset from the forecasted need.
7.3.1.4 Period Summaries
In addition to reviewing the capacity load of a work center, you can also evaluate the load that is placed on a work center. Evaluate the load by period and by item. You can review:
-
The items that are scheduled for a work center.
-
The number of units of an item that make up the load.
-
The percent of the total load on the work center that is for a specific item's forecast.
The system summarizes the load by the period, using the unit of measure that you specify.
You use this information to determine whether to adjust the forecast or the capacity at the work center.
7.3.1.5 Message Detail
Each time that you generate a resource requirements plan, the system creates messages to identify work centers with loads that conflict with planned capacity. Review Message Detail indicates whether you have overload or underload conditions. Messages for each work center appear alphabetically by message type.
Use the Capacity Planning Message Revisions program to clear, hold, or delete messages. You cannot process capacity messages. You can add remarks for each message to record the actions that you take. In addition, you can access related forms to confirm or change dates, amounts, and manufacturing data for key plants for the work center.
You can generate a plan more than once. When you regenerate a resource requirements plan, the system deletes all messages except:
-
Messages that you entered manually.
-
Messages that you placed on hold.
7.3.2 Forms Used to Validate Resource Requirements Plans
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With Capacity Message Summary | W3301A | Daily Resource Requirements Planning (G3311), Review Dispatch Group | Determine how capacity affects work centers. |
| Review Work Center Load | W3313A | Daily Resource Requirements Planning (G3311), Review Work Center Load | Determine required adjustments to capacity or forecast. |
| Work With Period Summary Review | W3312A | Daily Resource Requirements Planning (G3311), Review Period Summary | Evaluate work center load. |
| Work With Capacity Messages | W3311B | Daily Resource Requirements Planning (G3311), Review Message Detail | Release, clear, or place messages on hold. |
| Capacity Message Revisions | W3311A | On the Work With Capacity Messages form, select Revisions from the Row menu. | Delete messages. |
7.3.3 Setting Processing Options for Capacity Message Summary (P3301)
Use these processing options to set default values and specify versions.
7.3.3.1 Defaults
These processing options specify the default processing.
- 1. Enter the Critical Work Center Code to be displayed or blank for all Work Centers
-
Specify a code that indicates whether the work center is critical or not critical when the system calculates capacity. Values are:
N: Not a critical work center.
1: A critical work center in calculating RRP only.
2: A critical work center in calculating RCCP and CRP.
3: A critical work center in calculating RRP, RCCP, and CRP. The system also displays Type 3 work centers when you select Type 1 or Type 2 in this field.
4: Not a capacity work center. The system does not include this work center in capacity planning.
Note:
The data selection is a system feature that processes certain groups of information with the RRP, RCCP, and CRP programs. - 2. Enter the Capacity Mode
-
Specify a code indicating which planning is being used. Values are:
1: Resource Requirements
2: Rough Cut Capacity
3: Capacity Requirements
- 3. Enter the default Unit of Measure
-
Specify a UDC (00/UM) that identifies the unit of measurement for an amount or quantity. For example, it can represent a barrel, box, cubic meter, liter, hour, and so on.
7.3.3.2 Versions
This processing option specifies the version of the program.
- Work Center Revision (P3006)
-
Specify the version for the Work Center Revision program. If left blank, version ZJDE0001 will be used. This processing option identifies a specific set of data selection and sequencing settings for the application. Versions may be named using any combination of alpha and numeric characters.
7.3.4 Reviewing Dispatch Groups
Access the Work With Capacity Message Summary form.
- Dispatch Group
-
Enter a category code used to group work centers within an overall business unit.
For example, you can use this code to group similar machines operating from several work centers that report to one business unit.
- All W/C (all work centers)
-
Select the option to specify the type of processing for an event.
- Critical W/C (critical work center)
-
Enter a code that indicates whether the work center is critical or not critical when the system calculates capacity. Values are:
N: Not a critical work center.
1: A critical work center in calculating RRP only.
2: A critical work center in calculating RCCP and CRP.
3: A critical work center in calculating RRP, RCCP, and CRP. The system also displays Type 3 work centers when you select Type 1 or Type 2 in this field.
4: Not a capacity work center. The system does not include this work center in capacity planning.
Note:
The data selection is a system feature that processes certain groups of information with the RRP, RCCP, and CRP programs. - Message Type
-
Enter a code that distinguishes different messages generated in Capacity Planning. Values are:
A: Warning messages
M: Manual messages
O: Over capacity
U: Under capacity
- U/M (unit of measure)
-
Enter a UDC (00/UM) that indicates the quantity in which to express an inventory item; for example, CS (case) or BX (box).
- Outstanding Messages
-
Enter a brief description of an item, remark, or explanation.
This value provides a summary of the detailed messages for the work center. For example, if the work center has four under-capacity messages (message type U), this field displays UUUU.
7.3.5 Setting Processing Options for Capacity Load (P3313)
Use these processing options to set default values and specify versions.
7.3.5.1 Defaults
These processing options specify the defaults for processing.
- 1. Enter the Capacity Mode
-
Specify a code indicating which level of planning is being used. Values are:
1: Resource Requirements
2: Rough Cut Capacity
3: Capacity Requirements
- 2. Enter the User Defined Code for the list of row descriptions to appear
-
Specify a code that identifies the table that contains UDCs. The table is also referred to as a UDC type.
- 3. Enter the default Unit of Measure
-
Specify a UDC (00/UM) that identifies the unit of measurement for an amount or quantity. For example, it can represent a barrel, box, cubic meter, liter, hour, and so on.
- 4. Enter the version of the Dispatch List program to call. The default is ZJDE0001.
-
Specify a user-defined set of specifications that control how applications and reports run. You use versions to group and save a set of user-defined processing option values and data selection and sequencing options. Interactive versions are associated with applications (usually as a menu selection). Batch versions are associated with batch jobs or reports. To run a batch process, you must select a version.
7.3.5.2 Versions
This processing option specifies the version of the Operation Dispatch Inquiry program. Enter the version for each program. If left blank, version ZJDE0001 will be used.
- Operation Dispatch Inquiry (P31220)
-
Specify the version of the program that the system uses. Specify a specific set of data selection and sequencing settings for the application.
7.3.6 Reviewing Work Center Loads
Access the Review Work Center Load form.
- Description
-
Review the type of calculation used to determine the work center load: Rated Profile, Loaded Profile,% Resource Used, Resource Available, Accumulated Resource Available.
7.3.7 Setting Processing Options for Period Summary (P3312)
Use these processing options to set system defaults and specify versions.
7.3.7.1 Defaults
These processing options specify the defaults used for processing.
- 1. Enter the Capacity Mode
-
Specify a code indicating which level of planning is being used. Values are:
1: Resource Requirements
2: Rough Cut Capacity
3: Capacity Requirements
- 2. Enter the default Unit of Measure
-
Specify a UDC (00/UM) that identifies the unit of measurement for an amount or quantity. For example, it can represent a barrel, box, cubic meter, liter, hour, and so on.
- 3. Enter the version of the Dispatch List to call
-
Specify a user-defined set of specifications that control how applications and reports run. You use versions to group and save a set of user-defined processing option values and data selection and sequencing options. The default version is ZJDE0001.
7.3.7.2 Versions
These processing options specify the version of the program. If left blank, version ZJDE0001 will be used.
- 1. Work Center Revision (P3006)
-
Specify a specific set of data selection and sequencing settings for the application. Versions may be named using any combination of alpha and numeric characters.
If left blank, version ZJDE0001 will be used.
- 2. Forecast Revision (P3460)
-
Specify a specific set of data selection and sequencing settings for the application. Versions may be named using any combination of alpha and numeric characters.
- 3. MRP/MPS Message Revision (P3411)
-
Specify a specific set of data selection and sequencing settings for the application. Versions may be named using any combination of alpha and numeric characters.
- 4. Mfg Scheduling Workbench (P31225) (manufacturing scheduling workbench (P31225))
-
Specify a specific set of data selection and sequencing settings for the application. Versions may be named using any combination of alpha and numeric characters.
7.3.8 Reviewing Period Summaries
Access the Work With Period Summary Review form.
- Period End
-
Displays the date that an item is scheduled to arrive or that an action is scheduled for completion.
- Units
-
Displays a value that represents the available quantity, which might consist of the on-hand balance minus commitments, reservations, and backorders. You enter this value in the Branch/Plant Constants program.
- Percent
-
Displays the percent received.
- Order Number
-
Displays a number that identifies an original document. This document can be a work order, a sales order, a forecast, a planned order, and so on.
7.3.9 Setting Processing Options for Capacity Planning Message Revisions (P3311)
Use these processing options to specify system defaults.
7.3.9.1 Defaults
These processing options specify the defaults used by the program.
- 1. Enter the Capacity Mode
-
Specify the capacity mode. Values are:
1: Resource Requirements
2: Rough Cut Capacity
3: Capacity Requirements
- 2. Enter the default Unit of Measure
-
Specify a UDC (00/UM) that identifies the unit of measurement for an amount or quantity. For example, it can represent a barrel, box, cubic meter, liter, hour, and so on.
- 3. Enter the default version of Work Center Revision (P3006)
-
Specify a specific set of data selection and sequencing settings for the application. Versions may be named using any combination of alpha and numeric characters.
7.3.10 Reviewing Capacity Planning Message Details
Access the Work With Capacity Messages form.
Figure 7-2 Work With Capacity Messages form

Description of ''Figure 7-2 Work With Capacity Messages form''
- Message Type
-
Displays a code that distinguishes different messages generated in Capacity Planning. Values are:
A: Warning messages
M: Manual messages
O: Over capacity
U: Under capacity
- Message
-
Review the associated message.
To clear a message, select it and select Clear from the Row menu.
To view cleared messages, check the Include Cleared box and click Find.
To hold or release a message, select it and select Hold/Release from the Row menu. Messages on hold are highlighted. The system retains held messages until you manually release, clear, or delete them.
- Total Units
-
Enter a value that represents the available quantity, which might consist of the on-hand balance minus commitments, reservations, and backorders. You enter this value in the Branch/Plant Constants program.
To delete a message, access the Capacity Message Revisions form, select the message, and click Delete.
- Planner Remark
-
Enter a remark about an item.