1 Introduction to JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management
This chapter contains the following topics:
-
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management Overview
-
Benefits of JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management
-
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management Integrations
-
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management Implementation
1.1 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management Overview
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system for suppliers is an integral part of the supply chain management and order management processes. Outbound Inventory Management enables sell-side Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) and consigned inventory in the order-to-cash process. Suppliers can use it with the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Inventory Management and Sales Order Management systems to manage inventory at their customers' location.
Some of the most important features of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system include:
-
Establish agreement between supplier and buyer for moving inventory between their locations
-
Ship consigned and vendor managed inventory to customer's location
-
Acknowledge receipt of outbound inventory at the customer's location
-
Report consumption of outbound inventory from customer's location
-
Replenish outbound inventory manually or automatically
-
Bill outbound inventory manual or automatically
-
Review timely information and reports about inventory status and ownership
-
Return unused or damaged inventory
You use the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system to manage consigned inventory and vendor managed inventory (VMI).
1.1.1 Consigned Inventory
Inventory that is in the possession of the customer (buyer), but is still owned by the supplier is called consigned inventory. Consigned inventory management is a common business process in life sciences, manufacturing, and wholesale and distribution industries.
After establishing an agreement, the supplier places some of their inventory in their customer's possession (in the customer's store or warehouse) and allows them to sell or consume directly from this inventory.
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system provides suppliers the ability to ship goods to a customer's location, but retain ownership until the goods are consumed. After the customer reports usage, the supplier invoices the customer for the consumed goods.
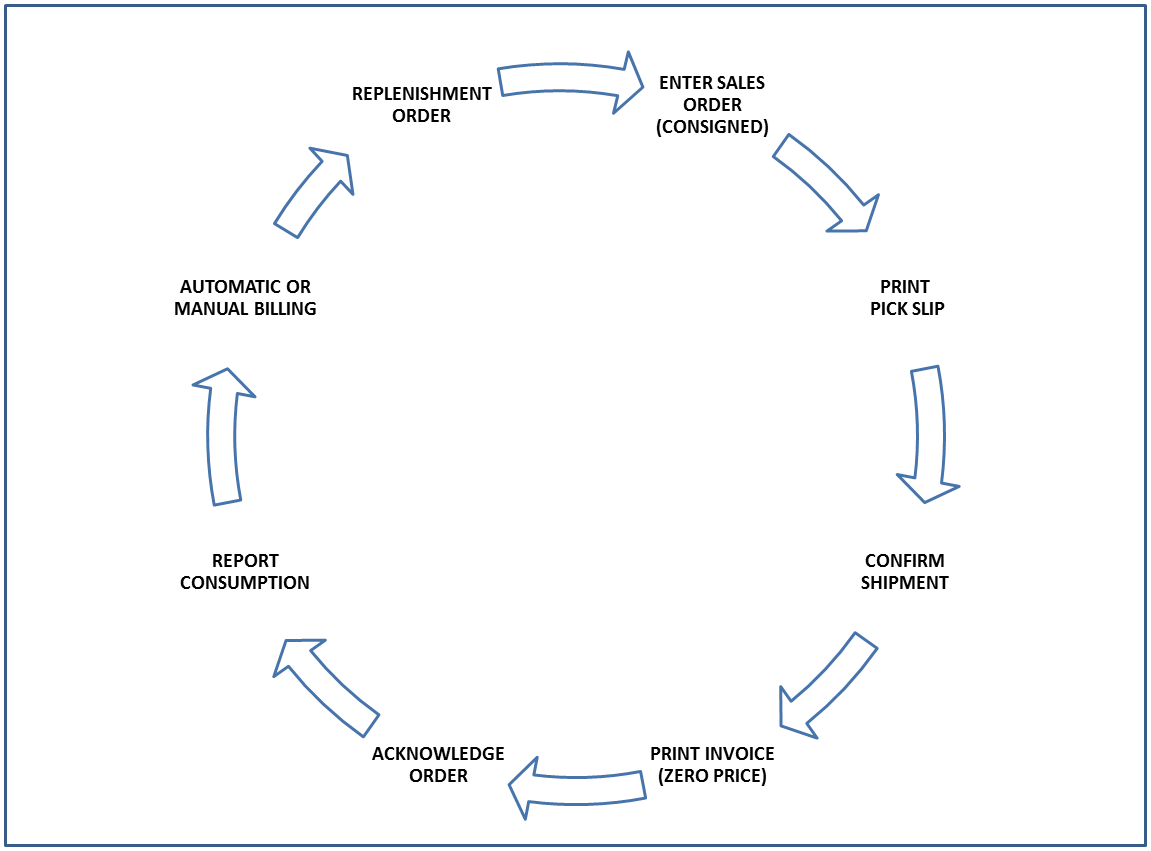
The following diagram describes the process flow for consigned inventory:
The following diagram illustrates the business process flow used by JD Edwards EnterpriseOne for consigned inventory:
The JD Edwards Outbound Inventory Management system uses the following process for consigned inventory management:
-
Supplier and customer establish an agreement for shipping and maintaining inventory at the customer's location
-
Supplier ships inventory to customer's location
-
Customer acknowledges the receipt of inventory
-
Customer reports consumption of inventory
-
Supplier invoices the customer after the customer reports consumption
-
Supplier replenishes inventory at customer's location based on agreed replenishment method
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system enables the use of the following replenishment methods for consigned inventory:
-
One-to-one replenishment
-
Reorder point replenishment
-
1.1.2 Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI)
The VMI process is a supply chain management strategy where a supplier manages the inventory at the customer's location. The inventory is owned either by the customer (VMI without consignment) or the supplier (VMI with consignment), but maintained by the supplier.
|
Note: JD Edwards EnterpriseOne supports both customer and supplier owned vendor managed inventory. Supplier owned vendor managed inventory business process works similar to consigned inventory. |
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system allows the supplier and customer to establish an agreement for the VMI process. Instead of the customer reordering when the inventory is exhausted, the supplier is responsible for replenishing and stocking inventory at the customer's location.
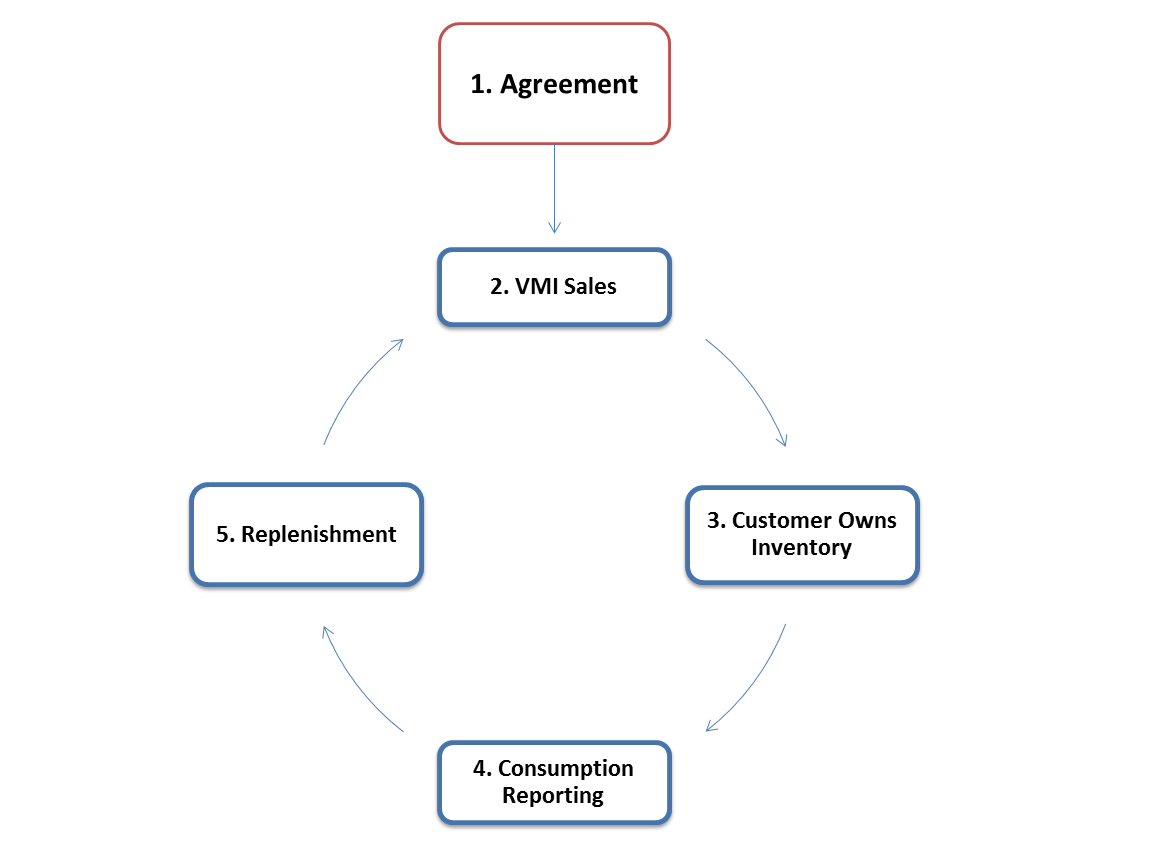
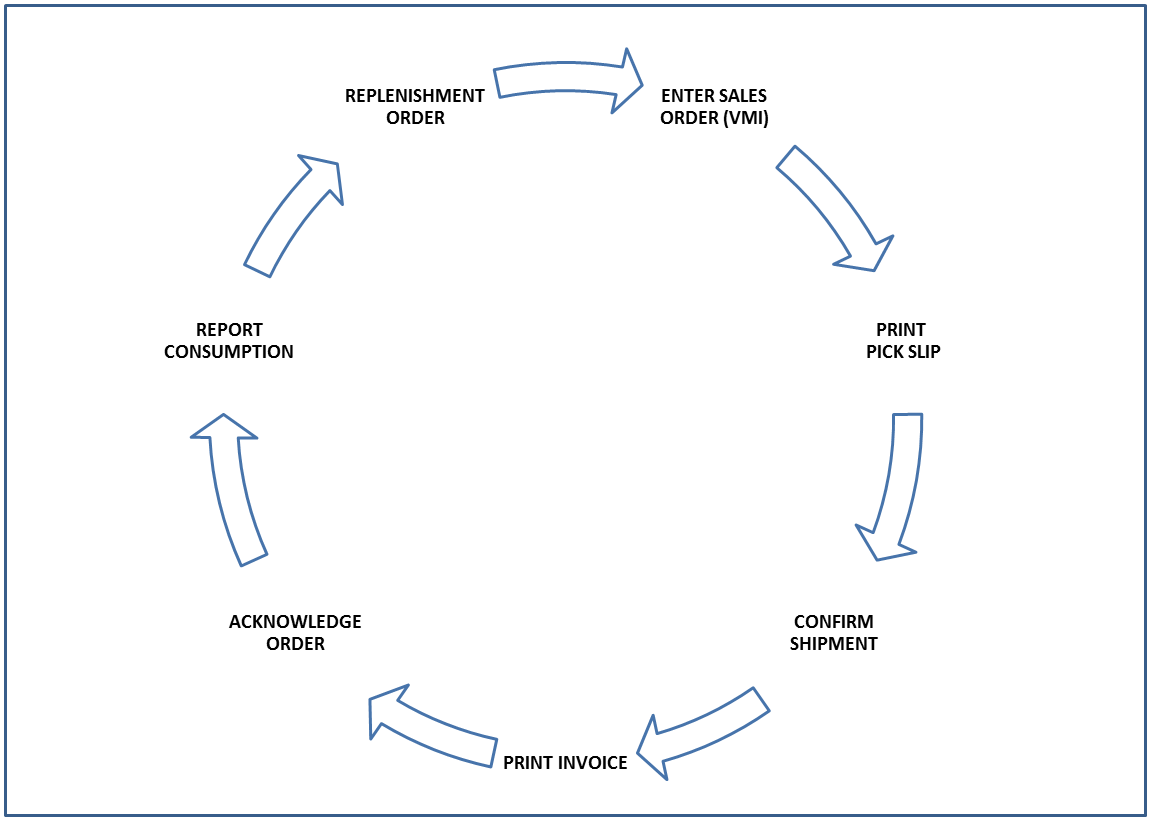
The following diagram describes the process flow for customer owned VMI:
The following diagram illustrates the business process flow used by JD Edwards EnterpriseOne for customer owned VMI (VMI with consignment):
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system uses the following process for customer owned VMI:
-
Supplier and customer establish a VMI agreement for shipping and maintaining inventory
-
Supplier sells inventory to customer
-
Supplier ships inventory to customer's location. The customer now owns the inventory
-
Customer reports consumption of goods
-
Supplier replenishes inventory at customer's location based on agreed replenishment method
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system enables the use of the following replenishment methods:
-
One-to-one replenishment
-
Reorder point replenishment
-
1.2 Benefits of JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management
With the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system, you can establish agreements, ship inventory, monitor usage, report consumption, replenish inventory, and bill your customer for consumption.
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system enables improved cohesion between suppliers and their customers by providing:
-
Improved management and tracking of outbound inventory agreements.
-
Improved forecasting to trigger replenishments for effective demand planning.
-
Fewer stock-outs and increased visibility into inventory movement.
-
Automated, efficient and effective response to outbound inventory consumption reporting.
-
Improved inventory management using customer acknowledgement for inventory received at customer's location.
1.2.1 Benefits for Suppliers
-
Increased sales
-
Reduced warehouse space resulting in reduced inventory holding costs
-
Reduced lead times to fill outbound inventory orders
-
Real-time outbound inventory consumption
-
Increased visibility into inventory movement
-
Reduced inventory holding costs for the customers
-
Secured business with the customer protecting their interests against competitors
1.3 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management Integrations
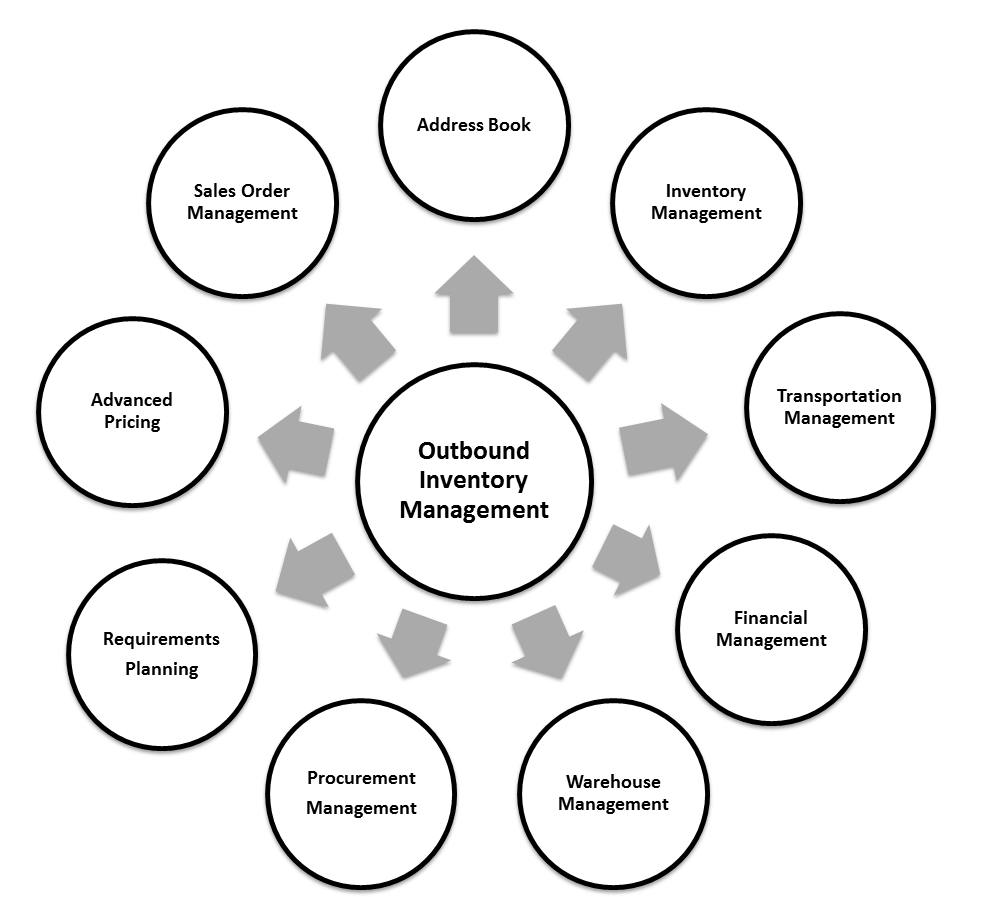
The following diagram illustrates the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne systems that integrate with the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system:
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system works with other supply chain management, and distribution and logistics systems to ensure that customer demand is met.
1.3.1 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Address Book
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Address Book system from Oracle stores current customer information, such as address, contact information, phone and fax numbers, billing instructions, and default shipping and invoicing information.
1.3.2 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Inventory Management
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Inventory Management system stores item information for the JD Edwards Outbound Inventory Management, Sales Order Management, Procurement, Manufacturing, and Supply Chain Management systems. JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Inventory Management system also stores sales and purchasing costs and quantities available by location, and tracks holds for locations from which items should not be sold.
1.3.3 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Sales Order Management
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Sales Order Management system enables you to process both simple and complex sales orders. It is closely integrated with inventory systems, and enables you to allocate inventory at the time of order entry.
1.3.4 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Transportation Management
You can integrate the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Sales Order Management and JD Edwards Outbound Inventory Management systems with the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Transportation Management system to provide carrier and shipment functionality to customers.
1.3.5 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Warehouse Management
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Warehouse Management is an integral part of manufacturing and distribution processes. It works with other JD Edwards EnterpriseOne distribution systems to manage inventory and the products that companies produce and ship.
1.3.6 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Financial Management
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system integrates with the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Ledger system and the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable system. With the use of automatic accounting instructions (AAIs) and user-input account numbers, the system relays pertinent transaction information to the accounting systems.
1.3.7 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement Management
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement system supports direct ship order and transfer order processing. You can use the system to release receipts for items on backorder.
1.3.8 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Requirements Planning
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Requirements Planning system from Oracle uses sales orders and forecasts to pass demand for items down through the bills of material to the components. The system also uses bills of material to determine component requirements for planned orders and work orders without a parts list.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Distribution Requirements Planning, JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Master Production Schedule, and JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Material Requirements Planning provide you with suggested purchasing and manufacturing orders that are required to maintain a valid production schedule.
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Forecast Management system generates sales projections that are used to create demand and develop the master production schedule. JD Edwards EnterpriseOne In-Memory Planning Advisor uses the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Forecast Management system to set up forecasts.
You can use the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Requirements Planning system with the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system to suggest forecasts for VMI business process.
1.3.9 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Pricing
With JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Pricing, you can adjust prices for each promotion or deal, and then combine adjustments into a pricing structure or schedule. You can define multiple price adjustments and combine regular discounts and promotions within the same schedule. Set up free goods catalogs to display and promote items and use rebates to encourage customers to purchase a greater volume of goods or services.
1.4 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management Implementation
This section lists the steps that are required to implement the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system globally.
1.4.1 Other Sources of Information
In the planning phase of the implementation, take advantage of all Oracle sources of information, including the installation guides and troubleshooting information.
When determining which electronic software updates (ESUs) to install for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management, use the EnterpriseOne and World Change Assistant. EnterpriseOne and World Change Assistant, a Java-based tool, reduces the time required to search and download ESUs by 75 percent or more, and enables you to install multiple ESUs simultaneously.
1.4.2 Global Implementation Steps
The following are the global implementation steps for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management:
-
Set up global user-defined codes.
See the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tools System Administration Guide.
-
Set up companies, fiscal date patterns, and business units.
-
Set up next numbers.
-
Set up multi-currency processing, including currency codes and exchange rates.
-
Set up ledger type rules.
-
Enter address book records.
-
Set up inventory information, such as branch/plant constants, default locations and printers, manufacturing and distribution automatic accounting instructions, and document types.
See "Setting Up the Inventory Management System" in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Applications Inventory Management Implementation Guide.
-
Set up shop floor calendars.
-
Set up manufacturing constants.
1.4.3 Outbound Inventory Management Implementation Steps
The following are the suggested application-specific implementation steps for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management:
-
Activate the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management module.
See Section 2.2, "Activating the Outbound Inventory Management System"
-
Set up UDCs for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management.
-
Set up Outbound Branch/Plant.
-
Set up outbound inventory locations.
-
Set up AAIs.
See Section 2.7, "Setting Up AAIs for Outbound Inventory Management"
-
Define order line types.
See Section 2.8, "Setting Up Outbound Inventory Order line Types"
-
Define order activity rules.
1.5 Outbound Inventory Management Information Structure
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system contains master maintenance and transaction processing tables.
1.5.1 Master Maintenance Tables
This table describes the master maintenance tables:
| Table ID | Table Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| F42I010 | Outbound Inventory Agreement Master | Contains information about the customer, agreement effective dates, and other information that the system uses to process outbound inventory agreements. |
| F38010 | Agreement Master | The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system uses the data structure of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Agreement Management system to store agreement information. The primary agreement information is stored in F38010 and information specific to JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management is stored in F42I010. |
| F42I011 | Outbound Inventory Agreement Details | Contains information about products and quantities/amounts, which partner is receiving or shipping the product, and the unit of measure for the product. |
| F38011 | Agreement Quantities | The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management system uses the data structure of the JD Edwards Agreement Management system to store agreement information. The primary agreement information is stored in stored in F38011 and information specific to JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Outbound Inventory Management is stored in F42I011. |
| F42I05 | Outbound Inventory Staging Locations | Contains information about the in-transit and hold locations used for outbound inventory management. |
| F42I14 | Outbound Inventory Frequency Schedule Master (Release 9.1 Update) | Contains master information about frequency schedules you create for outbound inventory replenishments. |
| F42I141 | Outbound Inventory Cycle Count Details (Release 9.1 Update) | Contains detail information about frequency schedules you create for outbound inventory replenishments. |
| F42I013 | Outbound Inventory Agreement Item Groups (Release 9.1 Update) | Contains information about outbound inventory item groups that you create for items with similar characteristics. |
1.5.2 Transaction Processing Tables
This table describes the transaction processing tables:
| Table ID | Table Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| F42I015 | Outbound Inventory Agreement Transaction File | Contains quantity and amount information for all outbound inventory agreement transactions and adjustments. |
| F42I02 | Outbound Inventory Agreement Acknowledge | Contains the quantity that is received at the customer's location and is to be acknowledged. |
| F42I03 | Outbound Order Consumption Report File | Contains the quantity that is ready for consumption. Also contains information about consumption. |
| F42I021 | Outbound Inventory Item Balance | Contains the latest quantity and amount information for all outbound inventory agreement transactions and adjustments. |
| F42I06 | Outbound Inventory Agreement Master Change History | Contains history information for changes made to outbound inventory agreement master information. |
| F42I07 | Outbound Inventory Agreement Quantities Change History | Contains history information for changes made to outbound inventory agreement details information. |
| F42I08 | Replenishment Quantity and Price Override Table | Contains information about price and quantity overrides made during replenishment order generation. |
| F42I20 | Outbound Inventory Cycle Count Header (Release 9.1 Update) | Contains master information about outbound inventory cycle counts. |
| F42I21 | Outbound Inventory Cycle Count Details (Release 9.1 Update) | Contains detail information about outbound inventory cycle counts. |