| Oracle® Real User Experience Insight Accelerator for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Guide Release 6.5.0 for Linux x86-64 Part Number E17371-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Real User Experience Insight Accelerator for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Guide Release 6.5.0 for Linux x86-64 Part Number E17371-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter explains how information within JD Edwards-based applications is captured and reported by RUEI. Information about specific mechanisms or characteristics to be aware of when monitoring JD Edwards-based applications are also highlighted. It is recommended you review this information to better understand the reporting of JD Edwards applications within RUEI.
A JD Edwards Implementation, and the JD Edwards instance, can be identified with a hostname. Generally, a JD Edwards suite can be accessed in two ways: using only the hostname, or using the fully-qualified hostname (including the domain). Generally, you only need to specify the domain.
Table 2-1 shows how an application's dimensions are reported in RUEI.
Table 2-1 JD Edwards Suite Definitions Mapping
| Dimension level | Content |
|---|---|
|
Application.name |
|
|
Application. page-group |
|
|
Application.page-name |
|
where:
application code is the code of the JD Edwards application used by the user. For example, the application code for "sales order entry" is p4210. formname is the name of the JD Edwards form used. For example, the form W01012b has the name "work with addresses".
application name is the name of the JD Edwards application used by the user. For example, the application name for p4210 is "sales order entry".
product code is the code for the JD Edwards product used by an JD Edwards application/form. For example, the address book application (p01012) is part of the JD Edwards product "addressbook" which has product code 01. In JD Edwards, this is sometimes referred to as "system code".
product name is the name for the JD Edwards product used by an JD Edwards application/form. For example, the address book application (p01012) is part of the JD Edwards product "addressbook" (product code 01).
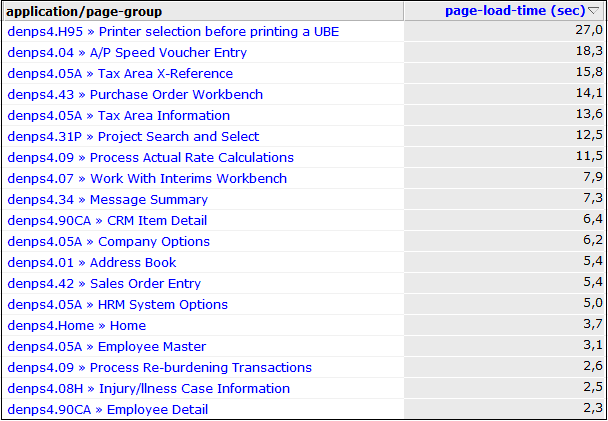
Figure 2-1 shows an example of how a JD Edwards application is reported in RUEI.
Figure 2-1 Example of JD Edwards Application Page-Group Reporting
The following JD Edwards database tables are used by the create_JDE_info.sh script to retrieve information about the customizations:
F9860: SIOBNM, SIMD, and SISY to generate JDE_applicationcode2applicationname.txt and (in conjunction with F0005) to generate JDE_applicationcode2productname.txt and JDE_applicationcode2productcode.txt (see below).
F9865: SWFMNM and SWMD to generate JDE_formcode2formname.txt.
F983051: VRPID, VRVERS, and VRJD to generate JDE_applicationversioncode2applicationversiondescription.txt.tmp.
F9203: FRDTAI and FRDSCA to generate JDE_errorcode2errordescription.txt.
F0005: DRSY, DRRT, and DRKY (in conjunction with F9860, see above) to generate both JDE_applicationcode2productname.txt and JDE_applicationcode2productcode.txt.
The JD Edwards-specific data items shown in Table 2-2 are reported by RUEI.
Table 2-2 Dimensions
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| JD Edwards suite/Code | The code of a JD Edwards suite, as defined in its configuration definition. This data makes it possible to distinguish between different monitored JD Edwards suites. |
| JD Edwards suite/Name | The name of a JD Edwards suite, as defined in its configuration definition. This data makes it possible to distinguish between different monitored JD Edwards suites. |
| JD Edwards form/ID | The ID of the JD Edwards form used. The JD Edwards form name is based on the form code (W...) and the JD Edwards database configuration. This makes it possible to distinguish between the different forms monitored during sessions. |
| JD Edwards form/Name | The name of the JD Edwards form used. The JD Edwards form name is based on the form code (W...) and the JD Edwards database configuration. This makes it possible to distinguish between the different forms monitored during sessions |
| JD Edwards action/ID | In forms/applications, people perform actions. These actions are monitored and reported here. (Note that most JD Edwards actions are encoded). |
| JD Edwards action/Name | In forms/applications, people perform actions. These actions are monitored and reported here. (Note that most JD Edwards actions are encoded). |
| JD Edwards application/ID | The ID of the JD Edwards application used. The JD Edwards application name is based on the application code (P...) and the JDE database configuration. This makes it possible to distinguish between the different applications monitored during sessions. |
| JD Edwards application/Name | The name of the JD Edwards application used. The JD Edwards application name is based on the application code (P...) and the JDE database configuration. This makes it possible to distinguish between the different applications monitored during sessions. |
| JD Edwards application version/ID | The ID of the JD Edwards application version used. |
| JD Edwards application version/Name | The ID of the JD Edwards application version used. |
| JD Edwards environment/Name | The environment selected when the user logged into JD Edwards. |
| JD Edwards product/Code | The code of the JD Edwards product used. JD Edwards applications are part of a product which is shown here. JD Edwards products are sometimes referred to by their system code or product code. |
| JD Edwards product/Name | The name of the JD Edwards product used. JD Edwards applications are part of a product which is shown here. JD Edwards products are sometimes referred to by system code or product code. |