TopBlend:
Here is the
first difference.
There are 8 differences.
is old.
 is new.
is new.
javax.swing.plaf.basic
Class BasicTextUI
java.lang.Object
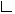 javax.swing.plaf.ComponentUI
javax.swing.plaf.ComponentUI
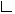 javax.swing.plaf.TextUI
javax.swing.plaf.TextUI
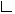 javax.swing.plaf.basic.BasicTextUI
javax.swing.plaf.basic.BasicTextUI
-
All Implemented Interfaces:
-
ViewFactory
-
Direct Known Subclasses:
-
BasicEditorPaneUI
,
BasicTextAreaUI
,
BasicTextFieldUI
,
DefaultTextUI
-
public abstract class BasicTextUI
- extends TextUI
- implements ViewFactory
Basis of a text components look-and-feel. This provides the basic editor view and controller services that may be useful when creating a look-and-feel for an extension of JTextComponent.
Most state is held in the associated JTextComponent as bound properties, and the UI installs default values for the various properties. This default will install something for all of the properties. Typically, a LAF implementation will do more however. At a minimum, a LAF would generally install key bindings.
This class also provides some concurrency support if the Document associated with the JTextComponent is a subclass of AbstractDocument. Access to the View (or View hierarchy) is serialized between any thread mutating the model and the Swing event thread (which is expected to render, do model/view coordinate translation, etc). Any access to the root view should first acquire a read-lock on the AbstractDocument and release that lock in a finally block.
An important method to define is the
getPropertyPrefix()
method which is used as the basis of the keys used to fetch defaults from the UIManager. The string should reflect the type of TextUI (eg. TextField, TextArea, etc) without the particular LAF part of the name (eg Metal, Motif, etc).
To build a view of the model, one of the following strategies can be employed.
-
One strategy is to simply redefine the ViewFactory interface in the UI. By default, this UI itself acts as the factory for View implementations. This is useful for simple factories. To do this reimplement the
create(javax.swing.text.Element)
method.
-

A common strategy for creating more complex types of documents is to have the EditorKit implementation return a factory. Since the EditorKit ties all of the pieces necessary to maintain a type of document, the factory is typically an important part of that and should be produced by the EditorKit implementation.
-
 A common strategy for creating more complex types of documents is to have the EditorKit implementation return a factory. Since the EditorKit ties all of the pieces necessary to maintain a type of document, the factory is typically an important part of that and should be produced by the EditorKit implementation.
A common strategy for creating more complex types of documents is to have the EditorKit implementation return a factory. Since the EditorKit ties all of the pieces necessary to maintain a type of document, the factory is typically an important part of that and should be produced by the EditorKit implementation.

A less common way to create more complex types is to have the UI implementation create a. separate object for the factory. To do this, the #createViewFactory method should be reimplemented to return some factory.
Warning: Serialized objects of this class will not be compatible with future Swing releases. The current serialization support is appropriate for short term storage or RMI between applications running the same version of Swing. As of 1.4, support for long term storage of all JavaBeans
TM
has been added to the java.beans package. Please see
XMLEncoder
.
|
Method Summary
|
|
View
|
create
(
Element
elem)
Creates a view for an element. |
|
View
|
create
(
Element
elem, int p0, int p1)
Creates a view for an element. |
|
protected
Caret
|
createCaret
()
Creates the object to use for a caret. |
|
protected
Highlighter
|
createHighlighter
()
Creates the object to use for adding highlights. |
|
protected
Keymap
|
createKeymap
()
Creates the keymap to use for the text component, and installs any necessary bindings into it. |
|
void |
damageRange
(
JTextComponent
tc, int p0, int p1)
Causes the portion of the view responsible for the given part of the model to be repainted. |
|
void |
damageRange
(
JTextComponent
t, int p0, int p1,
Position.Bias
p0Bias,
Position.Bias
p1Bias)
Causes the portion of the view responsible for the given part of the model to be repainted. |
|
protected
JTextComponent
|
getComponent
()
Fetches the text component associated with this UI implementation. |
|
EditorKit
|
getEditorKit
(
JTextComponent
tc)
Fetches the EditorKit for the UI. |
|
protected
String
|
getKeymapName
()
Fetches the name of the keymap that will be installed/used by default for this UI. |
|
Dimension
|
getMaximumSize
(
JComponent
c)
Gets the maximum size for the editor component. |
|
Dimension
|
getMinimumSize
(
JComponent
c)
Gets the minimum size for the editor component. |
|
int |
getNextVisualPositionFrom
(
JTextComponent
t, int pos,
Position.Bias
b, int direction,
Position.Bias
[] biasRet)
Provides a way to determine the next visually represented model location that one might place a caret. |
|
Dimension
|
getPreferredSize
(
JComponent
c)
Gets the preferred size for the editor component. |
|
protected abstract
String
|
getPropertyPrefix
()
Gets the name used as a key to look up properties through the UIManager. |
|
View
|
getRootView
(
JTextComponent
tc)
Fetches a View with the allocation of the associated text component (i.e. |
|
String
|
getToolTipText
(
JTextComponent
t,
Point
pt)
Returns the string to be used as the tooltip at the passed in location. |
|
protected
Rectangle
|
getVisibleEditorRect
()
Gets the allocation to give the root View. |
|
protected void |
installDefaults
()
Initializes component properties, e.g. |
|
protected void |
installKeyboardActions
()
|
|
protected void |
installListeners
()
Installs listeners for the UI. |
|
void |
installUI
(
JComponent
c)
Installs the UI for a component. |
|
protected void |
modelChanged
()
Flags model changes. |
|
Rectangle
|
modelToView
(
JTextComponent
tc, int pos)
Converts the given location in the model to a place in the view coordinate system. |
|
Rectangle
|
modelToView
(
JTextComponent
tc, int pos,
Position.Bias
bias)
Converts the given location in the model to a place in the view coordinate system. |
|
void |
paint
(
Graphics
g,
JComponent
c)
Paints the interface. |
|
protected void |
paintBackground
(
Graphics
g)
Paints a background for the view. |
|
protected void |
paintSafely
(
Graphics
g)
Paints the interface safely with a guarantee that the model won't change from the view of this thread. |
|
protected void |
propertyChange
(
PropertyChangeEvent
evt)
This method gets called when a bound property is changed on the associated JTextComponent. |
|
protected void |
setView
(
View
v)
Sets the current root of the view hierarchy and calls invalidate(). |
|
protected void |
uninstallDefaults
()
Sets the component properties that haven't been explicitly overridden to null. |
|
protected void |
uninstallKeyboardActions
()
|
|
protected void |
uninstallListeners
()
Uninstalls listeners for the UI. |
|
void |
uninstallUI
(
JComponent
c)
Deinstalls the UI for a component. |
|
void |
update
(
Graphics
g,
JComponent
c)
Superclass paints background in an uncontrollable way (i.e. |
|
int |
viewToModel
(
JTextComponent
tc,
Point
pt)
Converts the given place in the view coordinate system to the nearest representative location in the model. |
|
int |
viewToModel
(
JTextComponent
tc,
Point
pt,
Position.Bias
[] biasReturn)
Converts the given place in the view coordinate system to the nearest representative location in the model. |
|
Methods inherited from class java.lang.
Object
|
|
clone
,
equals
,
finalize
,
getClass
,
hashCode
,
notify
,
notifyAll
,
toString
,
wait
,
wait
,
wait
|
BasicTextUI
public BasicTextUI()
-
Creates a new UI.
createCaret
protected Caret createCaret()
-
Creates the object to use for a caret. By default an instance of BasicCaret is created. This method can be redefined to provide something else that implements the InputPosition interface or a subclass of JCaret.
-
-
-
Returns:
-
the caret object
createHighlighter
protected Highlighter createHighlighter()
-
Creates the object to use for adding highlights. By default an instance of BasicHighlighter is created. This method can be redefined to provide something else that implements the Highlighter interface or a subclass of DefaultHighlighter.
-
-
-
Returns:
-
the highlighter
getKeymapName
protected String getKeymapName()
-
Fetches the name of the keymap that will be installed/used by default for this UI. This is implemented to create a name based upon the classname. The name is the the name of the class with the package prefix removed.
-
-
-
Returns:
-
the name
createKeymap
protected Keymap createKeymap()
-
Creates the keymap to use for the text component, and installs any necessary bindings into it. By default, the keymap is shared between all instances of this type of TextUI. The keymap has the name defined by the getKeymapName method. If the keymap is not found, then DEFAULT_KEYMAP from JTextComponent is used.
The set of bindings used to create the keymap is fetched from the UIManager using a key formed by combining the
getPropertyPrefix()
method and the string .keyBindings. The type is expected to be JTextComponent.KeyBinding[].
-
-
-
Returns:
-
the keymap
-
See Also:
-
getKeymapName()
,
JTextComponent
propertyChange
protected void propertyChange(PropertyChangeEvent evt)
-
This method gets called when a bound property is changed on the associated JTextComponent. This is a hook which UI implementations may change to reflect how the UI displays bound properties of JTextComponent subclasses. This is implemented to do nothing (i.e. the response to properties in JTextComponent itself are handled prior to calling this method).
 This implementation updates the background of the text component if the editable and/or enabled state changes.
This implementation updates the background of the text component if the editable and/or enabled state changes.
-
-
-
Parameters:
-
evt - the property change event
getPropertyPrefix
protected abstract String getPropertyPrefix()
-
Gets the name used as a key to look up properties through the UIManager. This is used as a prefix to all the standard text properties.
-
-
-
Returns:
-
the name
installDefaults
protected void installDefaults()
-
Initializes component properties, e.g. font, foreground, background, caret color, selection color, selected text color, disabled text color, and border color. The font, foreground, and background properties are only set if their current value is either null or a UIResource, other properties are set if the current value is null.
-
-
-
See Also:
-
uninstallDefaults()
,
installUI(javax.swing.JComponent)
uninstallDefaults
protected void uninstallDefaults()
-
Sets the component properties that haven't been explicitly overridden to null. A property is considered overridden if its current value is not a UIResource.
-
-
-
See Also:
-
installDefaults()
,
uninstallUI(javax.swing.JComponent)
installListeners
protected void installListeners()
-
Installs listeners for the UI.
-
-
uninstallListeners
protected void uninstallListeners()
-
Uninstalls listeners for the UI.
-
-
installKeyboardActions
protected void installKeyboardActions()
-
-
uninstallKeyboardActions
protected void uninstallKeyboardActions()
-
-
paintBackground
protected void paintBackground(Graphics g)
-
Paints a background for the view. This will only be called if isOpaque() on the associated component is true. The default is to paint the background color of the component.
-
-
-
Parameters:
-
g - the graphics context
getComponent
protected final JTextComponent getComponent()
-
Fetches the text component associated with this UI implementation. This will be null until the ui has been installed.
-
-
-
Returns:
-
the editor component
modelChanged
protected void modelChanged()
-
Flags model changes. This is called whenever the model has changed. It is implemented to rebuild the view hierarchy to represent the default root element of the associated model.
-
-
setView
protected final void setView(View v)
-
Sets the current root of the view hierarchy and calls invalidate(). If there were any child components, they will be removed (i.e. there are assumed to have come from components embedded in views).
-
-
-
Parameters:
-
v - the root view
paintSafely
protected void paintSafely(Graphics g)
-
Paints the interface safely with a guarantee that the model won't change from the view of this thread. This does the following things, rendering from back to front.
-
If the component is marked as opaque, the background is painted in the current background color of the component.
-
The highlights (if any) are painted.
-
The view hierarchy is painted.
-
The caret is painted.
-
-
-
Parameters:
-
g - the graphics context
installUI
public void installUI(JComponent c)
-
Installs the UI for a component. This does the following things.
-
Set the associated component to opaque (can be changed easily by a subclass or on JTextComponent directly), which is the most common case. This will cause the component's background color to be painted.
-
Install the default caret and highlighter into the associated component.
-
Attach to the editor and model. If there is no model, a default one is created.
-
create the view factory and the view hierarchy used to represent the model.
-
-
Overrides:
-
installUI
in class
ComponentUI
-
-
Parameters:
-
c - the editor component
-
See Also:
-
ComponentUI.installUI(javax.swing.JComponent)
uninstallUI
public void uninstallUI(JComponent c)
-
Deinstalls the UI for a component. This removes the listeners, uninstalls the highlighter, removes views, and nulls out the keymap.
-
-
Overrides:
-
uninstallUI
in class
ComponentUI
-
-
Parameters:
-
c - the editor component
-
See Also:
-
ComponentUI.uninstallUI(javax.swing.JComponent)
update
public void update(Graphics g,
JComponent c)
-
Superclass paints background in an uncontrollable way (i.e. one might want an image tiled into the background). To prevent this from happening twice, this method is reimplemented to simply paint.
NOTE: Superclass is also not thread-safe in it's rendering of the background, although that's not an issue with the default rendering.
-
-
Overrides:
-
update
in class
ComponentUI
-
-
Parameters:
-
g - the Graphics context in which to paint
-
c - the component being painted; this argument is often ignored, but might be used if the UI object is stateless and shared by multiple components
-
See Also:
-
ComponentUI.paint(java.awt.Graphics, javax.swing.JComponent)
,
JComponent.paintComponent(java.awt.Graphics)
paint
public final void paint(Graphics g,
JComponent c)
-
Paints the interface. This is routed to the paintSafely method under the guarantee that the model won't change from the view of this thread while it's rendering (if the associated model is derived from AbstractDocument). This enables the model to potentially be updated asynchronously.
-
-
Overrides:
-
paint
in class
ComponentUI
-
-
Parameters:
-
g - the graphics context
-
c - the editor component
-
See Also:
-
ComponentUI.update(java.awt.Graphics, javax.swing.JComponent)
getPreferredSize
public Dimension getPreferredSize(JComponent c)
-
Gets the preferred size for the editor component. If the component has been given a size prior to receiving this request, it will set the size of the view hierarchy to reflect the size of the component before requesting the preferred size of the view hierarchy. This allows formatted views to format to the current component size before answering the request. Other views don't care about currently formatted size and give the same answer either way.
-
-
Overrides:
-
getPreferredSize
in class
ComponentUI
-
-
Parameters:
-
c - the editor component
-
Returns:
-
the size
-
See Also:
-
JComponent.getPreferredSize()
,
LayoutManager.preferredLayoutSize(java.awt.Container)
getMinimumSize
public Dimension getMinimumSize(JComponent c)
-
Gets the minimum size for the editor component.
-
-
Overrides:
-
getMinimumSize
in class
ComponentUI
-
-
Parameters:
-
c - the editor component
-
Returns:
-
the size
-
See Also:
-
JComponent.getMinimumSize()
,
LayoutManager.minimumLayoutSize(java.awt.Container)
,
ComponentUI.getPreferredSize(javax.swing.JComponent)
getMaximumSize
public Dimension getMaximumSize(JComponent c)
-
Gets the maximum size for the editor component.
-
-
Overrides:
-
getMaximumSize
in class
ComponentUI
-
-
Parameters:
-
c - the editor component
-
Returns:
-
the size
-
See Also:
-
JComponent.getMaximumSize()
,
LayoutManager2.maximumLayoutSize(java.awt.Container)
getVisibleEditorRect
protected Rectangle getVisibleEditorRect()
-
Gets the allocation to give the root View. Due to an unfortunate set of historical events this method is inappropriately named. The Rectangle returned has nothing to do with visibility. The component must have a non-zero positive size for this translation to be computed.
-
-
-
Returns:
-
the bounding box for the root view
modelToView
public Rectangle modelToView(JTextComponent tc,
int pos)
throws BadLocationException
-
Converts the given location in the model to a place in the view coordinate system. The component must have a non-zero positive size for this translation to be computed.
-
-
Specified by:
-
modelToView
in class
TextUI
-
-
Parameters:
-
tc - the text component for which this UI is installed
-
pos - the local location in the model to translate >= 0
-
Returns:
-
the coordinates as a rectangle, null if the model is not painted
-
Throws:
-
BadLocationException
- if the given position does not represent a valid location in the associated document
-
See Also:
-
TextUI.modelToView(javax.swing.text.JTextComponent, int)
modelToView
public Rectangle modelToView(JTextComponent tc,
int pos,
Position.Bias bias)
throws BadLocationException
-
Converts the given location in the model to a place in the view coordinate system. The component must have a non-zero positive size for this translation to be computed.
-
-
Specified by:
-
modelToView
in class
TextUI
-
-
Parameters:
-
tc - the text component for which this UI is installed
-
pos - the local location in the model to translate >= 0
-
Returns:
-
the coordinates as a rectangle, null if the model is not painted
-
Throws:
-
BadLocationException
- if the given position does not represent a valid location in the associated document
-
See Also:
-
TextUI.modelToView(javax.swing.text.JTextComponent, int)
viewToModel
public int viewToModel(JTextComponent tc,
Point pt)
-
Converts the given place in the view coordinate system to the nearest representative location in the model. The component must have a non-zero positive size for this translation to be computed.
-
-
Specified by:
-
viewToModel
in class
TextUI
-
-
Parameters:
-
tc - the text component for which this UI is installed
-
pt - the location in the view to translate. This should be in the same coordinate system as the mouse events.
-
Returns:
-
the offset from the start of the document >= 0, -1 if not painted
-
See Also:
-
TextUI.viewToModel(javax.swing.text.JTextComponent, java.awt.Point)
viewToModel
public int viewToModel(JTextComponent tc,
Point pt,
Position.Bias[] biasReturn)
-
Converts the given place in the view coordinate system to the nearest representative location in the model. The component must have a non-zero positive size for this translation to be computed.
-
-
Specified by:
-
viewToModel
in class
TextUI
-
-
Parameters:
-
tc - the text component for which this UI is installed
-
pt - the location in the view to translate. This should be in the same coordinate system as the mouse events.
-
biasReturn - filled in by this method to indicate whether the point given is closer to the previous or the next character in the model
-
Returns:
-
the offset from the start of the document >= 0, -1 if the component doesn't yet have a positive size.
-
See Also:
-
TextUI.viewToModel(javax.swing.text.JTextComponent, java.awt.Point)
getNextVisualPositionFrom
public int getNextVisualPositionFrom(JTextComponent t,
int pos,
Position.Bias b,
int direction,
Position.Bias[] biasRet)
throws BadLocationException
-
Provides a way to determine the next visually represented model location that one might place a caret. Some views may not be visible, they might not be in the same order found in the model, or they just might not allow access to some of the locations in the model.
-
-
Specified by:
-
getNextVisualPositionFrom
in class
TextUI
-
-
Parameters:
-
 t - the text component for which this UI is installed
t - the text component for which this UI is installed
-
pos - the position to convert >= 0
-
 b - the bias for the position
b - the bias for the position

a - the allocated region to render into
-
direction - the direction from the current position that can be thought of as the arrow keys typically found on a keyboard.
 This may be SwingConstants.WEST, SwingConstants.EAST, SwingConstants.NORTH, or SwingConstants.SOUTH
This may be SwingConstants.WEST, SwingConstants.EAST, SwingConstants.NORTH, or SwingConstants.SOUTH
-
 biasRet - an array to contain the bias for the returned position
biasRet - an array to contain the bias for the returned position

This may be SwingConstants.WEST, SwingConstants.EAST, SwingConstants.NORTH, or SwingConstants.SOUTH.
-
Returns:
-
the location within the model that best represents the next location visual
 position
position

position.
-
Throws:
-
BadLocationException
-

IllegalArgumentException

- for an invalid direction
damageRange
public void damageRange(JTextComponent tc,
int p0,
int p1)
-
Causes the portion of the view responsible for the given part of the model to be repainted. Does nothing if the view is not currently painted.
-
-
Specified by:
-
damageRange
in class
TextUI
-
-
Parameters:
-
tc - the text component for which this UI is installed
-
p0 - the beginning of the range >= 0
-
p1 - the end of the range >= p0
-
See Also:
-
TextUI.damageRange(javax.swing.text.JTextComponent, int, int)
damageRange
public void damageRange(JTextComponent t,
int p0,
int p1,
Position.Bias p0Bias,
Position.Bias p1Bias)
-
Causes the portion of the view responsible for the given part of the model to be repainted.
-
-
Specified by:
-
damageRange
in class
TextUI
-
-
Parameters:
-
p0 - the beginning of the range >= 0
-
p1 - the end of the range >= p0
getEditorKit
public EditorKit getEditorKit(JTextComponent tc)
-
Fetches the EditorKit for the UI.
-
-
Specified by:
-
getEditorKit
in class
TextUI
-
-
Parameters:
-
tc - the text component for which this UI is installed
-
Returns:
-
the editor capabilities
-
See Also:
-
TextUI.getEditorKit(javax.swing.text.JTextComponent)
getRootView
public View getRootView(JTextComponent tc)
-
Fetches a View with the allocation of the associated text component (i.e. the root of the hierarchy) that can be traversed to determine how the model is being represented spatially.
NOTE:
The View hierarchy can be traversed from the root view, and other things can be done as well. Things done in this way cannot be protected like simple method calls through the TextUI. Therefore, proper operation in the presence of concurrency must be arranged by any logic that calls this method!
-
-
Specified by:
-
getRootView
in class
TextUI
-
-
Parameters:
-
tc - the text component for which this UI is installed
-
Returns:
-
the view
-
See Also:
-
TextUI.getRootView(javax.swing.text.JTextComponent)
getToolTipText
public String getToolTipText(JTextComponent t,
Point pt)
-
Returns the string to be used as the tooltip at the passed in location. This forwards the method onto the root View.
-
-
Overrides:
-
getToolTipText
in class
TextUI
-
-
Since:
-
1.4
-
See Also:
-
JTextComponent.getToolTipText(java.awt.event.MouseEvent)
,
View.getToolTipText(float, float, java.awt.Shape)
create
public View create(Element elem)
-
Creates a view for an element. If a subclass wishes to directly implement the factory producing the view(s), it should reimplement this method. By default it simply returns null indicating it is unable to represent the element.
-
-
Specified by:
-
create
in interface
ViewFactory
-
-
Parameters:
-
elem - the element
-
Returns:
-
the view
-
See Also:
-
View
create
public View create(Element elem,
int p0,
int p1)
-
Creates a view for an element. If a subclass wishes to directly implement the factory producing the view(s), it should reimplement this method. By default it simply returns null indicating it is unable to represent the part of the element.
-
-
-
Parameters:
-
elem - the element
-
p0 - the starting offset >= 0
-
p1 - the ending offset >= p0
-
Returns:
-
the view
 javax.swing.plaf.ComponentUI
javax.swing.plaf.ComponentUI
 javax.swing.plaf.TextUI
javax.swing.plaf.TextUI
 javax.swing.plaf.basic.BasicTextUI
javax.swing.plaf.basic.BasicTextUI

 is new.
is new.
javax.swing.plaf.ComponentUI
javax.swing.plaf.TextUI
javax.swing.plaf.basic.BasicTextUI

 A common strategy for creating more complex types of documents is to have the EditorKit implementation return a factory. Since the EditorKit ties all of the pieces necessary to maintain a type of document, the factory is typically an important part of that and should be produced by the EditorKit implementation.
A common strategy for creating more complex types of documents is to have the EditorKit implementation return a factory. Since the EditorKit ties all of the pieces necessary to maintain a type of document, the factory is typically an important part of that and should be produced by the EditorKit implementation.

 This implementation updates the background of the text component if the editable and/or enabled state changes.
This implementation updates the background of the text component if the editable and/or enabled state changes.
 t - the text component for which this UI is installed
t - the text component for which this UI is installed
 b - the bias for the position
b - the bias for the position

 This may be SwingConstants.WEST, SwingConstants.EAST, SwingConstants.NORTH, or SwingConstants.SOUTH
This may be SwingConstants.WEST, SwingConstants.EAST, SwingConstants.NORTH, or SwingConstants.SOUTH
 biasRet - an array to contain the bias for the returned position
biasRet - an array to contain the bias for the returned position

 position
position


