6 Extending the Domain with SOA Components
This chapter describes how to extend a domain with Oracle WSM Policy Manager and SOA components using the Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard. You can extend the resulting domain to add other Fusion Middleware components. It is assumed that a SOA ORACLE_HOME (binaries) has already been installed and is available from SOAHOST1 and SOAHOST2 and that a domain with an Administration Server has been created. This is the domain that will be extended in this chapter to support SOA components.
Important:
Oracle strongly recommends that you read the release notes for any additional installation and deployment considerations prior to starting the setup process.This chapter contains the following sections:
-
Section 6.2, "Enabling SOAHOST1VHN1 on SOAHOST1 and SOAHOST2VHN1 on SOAHOST2"
-
Section 6.3, "Running the Configuration Wizard on SOAHOST1 to Extend the Current Domain"
-
Section 6.5, "Configuring Oracle Coherence for Deploying Composites"
-
Section 6.6, "Disabling Host Name Verification for the WLS_SOA Managed Servers"
-
Section 6.7, "Starting and Validating the WLS_SOA1 Managed Server on SOAHOST1"
-
Section 6.8, "Propagating the Domain Configuration to SOAHOST2 Using the unpack Utility"
-
Section 6.10, "Starting and Validating the WLS_SOA2 Managed Server"
-
Section 6.11, "Configuring the Java Object Cache for Oracle Web Services Manager"
-
Section 6.12, "Configuring Oracle HTTP Server for the WLS_SOA Managed Servers"
-
Section 6.13, "Validating Access Through Oracle HTTP Server"
-
Section 6.16, "Configuring a Default Persistence Store for Transaction Recovery"
-
Section 6.17, "Enabling High Availability for Oracle File and FTP Adapters"
-
Section 6.19, "Configuring Node Manager for the WLS_SOA Managed Servers"
-
Section 6.20, "Configuring Server Migration for the WLS_SOA Managed Servers"
6.1 Backing Up the Installation
It is strongly recommended that you back up the existing Fusion Middleware Home and domain:
SOAHOST1> tar -cvpf fmwhomeback.tar ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw SOAHOST1> tar -cvpf domainhomeback.tar ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver/domain_name
This creates a backup of the installation files for both Oracle WebLogic Server and Oracle Fusion Middleware as well as the domain configuration.
6.2 Enabling SOAHOST1VHN1 on SOAHOST1 and SOAHOST2VHN1 on SOAHOST2
This step is required for server migration of WLS_SOA1 and WLS_SOA2. You will associate the WLS_SOA1 and WLS_SOA2 servers with virtual host names (SOAHOST1VHN1 and SOAHOST2VHN1). Check that these virtual host names are enabled by DNS or /etc/hosts resolution in your system and that they map to the appropriate VIPs (VIP2 and VIP3).
To enable the virtual IP, run the ifconfig command as root:
/sbin/ifconfig interface:index IP_address netmask netmask /sbin/arping -q -U -c 3 -I interface IP_address
For example:
/sbin/ifconfig ethX:Y 100.200.140.205 netmask 255.255.255.0
Enable your network to register the new location of the virtual IP, for example:
/sbin/arping -q -U -c 3 -I ethX 100.200.140.205
Validate that the address is available by pinging it from another node, for example:
/bin/ping 100.200.140.205
Note:
In these examples, 'ethX' is the ethernet interface (eth0 or eth1) and Y is the index (0, 1, 2, etc.).6.3 Running the Configuration Wizard on SOAHOST1 to Extend the Current Domain
Run the Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard from the SOA home directory to extend a domain containing an Administration Server to support Oracle Web Services Manager and SOA components.
-
Make sure that the database where you installed the repository is running. For Oracle RAC databases, it is recommended that all instances are running, so that the validation check later on becomes more reliable.
-
Change the directory to the location of the Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard:
SOAHOST1> cd ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin -
Start the Configuration Wizard:
SOAHOST1> ./config.sh
-
In the Welcome screen, select Extend an Existing WebLogic Domain, and click Next.
-
In the WebLogic Domain Directory screen, select the WebLogic domain directory (ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver/domain_name), and click Next.
-
The Select Extension Source screen opens. In this screen, do the following (as shown in Figure 6-1):
-
Select Extend my domain automatically to support the following added products.
-
Select the following products:
-
Basic WebLogic Server Domain - 10.3.4.0 [wlserver_10.3] (this should already be selected and grayed out)
-
Oracle Enterprise Manager - 11.1.1.0 [oracle_common] (this should already be selected and grayed out)
-
Oracle SOA Suite - 11.1.1.0 [soa]
-
Oracle WSM Policy Manager - 11.1.1.0 [oracle_common] (selected automatically when Oracle SOA suite is selected)
-
Oracle JRF - 11.1.1.0 [oracle_common] (this should already be selected and grayed out)
-
Figure 6-1 Select Extension Source screen for Oracle SOA

Description of "Figure 6-1 Select Extension Source screen for Oracle SOA"
If you accidentally deselect some of the targets, make sure that the following selections are made in this screen:
-
Oracle SOA Suite
-
Oracle WSM Policy Manager
Click Next.
-
-
The Configure JDBC Component Schema screen opens. In this screen, do the following (as shown in Figure 6-2):
-
Select the following component schemas:
-
SOA Infrastructure
-
User Messaging Service
-
OWSM MDS Schema
-
SOA MDS Schema
-
-
Select Configure selected component schemas as RAC multi data source schemas in the next panel.
Click Next.
Figure 6-2 Configure JDBC Component Schema Screen for Oracle SOA
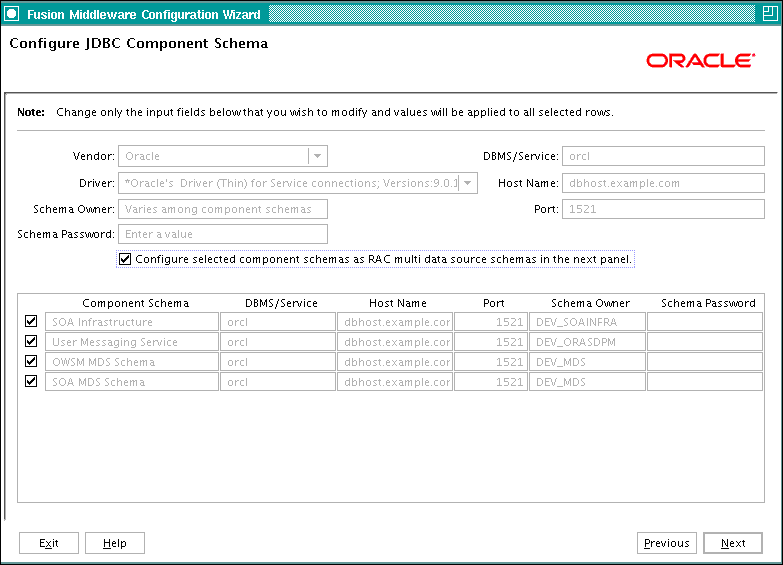
Description of "Figure 6-2 Configure JDBC Component Schema Screen for Oracle SOA"
-
-
The Configure RAC Multi Data Sources Component Schema screen opens. In this screen, enter values for the fields below, specifying the connect information for the Oracle RAC database that was seeded with RCU. Enter this information for each schema (you can select multiple schemas and specify values that are common to all):
Note:
Oracle recommends using the database used for identity management (see Chapter 11, "Integration with Oracle Identity Management") to store the Oracle WSM policies. It is therefore expected to use the IM database information has been seeded with RCU (as recommended in Chapter 2, "Database and Environment Preconfiguration") to store the WSM metadata and that this IM database information will be used in this screen for the OWSM MDS schemas. (This database connection information will be different from the one used for the rest of SOA Suite schemas.)-
Host name, instance name, and port for the first Oracle RAC database instance. Then click Add and repeat for each Oracle RAC instance.
-
Driver: Select Oracle driver (Thin) for RAC Service-Instance connections, Versions: 10 and later.
-
Service Name: Enter the service name of the database (for example, ecmedg.mycompany.com).
-
Username: Enter the complete user name (including the prefix) for the schemas. You can enter a value with all schemas selected (like the prefix) and then select each schema individually to change the rest of the schema name.
-
Password: Enter the password to use to access the schemas.
Click Next when you are done.
-
-
In the Test JDBC Data Sources screen, the connections should be tested automatically. The Status column displays the results. Ensure that all connections were successful. If not, click Previous to return to the previous screen and correct your entries.
Click Next when all the connections are successful.
-
In the Optional Configuration screen, select the following:
-
JMS Distributed Destination
-
Managed Servers, Clusters and Machines
-
Deployment and Services
Click Next.
-
-
In the Select JMS Distributed Destination Type screen, accept the default destination type (UDD) for all resources (UMSJMSSystemResource and SOAJMSModule) and click Next.
If an override warning appears, click OK to acknowledge it.
-
In the Configure Managed Servers screen, add the required managed servers.
A server called
soa_server1is created automatically. Rename this to WLS_SOA1 and add a new server called WLS_SOA2. Give these server the attributes listed in Table 6-1. Do not modify the other servers that are shown in this screen; leave them as they are.Name Listen Address Listen Port SSL Listen Port SSL Enabled WLS_SOA1
SOAHOST1VHN1
8001
n/a
No
WLS_SOA2
SOAHOST2VHN1
8001
n/a
No
Click Next.
-
In the Configure Clusters screen, add the clusters as listed in Table 6-2. Do not modify the other clusters that are shown in this screen; leave them as they are.
Name Cluster Messaging Mode Multicast Address Multicast Port Cluster Address SOA_Cluster
unicast
n/a
n/a
Leave it empty.
Click Next.
-
In the Assign Servers to Clusters screen, assign servers to clusters as shown below. Do not modify the other assignments that are shown in this screen; leave them as they are.
-
SOA_Cluster:
-
WLS_SOA1
-
WLS_SOA2
-
Click Next.
-
-
In the Configure Machines screen, delete the LocalMachine that appears by default and open the Unix Machine tab. You should add the SOAHOST1 and SOAHOST2 machines and eventually have the following entries:
Name Node Manager Listen Address SOAHOST1
SOAHOST1
SOAHOST2
SOAHOST2
ADMINHOST
localhost
Leave all other fields to their default values. Please note that the machine names do not need to be valid host names or listen addresses; they are just unique identifiers of Node Manager locations.
Click Next.
-
In the Assign Servers to Machines screen, assign servers to machines as follows:
-
ADMINHOST:
-
AdminServer
-
-
SOAHOST1:
-
WLS_SOA1
-
-
SOAHOST2:
-
WLS_SOA2
-
Click Next.
-
-
In the Target Deployments to Clusters or Servers screen, ensure the following targets:
-
usermessagingserver and usermessagingdriver-email should be targeted only to SOA_Cluster. (The usermessaging-xmpp, usermessaging-smpp, and usermessaging-voicexml applications are optional.)
-
WSM-PM should be targeted only to SOA_Cluster.
-
The oracle.rules#*, oracle.sdp.*, and oracle.soa.* deployments should be targeted only to SOA_Cluster.
-
The oracle.wsm.seedpolicies library should be targeted only to SOA_Cluster.
Click Next.
-
-
In the Target Services to Clusters or Servers screen, make sure that the JOC Startup Class and JOC Shutdown Class are targeted only to SOA_Cluster.
Click Next.
-
In the Configuration Summary screen, click Extend.
The domain is extended to include the SOA components.
-
In the Create Domain screen, click Done.
-
Restart the Administration Server to enable these changes to take effect.
6.4 Creating a Separate Domain Directory for Managed Servers in the Same Node as the Administration Server
Use the pack and unpack commands to separate the domain directory used by the Administration Server from the domain directory used by the managed server in SOAHOST1 as recommended in Chapter 2, "Database and Environment Preconfiguration."
-
Run the
packcommand on SOAHOST1 to create a template pack using the following commands:SOAHOST1> cd ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin SOAHOST1> ./pack.sh -managed=true -domain=ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver/domain_name -template=edgdomaintemplate.jar -template_name=edgdomain_template
-
Run the
unpackcommand on SOAHOST1 tounpackthe template to the domain directory of the managed server using the following command:SOAHOST1> cd ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin SOAHOST1> ./unpack.sh -domain=ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/mserver/domain_name -template=edgdomaintemplate.jar -app_dir=ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/mserver/applications
6.5 Configuring Oracle Coherence for Deploying Composites
Although deploying composites uses multicast communication by default, Oracle recommends using unicast communication instead in SOA enterprise deployments. Use unicast if you disable multicast communication for security reasons.
Note:
An incorrect configuration of the Oracle Coherence framework that is used for deployment may prevent the SOA system from starting. The deployment framework must be properly customized for the network environment on which the SOA system runs. Oracle recommends the configuration described in this section.Enabling Communication for Deployment Using Unicast Communication
Multicast communication enables Oracle Fusion Middleware SOA to discover all of the members of a cluster to which it deploys composites dynamically. However, unicast communication does not enable nodes to discover other cluster members in this way. Consequently, you must specify the nodes that belong to the cluster. You do not need to specify all of the nodes of a cluster, however. You need only specify enough nodes so that a new node added to the cluster can discover one of the existing nodes. As a result, when a new node has joined the cluster, it is able to discover all of the other nodes in the cluster. Additionally, in configurations such as SOA enterprise deployments where multiple IPs are available in the same box, you must configure Oracle Coherence to use a specific host name to create the Oracle Coherence cluster.
Tip:
To guarantee high availability during deployments of SOA composites, specify enough nodes so that at least one of them is running at any given time.Specify the nodes using the tangosol.coherence.wkaX system property, where X is a number between 1 and 9. You can specify up to nine nodes. Start the numbering at 1. This numbering must be sequential and must not contain gaps. In addition, specify the host name used by Oracle Coherence to create a cluster through the tangosol.coherence.localhost system property. This local host name should be the virtual host name used by the SOA server as the listener addresses (SOAHOST1VHN1 and SOAHOST2VHN1). Set this property by adding the -Dtangosol.coherence.localhost parameter to the Arguments field of the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console's Server Start tab (Figure 6-3).
Note:
SOAHOST1VHN1 is the virtual host name that maps to the virtual IP where WLS_SOA1 listening (in SOAHOST1). SOAHOST2VHN1 is the virtual host name that maps to the virtual IP where WLS_SOA2 is listening (in SOAHOST2).Figure 6-3 Start Server Tab of Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console
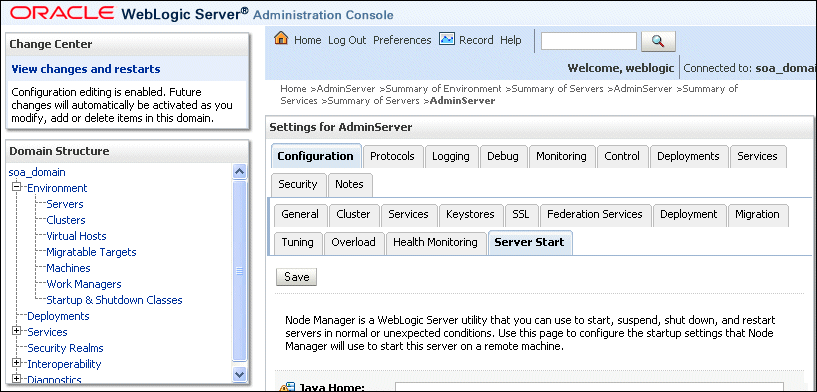
Description of "Figure 6-3 Start Server Tab of Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console"
Perform these steps to add the host name used by Oracle Coherence:
-
Log in to the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
In the Domain Structure window, expand the Environment node.
-
Click Servers. The Summary of Servers page opens.
-
Click the name of the server (WLS_SOA1 or WLS_SOA2), which are represented as hyperlinks in the Name column of the table. The settings page for the selected server opens.
-
Click Lock & Edit.
-
Click the Configuration tab, and then the Server Start tab.
-
Enter the following for WLS_SOA1 and WLS_SOA2 in the Arguments field.
For WLS_SOA1, enter the following (on a single line, without a carriage return):
-Dtangosol.coherence.wka1=SOAHOST1VHN1 -Dtangosol.coherence.wka2=SOAHOST2VHN1 -Dtangosol.coherence.localhost=SOAHOST1VHN1
For WLS_SOA2, enter the following (on a single line, without a carriage return):
-Dtangosol.coherence.wka1=SOAHOST1VHN1-Dtangosol.coherence.wka2=SOAHOST2VHN1 -Dtangosol.coherence.localhost=SOAHOST2VHN1
Note:
All arguments above are entered in one single line; that is, do not insert new lines in the Java arguments field in the Administration Console. Also, do not copy and paste the text from above to your Administration Console's arguments text field. This may result in extraneous characters being inserted in the Java arguments. The text should not contain other text or characters than the ones shown above.The Coherence cluster used for deployment uses port 8088 by default. This port can be changed by specifying a different port (for example, 8089) using the
-Dtangosol.coherence.wkan.portand-Dtangosol.coherence.localportstartup parameters, for example:-
WLS_SOA1 (enter the following into the Arguments field on a single line, without a carriage return):
-Dtangosol.coherence.wka1=SOAHOST1VHN1 -Dtangosol.coherence.wka2=SOAHOST2VHN1 -Dtangosol.coherence.localhost=SOAHOST1VHN1 -Dtangosol.coherence.wka1.port=8089 -Dtangosol.coherence.wka2.port=8089 -Dtangosol.coherence.localport=8089
-
WLS_SOA2 (enter the following into the Arguments field on a single line, without a carriage return):
-Dtangosol.coherence.wka1=SOAHOST1VHN1 -Dtangosol.coherence.wka2=SOAHOST2VHN1 -Dtangosol.coherence.localhost=SOAHOST2VHN1 -Dtangosol.coherence.wka1.port=8089 -Dtangosol.coherence.wka2.port=8089 -Dtangosol.coherence.localport=8089
-
-
Click Save and Activate Changes.
Note:
You must ensure that these variables are passed to the managed server correctly. (They should be reflected in the server's output log.) Failure of the Oracle Coherence framework can prevent the soa-infra application from starting.Note:
The multicast and unicast addresses are different from the ones used by the WebLogic Server cluster for cluster communication. SOA guarantees that composites are deployed to members of a single WebLogic Server cluster even though the communication protocol for the two entities (the WebLogic Server cluster and the groups to which composites are deployed) are different.6.6 Disabling Host Name Verification for the WLS_SOA Managed Servers
This step is required if you have not set up the appropriate certificates to authenticate the different nodes with the administration server (see Chapter 9, "Setting Up Node Manager"). If you have not configured the server certificates, you will receive errors when managing the different WebLogic Servers. To avoid these errors, disable host name verification while setting up and validating the topology, and enable it again once the EDG topology configuration is complete as described in Chapter 9, "Setting Up Node Manager."
Perform these steps to disable host name verification:
-
Log in to Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
Click Lock & Edit.
-
Expand the Environment node in the Domain Structure window.
-
Select WLS_SOA1 in the Names column of the table. The settings page for the server opens.
-
Open the SSL tab.
-
Expand the Advanced section of the page.
-
Click Save.
-
Save and activate the changes.
-
Restart Node Manager:
-
Stop Node Manager by stopping the process associated with it.
If it is running in the foreground in a shell, simply use Ctrl+c.
If it is running in the background in the shell, find the associate process and use the
killcommand to stop it. For example:SOAHOST1> ps -ef | grep NodeManager orcl 9139 9120 0 Mar03 pts/6 00:00:00 /bin/sh ./startNodeManager.sh SOAHOST1>kill -9 9139
-
Start Node Manager:
SOAHOST1> ./startNodeManager.sh
-
6.7 Starting and Validating the WLS_SOA1 Managed Server on SOAHOST1
Perform these steps to start the WLS_SOA1 managed server and check that it is configured correctly:
-
Start the WLS_SOA1 managed server using the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console as follows:
-
Expand the Environment node in the Domain Structure window.
-
Choose Servers. The Summary of Servers page opens.
-
Click the Control tab.
-
Select WLS_SOA1 and then click Start.
-
-
Verify that the server status is reported as "Running" in the Administration Console. If the server is shown as "Starting" or "Resuming," wait for the server status to change to "Started." If another status is reported (such as "Admin" or "Failed"), check the server output log files for errors. See Section 12.8, "Troubleshooting" for possible causes.
-
Access the following URLs:
-
Access http://SOAHOST1VHN1:8001/soa-infra to verify the status of WLS_SOA1.
-
Access http://SOAHOST1VHN1:8001/wsm-pm to verify the status of Web Services Manager. Click Validate Policy Manager. A list of policies and assertion templates available in the data store opens.
Note:
The configuration is incorrect if no policies or assertion templates appear. -
Access http://SOAHOST1VHN1:8001/integration/worklistapp to verify the status of the worklist application.
-
6.8 Propagating the Domain Configuration to SOAHOST2 Using the unpack Utility
Perform these steps to propagate the domain configuration:
-
Run the following command on SOAHOST1 to copy the template file created in Section 6.4, "Creating a Separate Domain Directory for Managed Servers in the Same Node as the Administration Server":
SOAHOST1> cd ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/oracle_common/common/bin SOAHOST1> scp edgdomaintemplate.jar oracle@SOAHOST2:ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/oracle_common/common/bin
-
Run the
unpackcommand on SOAHOST2 to unpack the propagated template.Note:
Rununpackfrom the ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin directory, not from WL_HOME/common/bin.SOAHOST2> cd ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin SOAHOST2> ./unpack.sh -domain=ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/mserver/domain_name -template=edgdomaintemplate.jar -app_dir=ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/mserver/applications
Note:
The ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/mserver directory must exist before runningunpack. In addition, the ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/mserver/applications must be empty.6.9 Starting Node Manager on SOAHOST2
Perform these steps to start Node Manager on SOAHOST2:
-
Run the setNMProps.sh script, which is located in the ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin directory, to set the
StartScriptEnabledproperty to 'true' before starting Node Manager:SOAHOST2> cd ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin SOAHOST2> ./setNMProps.shNote:
You must use theStartScriptEnabledproperty to avoid class loading failures and other problems. See also Section 12.8.3, "Incomplete Policy Migration After Failed Restart of SOA Server." -
Start Node Manager:
SOAHOST2> cd WL_HOME/server/bin SOAHOST2> ./startNodeManager.sh
6.10 Starting and Validating the WLS_SOA2 Managed Server
Perform these steps to start the WLS_SOA2 managed server and check that it is configured correctly:
-
Start the WLS_SOA2 managed server using the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console as follows:
-
Expand the Environment node in the Domain Structure window.
-
Choose Servers. The Summary of Servers page opens.
-
Click the Control tab.
-
Select WLS_SOA2 and then click Start.
-
-
Verify that the server status is reported as "Running" in the Administration Console. If the server is shown as "Starting" or "Resuming," wait for the server status to change to "Started." If another status is reported (such as "Admin" or "Failed"), check the server output log files for errors. See Section 12.8, "Troubleshooting" for possible causes.
-
Access the following URLs:
-
Access http://SOAHOST2VHN1:8001/soa-infra to verify the status of WLS_SOA2.
-
Access http://SOAHOST2VHN1:8001/wsm-pm to verify the status of Web Services Manager. Click Validate Policy Manager. A list of policies and assertion templates available in the data store opens.
Note:
The configuration is incorrect if no policies or assertion templates appear. -
Access http://SOAHOST2VHN1:8001/integration/worklistapp to verify the status of the worklist application.
-
6.11 Configuring the Java Object Cache for Oracle Web Services Manager
The Java Object Cache (JOC) should be configured among all the servers running Oracle Web Services Manager (WSM). This local cache is provided to increase the performance of Oracle WSM. The Java Object Cache can be configured using the MW_HOME/oracle_common/bin/configure-joc.py script. This is a Python script which can be used to configure JOC in the managed servers. The script runs in WLST online mode and expects the Administration Server to be up and running.
When configuring JOC ports for Oracle products, Oracle recommends using ports in the 9988 to 9998 range.
Note:
After configuring the Java Object Cache using the wlst commands or configure-joc.py script, all affected managed servers should be restarted for the configurations to take effect.Perform these steps to configure the Java Object Cache for Oracle WSM:
-
Connect to the Administration Server using the command-line Oracle WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST), for example:
MW_HOME/oracle_common/common/bin/wlst.sh $ connect()Enter the server URL, Oracle Weblogic Administration user name and password when prompted.
-
After connecting to the Administration Server using wlst, start the script using the
execfilecommand, for example:wls:/mydomain/serverConfig>execfile('MW_HOME/oracle_common/bin/configure-joc.py')
Specifically, for EDG environments, the first cluster option in step 2 should be used. Here is a walkthrough for using configure-joc.py for EDG environments (see below for the script input parameters):
Execfile('MW_HOME/oracle_common/bin/configure-joc.py').
Enter Hostnames (eg host1,host2) : SOAHOST1VHN1, SOAHOST2VHN1
.
Do you want to specify a cluster name (y/n) <y>y
.
Enter Cluster Name : SOA_Cluster
.
Enter Discover Port : 9991
.
Enter Distribute Mode (true|false) <true> : true
.
Do you want to exclude any server(s) from JOC configuration (y/n) <n> n
You can also configure the Java Object Cache (JOC) using the HA Power Tools tab in the Oracle WebLogic Administration Console as described in the Oracle Fusion Middleware High Availability Guide.
The input parameters are prompted by the script. The script can be used to perform the following JOC configurations:
-
Configure JOC for all specified managed servers for a given cluster. Enter 'y' when the script prompts whether you want to specify a cluster name, and also specify the cluster name and discover port, when prompted. This discovers all the managed servers for the given cluster and configures the JOC. The discover port is common for the entire JOC configuration across the cluster. For example:
Do you want to specify a cluster name (y/n) <y> Enter Cluster Name : SOA_Cluster Enter Discover Port : 9991
-
Configure JOC for all specified managed servers. Enter 'n' when the script prompts whether you want to specify a cluster name, and also specify the managed server and discover port, when prompted. For example:
Do you want to specify a cluster name (y/n) <y>n Enter Managed Server and Discover Port (eg WLS_SOA1:9991, WLS_SOA21:9991) : WLS_SOA1:9999,WLS_SOA2:9999
This example configures JOC only for the specified managed servers (that is, WLS_SOA1 and WLS_SOA2). The discover port is specified with the managed server (for example,
WLS_SOA1:2222). -
Exclude JOC configuration for some managed servers. The script allows you to specify the list of managed servers for which the JOC configuration "DistributeMode" will be set to 'false'. Enter 'y' when the script prompts whether you want to exclude any servers from JOC configuration, and enter the managed server names to be excluded, when prompted. For example:
Do you want to exclude any server(s) from JOC configuration (y/n) <n>y Exclude Managed Server List (eg Server1,Server2) : WLS_SOA1,WLS_SOA2
-
Disable the distribution mode for all managed servers. The script allows you to disable the distribution to all the managed servers for a specified cluster. Specify 'false' when the script prompts for the distribution mode. By default, the distribution mode is set to 'true'.
6.12 Configuring Oracle HTTP Server for the WLS_SOA Managed Servers
To enable Oracle HTTP Server to route to SOA_Cluster, which contain the WLS_SOAn managed servers, you must set the WebLogicCluster parameter to the list of nodes in the cluster:
-
On WEBHOST1 and WEBHOST2, add the following lines to the ORACLE_BASE/ admin/instance_name/config/OHS/component_name/mod_wl_ohs.conf file:
# WSM-PM <Location /wsm-pm> WebLogicCluster SOAHOST1VHN1:8001,SOAHOST2VHN1:8001 SetHandler weblogic-handler WLProxySSL ON WLProxySSLPassThrough ON </Location> # SOA soa-infra app <Location /soa-infra> WebLogicCluster SOAHOST1VHN1:8001,SOAHOST2VHN1:8001 SetHandler weblogic-handler WLProxySSL ON WLProxySSLPassThrough ON </Location> # SOA inspection.wsil <Location /inspection.wsil> WebLogicCluster SOAHOST1VHN1:8001,SOAHOST2VHN1:8001 SetHandler weblogic-handler WLProxySSL ON WLProxySSLPassThrough ON </Location> # Worklist <Location /integration/> WebLogicCluster SOAHOST1VHN1:8001,SOAHOST2VHN1:8001 SetHandler weblogic-handler WLProxySSL ON WLProxySSLPassThrough ON </Location> # UMS prefs <Location /sdpmessaging/userprefs-ui> WebLogicCluster SOAHOST1VHN1:8001,SOAHOST2VHN1:8001 SetHandler weblogic-handler WLProxySSL ON WLProxySSLPassThrough ON </Location> # Default to-do taskflow <Location /DefaultToDoTaskFlow/> WebLogicCluster SOAHOST1VHN1:8001,SOAHOST2VHN1:8001 SetHandler weblogic-handler WLProxySSL ON WLProxySSLPassThrough ON </Location> # Workflow <Location /workflow> WebLogicCluster SOAHOST1VHN1:8001,SOAHOST2VHN1:8001 SetHandler weblogic-handler WLProxySSL ON WLProxySSLPassThrough ON </Location> #SOA Composer <Location /soa/composer> WebLogicCluster SOAHOST1VHN1:8001,SOAHOST2VHN1:8001 SetHandler weblogic-handler WLProxySSL ON WLProxySSLPassThrough ON </Location> -
Make sure the httpd.conf file located in the same directory as the mod_wl_ohs file contains the following lines:
NameVirtualHost *:7777 <VirtualHost *:7777> ServerName https://ecm.mycompany.com:443 ServerAdmin you@your.address RewriteEngine On RewriteOptions inherit </VirtualHost> NameVirtualHost *:7777 <VirtualHost *:7777> ServerName admin.mycompany.com:80 ServerAdmin you@your.address RewriteEngine On RewriteOptions inherit </VirtualHost>Note:
Values such as ecm.mycompany.com:443, admin.mycompany.com:80 and you@youraddress that are noted in this document serve as examples only. Enter values based on the actual environment. -
Restart Oracle HTTP Server on both WEBHOST1 and WEBHOST2.
WEBHOST1> ORACLE_BASE/admin/instance_name/bin/opmnctl restartproc ias-component=ohs1 WEBHOST2> ORACLE_BASE/admin/instance_name/bin/opmnctl restartproc ias-component=ohs2
The servers specified in the WebLogicCluster parameter are only important at startup time for the plug-in. The list needs to provide at least one running cluster member for the plug-in to discover other members of the cluster. Please note that the listed cluster member must be running when Oracle HTTP Server is started. Oracle WebLogic Server and the plug-in work together to update the server list automatically with new, failed, and recovered cluster members.
Sample scenarios:
-
Example 1: If you have a two-node cluster and then add a third member, you do not need to update the configuration to add the third member. The third member will be discovered on the fly at run time.
-
Example 2: You have a three-node cluster but only two nodes are listed in the configuration. However, if both listed nodes are down when you start Oracle HTTP Server, then the plug-in would fail to route to the cluster. You must ensure that at least one of the listed nodes is running when you start Oracle HTTP Server.
If you list all members of the cluster, then you guarantee you can route to the cluster, assuming at least one member is running when Oracle HTTP Server is started.
For more information on configuring the WebLogic Server plug-in, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Using Web Server Plug-Ins with Oracle WebLogic Server Guide.
6.13 Validating Access Through Oracle HTTP Server
Verify that the server status is reported as "Running" in the Administration Console. If the server is shown as "Starting" or "Resuming," wait for the server status to change to "Started." If another status is reported (such as "Admin" or "Failed"), check the server output log files for errors. See Section 12.8, "Troubleshooting" for possible causes.
Validate WSM_Cluster through Oracle HTTP Server using the following URLs (for both WEBHOST1 and WEBHOST2):
-
http://WEBHOSTn:7777/soa-infra
-
http://WEBHOSTn:7777/integration/worklistapp
-
http://WEBHOSTn:7777/sdpmessaging/userprefs-ui
-
http://WEBHOSTn:7777/soa/composer
-
http://WEBHOSTn:7777/wsm-pm
For information on configuring system access through the load balancer, see Section 2.2.2, "Load Balancers."
Note:
After the registering Oracle HTTP Server as described in Section 5.9, "Registering Oracle HTTP Server with WebLogic Server," Oracle HTTP Server should appear as a manageable target in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console. To verify this, log in to the Enterprise Manager Console. The WebTier item in the navigation tree should show that Oracle HTTP Server has been registered.6.14 Setting the Frontend HTTP Host and Port
You must set the frontend HTTP host and port for the Oracle WebLogic Server cluster hosting the SOA servers:
-
Log in to Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
Go to the Change Center section and click Lock & Edit.
-
Expand the Environment node in the Domain Structure window.
-
Click Clusters. The Summary of Clusters page opens.
-
Select SOA_Cluster.
-
Click the HTTP tab.
-
Set the following values:
-
Frontend Host: ecm.mycompany.com
-
Frontend HTTPS Port: 443
-
Frontend HTTP Port: 80 (if not using SSL)
-
-
Click Save.
-
Click Activate Changes in the Change Center section of the Administration Console.
-
Restart the servers to make the frontend host directive in the cluster take effect.
6.15 Configuring a Shared JMS Persistence Store
Configure the location for all of the persistence stores as a directory that is visible from both nodes. See Section 2.3, "Shared Storage and Recommended Directory Structure" for more information. You must change all of the persistent stores to use this shared base directory as follows:
-
Log in to the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
In the Domain Structure window, expand the Services node and then click the Persistence Stores node. The Summary of Persistence Stores page opens.
-
Select the persistence store (represented as a hyperlink) from the Name column of the table. The Settings page for the persistence store opens.
-
Open the Configuration tab.
-
Click Lock & Edit.
-
In the Directory field, enter the location of a persistent storage solution (such as NAS or SAN) that is available to other servers in the cluster. Specifying this location enables pending JMS messages to be sent. The location should follow the following directory structure:
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/soa_cluster_name/jms
Note:
Both WLS_SOA1 and WLS_SOA2 must be able to access this directory. This directory must also exist before you restart the server. -
Click Save and Activate.
-
Restart the servers to make the change in the persistent stores take effect.
6.16 Configuring a Default Persistence Store for Transaction Recovery
Each server has a transaction log that stores information about committed transactions that are coordinated by the server that may not have been completed. The WebLogic Server uses this transaction log for recovery from system crashes or network failures. To leverage the migration capability of the Transaction Recovery Service for the servers within a cluster, store the transaction log in a location accessible to a server and its backup servers.
Note:
Preferably, this location should be a dual-ported SCSI disk or on a Storage Area Network (SAN).Perform these steps to set the location for the default persistence store:
-
Log in to the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
In the Domain Structure window, expand the Environment node and then click the Servers node. The Summary of Servers page opens.
-
Click the name of the server (represented as a hyperlink) in the Name column of the table. The settings page for the selected server opens and defaults to the Configuration tab.
-
Open the Services tab within the Configuration tab (not the top-level Services tab).
-
In the Default Store section of the page, enter the path to the folder where the default persistent stores will store its data files. The directory structure of the path is as follows:
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/soa_cluster_name/tlogs
-
Save and activate the changes.
-
Restart the WLS_SOA1 and WLS_SOA2 managed servers.
Note:
To enable migration of the Transaction Recovery Service, specify a location on a persistent storage solution that is available to other servers in the cluster. Both WLS_SOA1 and WLS_SOA2 must be able to access this directory.6.17 Enabling High Availability for Oracle File and FTP Adapters
Note:
this step is optional and applies only to those deployments that require adapter support for the BPEL processes that are invoked by I/PM.The Oracle File and FTP Adapters enable a BPEL process or an Oracle Mediator to read and write files on local file systems and on remote file systems through FTP (File Transfer Protocol).These adapters support high availability for an active-active topology with Oracle BPEL Process Manager and Oracle Mediator service engines for both inbound and outbound operations. To make Oracle File and FTP Adapters highly available for outbound operations, use the database mutex locking operation as described in "High Availability in Outbound Operations" in Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Technology Adapters. The database mutex locking operation enables these adapters to ensure that multiple references do not overwrite one another if they write to the same directory.
Note:
The File Adapter picks up a file from the inbound directory, processes it, and then outputs a file to the output directory. Because the File Adapter is non-transactional, files can be processed twice. As a result, it is possible to get duplicate files when there is failover in the Oracle RAC back-end or in the SOA-managed servers.Using the Database Mutex Locking Operation
To make an outbound Oracle File or FTP Adapter service highly available using database table as a coordinator, you must modify the Oracle File Adapter deployment descriptor for the connection-instance corresponding to eis/HAFileAdapter in the Oracle WebLogic Server console:
Note:
You must increase global transaction timeouts if you use database as a coordinator.-
Log in to the Oracle WebLogic Server console. To access the console, navigate to http://server_name:port_number/console.
-
Click Deployments in the left pane for Domain Structure.
-
Click FileAdapter under Summary of Deployments on the right pane.
-
Open the Configuration tab.
-
Open the Outbound Connection Pools tab, and expand javax.resource.cci.ConnectionFactory to see the configured connection factories.
-
Click eis/HAFileAdapter. The Outbound Connection Properties screen for the connection factory corresponding to high availability opens. The connection factory properties are displayed as shown in Figure 6-4.
Figure 6-4 Oracle WebLogic Server Console - Settings for javax.resource.cci.Connectionfactory Page
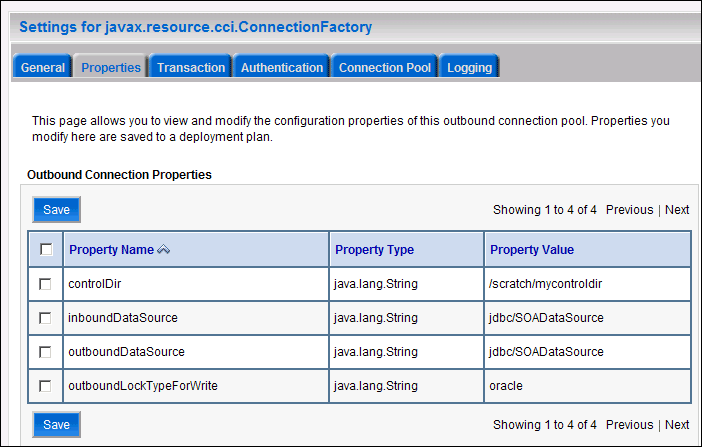
Description of "Figure 6-4 Oracle WebLogic Server Console - Settings for javax.resource.cci.Connectionfactory Page"
-
Click Lock & Edit. After this, the property value column becomes editable (you can click on any of the rows under "Property Value" and modify its value).
The new parameters in connection factory for Oracle File and FTP Adapters are as follows:
-
controlDir: Set it to the directory structure where you want the control files to be stored. You must set it to a shared location if multiple WebLogic Server instances run in a cluster. Structure the directory for shared storage as follows:
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/cluster_name/fadapter
-
inboundDataSource: Set the value to 'jdbc/SOADataSource'. This is the data source where the schemas corresponding to high availability are pre-created. The pre-created schemas can be found under ORACLE_HOME/rcu/integration/soainfra/sql/adapter/createschema_adapter_oracle.sql. If you want to create the schemas elsewhere, use this script. You must set the inboundDataSource property accordingly if you choose a different schema.
-
outboundDataSource: Set the value to 'jdbc/SOADataSource'. This is the data source where the schemas corresponding to high availability are pre-created. The pre-created schemas can be found under ORACLE_HOME/rcu/integration/soainfra/sql/adapter/createschema_adapter_oracle.sql. If you want to create the schemas elsewhere, use this script. You must set the outboundDataSource property if you choose to do so.
-
outboundLockTypeForWrite: Set the value to 'oracle' if you are using Oracle Database. By default, the Oracle File and FTP Adapters use an in-memory mutex to lock outbound write operations. You must choose from the following values for synchronizing write operations:
-
memory: The Oracle File and FTP Adapters use an in-memory mutex to synchronize access to the file system.
-
oracle: The adapter uses Oracle Database sequence.
-
db: The adapter uses a pre-created database table (FILEADAPTER_MUTEX) as the locking mechanism. You must use this option only if you are using a schema other than the Oracle Database schema.
-
user-defined: The adapter uses a user-defined mutex. To configure the user-defined mutex, you must implement the mutex interface (oracle.tip.adapter.file.Mutex) and then configure a new binding-property with the name 'oracle.tip.adapter.file.mutex' and value as the fully qualified class name for the mutex for the outbound reference.
-
Note:
The parameters available for FTP Adapters are slightly different than for the connection factory, but from a high-availability standpoint, just setting the control directory to a shared storage location is what matters. -
-
Click Save after you update the properties. The Save Deployment Plan page opens.
-
Enter a shared storage location for the deployment plan. The directory structure is as follows:
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/cluster_name/dp/Plan.xml
-
Click Save and Activate.
-
Configure BPEL Process or Mediator Scenario to use the connection factory as shown in the following example:
<adapter-config name="FlatStructureOut" adapter="File Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata"> <connection-factory location="eis/HAFileAdapter" adapterRef=""/> <endpoint-interaction portType="Write_ptt" operation="Write"><interaction-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.outbound.FileInteractionSpec"> <property../> <property../> </interaction-spec> </endpoint-interaction></adapter-config>
Note:
The location attribute is set toeis/HAFileAdapterfor the connection factory.
6.18 Scaling the Oracle Database Adapter
Note:
this step is optional and applies only to those deployments that require adapter support for the BPEL processes that are invoked by I/PM.If you are using Logical Delete polling and you set MarkReservedValue, skip locking is not used. Formerly, the best practice for multiple Oracle Database Adapter process instances deployed to multiple Oracle BPEL Process Manager or Oracle Mediator nodes was essentially using LogicalDeletePollingStrategy or DeletePollingStrategy with a unique MarkReservedValue on each polling node, and setting MaxTransactionSize. However, with the introduction of skip locking in Oracle FMW 11gR1 PS1, that approach has now been superseded. If you were using this approach previously, you can simply remove (in db.jca) or clear (on the Logical Delete wizard page) the MarkReservedValue, and you will automatically get skip locking.
The benefits of using skip locking over a reserved value include:
-
Skip locking scales better in a cluster and under load.
-
All work is in one transaction (as opposed to update/reserve, then commit, then select in a new transaction), so the risk of facing non-recoverable situations in high-availability environments is minimized.
-
No unique
MarkReservedValueneeds to be specified. Previously, for this to work, you had to configure a complex variable, such asR${weblogic.Name-2}-${IP-2}-${instance}.
For more information, see "Scalability" and "Polling Strategies" in Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Technology Adapters.
6.19 Configuring Node Manager for the WLS_SOA Managed Servers
Oracle recommends using host name verification for the communication between Node Manager and the servers in the domain. This requires the use of certificates for the different addresses communicating with the Administration Server and other servers. See Chapter 9, "Setting Up Node Manager" for further details. The procedures in that chapter must be performed twice using the following information:
| Run | Host Name (HOST) | Virtual IP (VIP) | Server Name (WLS_SERVER) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Run 1: | SOAHOST1 | SOAHOST1VHN1 | WLS_SOA1 |
| Run 2: | SOAHOST2 | SOAHOST2VHN1 | WLS_SOA2 |
6.20 Configuring Server Migration for the WLS_SOA Managed Servers
Server migration is required for proper failover of the SOA components in the event of failure in any of the SOAHOST1 and SOAHOST2 nodes. See Chapter 10, "Configuring Server Migration" for further details. For SOA, use the following values for the variables in that chapter:
-
Server names:
-
WLS_SERVER1: WLS_SOA1
-
WLS_SERVER2: WLS_SOA2
-
-
Host names:
-
HOST1: SOAHOST1
-
HOST2: SOAHOST2
-
-
Cluster name:
-
CLUSTER: SOA_Cluster
-
6.21 Backing Up the Installation
After you have verified that the extended domain is working, back up the installation. This is a quick backup for the express purpose of immediate restore in case of problems in the further steps. The backup destination is the local disk. This backup can be discarded once the enterprise deployment setup is complete. At that point, the regular deployment-specific backup and recovery process can be initiated. The Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide provides further details. For information on describing the Oracle HTTP Server data that must be backed up and restored, refer to the "Backup and Recovery Recommendations for Oracle HTTP Server" section in that guide. For information on how to recover components, see the "Recovery of Components" and "Recovery After Loss of Component" sections in the guide. For recommendations specific to recovering from the loss of a host, see the "Recovering Oracle HTTP Server to a Different Host" section in the guide. Also refer to the Oracle Database Backup and Recovery Guide for information on database backup.
Perform these steps to back up the installation at this point:
-
Back up the web tier:
-
Shut down the instance using
opmnctl:WEBHOST1> ORACLE_BASE/admin/instance_name/bin/opmnctl stopall
-
Back up the Middleware Home on the web tier using the following command (as root):
WEBHOST1> tar -cvpf BACKUP_LOCATION/web.tar MW_HOME
-
Back up the Oracle Instance Home on the web tier using the following command:
WEBHOST1> tar -cvpf BACKUP_LOCATION/web_instance_name.tar ORACLE_INSTANCE
-
Start the instance using
opmnctl:WEBHOST1> cd ORACLE_BASE/admin/instance_name/bin WEBHOST1> opmnctl startall
-
-
Back up the database. This is a full database backup (either hot or cold) using Oracle Recovery Manager (recommended) or operating system tools such as tar for cold backups if possible.
-
Back up the Administration Server and managed server domain directories to save your domain configuration. The configuration files all exist in the ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name directory. Run the following command to create the backup:
SOAHOST1> tar -cvpf edgdomainback.tar ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name