4 Creating JD Edwards EnterpriseOne BI Publisher Report Definitions
This chapter contains the following topics:
-
Section 4.1, "Understanding JD Edwards EnterpriseOne BI Publisher Report Definitions"
-
Section 4.5, "Managing BI Publisher Objects in Object Management Workbench"
-
Section 4.6, "Configuring BI Publisher Objects for Object Management Workbench"
4.1 Understanding JD Edwards EnterpriseOne BI Publisher Report Definitions
Report definitions specify the information that BI Publisher requires to process and deliver BI Publisher output. The details in a report definition include:
-
The UBE and optional version to use as the data source.
-
Associated templates, transformations, and localizations.
-
Output types.
-
Language options.
-
Bursting options.
-
Delivery options.
You use the BI Publisher Report Definitions application (P95620) to create, update, copy, and delete report definitions. After a report definition is created, it can be submitted to BI Publisher to produce the defined output types.
Note:
Before creating a report definition, ensure that the necessary templates have been created and uploaded into the BI Publisher Object Repository (P95600).See Chapter 3, "Creating JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Embedded BI Publisher Objects".
4.2 Creating BI Publisher Report Definitions
This section provides an overview of the report definition process and discusses how to:
-
Define the source of data, template names, and transformations.
-
Define languages and output types.
-
Define bursting and delivery options.
4.2.1 Understanding the Report Definition Process
Although the BI Publisher Report Definitions application (P95620) is available on both the web client and the Microsoft Windows client, you must use the Microsoft Windows client to create a new report definition or to modify an existing report definition.
Adding a report definition is a three-step process. The first step consists of entering the required details for the report definition and defining the source of data and the templates to process. Additionally, if a template uses one or more transformations, they are defined in this step.
Second, you define the output types that a user can select when submitting the report definition. You also define the default output types and default languages for the XML output.
In the third step, you define the optional bursting field for the report definition, as well as the delivery options for the output. A report definition must comply with the following conditions to allow bursting to be configured:
-
Templates of type TL (Microsoft Excel) and TS (XSL) cannot be used.
-
A transformation cannot be used.
-
Microsoft PowerPoint and XML output types cannot be used.
4.2.2 Forms Used to Create BI Publisher Report Definitions
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| BI Publisher Report Definitions | W95620A | On JD Edwards Solution Explorer EnterpriseOne Life Cycle Tools task view, select Report Management, BI Publisher, Report Definitions or enter P95620 in the Fast Path field. field. | Select a BI Publisher report definition. |
| Add Report Definition | W95620C | Click Add on the BI Publisher Report Definitions form. | Add a report definition. |
| Add Report Definition-Languages and Output Types | W95620H | Click Next on the Add Report Definition form. | Define available output types, default output types, and default languages. |
| Add Report Definition-Bursting and Delivery | W95620J | Click Next on the Add Report Definitions-Languages and Output Types form. | Define an optional bursting field for the report definition, and delivery details for the output. |
| Update Report Definition | W95620C | On the BI Publisher Report Definitions form, select a record in the grid and then click Select. | Update a report definition. |
4.2.3 Defining Source of Data, Template Names, and Transformations
Access the Add Report Definition form.
- Report Definition
-
Enter the name of the report definition, using a maximum of 10 characters. Oracle recommends that report definition names start with the letters RD.
- Description
-
Enter a meaningful description for the report definition.
- Product Code
-
Select a product code from the 55–59 client reserved range.
- Product System Code
-
Select a product code that indicates where the reporting data resides.
- Source Type
-
The source type (user-defined code (UDC) H95|RY) appears automatically and is based on the source type of the data that the report definition uses.
- Source UBE
-
Enter the name of the Report Design Aid (RDA) report template that is used to generate data for the report definition.
You can also use a subsystem report, such as R42520/XJDE0006, Print Pick Slips - Subsystem, as the source UBE and version for a report definition. Subsystem reports are batch processes that continually run independently of, but asynchronously with, JD Edwards EnterpriseOne applications. Subsystem reports offer many advantages, such as the elimination of startup time, one-time initialization of environment and specifications, and better utilization of the processor on the server.
For information about subsystem jobs, see "Working with Subsystem Jobs" in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tools Development Tools: Report Design Aid Guide.
- Source Version
-
(Optional) Enter the name of a version only if the report definition is limited to one version of the UBE. If a version is not specified, the user will have to select a version at submission time.
- Blind Submission
-
(Optional) Leave this option blank to prompt the user with the available output, delivery, and language options when submitting the report definition to BI Publisher. If blind submission is selected, the user is not allowed to change the report definition options when submitting the report definition.
- Template Name
-
Enter the name of the template that you want to associate with the report definition.
- Template Description
-
The template description appears automatically and cannot be changed.
- Active Status
-
Active Status is determined by the effective dates of the template. The status appears automatically and indicates whether the template is active or inactive.
- Transformation Name
-
(Optional) Enter the name of the transformation that you want to associate with the report description.
- Transformation Description
-
The transformation description appears automatically and cannot be changed.
- Active Status
-
Active Status is determined by the effective dates of the transformation. The status appears automatically and indicates whether the transformation is active or inactive.
After entering the required report definition details, click Next to move to the Languages and Output Types form.
4.2.4 Defining Languages and Output Types
Access the Languages and Output Types form.
Figure 4-2 Report Definition-Languages and Output Types form
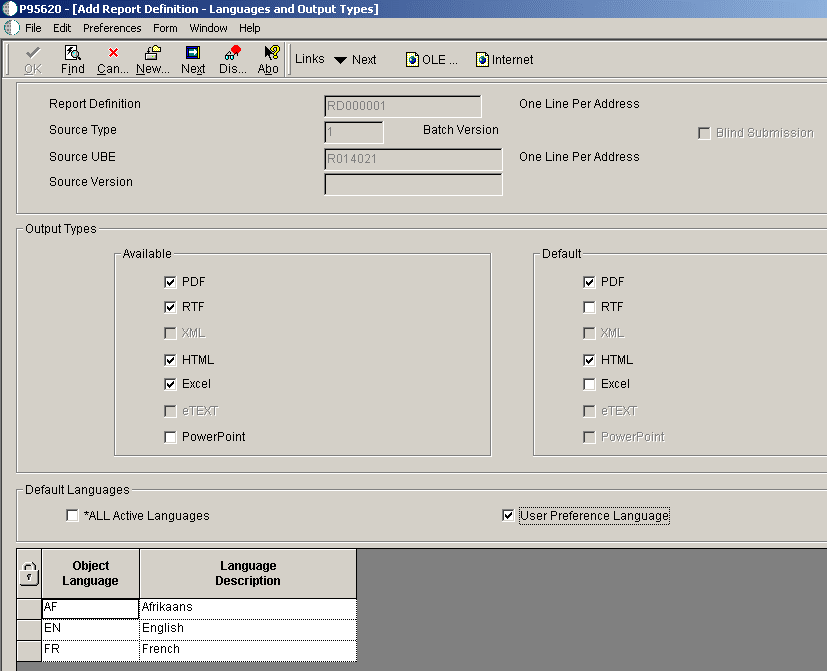
Description of "Figure 4-2 Report Definition-Languages and Output Types form"
Note:
The templates, translations, and localizations that are attached to the report definition determine the languages that appear in the Object Language column.- Available Output Types
-
Select the output types to be available to users when they are submitting the report definition. The type of template attached to the report definition determines which output types are available.
- Default Output Types
-
Select the default output types that will be selected when the report definition is submitted. Default output types are not enabled unless they are first defined as available output types. If the report definition is defined as blind submission, the default values indicate the type of output that will be produced when the report definition is submitted to BI Publisher.
Note:
When you run a report definition, the system does not automatically generate a PDF. - *ALL Active Languages
-
If this option is selected, all languages for the defined templates, localized templates, and translations that are active will process when a report definition is submitted to BI Publisher. Languages associated with the templates are displayed in the grid.
- User Preference Language
-
If this option is selected, when a report definition is submitted to BI Publisher and the sign on user's language preference has been defined, the language preference for the sign on user is processed. A user's language preference is defined in the user's system profile. The User Preference Language option is not enabled if *ALL Active Languages is selected.
- Object Language
-
A code that indicates the language defined for a template, localization, or translation.
- Language Description
-
A description of the language code assigned to a template, localization, or translation.
The output types available depend on the type of template that is used, as described in this table:
| Template Type | Output Type |
|---|---|
| RTF | PDF, RTF, Excel, HTML |
| EFT/EDI (eText) | eText |
| Excel | Excel |
| XSL | XML |
After defining the output types and languages, click Next to move to the Add Report Definition-Bursting and Delivery form.
4.2.5 Defining Bursting and Delivery Options
Access the Add Report Definitions-Bursting and Delivery form.
Figure 4-3 Add Report Definitions - Bursting and Delivery form
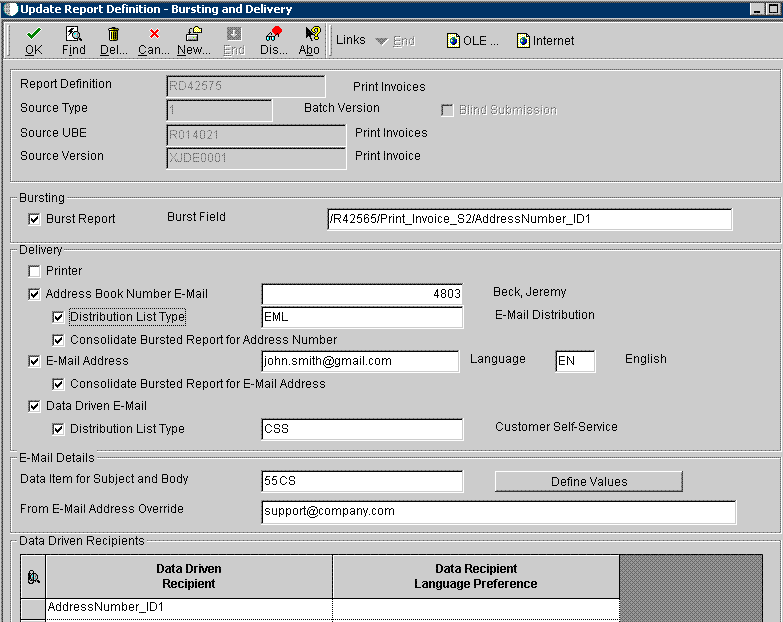
Description of "Figure 4-3 Add Report Definitions - Bursting and Delivery form"
- Burst Report
-
(Optional) Select this option if bursting will be performed for a report definition.
- Burst Field
-
A report definition can burst on any level break section defined within the batch or report version that is used as its source of data. Typically, when you burst a report, you break on a level break header section. The field must contain the complete XPath as it appears in the XML data output that was created from the batch process.
- Printer
-
Select this option to direct output to a printer.
- Address Book Number E-Mail
-
Select this option to deliver output to the email address that is associated with a specific Address Book number. When a report definition is submitted to BI Publisher, all output produced is sent to the email address.
- Distribution List Type
-
Select this option to deliver output to all members of the distribution list type who are associated with the provided Address Book number. If the distribution list type is not entered, the output is sent to the primary email address associated with the Address Book number.
- Consolidate Bursted Report for Address Number
-
Select this option to deliver all the bursted output in a single report to the email address associated with the provided Address Book number.
- E-Mail Address
-
Select this option to deliver output to a specific email address. When the report definition is submitted to BI Publisher and an email delivery address has been defined, all output produced is sent to the defined email address.
- Language
-
Select the language in which you want the output delivered.
- Consolidate Bursted Report for E-Mail Address
-
Select this option to deliver all the bursted output in a single report to the email address.
- Data Driven E-Mail
-
Select this option to deliver the output to email recipients based on the data generated by the source batch version or report version.
- Distribution List Type
-
Select this option to deliver output to all members of a distribution list and distribution list type that are associated with the data. If the distribution list type is not entered, the output is sent to the primary email address associated with the Address Book number.
- Data Item for Subject and Body
-
(Optional) Specify a data dictionary glossary item for the subject and body of the delivery email.
- From E-Mail Address Override
-
Specify an alternate email address if you want to override the from email address for the delivery email.
- Data Driven Recipient
-
(Optional) To deliver the report definition output to recipients as determined by the data from a particular item within the XML output, specify the XPath field that contains the recipient data.
- Data Recipient Language Preference
-
(Optional) Select this option if you want to deliver the report definition output to the recipients determined by the language preference within the XML output. The field must contain language data from the 01/LP or the H95/XL UDCs (User Defined Code).
After defining bursting and delivery details, click End to save the report definition and exit.
4.2.6 Delivery Email Subject and Body
If report definition output is sent to an email address, you can define a customized subject and body for the email message. To utilize this enhancement, a data dictionary glossary item (glossary group E) must be associated with the report definition.
Glossary group E designates error, warning, and information messages. If a message contains values that will be substituted by data items from a data structure, the message will have a placeholder for each text-substituted value. The placeholders are indicated by an ampersand (&) and a number in the message text.
The following example shows a custom data dictionary glossary item with text-substitution placeholders. This glossary item could be used as the email subject and body for a report definition that produces customer invoices.
Figure 4-4 Data Dictionary Glossary Items form
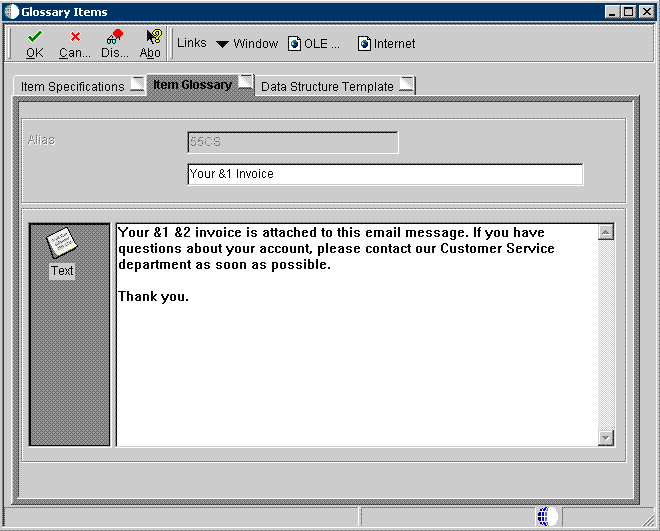
Description of "Figure 4-4 Data Dictionary Glossary Items form"
In this example, &1 could be the date of the invoice and &2 the type of invoice. Invoices can be produced on a daily, weekly, bi-weekly, semi-monthly, or monthly basis. When users submit the report definition, they can enter values for the &1 and &2 variables so that the subject of the email could be "Your 6/30/10 Invoice," and the body of the message could be "Your 6/30/10 monthly invoice is attached to this email message. If you have questions about your account, please contact our Customer Service department as soon as possible. Thank you."
Data Structure Template
Text-substituted values are defined by data dictionary items in the data structure associated with a data dictionary glossary item. The Data Structure Template tab shows the name of the associated data structure. In the following example, a custom data structure template has been associated with the glossary item.
Figure 4-5 Glossary Items form - Data Structure Template tab
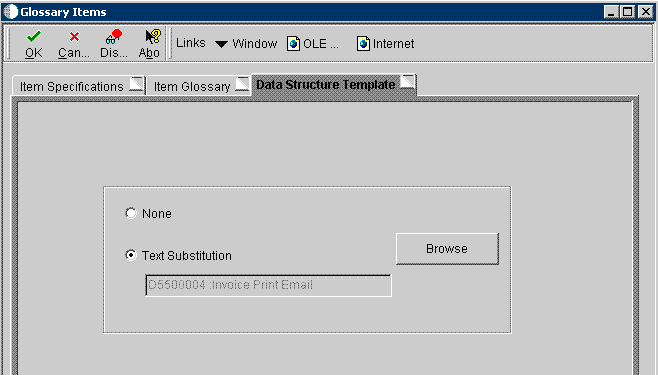
Description of "Figure 4-5 Glossary Items form - Data Structure Template tab"
The data structure consists of a data item for each text-substituted value in the subject and body of the glossary data item. Because the message in this example has two text-substituted values, the associated data structure consists of two data items, as shown in the following example.
Figure 4-6 Data structure with data items for text-substitution values
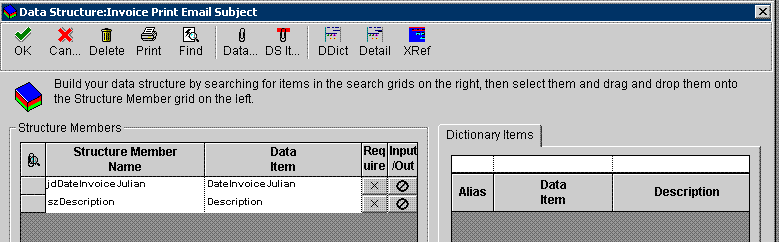
Description of "Figure 4-6 Data structure with data items for text-substitution values"
4.2.6.1 Report Definition Data Item for Subject and Body
To provide the subject and text for an email message, enter the name of a glossary data item in the Data Item for Subject and Body field on the Bursting and Delivery form.
If a glossary data item with an associated text-substitution data structure has been defined for the report definition, you can click the Define Values button to enter specific text for the email message when the report definition is submitted. The text entered in the Structure Member Value field on the Structure Member Value Revisions form will be substituted for the variables in the subject and body of the email message. In the following example, 6/30/10 and Monthly are the values for the text-substituted variables.
Figure 4-7 Structure Member Value Revisions form
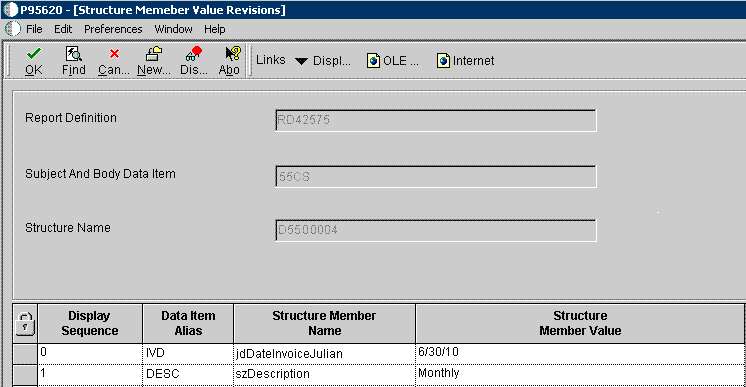
Description of "Figure 4-7 Structure Member Value Revisions form"
4.2.6.1.1 Dynamic Text-Substitution
Another text-substitution option is to use an XPath (from the XML data output) for the structure member value. Using an XPath enables dynamic text-substitution to occur for text-substituted values in the email subject and body. For bursted reports, the XPath value could be different for each recipient, depending on which XPath was used.
For example, if you wanted the email subject line to dynamically include the invoice date each time the report definition was published, you would provide an XPath similar to the following for the Structure Member Value:
Figure 4-8 Structure Member Value Revisions form
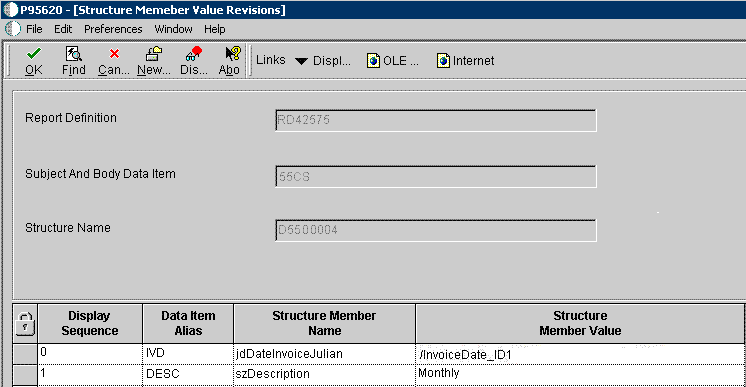
Description of "Figure 4-8 Structure Member Value Revisions form"
In the same way, a data item could be included in the data structure for the invoice number. With dynamic text-substitution, the invoice number would change for each customer in a bursted report.
Important:
The XPath must be preceded by a forward slash to be recognized as an XPath and not as a literal value. For example, if you want to dynamically substitute the customer invoice number, you would enter /CustomerInvoiceNumber_ID1 for the Structure Member Value, assuming that is the XPath in your XML output.4.2.6.2 Defining a Data Structure
Access Object Management Workbench.
-
In Object Management Workbench, select a project.
-
Click the Add button.
-
On the Add EnterpriseOne Object to the Project form, select Data Structure, and then click OK.
-
On the Add Object form, enter the appropriate information, and then click OK.
-
In the Object Management Workbench project, select the data structure object and then click the Design button.
-
Click the Design Tools tab, and then click the Data Structure Design button.
-
On the Dictionary Items tab, use the QBE line to locate the data dictionary items that you want to include in the data structure.
-
To include data items in the data structure, drag them from the Dictionary Items tab to Structure Members.
-
When the data structure is complete, click OK.
4.2.6.3 Defining a Glossary Data Item
Access Object Management Workbench.
-
In Object Management Workbench, select a project.
-
Click the Add button.
-
On the Add EnterpriseOne Object to the Project form, select Data Item, and then click OK.
The Data Dictionary Item Type message box appears.
-
Click Yes to add a glossary data item.
-
On the Item Specifications tab, complete the fields as follows:
Field Description Alias Enter a name that identifies the glossary item. Glossary Group Enter E for the glossary group. Glossary group E is used for error messages, warning messages, and information messages. Product Code Use product codes 55-59 for custom data items. Product Reporting Code Use product reporting codes 55-59 for custom data items. Description The description is used as the email subject when the report definition is submitted. You can use text-substituted variables in the description. Error Level Enter 3 to define the glossary item as an information message. -
Click the Item Glossary tab.
-
Enter the body of the message in the text area, inserting text-substitution variables as required.
-
Click the Data Structure Template tab.
-
Click the Text Substitution option.
-
Click the Browse button to locate and select the data structure with the data items that will be used for the text-substituted variables.
-
Click OK to save the glossary item.
Note:
You could also use the Work With Data Dictionary Items or the Error Messages selection on menu GH951 to add a type E glossary data item.4.3 Modifying BI Publisher Report Definitions
Access the BI Publisher Report Definitions form on the Microsoft Windows client.
-
On the BI Publisher Report Definitions form, select a report definition in the grid and then click Select.
-
On the Update Report Definition form, you can modify these options:
-
Description
-
Product code
-
Product system code
-
Source UBE
-
Version
-
Template
-
-
To modify output or language options, select Output/Languages from the Form menu.
-
On the Update Report Definition-Languages and Output types form, add options, modify options, or delete options, and then click OK.
-
To modify bursting or delivery options, select Burst/Delivery from the Form menu.
-
On the Update Report Definition-Bursting and Delivery form, add options, modify options, or delete options, and then click OK.
-
On the Update Report Definition form, click OK to save the report definition modifications.
Note:
Modifying the Source UBE, Version, or Template fields could invalidate the languages, output types, bursting, and delivery options that were defined previously for the report definition. If you modify any of these values, the Languages and Output Types form and the Bursting and Delivery form will appear automatically, enabling you to make any necessary changes.4.4 Copying BI Publisher Report Definitions
Copying and modifying a report definition might be more efficient than creating a new, but similar, report definition. The copy feature is available only in the Microsoft Windows version of the BI Publisher Report Definitions application.
To copy a report definition:
-
Enter P95620 in the Fast Path field.
-
On the BI Publisher Report Definitions form, select a report definition and then click Copy.
-
On the Copy Report Definition form, enter a name and description for the new report definition.
-
If the report definition will be submitted without user input, click Blind Submission.
-
After completing the required information, click OK.
4.5 Managing BI Publisher Objects in Object Management Workbench
When you access the BI Publisher Repository (P95600) or BI Publisher Report Definitions (P95620) applications from JD Edwards Solution Explorer, the objects that you create are added to your default project in Object Management Workbench (OMW). As non-Object Librarian objects, templates and report definitions are not available to users in other environments until they are advanced through project statuses and, finally, transferred to a data source. To advance the status of an object, you must move it from your default project to a project.
In addition to being available in JD Edwards Solution Explorer, you can also access the BI Publisher Repository and BI Publisher Report Definitions applications through OMW. To add new objects within OMW, select an OMW project and then click Add. Select either Report Definition or BI Publisher Object, as this form illustrates:
Figure 4-9 Object Management Workbench - Add Enterprise Object to the Project form
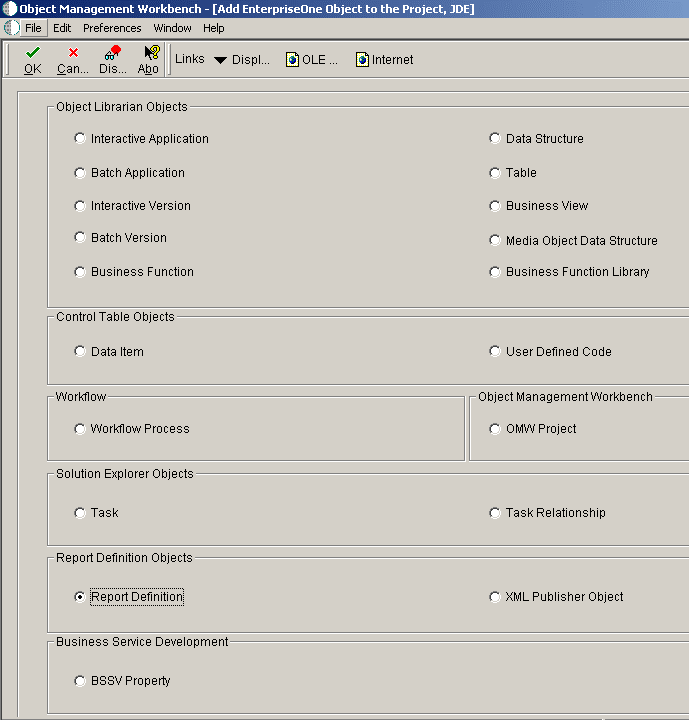
Description of "Figure 4-9 Object Management Workbench - Add Enterprise Object to the Project form"
When you click OK, either the BI Publisher Repository application or the BI Publisher Report Definition application launches, depending on the type of object that you are creating.
Once the objects exist in OMW, you can modify them by clicking the Design button, which will launch the appropriate application. You can also use OMW to copy or delete templates and report definitions, as you would with other OMW objects.
See the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tools Object Management Workbench Guide.
4.5.1 Searching for BI Publisher Objects
To search for BI Publisher objects or report definitions within OMW, in the Category field select either XML Publisher Objects or Report Definitions. After selecting the category, the Search Type field enables you to search by object name, description, or system code.
When you perform an Advanced Search within OMW, BI Publisher Objects are type XMLP and report definitions are type RPDF.
4.6 Configuring BI Publisher Objects for Object Management Workbench
To perform actions on BI Publisher objects and report definitions within OMW projects, you must configure object transfer activity rules. For each object type on which you want to perform an action, you must define this information:
-
Project statuses at which users can add, design, and delete objects.
-
Status changes at which objects will be transferred.
-
Project statuses at which object tokens are released.
See the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tools Object Management Workbench Guide.
