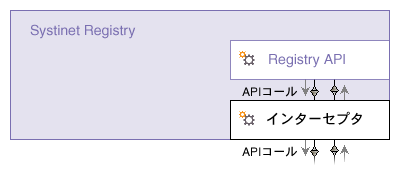
インターセプタ 目次
図9に示すように、インターセプタによって、Oracle Service Registryのリクエストおよびレスポンスを監視または変更できます。 インターセプタは、Oracle Service Registry APIコール処理の最下位レベルにあり、次の目的で使用されます。
-
リクエストのロギング。詳細は、「ロギング・インターセプタのサンプル」を参照してください。
-
メッセージ統計の計算。詳細は、「リクエスト・カウンタ・インターセプタのサンプル」を参照してください。
-
リクエスト引数の変更(デフォルト値の追加)。
-
一部のAPIコールの禁止。
Oracle Service Registryインターセプタには、次の3つのタイプがあります。
-
リクエスト・インターセプタ: リクエスト引数の監視または変更、リクエストの処理の停止あるいは例外のスローを行います。このタイプのインターセプタでは、コールされたメソッド・オブジェクトおよびその引数が受け入れられます。
-
レスポンス・インターセプタ: レスポンス値の監視または変更、あるいは例外のスローを行います。このインターセプタでは、コールされたメソッド・オブジェクトおよびそのレスポンス値が受け入れられます。
-
例外インターセプタ: 例外を監視または変更します。このインターセプタでは、コールされたメソッド・オブジェクトおよびスローされる例外が受け入れられます。
Oracle Service Registry APIに直接アクセスする場合の詳細は、「Registry APIへのアクセス」を参照してください。
インターセプタの作成およびデプロイ 目次
インターセプタを作成するには、次の手順を実行します。
-
org.systinet.uddi.interceptorを実装するクラスを作成します。
-
インターセプタ実装クラスをREGISTRY_HOME/app/uddi/services/Wasp-inf/classesディレクトリにコピーします。
-
インターセプタの構成ファイルをREGISTRY_HOME/app/uddi/confディレクトリに作成します。詳細は、「インターセプタの構成」を参照してください。
-
Oracle Service Registryを停止し、REGISTRY_HOME/workディレクトリを削除して、レジストリを再起動します。
ロギング・インターセプタのサンプル 目次
この項では、リクエストのロギングを行うインターセプタを作成する方法について説明します。
ロギング・インターセプタを作成するには、次の手順を実行します。
-
例8に示すように、JavaファイルLoggingInterceptor.javaを作成します。
-
Java -classpath "%REGISTRY_HOME%¥app¥uddi¥services¥Wasp-inf¥lib¥application_core.jar; %REGISTRY_HOME%¥lib¥wasp.jar" LoggingInterceptor.javaを使用してインターセプタをコンパイルします。
-
LoggingInterceptor.classをREGISTRY_HOME/app/uddi/services/Wasp-inf/classes/interceptorディレクトリにコピーします。
-
構成ファイルMyinterceptor.xmlをREGISTRY_HOME/app/uddi/confフォルダに作成します。 詳細は、例9を参照してください。
-
Oracle Service Registryを停止し、REGISTRY_HOME/workディレクトリを削除して、レジストリを再起動します。
例8 ロギング・インターセプタ・クラス
package interceptor;
import org.idoox.config.Configurable;
import org.idoox.wasp.WaspInternalException;
import org.idoox.wasp.interceptor.InterceptorChain;
import org.systinet.uddi.interceptor.ExceptionInterceptor;
import org.systinet.uddi.interceptor.RequestInterceptor;
import org.systinet.uddi.interceptor.ResponseInterceptor;
import org.systinet.uddi.interceptor.StopProcessingException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class LoggingInterceptor implements RequestInterceptor,
ResponseInterceptor, ExceptionInterceptor {
public void load(Configurable config)
throws WaspInternalException {
// no initialization required
}
public void destroy() {
// no destroy required
}
public void intercept(Method method,
Object[] args,
InterceptorChain chain,
int position)
throws StopProcessingException, Exception {
System.out.println("request: " + method.getName());
}
public Object intercept(Method method,
Object returnValue,
InterceptorChain chain,
int position)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("response: " + method.getName());
return returnValue;
}
public Exception intercept(Method method,
Exception e,
InterceptorChain chain,
int position) {
System.out.println("exception: " + method.getName());
return e;
}
}例9 ロギング・インターセプタの構成ファイル
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<config name="MyInterceptorConfig">
<UDDIInterceptorInstance name="LoggingInterceptorInstance"
instancePerCall="false"
className="interceptor.LoggingInterceptor"/>
<UDDIInterceptor name="LoggingInterceptor"
instanceName="LoggingInterceptorInstance"
interceptorChain="inquiry_v3"
request="true"
response="true"
fault="true" />
</config>インターセプタの構成 目次
構成ファイルは、REGISTRY_HOME/app/uddi/confディレクトリに存在している必要があります。 詳細は、例9を参照してください。インターセプタは、構成ファイルに表示される順序と同じ順序でコールされます。
-
構成名: 構成の一意な(不明確でない)名前。
-
UDDIInterceptorInstance: 実装クラスおよびそのインスタンス化に関する情報が含まれています。
-
name: インターセプタ・インスタンスの名前。この名前は、構成のUDDIInterceptor/instanceNameセクションへのリンクとして使用されます。
-
instancePerCall: instancePerCall属性がtrueの場合、クラスはAPIコールごとにインスタンス化されます。trueでない場合、このインターセプタは、すべてのコールに対して1回のみインスタンス化されます。
-
className: インターセプタを実装するクラスの名前。
-
-
UDDIInterceptor: UDDIInterceptorには、UDDIインターセプタおよびそのタイプへの参照が含まれています。
-
name: インターセプタの名前。
-
instanceName: この属性には、構成ファイルのUDDIInterceptorInstanceセクションの名前が含まれています。
-
interceptorChain: UDDIInterceptorChainは、構成ファイルでAPIごとに定義されます。この属性には、必須APIへの参照が含まれています。
-
request: trueの場合、インターセプタによってリクエストが捕捉されます。
-
response: trueの場合、インターセプタによってレスポンスが捕捉されます。
-
fault: trueの場合、インターセプタによって障害が捕捉されます。
-
リクエスト・カウンタ・インターセプタのサンプル 目次
この項では、リクエストをカウントし、リクエスト数を構成ファイルに保存するインターセプタを作成します。リクエスト・カウンタ・インターセプタを作成するために行う必要がある手順は、「ロギング・インターセプタのサンプル」で説明されている手順と同じです。
例10にインターセプタの実装、例11に構成ファイルを示します。
例10 リクエスト・カウンタ・インターセプタ・クラス
package interceptor;
import org.idoox.config.Configurable;
import org.idoox.wasp.WaspInternalException;
import org.idoox.wasp.interceptor.InterceptorChain;
import org.systinet.uddi.interceptor.RequestInterceptor;
import org.systinet.uddi.interceptor.StopProcessingException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class RequestCounterInterceptor implements RequestInterceptor {
private long request = 0;
private RequestCounterInterceptorConfig.Counter counter;
/**
* RequestCounterInterceptor config interface
*/
interface RequestCounterInterceptorConfig {
public Counter getCounter();
public void setCounter(Counter counter);
public Counter newCounter();
interface Counter {
public long getRequest();
public void setRequest(long request);
}
}
public void intercept(Method method,
Object[] args,
InterceptorChain chain,
int position)
throws StopProcessingException, Exception {
counter.setRequest(++request);
System.out.println("request: " + request);
}
public void load(Configurable config)
throws WaspInternalException {
RequestCounterInterceptorConfig intinterceptorConfig =
(RequestCounterInterceptorConfig)
config.narrow(RequestCounterInterceptorConfig.class);
if (intinterceptorConfig != null) {
counter = intinterceptorConfig.getCounter();
if (counter == null) {
counter = intinterceptorConfig.newCounter();
intinterceptorConfig.setCounter(counter);
}
try {
request = counter.getRequest();
} catch (Exception e) {
counter.setRequest(0);
}
}
}
/**
* Destroys the interceptor.
*/
public void destroy() {
// no destroy required
}
}例11 リクエスト・カウンタ・インターセプタの構成ファイル
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<config name="myInterceptors">
<UDDIInterceptorInstance className="interceptor.RequestCounterInterceptor"
instancePerCall="false" name="RequestCounterInterceptorSampleInstance">
</UDDIInterceptorInstance>
<UDDIInterceptor fault="false"
instanceName="RequestCounterInterceptorSampleInstance"
interceptorChain="inquiry_v3" name="RequestCounter" request="true"
response="false"/>
</config>