Inflation Accounting for Assets Setup
Overview
Inflation Accounting for Assets provides the functionality to support revaluation of fixed assets and associated accounting entries. This is part of the UK government’s initiative on resource accounting and budgeting.
Setting Up Price Indexes
Price indexes represent the rate of change in the value of assets. Multiple price indexes can be set up, and linked to appropriate asset categories.
Price indexes can be updated as necessary. Estimates of anticipated price index changes can be entered and used in the Inflation Accounting Projection report. This report displays future depreciation charges for assets based on estimated price indexes.
Inflation Accounting Options
The Inflation Accounting Options window enables corporate books to be used with inflation accounting. You can perform these tasks:
-
Select the journal categories used for inflation accounting entries.
-
Define the default revaluation month for asset costs and associated depreciation.
-
Select additional accounts specific to inflation accounting for assets, for example, backlog accumulated depreciation, General Fund, and Operating Account.
-
Select the price index used in the revaluation of assets within a selected category.
-
Allow indexed or professional revaluation of assets within a selected category.
For information on setting up or modifying assets, see Changing Asset Details, Oracle Assets User Guide.
Setting Up the Import/Export Process
Inflation Accounting for Assets includes migrating from Modified Historic Cost Accounting and corporate books in Oracle Assets. These profile options are available:
-
The directory location for storing import and export data files.
-
Whether the import and export processes are performed using comma-separated data files, or spreadsheet templates generated by WebADI.
For information on the migration process, see Inflation Accounting for Assets Implementation Procedures.
For information on the Web ADI solution, see Oracle Web Applications Desktop Integrator User Guide.
Prerequisites
Before implementing Inflation Accounting for Assets, you should read the Inflation Accounting for Assets process information.
For information on inflation accounting, see Inflation Accounting for Assets Process, Oracle Public Sector Financials (International) User Guide.
Inflation Accounting for Assets Setup Steps
This table describes the setup steps for Inflation Accounting for Assets which include Oracle Assets and General Ledger setup.
| Step Number | Step Description | Required or Optional |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Descriptive Flexfield Concepts, Oracle Applications Flexfields Guide | Optional |
| 2 | Account Generator. See Overview of the Account Generator, Oracle Applications Flexfields Guide | Required |
| 3 | Define Default Accounting Rules | Required |
| 4 | Asset Key Flexfields. See Key Flexfield Segments Window, Oracle Applications Flexfields Guide |
Required |
| 5 | Asset Category Flexfields. See Segment Values Window, Oracle Applications Flexfields Guide | Required |
| 6 | Location Flexfields. See Segment Values Window, Oracle Applications Flexfields Guide | Optional |
| 7 | Set UpProfile Options | Required |
| 8 | Define Ledgers. See Ledgers Window, Oracle General Ledger User Guide |
Required |
| 9 | Define Journal Sources, Oracle General Ledger User Guide | Required |
| 10 | Define Journal Categories, Oracle General Ledger User Guide | Required |
| 11 | Define Unit of Measure Classes, Oracle Inventory User's Guide | Optional |
| 12 | Define Unit of Measure Classes, Oracle Inventory User's Guide | Optional |
| 13 | Define Suppliers, Oracle Payables User Guide | Optional |
| 14 | Enter Person, Oracle HRMS HR Foundation | Optional |
| 15 | Set Up Security, Oracle Human Resources Management Systems User's Guide | Optional |
| 16 | Set Up Numbering. See Specifying System Controls, Oracle Assets User Guide |
Optional |
| 17 | Specifying System Controls, Oracle Assets User Guide | Required |
| 18 | Define Locations, Oracle Assets User Guide | Required |
| 19 | Define Asset Keys, Oracle Assets User Guide | Optional |
| 20 | Enter Quick Codes, Oracle Assets User Guide | Optional |
| 21 | Create Fiscal Years, Oracle Assets User Guide | Required |
| 22 | Specify Dates for Calendar Periods, Oracle Assets User Guide | Required |
| 23 | Set Up Security by Book, Oracle Assets User Guide | Required |
| 24 | Define Book Controls. See Asset Books Setup, Oracle Public Sector Financials (International) User's Guide, Historic or Corporate Books Setup, Oracle Public Sector Financials (International) User's Guide, and Defining Depreciation Books, Oracle Assets User Guide. |
Required |
| 25 | Enable Intercompany Accounting. See Entering Accounting Rules for a Book, Oracle Assets User Guide |
Optional |
| 26 | Define Additional Depreciation Methods, Oracle Assets User Guide | Required |
| 27 | Set Up Depreciation Ceilings, Oracle Assets User Guide | Optional |
| 28 | Investment Tax Credit. See Tax Workbench, Oracle Assets User Guide |
Optional |
| 29 | Specify Dates for Prorate Conventions, Oracle Assets User Guide | Required |
| 30 | Define Price Indexes, Oracle Assets User Guide | Optional |
| 31 | Set Up Asset Categories, Oracle Assets User Guide | Required |
| 32 | Define Distribution Sets, Oracle Assets User Guide | Optional |
| 33 | Enter Leases, Oracle Assets User Guide | Optional |
| 34 | Define Asset Warranties, Oracle Assets User Guide | Optional |
| 35 | Insurance. See Fixed Assets Insurance Window Reference, Oracle Assets User Guide |
Optional |
| 36 | Set Up Calendar Price Indexes for Inflation Accounting Procedure | Required |
| 37 | Enable Corporate Books | Required |
| 38 | Specify Directory Location for Export/Import Data Files | Optional |
Define Default Accounting Rules
Oracle Assets includes the following Application Accounting Definitions (AAD):
-
Assets Standard Accounting with Inflation Accounting: New AAD for users using Inflation Accounting for Assets.
-
Assets Standard Accounting: For users not using Inflation Accounting for Assets.
Inflation Accounting for Assets does not use the default subledger accounting method and, therefore, you must modify the seeded subledger accounting method and assign the new AAD to Oracle Assets. The Assets Standard Accounting with Inflation Accounting AAD is the same as Assets Standard Accounting Application Accounting Definition except for a new Journal Line Definition (JLD) called Inflation Standard Accounting JLD, which performs additional calculations for inflation by creating a common set or subset of journal entries for each event. The Journal Line Definition applies to all event classes and event types.
The following table describes the journal line types that are defined and assigned to the Inflation Standard Accounting JLD:
| Journal Line Type | Debit (Dr) or Credit (Cr) |
|---|---|
| Cost | Dr |
| Depreciation Expense | Dr |
| Depreciation Reserve | Cr |
| Backlog Reserve | Cr |
| Operating Expense | Dr |
| General Fund | Cr |
| Revaluation Reserve | Cr |
| Revaluation Reserve Retire | Cr |
The following are the default account derivation rule for each journal line type:
| Journal Line Type | Account Derivation Rules |
|---|---|
| Cost | CCID defined for Asset Category |
| Depreciation Expense | CCID defined for Asset Category |
| Depreciation Reserve | CCID defined for Asset Category |
| Backlog Reserve | CCID defined in Inflation Accounting Options for an Asset Category |
| Operating Expense | CCID defined in Inflation Accounting Options for an Asset Category |
| General Fund | CCID defined in Inflation Accounting Options for an Asset Category |
| Revaluation Reserve | CCID defined in Inflation Accounting Options for an Asset Category |
| Revaluation Reserve Retire | CCID defined in Inflation Accounting Options for an Asset Category |
The following are the seeded journal entry descriptions from source:
-
Inflation Journal Entry Description: This constitutes transaction meaning and the account date. For example, Addition 14-Dec-2007 13:00:00
-
Inflation Journal Entry Line Description: This constitutes transaction meaning, adjustment meaning and accounting date. For example, Depreciation Expense Backlog 14-Dec-2007 13:00:00
Accounting Methods Builder (AMB) Overview, Oracle Subledger Accounting Implementation Guide
Application Accounting Definitions, Oracle Subledger Accounting Implementation Guide
Subledger Accounting Method, Oracle Subledger Accounting Implementation Guide
Journal Line Types, Oracle Subledger Accounting Implementation Guide
Account Derivation Rules, Oracle Subledger Accounting Implementation Guide
Journal Entry Descriptions, Oracle Subledger Accounting Implementation Guide
Event Models
Accounting events are transactions that have a financial accounting impact. Examples of accounting events are issuing an invoice and disposing an asset. Financial accounting information are recorded for these events. Accounting events must be captured when transactions are committed in the subledgers. Accounting events are categorized into event types. Event types are grouped into event classes that in turn are grouped into event entities.
Inflation Accounting for Assets uses the following event entities of Oracle Assets:
-
Depreciation
-
Transaction
Inflation Accounting for Assets uses the following event classes of Oracle Assets in addition to its own event class Inflation Revaluation:
-
Depreciation
-
Additions
-
Adjustments
-
Category Reclass
-
Retirements
-
Transfers
Note: Inflation Accounting for Assets creates a process category called Inflation Revaluation for its event class.
Inflation Accounting for Assets uses the following event types of Oracle Assets in addition to its own event type Inflation Revaluation:
-
Depreciation
-
Additions
-
Adjustments
-
Category Reclass
-
Retirements
-
Reinstatements
-
Transfers
Event Model, Oracle Subledger Accounting Implementation Guide
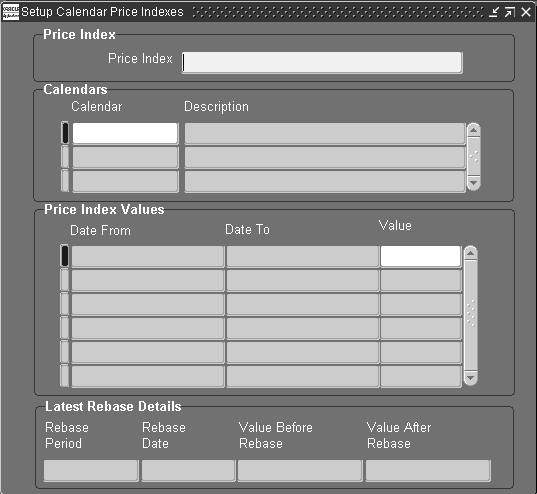
Setting Up Calendar Price Indexes for Inflation Accounting
To set up calendar price indexes for inflation accounting:
-
Navigate to the Setup Calendar Price Indexes window.
-
Enter a unique price index name.
Note: The price index cannot be modified if it is associated with an asset category.
-
In the Calendar field, select a calendar type to link to the price index. Duplicate calendar types cannot be attached to the same price index.
In the Price Index Values region, the Date From and Date To fields are automatically populated.
-
In the Value field, overtype the initial value and enter a price index value for the displayed dates.
Note: Early unwanted periods can have an initial value of 9999.99 if there are valid index values for the earliest date placed in service of any asset to be used with an asset category that uses this price index. If no price index values exist for the earliest date in service and the assets become part of a periodic revaluation (at depreciation runtime) or occasional revaluation, the revaluation process will fail.
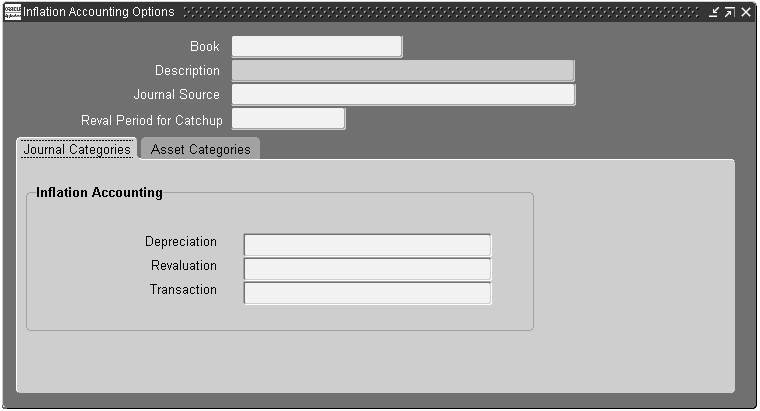
Enabling Corporate Books
To enable corporate books for use with inflation accounting:
-
Navigate to the Inflation Accounting Options window.
-
Select a corporate book.
-
In the Journal Source field, select a source.
Note: The default value is inflation accounting. The journal source cannot be changed once saved.
-
In the Reval Period for Catchup field, select a fiscal period number for the book.
-
Select the Journal Categories tab.
-
In the Depreciation field, select a depreciation journal category.
-
In the Revaluation field, select a revaluation journal category.
-
In the Transaction field, select a transaction journal category.
-
Select the Asset Categories tab.
-
In the Category field, select a major and minor asset category flexfield.
-
In the Backlog Account field, select a backlog account flexfield combination.
-
In the General Fund field, select a general fund flexfield combination.
-
In the Operating Account field, select an operating expense account flexfield combination.
-
In the Reval Reserve field, select a revaluation reserve flexfield combination.
-
In the Reval Reserve Retired field, select a retired revaluation reserve flexfield combination.
-
In the Price Index Name field, select a price index if Allow Indexed Reval is selected.
-
To enable indexed revaluation, select Allow Indexed Reval.
Note: If the Allow Indexed Revaluation profile option is set to No, deselect it.
-
To enable professional revaluation, select Allow Prof Reval.
Note: If the Allow Professional Revaluation profile option is set to No, deselect it.
Note: All asset categories assigned to an asset corporate book should be assigned in the Inflation Accounting Options window if assets categories are selected as part of the Inflation Accounting revaluation process. If unassigned, the revaluation process will fail.
Specifying Directory Location for Export/Import Data Files
To specify the directory location for exporting and importing data files during Inflation Accounting for Assets implementation:
-
Navigate to the Profile window.
-
Select User.
-
Select the user name.
-
In the Profile field, select Inflation Accounting: Implementation Import/Export File Location.
-
Click Find.
-
In the Site field, enter the full pathname of the directory location in which to store the export and import data files, for example, /home/user/IHP/.
Specifying Method for Exporting/Importing Data Files
To specify the method for exporting and importing data files during Inflation Accounting for Assets implementation:
-
Navigate to the Profile window.
-
In the Profile field, select Inflation Accounting: Use WebADI to Import/Export.
-
Click Find.
-
In the Site field, select Yes to import and export data using a WebADI spreadsheet template.