Building Compensation Plans
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Overview of Building Compensation Plans
- Creating a Compensation Plan
- Creating a View for Compensation Plans
- Maintaining Compensation Plans
- Defining Plan Elements
- Assigning Eligible Products
- Assigning Rate Tables
- Defining Rate Tables
- Defining Rate Dimensions
- Defining Quotas
- Distributing Target, Fixed Amount, and Performance Goal
- Creating a Bonus Plan Element
- Using Accelerators and Transaction Factors
- Using Interdependent Plan Elements
- Defining Formulas
- Calculation Expressions
- Defining Calculation Expressions
- Export and Import Compensation Plans
Overview of Building Compensation Plans
A typical compensation plan consists of one or more modular components, or plan elements. Plan elements may reflect variations of commission or perhaps a bonus that is not based on transaction information. Plan elements can also be configured for tracking nonmonetary credits such as managerial points or production credits.
A compensation plan is built from plan elements and is assigned an effective start date and an effective end date. The plan can then be assigned to one or more Sales Compensation or Incentive Compensation roles.
All modular components used in the system can be configured and reused in different combinations. Taking full advantage of this capability simplifies system configuration as well as administration. For example, from a relatively small library of plan elements, you can configure many compensation plans. These modular components have several distinct functions:
-
Products are user-defined categories of sales for which your organization awards compensation. Each product represents a different kind of sale for which your organization pays compensation. Classification rules are used to determine the event eligible for compensation and the basis of calculation.
-
Formulas determine how the compensation will be calculated.
-
Rate Tables are the part of a formula that determines the rate at which achievements are compensated. Rate dimensions are the structural part of a rate table to which values are added.
-
Expressions are interchangeable, reusable parts that are used as input and output expressions of formulas, in expression-based rate dimensions, and in performance measures.
Compensation Plan Creation Flow
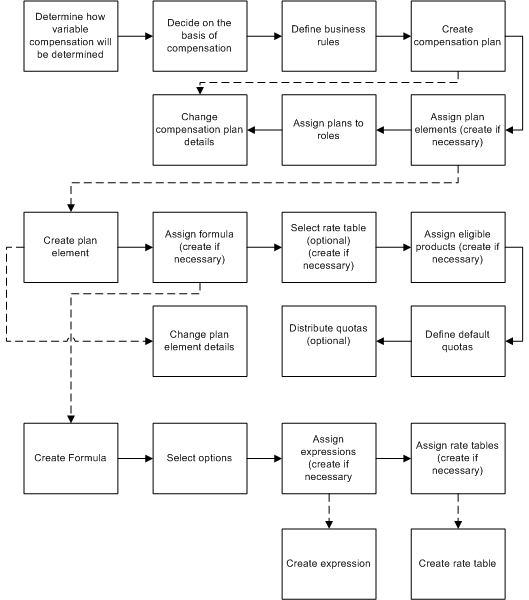
When you are building a compensation plan, you can always use pieces that are previously defined. All you need to do is add another row and select the component from the list of values. At each step, though, you can create the component you need by clicking the Create button and following the process.
When resources have customized compensation plans the values are stored in the CN_SRP_QUOTA_ASSIGNS table but the column names are the same as for the Plan Element values above:
-
Target => CN_SRP_QUOTA_ASSIGNS.TARGET
-
Fixed Amount => CN_SRP_QUOTA_ASSIGNS.PAYMENT_AMOUNT
-
Goal => CN_SRP_QUOTA_ASSIGNS.PERFORMANCE_GOAL
When setting these values for specific periods or distributing the amounts over a given period, click the Distribute button at the bottom of the Plan Element Details page.
To use these values in an expression, select the following columns from the Calculation Values list of values on the Calculation Expressions page:
-
Quota => CN_PERIOD_QUOTAS.PERIOD_TARGET
-
Fixed Amount => CN_PERIODS_QUOTAS.ITD_PAYMENT
-
Performance Goal => CN_PERIOD_QUOTAS.PERFORMANCE_GOAL
When defining these values for periods that are specific to individual resources, use the same columns as for the plan element but select them from the CN_SRP_PERIOD_QUOTAS table.
-
Quota => CN_SRP_PERIOD_QUOTAS.PERIOD_TARGET
-
Fixed Amount => CN_SRP_PERIODS_QUOTAS.ITD_PAYMENT
-
Performance Goal => CN_SRP_PERIOD_QUOTAS.PERFORMANCE_GOAL
There are numerous columns that derive their values from these column amounts. They can be identified by the inclusion of an ITD or PTD flag in the column name, for example, ITD_PAYMENT is the Interval to Date Payment (Fixed Amount).
You have the option of introducing seasonality into the achievement by using the Distribute button on the Plan Element Details page. When you click this button, the Plan Element Details - Distribute Variables page displays all of the open periods for the plan element. You can manually enter the desired quota amount for each period to create seasonality for the target, performance goal, or fixed amount distribution.
Creating a Compensation Plan
The Plan Administrator creates and maintains compensation plans. Below is a screenshot of the initial page seen by the Plan Administrator.
After you assign the plan an effective start date and end date, you can assign it to multiple sales roles.
The Plan Design page provides a consolidated view of the details of an established compensation plan. You can click the subtabs to view more detailed information.
Warning: Do not open a new window during a browser session and navigate to the same page in the two windows simultaneously while you are defining a compensation plan.
Navigation
Plan Administrator > Create Compensation Plan
Notes
-
For easy identification, define compensation plan names by job titles or area of sales you are compensating.
-
Check the Allow Eligible Products Overlap box if you want multiple plan elements to use the same eligible products. Use this option when you need to compensate a resource more than once for a transaction. For example, you may have two plan elements, with one used to calculate a monthly commission and the other used to calculate a quarterly bonus.
-
When you enter a sequence number for multiple plan elements, this tells the application the order in which to process the plan elements. Sequencing of plan elements is important when one plan element relies on the calculation results of another. For example, with independent plan elements, the dependent plan element requires that the necessary plan element be calculated first so that the most up-to-date data is present. See Interdependent Plan Elements.
-
When you click Apply to validate the compensation plan, it ensures that you have entered the plan information correctly, and verifies the following:
-
The plan has a name and start and end dates.
-
The plan has one or more plan elements assigned with start and end dates within the plan start and end dates.
-
Each plan element that uses a rate table has contiguous tiers with start and end dates within the plan start and end dates.
-
Each plan element has at least one eligible product assigned, with start and end dates within the plan start and end dates.
-
If each of the above conditions is met, then the Status field shows Complete. If the Status field displays Incomplete, the plan cannot be used to calculate compensation. You must check the items shown above and fix any problems and then Update the compensation plan again. Do this until you receive a validation status of Complete.
-
This page supports an optional descriptive flexfield, which you can configure to your requirements. For more information on flexfields, see the Flexfields appendix or the Oracle Applications Flexfields Guide.
-
-
To view or change details for an already created compensation plan, select Maintain Compensation Plans in the Navigator.
-
You can use the search field at the top of the page. Select a saved search from the drop-down list, or click Personalize to create a new search. See Creating a Personalized Search for Compensation plans following.
-
To create a new compensation plan, click Create Compensation Plan in the Navigator. This takes you to the Plan Design page.
-
You can navigate also to the Compensation Plans - Design page from the Search Compensation page, by clicking a compensation plan from the list, or click the "Duplicate" icon, associated with the plan.
-
If you have clicked the "Duplicate" icon and navigated to this page, then Oracle Incentive Compensation will create a copy of the compensation plan. See: Maintaining Compensation Plan (Copying Compensation Plan).
-
If you have clicked on a particular compensation plan and navigated to this page, then you can download the details of the compensation, into your local system. See: Maintaining Compensation Plan (Viewing Compensation Plan - XML Document)
-
Creating a View for Compensation Plans
You can create a customized search, or view, by specifying the search parameters you want to use. This can save you time if you have a large number of compensation plans. The My Plans view is seeded in the application and cannot be removed. For more information, see the Saved Search feature in the OA Personalization Guide.
Navigation
Plan Administrator > Maintain Compensation Plans > Views > Personalize
Notes
-
Only the Description field can be removed from the Displayed Columns area. The other columns are required.
-
Make sure to save the view with a unique name. If you are making changes to an existing view, leave the name the same.
-
You can set the number of rows that you want to display. However, you cannot change the number of rows that are displayed in any view that is seeded data.
-
Check the Default box if you want your new customized search to be the one that displays compensation plans automatically when you open the Compensation Plan page.
-
The application allows for three levels of sorting. Choose the sort parameter order on the left side and on the right side, select ascending or descending order.
-
You can rename the columns if it makes more sense in your search.
-
You can set the view to show table data when all conditions are met or when any conditions are met. The second setting should be used sparingly.
-
The five variables in the dropdown list--Contains, ends with, is, is not, and starts with--enable further personalization. Views created using Is and Starts with perform better than views created using the other variables.
Maintaining Compensation Plans
Oracle Incentive Compensation provides a consolidated view of the details of an established compensation plan. The Plan Design page for an existing plan displays the plan elements, earnings rules, eligible products, rate tables, and default quotas for the compensation plan. You can click the links to view more detailed information. You can sort each section on any column that has a header with an underscore.
The Eligibility tab lists all roles that have been assigned the compensation plan. The Plan Administrator can export resources from this page.
Plan Administrators have access to a Notes feature, which they can add to or review. Notes help to keep track of changes for historical reference. Notes may be system generated or created by the Plan Administrator.
Navigation
Plan Administrator > Maintain Compensation Plans
Notes
-
The following plan data can be changed.
-
Name
-
Description
-
Start date
-
End date
-
Flexfields information
-
Allow Eligible Product Overlap box
Use this option when you need to use an eligible product for more than one plan element. For example, you may have a quota type plan element as well as a bonus based on achieving revenue targets that use the same eligible product.
Some changes may not be permitted, for example, the start date of a compensation plan cannot be changed if by doing so the role assignment dates are outside the date range of the plan.
-
-
You can change or restructure any aspect of a compensation plan. Because you can assign the same plan to many salespeople, however, be aware of how the changes you are making impact individual resources.
-
When you change a compensation plan, the changes propagate to the resources assigned to the plans. For customized plans, the resource receives all changes except the customized plan.
Viewing Compensation Plan - XML Document
As a Plan Administrator, after you have successfully created a compensation plan, you may need approval from Compensation Manager or other stakeholders. Oracle Incentive Compensation allows you to report on the elements that make up the compensation plan. You can navigate to the following pages to download and view the plan document:
-
Search Compensation Plan page
-
Navigation: Plan Administrator > Maintain Compensation Plans
-
Click "View Document" icon.
-
-
Compensation Plan Design page
-
Navigation: Plan Administrator > Maintain Compensation Plans
-
Click on the Compensation Plan, which you want to download, to reach the Compensation Plan Design page.
-
Click View Plan Document.
-
Note: To specify the maximum number of periods that the application will display in the Plan Element Default Quota Distribution table, in the plan document, set the "OIC:XML Document Max Quota Period" profile option.
To specify the order in which application will display the periods, in the plan document, set the "OIC:XML Document Quota Periods Display Order" profile option.
To specify the maximum number of records the application will display in each rate table, in the plan document, set the "OIC:XML Document Max Rate Tiers Per Table" profile option.
For more information on profile options, see: Table of Profile Options, Oracle Incentive Compensation Implementation Guide.
Copying Compensation Plan
You can copy a compensation plan by clicking the Duplicate icon, in the Search Compensation page. This process creates a copy of the plan in the same operating system as the source, and is called Inline Copy. When you create a copy of the source plan, Oracle Incentive Compensation does not create any additional objects within the compensation plan. The new plan is created with references to the plan elements and formulas that were contained in the source compensation plan. Also, the application does not copy notes history to the newly-created compensation plan. If you want to make a new "sub element", then use the corresponding Inline Copy feature for that element and change the copied plan or plan element to reference the newly created sub elements.
Oracle Incentive Compensation ensures that two compensation plans, or any other objects, such as, formulas, rate dimensions, expressions, and plan elements, do not have the same name, when you are creating a copy of any of these objects. The application appends the object name with "_copyXXX", during copying, where "XXX" is a system-generated random three digit number.
Caution: Mark the "Allow Eligible Products Overlap" check box, if there multiple plan elements with the same products, and you want to retain the products, in the plan elements, within the newly created compensation plan.
Defining Plan Elements
A plan element is part of a compensation plan. It specifies the conditions a resource must meet to be eligible for compensation, and it determines how the compensation is calculated. You can assign multiple plan elements to a compensation plan and you can assign a plan element to multiple compensation plans.
Creating a plan element is made simpler by the plan element creation task list. As you proceed through this list, you must perform one procedure at a time before the next one is accessible. The screenshot below shows the task list when it first appears. After the General Information step is completed, the Go to Task icon is activated for Earnings Rules setup.
The Earnings Rule subtab lists the high-level configurations for the Plan Element. This includes:
-
Formula Name
-
Interval Types
-
Process Transactions (Individually or Grouped)
-
Split Options
-
Payment Options (Group Code, Credit Type)
-
Integration with A/P (Expense and Liability Accounts)
These items are grouped under Earnings Rule because they affect the frequency and nature (whether or not to aggregate) of transaction collection, and consequently how earnings are defined and calculated.
The Plan Element Creation Task List
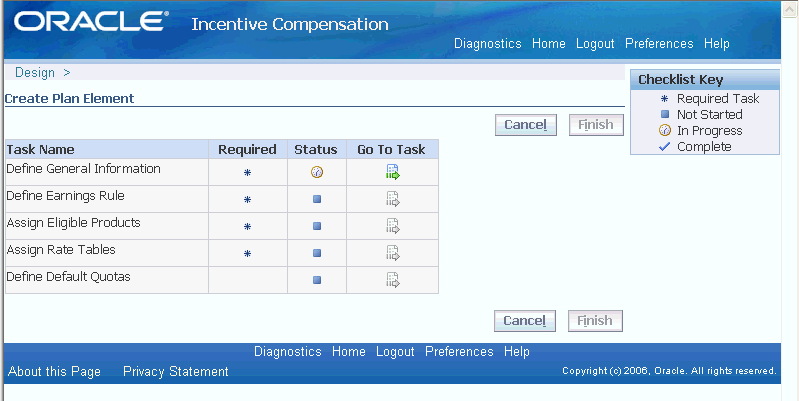
When building a compensation plan, you can use any formula, rate tables, and eligible products that you have already created. Or, at each stage of building the plan, you have the option of creating a new component.
Formulas are based on the Commission incentive type of a compensation plan. Bonus incentives, which are based on the Bonus incentive type, are additional compensation based on aggregated transactions. Note: When you are defining the earnings rules, the Formula list of values displays only formulas that match the incentive type value selected in the Incentive Type drop-down list.
Warning: If you want to change the setup of plan elements for new periods, for example, at the beginning of a new year, end date the existing plan elements--do not delete them. When you delete a plan element by replacing it with a new one, you lose the resource setup data.
Warning: Do not open a new window during a browser session and navigate to the same page in the two windows simultaneously while you are creating a plan element.
Navigation
Plan Administrator > Maintain Component Library > Plan Element
General Information
-
The Element Group Code offers three choices. If you select:
-
None: The plan element name does not display in the Year to Date Summary.
-
Bonus: The plan element displays in the Bonus category of the Year to Date Summary.
-
Quota: The plan element name displays in the Quota category of the Year to Date Summary.
-
-
The Create Plan Element: General Information page supports an optional descriptive flexfield, which you can configure to your requirements. For more information on flexfields, see the Flexfields appendix or the Oracle Applications Flexfields Guide.
-
The commonly used intervals are Period (month), Quarter, and Year. However, you can define a custom interval using the Configuration Workbench. After a compensation plan has been assigned to a sales role, in order to change the interval, you must remove the plan assignment, change the plan element's interval, then reassign the compensation plan.
-
Formula types can be Formula or PL/SQL Package. Each formula type requires a different action:
-
Formula: Select a formula from the list of values.
-
External: Enter a PL/SQL package name in the Package Name field. This enables the application to find the external formula.
-
-
If you choose an external formula type, you must enter the name of the PL/SQL package in the Package Name field.
-
To create a formula, go to Define Formulas
-
The Payment Group Code setting is used to set how you want payments from a resource's payment plan to be allocated between plan elements. The payment group codes are customizable using a lookup; the default setting is Standard. If all plan elements are set to Standard, the payment plan amounts are allocated equally.
-
The credit type is normally the preset functional currency, but it can be any type that you define in the application. Changing the credit type of a plan element after it has been used in a compensation plan to pay compensation is not recommended. This can affect payment amounts. Payment can be made only in the functional currency credit type.
-
Click the Paid Through Third Party Yes button if you want to assign the payment to someone other than the resource receiving the sales credit. For example, this feature may be used if the credit receiver leaves the company and a new resource takes over an account. It can also be used to assign credit to a resource's company instead of to the resource directly. See Setting Up Payees.
-
Optionally, you can identify a liability or expense account (if the application is integrated with Oracle Payable). Liability and expense accounts can be identified at the plan element level. Earnings for the plan element are assigned to the specified liability or expense account.
-
Select Yes for Use Eligible Products Worksheets to combine the amounts from all products assigned to the plan element to meet a target or goal.
-
Target is the specific amount set for resources as their attainment amount. The most common way that a target is used in an expression is for evaluating transactions as a percentage of quota. Goal is the amount that management sets as the actual goal expected of the resources. This amount is typically used for reporting purposes and is not exposed to the resources. Fixed Amount is a constant amount that is used for calculation purposes.
-
Target, Goal, and Fixed Amount are indicated here in the application, but are used when building calculation expressions.
Copying Plan Elements
You can create a copy of a plan element, that already exists in the operating unit. This way you need not create a new plan element, whose parameters are similar to an existing plan element. Oracle incentive compensation will create a copy, and then you change the parameters.
When you create copy of a plan element, the application does not make copies of rate tables and expressions within the original plan element, but references the original rate tables and expressions. If you want to make a new expression, then use the corresponding Inline Copy feature for Expressions and change the copied plan element to reference the newly created expressions.
Steps:
-
Navigate: Plan Administrator > Maintain Component Library > Plan Element
-
Search for the plan element.
-
Click "Duplicate" icon.
Note: For more information on copying objects, see: Maintaining Compensation Plans (Copying Compensation Plan).
Assigning Eligible Products
You must assign at least one eligible product for each plan element. You can add an already created product or create a new one if necessary.
On this page, you can indicate how you want indirect credit to be paid.
-
All: Every transaction that is available to this plan element is calculated. This includes the resource's own sales as well as sales or transactions that have rolled up to him or her through the Sales Compensation Hierarchy. This is the default setting.
-
Credit Receiver has Manager Role: Rolled up transactions (and direct sales) are calculated for those resources who have a Manager type of sales role.
-
None: Only direct credits are calculated for any resource who has this plan element.
Navigation
Plan Administrator > Create Plan Element > Assign Eligible Products
Assigning Rate Tables
Rate tables are used to establish compensation percentage rates or fixed amounts for different performance levels. The compensation formula and plan element determine the type of information to be compared to the rate table as well as how the resulting rate is used in the calculation.
You can assign parent rate tables and also a child rate table to a plan element, if the formula is nested.
Rate tables must be created before they can be assigned to a formula.
Navigation
Plan Administrator > Create Plan Element > Assign Rate Tables
Notes
-
You can view the rates by clicking the Update Rate Table icon.
-
You can enter a child rate table. Use the same steps as you used for the Parent Rate Table section. See example.
-
You can click the Plan Element Name link at the top to return to the Plan Element Detail page.
Example
Child rate tables are referenced within embedded formulas. The following example illustrates how child rate tables are used.
First, you create the formula to be embedded, and then create the formula that is referenced by the plan element, which includes the embedded formula within it. Assume that you want to calculate compensation based on percentage of quota, but only for transactions where the sales credit is greater than $1,000. First you must create an expression to determine if the sales credit is greater than $1000. The expression looks like this:
Commission.Headers.TRANSACTION_AMOUNT/1000
Use this expression as the input expression for the embedded formula. If the result is greater than 1, then you know that the sales credit is greater than $1000.
Next, configure an amount rate table with two tiers (one tier for values less than 1 and one tier for values greater than 1):
| Amount | Rate |
|---|---|
| 0-1 | 0 |
| 1-999,999,999 | 1 |
In this example, the first tier with an amount of less than 1 has a rate of 0, and in the second tier, anything greater than one has a rate of 1.
Create an output expression that references the rate table result. Select Others from the H-grid in the Expression screen and click Rate Table Result.
Next, you need to configure the embedded formula out of the input expression, rate table, and output expression you have just created. It will be referenced by the other formula.
Now you can configure the formula that will be referenced by your plan element. First, configure an expression to reference the formula that you just created. This expression looks like this:
Commission Headers.TRANSACTION_AMOUNT/SRP Period Quota.TARGET_AMOUNT*<embedded formula>.
Next, create the rate table for your formula, as follows:
| Percent | Rate |
|---|---|
| 0-100% | 3% |
| 100-9999% | 4% |
Finally, create an output expression that multiplies your rate table result by the transaction amount:
Rate Table Result*Transaction_Amount
When you build this formula, use the expressions and the rate table you have just created. Then, when you configure your plan element, reference the second formula that you created.
When you save the plan element, the rate tables associated with the formula and with the embedded formula are both associated with the plan element. When you view the rate tables associated with the plan element on the Rate Tables subtab of the Plan Design page, the Parent Rate Table section shows the rate table that was created for the second formula, while the Child Rate Tables section displays the rate table associated with the embedded formula. Because it is possible to create multiple embedded formulas, OIC provides a drop-down menu that enables you to select any one of the embedded formulas that you may have configured.
Defining Rate Tables
Rate tables are used to establish compensation percentage rates or fixed amounts for different performance levels. The compensation formula and plan element determine the type of information to be compared to the rate table as well as how the resulting rate is used in the calculation.
Rate tables contain one or more dimension, of an amount, percent, expression, or string type. The rate table input depends on the kind of dimensions that are used. A multidimensional rate table can use different kinds of dimensions to generate a percent or amount result.
You can customize rate table for individual resources. See Customizing a Compensation Plan.
Navigation
Plan Administrator > Maintain Component Library > Rate Tables
Steps
-
Enter name and click Update.
-
To assign or change rates, click the Update Rates button to go to the Update Rates page.
-
To create a new dimension while you're creating a rate table, click Create in the Dimension section and build it on the separate page.
-
Click Apply.
If a rate table is already assigned to a formula or plan element, it cannot be deleted and the commission type cannot be updated. Dimension assignments cannot be changed. An error message displays if you attempt to delete or change a rate table that is already assigned.
If you have string-based dimensions in a rate table, you must assign the same table or one of similar structure to the formula in the plan element. If you do not do this, the generated formula package assumes that all of the inputs evaluate to numeric values, and an error message and XCALC status results.
If a transaction matches the amount or percent that is the top of one tier and the bottom of the next higher tier, it is calculated using the higher tier. For example, using the percentage rate table below, a transaction that matches 50% exactly is paid at the 3% rate.
| Percentage of Target | Commission |
|---|---|
| 1-25% | 1% |
| 25-50% | 2% |
| 50-75% | 3% |
| 75-100% | 4% |
A rate table can be customized for an individual resource.
Defining Rate Dimensions
Rate dimensions define the tiers that are used in a rate table. The Dimensions summary page displays all of the rate dimensions that have already been created.
A dimension must have at least one tier, but can have as many as you need. See above regarding dimension type.
There are four kinds of rate dimensions:
-
Amount: The rate tiers are amounts.
-
Percent: The rate tiers are percentages of a quota.
-
Expression: These rate dimensions reference calculation expressions, and can be used to create more complex rate tiers. For example, rather than creating a static set of rate tiers such as 0% to 25%, 25% to 50%, and so on, an expression rate dimension can be configured as 10% * Quota, 25% * Quota, and so on, using a calculation expression.
-
String: The rate tiers are alphanumeric, such as product numbers or the names of states.
These values comprise the ranges from which compensation is calculated in a rate table.
If a rate is based on multiple criteria, then a multidimensional rate table can be created to reflect all criteria. Use one dimension per criterion.
Oracle Incentive Compensation supports accumulated revenue with multidimensional rate tables. Accumulation is limited to one dimension.
Navigation
Plan Administrator > Maintain Component Library > Rate Dimensions > Create
Notes
-
For Amount or Percent dimensions, in the Rate Tiers area, you must enter numbers in the From and To columns. Follow the sequence, and do not leave any gaps in the rates.
-
For String dimensions, enter the string value for the rate tier.
-
For Expression dimensions, select expressions from the list of values for the From and To columns.
-
You can also create rate dimensions on the Rate Table Details page by clicking the Create button.
-
After you create a rate dimension with a type of String or Expression, you cannot change the type with a future update. For rate dimensions of the Amount or Percent type, you can update the type definition, switching Amount to Percent or Percent to Amount only.
-
For expression rate dimensions, expressions must be defined in the application in order for the list of values to contain any selectable values.
-
If the application is unable to find a match in a string dimension in a rate table, the application picks the last rate value by default. For example, suppose that in the example above, a transaction has dimension values of 10,000, Iowa, and Service. No matches occur, and the rate table result is 9.25%, the last value in the Rate column. This setup permits you to define a catch-all tier that captures all unmatched values. If you want the non-matching transactions to receive no compensation, add OTHER as the last string value to each string dimension with a corresponding rate of 0%, for example. Another method of dealing with non-matching transactions is to use classification rules. Transactions with attributes that do not match your classification rules will have a failed classification status. You can correct these failed transactions' attributes by changing their values and maintain a record of the adjustment through the manual adjustments window.
Copying Rate Dimensions
You can create a copy of a rate dimension, that already exists in the operating unit. This way you need not create a new rate dimension, whose parameters are similar to an existing rate dimension. Oracle incentive compensation will create a copy, and then you change the parameters.
Steps:
-
Navigate: Plan Administrator > Maintain Component Library > Rate Dimensions
-
Search for the rate dimension whose copy you want to create.
-
Click "Duplicate" icon
Note: For more information on copying objects, see: Maintaining Compensation Plans (Copying Compensation Plan).
Defining Quotas
Target, Fixed Amount, and Goal are used during Calculation as a basis for quota achievements or as a stated goal, which can be used as a constant value. How these values are used in the actual calculation of compensation is up to you.
Target is the specific amount set for resources as their attainment amount. Resources have views of this figure through their contract. The most common way that a target is used in an expression is for evaluating transactions as a percentage of quota. The expression typically looks like this:
TRANSACTION_AMOUNT/TARGET
This expression gives you the percentage of quota a particular transaction yields.
Note: Target and Quota amounts are used interchangeably.
Performance Goal is the amount that management sets as the actual goal expected of the resources. This amount is typically used for reporting purposes and is not exposed to the resources. Performance Goal amounts are used to determine performance against a constant value for interval and period to date calculations.
Fixed Amount is a constant amount that is used for calculation purposes. Resources do not have a view or access to the fixed amount.
By entering the achievement levels at the plan element level, you create a generic plan. All resources assigned the compensation plan receive this quota figure.
To use Target, Goal, and Fixed Amount in an expression, select the following columns from the Calculation Values list of values on the Calculation Expressions page:
-
Target => CN_QUOTAS.TARGET
-
Fixed Amount => CN_QUOTAS.PAYMENT_AMOUNT
-
Goal => CN_QUOTAS.PERFORMANCE_GOAL
Distributing Target, Fixed Amount, and Performance Goal
You can distribute targets, fixed amounts, and performance goals to all periods in the interval. The distribution is based on the Calendar that is specified in the System Parameters.
When you distribute these variables, the amounts that you defined are applied evenly when you click the Distribute Evenly button, with the specified amount duplicated in each interval. For example, if you set a target of $5,000 for a period, $5,000 is displayed for each month on the Distribute Quotas page.
On the Distribution page, you can select a view of Period, Quarter, or Year. When you apply a different view, the amounts change to reflect this. For example, if you set a target of $5,000, that amount is displayed for each period in the Period view. If you select and apply a Quarter view, each quarter shows $15,000. A Year view shows $60,000 for the entire year.
After the amounts are evenly distributed, you can change them manually for a period to reflect variations in expected sales or seasonality. You can make your changes by percent or amount. Select one radio button to set this choice.
If you alter the amounts, when you save, the percentages display the correct percentages. If you change the percentages to something different from equal distribution, the amounts change to match. However, if, after setting the percentages, you change the target amount to be distributed, the percentages will not remain constant. Because the application saves the amounts and not the percentages, the percentages will reflect the relationship of the saved amounts to the new target amount.
For example, suppose you initially set a target amount is $10,000, with custom distribution percentages as follows:
-
Jan 07 - 5%
-
Feb 07 - 5%
-
Mar 07 - 5%
-
Apr 07 - 10%
-
May 07 - 10%
-
Jun 07 - 10%
-
Jul 07 - 5%
-
Aug 07 - 5%
-
Sep 07 - 5%
-
Oct 07 - 10%
-
Nov 07 - 10%
-
Dec 07 - 20%
If you distribute these percentages, which add up to 100%, the amounts display correctly. Jan 07 displays $500, May 07 displays $1,000, and Dec 07 displays $2,000. For this example, suppose you decide to change the target amount to $5,000, or one half of the original amount. When you distribute this amount, the amounts are not cut in half, but the percentages double.
-
Jan 07 - 10%
-
Feb 07 - 10%
-
Mar 07 - 10%
-
Apr 07 - 20%
The pattern continues throughout the year. The percentages are twice what they were for $10,000. This occurs because the amounts are stored in the application, not the percentages. Jan 07 is still $500 and Apr 07 remains $1,000, but the stored numbers represent double the percentage of the new target amount.
Navigation
Plan Administrator > Create Plan Element > Define Default Quotas
Notes
-
You can click the Plan Element name link to return to the Plan Element Details page.
-
When you select an interval, regardless of the view, variables are distributed equally to each period.
-
When you click Distribute Target, the amounts are equally distributed to each period, duplicating the amount set in the Variables area of the Plan Element Details page.
-
If you do not enter an End Date on the Plan Element Details page, the application automatically distributes the variables for all remaining periods defined in the predefined Calendar for the application.
-
If the plan element uses a partial year, then the distributed amounts are prorated. For example, if the periods start with April, and the target amount for each period is $5,000, then the quarterly view will show as $15,000 each, but the Year view will be $45,000.
Creating a Bonus Plan Element
This is an example of creating a bonus plan element. Bonus calculation is normally based on the total compensation earned by the resource or transaction total (sales credit total) of the resource. But in this case the bonus is calculated based on the compensation earned by the resource.
The resource has a commission plan element with the following details:
-
Input expression = Transaction Amount
-
Output expression = Transaction Amount * Rate table result /100
-
Rate table for the commission plan element:
Amount Commission 0-10,000 1% 10,000-50,000 2% 50,000-100,000 3% 100,000-999999999999 4% -
Commission Plan element Interval = Period
-
Apply transaction= Individually
This resource also has bonus plan element with the following details.
-
Input expression = Commission_paid_ptd column from a view created based on the cn_srp_period_quotas.
-
Output expression = Commission_paid_ptd of the view * Rate table Result /100
-
Rate table for the bonus plan element:
Amount Bonus 0-500 75 500-1,000 65 1,000-5,000 55 5,000-10,000 45 10,000-99999999999 25 -
Bonus Plan element Interval = Period.
The resource has the following transactions:
| Date | Transaction Amount |
|---|---|
| 01-Jan-01 | 9,000 |
| 02-Jan-01 | 15,000 |
| 01-Feb-01 | 40,000 |
Compensation calculated for the above transactions using the commission plan above is:
| Date | Transaction Amount | Rate | Commission |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01-Jan-01 | 9,000 | 1 | 90 |
| 02-Jan-01 | 15,000 | 2 | 300 |
| 01-Feb-01 | 40,000 | 2 | 800 |
Data from the view used for bonus calculation:
| Period-id | Input_achieved_ptd | Commission_paid_ptd |
|---|---|---|
| 2001001 | 24,000 | 390 |
| 2001002 | 40,000 | 800 |
Bonus calculation using the bonus plan and bonus rate table
| Period_id | Input_achieved_ptd | Commission_paid_ptd | Rate | Bonus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001001 | 24,000 | 390 | 75 | 292.5 |
| 2001002 | 40,000 | 800 | 65 | 520.0 |
Notes
-
Use Commission_paid_ptd in the bonus input expression if your bonus is based on the compensation of the resource. Use Input_achieved_ptd in the bonus input expression if your bonus is based on the total sales credit of the resource.
-
Here is a suggested view definition for the quarterly bonus that you can build to create the example shown previously:
select salesrep_id, max(a.period_id) last_period_id, sum(input_achieved_ptd) input_achieved_ptd, sum(commission_payed_ptd) commission_paid_ptd from cn_srp_period_quotas a, cn_quotas_v b where a.period_id between 2001001 and 2001012 and b.incentive_type_code = 'COMMISSION' group by salesrep_id, ceil((a.period_id - 2001000)/3)
Using Accelerators and Transaction Factors
In a plan element, you can modify the incentive amounts by using accelerators, as well as transaction factors and other factors. You define the effective period for these temporary changes by assigning a Start Date and an End Date. Accelerators increase compensation during that time period, and can be used as incentives for resources. Transaction factors stage sales credit over the life of a sale.
For each product, at plan element level, you can define accelerators. Oracle Incentive Compensation provides two types of accelerators:
-
Earnings Factor: Increases the resource's commission payment without affecting the level of quota achievement
-
Multiplier: Increases a resource's quota credit, that is, level of quota achievement
When you want to provide an incentive without affecting a resource's quota achievement, you can define an earnings factor. The earnings factor is a percentage factor multiplied against the net sales credit, resulting in compensation credit. The application then applies the compensation rate to this compensation credit to calculate the compensation. Thus, an earnings factor results in a higher or lower compensation amount but no change in quota achievement.
For example, an earnings factor of 200 has been put onto the eligible product of LIC-DB compensation plans for field resources to promote sales of this type of license. When Salesrep A sells something with the eligible product of LIC-DB, the application takes the transaction amount and calculates the amount of sales credit due to Salesrep A. As an example, the net sales credit is $1,000. The earnings factor of 200 (200%) is multiplied against this amount to get to the total compensation amount due to Salesrep A, which is $2,000.
How the accelerators and transaction factors are used depends on how your calculation expression is defined. For example, a common input expression that complements a percentage rate table is as follows:
EVENT_FACTOR* MULTIPLIER*TRANSACTION_AMOUNT/TARGET.
A typical output expression looks like this:
Rate_ Result* TRANSACTION_AMOUNT* EVENT_FACTOR* EARNINGS_FACTOR.
A multiplier enables a resource to reach higher levels of quota achievement more quickly, resulting in higher compensation payments. This is because Oracle Incentive Compensation uses quota achievement to determine which rate to use.
An earnings factor or a multiplier is a percentage expressed as a whole number. If you explicitly choose to use an earnings factor or multiplier in an expression, the default value is zero. You must assign a specific value for earnings factors or multipliers. For example, an earnings factor of 200 means to multiply the commission amount by 200% or a factor of 2 (as in the above examples). A multiplier of 50 multiplies the values in the expression by .5, effectively cutting the final amount in half.
Earnings factors work only when they are used in the calculation output expression assigned to the formula. For example:
-
(Rate Table Result*Transaction_Amount)*Earnings_Factor
Multipliers work only when they are used by the calculation input expression assigned to the formula. For example:
-
(Transaction_Amount*Multiplier)/Target
Earnings factors can only be used when the Apply Transaction Type is set to Individually as they apply to each individual eligible product. Earnings factors have no meaning if the Apply Transaction Type is set to Group by Interval.
Transaction factors help you stage sales credit over the life of a sale, assigning percentages of the transaction amount to important events in the sales process, including Invoice, Order, and Payment.
Transaction factors must add up to 100%. For example, you can have 50% of the commission calculated upon order, 20% calculated at invoice value and the final 30% calculated upon payment.
Other factors are used to indicate if any activity related to a sale, such as a credit memo or order return, should be credited at a percentage other than 100%:
-
Clawback: When the invoice due date grace period is exceeded, the outstanding amount of compensation credited for this sale is taken back.
-
Credit Memo: A credit memo is generated when an invoice is fully or partially reversed and posted to Oracle General Ledger. Credit memos are later collected and applied against transactions.
-
Deposit
-
Debit Memo: A debit memo is generated to fully or partially increase an invoice. It is posted to Oracle General Ledger. Debit memos are later collected and applied against transactions.
-
Giveback: If an invoice for which a clawback has been performed is subsequently paid, then a giveback is used to restore credit to a resource.
-
Manual Transaction: A transaction created by a user to reverse or change sales credit.
-
Order Return
-
Write-off: A sale is written off the books for a variety of reasons and posted to Oracle General Ledger.
Unlike transaction factors, other factors are each calculated separately, and do not need to total 100%. Each can be over or under 100%. For example, you can set the other factor of Order Return to be credited at 80%, or clawbacks at 110% to match your business procedures.
Eligible products must already be assigned.
Navigation
Plan Administrator > Maintain Component Library > Plan Elements> Assign Eligible Products > Update Factors
Notes
-
For accelerators, the default is 100, which is the full amount. Entries can be above or below 100.
-
For transaction factors, you can enter numbers to indicate how you want to stage the payment of commission.
-
In the Other Factors area, the default entry for each column is 100.
Using Interdependent Plan Elements
Interdependent plan elements use the calculated totals of one plan element to calculate for commission for another plan element.
To set up an interdependent plan element, you must create an expression that accesses specific plan element totals.
To set up an independent plan element, you need to create the input expression you need for it. See Defining Calculation Expressions for more details on creating expressions.
To be used in an input expression, a plan element must already be created.
Navigation
Plan Administrator > Maintain Component Library > Expressions > Create
Notes
-
If you are using transaction data from calculation expressions and mixing the plan element total with transaction data:
-
Select a type from the Type drop-down list. The six selections represent groups of calculation elements, such as expressions, formulas, and SQL functions. The choices for your selection are displayed in the Calculation Values box.
-
Select the column you want to use in the expression from the Calculation Values box.
-
After you have created the interdependent plan elements, build a compensation plan using the plan elements. Use the expression as the input expression of the formula of a new plan element. See Creating a Compensation Plan for steps to creating a compensation plan.
The new plan element you create calculates compensation based on totals from the plan element that you built into the expression.
Example
A sales manager wants a resource to receive an additional $1,000 bonus if she sells 100% of her target for a certain product. Because the bonus requires knowledge from the plan element for this product, you must create an interdependent plan element. These are the steps the compensation analyst performs to create an interdependent plan element in the resource's compensation plan.
First, the compensation analyst creates a commission plan element that includes the input and output expressions and a rate table to calculate compensation. This plan element pays the regular compensation on the product and aggregates credits and the target.
Secondly, the compensation analyst creates the plan element that pays the bonus if 100 percent of the target of the first plan element is met. This requires a formula that utilizes an input expression that references the achievement of the first plan element. This input expression divides the accumulated total from the first plan element by the ITD_Target total, which determines the achievement.
Finally, the plan elements must be sequenced in the final compensation plan so that the transactions are collected and calculated for the commission plan element first. That way, the total from all of the transactions for the first (commission) plan element can be used accurately in the input expression of the second (bonus) plan element.
If, after all transactions are collected and calculated, the result of the expression in the bonus plan element is 100 percent or greater, then the resource receives her $1,000 bonus credit.
Defining Formulas
You have complete flexibility to create formulas for calculating compensation. Some formulas can be embedded in another formula definition or in a plan element definition. You can save an incomplete formula and return to complete it later.
You can use expressions or rate tables in a formula that are already created or you can create them as you build the formula. Expressions can be repeated in your formula and can be reused in other formulas as well. See Defining Calculation Expressions for more information on the types of calculation expressions that you can use for commission and bonus formulas.
Warning: Do not open a new window during a browser session and navigate to the same page in the two windows simultaneously while you are defining formulas.
Navigation
Plan Administrator > Maintain Component Library > Formulas > Create
Steps
-
Select an operating unit.
-
Enter a type of Commission or Bonus. See Restrictions.
A Bonus Formula is a type of Formula where there are no links or references to transactions.
-
Indicate whether to apply transactions Individually or Grouped by Interval.
This affects how compensation is calculated. See Restrictions.
-
Indicate any splits.
Do not split tiers if you want a rate from the rate table applied to the full amount. Split tiers if you want portions of the full amount paid at each rate up to the top qualifying rate. See Restrictions.
-
Check the Accumulate Transactions box if transactions are required to be aggregated in total.
The rate applied will be determined by the transactions-total achieved to date within the interval. See Restrictions.
-
Check the Interval To Date box if you want to base the calculation on a period different from the plan element interval. See Restrictions.
-
Click Apply.
-
Click the Expressions subtab.
-
Select an input expression. To create a new expression click Create. See Defining Calculation Expressions
You can use more than one input expression, but the number of input expressions must equal the number of dimensions in the rate table that you select later.
-
You can assign a forecast if you need it for Projected Compensation.
-
Select an Output expression and a forecast as needed.
-
Select a performance measure if you want to use it in the Year To Date Summary Report for comparison with achievement.
-
Click Apply.
-
Click the Rate Tables subtab, the Add Another Row button, and view the rate table.
To create a new rate table, see Define Rate Tables.
-
After all of the components are in place, click Save and Generate.
If you have successfully created the formula, the status field above the Generate button changes from Incomplete to Complete. See Restrictions.
-
Click Update.
Copying Formulas
You can create a copy of a formula, that already exists in the operating unit. This way you need not create a new formula, whose parameters are similar to the existing formula.
When you create copy of a formula, the application does not make copies of rate tables, rate dimensions, or expressions, but references these elements, in the newly created formula. If you want to make new rate dimensions or expressions, then use the corresponding Inline Copy feature for those elements and change the copied formula to reference the newly created elements.
Steps:
-
Navigate: Plan Administrator > Maintain Component Library > Formulas
-
Search for formula, whose duplicate you want to create.
-
Click "Duplicate" icon.
Note: For more information on copying objects, see: Maintaining Compensation Plans (Copying Compensation Plan).
For commission formulas, Individual Option for Transactions can be used with any Cumulative/Interval to Date option.
-
By default Interval to Date and Cumulative options must be used together. You cannot select Interval to Date by itself. Split options are selectable (each is mutually exclusive).
-
Accumulate can be selected by itself. Split options are selectable (each is mutually exclusive).
In commission formulas, Group by Interval for Transactions must be used with Cumulative. The difference between Group by Interval and Cumulative individual calculation is that Cumulative individual calculation calculates the compensation for each individual transaction, whereas Group by Interval only calculates the total compensation at the end of the interval.
Use interval-to-date quotas and fixed amounts if:
-
Calculation is to occur before the end of the plan element interval (for example, if the interval is quarter and calculation occurs monthly)
-
Quotas are set cumulatively within the interval
-
Performance to date is to be compared to the quota to date
Bonus formulas calculate only against Individual transaction options. Split options are selectable (each is mutually exclusive).
Performance measures must use numeric expressions to work correctly. In a formula, if no performance measure is assigned, the application uses the first input expression. If that expression evaluates to string values, the calculation will fail. Therefore, it is important to assign a numeric performance measure when the first input expression is not numeric.
You must generate a formula for it to be available when you are selecting formulas for a plan element. Formulas that do not have a Complete status do not appear in the Formulas list of values. When you generate a formula the application verifies that the expressions and rate tables are compatible and that they will work when they are called during the calculation.
Example of Split Tiers
A rate table shows 0 to 1000 at 1%, 1000 to 2000 at 2%. The transaction amount is 1500. If you select No Split in the drop-down list, 2% is applied to the whole transaction amount of 1500. If you select Non-Proportional in the drop-down list, 1% is applied to 1000 and 2% is applied to 500.
The Proportional selection in the Split drop-down list is intended for use with amount rate tables. For example, if the rate table shows 0 to 1000 at 100, 1000 to 2000 at 200. The first transaction amount is 200. The compensation for this transaction is 20 because 200 is one fifth of the first rate tier and one fifth of the 100 rate is 20. If the second transaction amount is 1300, the remaining four fifths of the first rate tier pays 80, and half of the second tier [(1300 minus 800)/(2000 minus 1000)] pays 100 (half of the rate 200). Total compensation for the second transaction is 180.
In a multidimensional rate table, only one dimension can have split rate tiers.
If you are selecting the Cumulative or Split functions, you can use percent, amount, or expression type rate dimensions. You cannot use string dimensions.
Calculation Expressions
Calculation expressions are interchangeable, reusable parts that are used in input and output expressions of formulas, expression-based rate dimensions, performance measures, forecast expressions, and for projected compensation.
You can use these calculation expressions as performance measures, input expressions, output expressions, or rate table dimensions. You can also embed one calculation expression within another. After they have been saved, the expressions can be assigned and reassigned to any number of formulas you need.
Any column from any table can be part of your expression, as long as the Calculation Value box for the column is selected in Columns and Tables.
You can place a formula inside a calculation expression if you want to be certain that the formula output result is used in the expression. Sequencing plan elements in a compensation plan can also assure that calculations are performed in the order you need.
You can add functions to an expression by selecting them from the Functions list of values. This feature is used in the procedure below.
For details on defining calculation expressions, see Defining Calculation Expressions.
Input Expressions
Input expressions tell Oracle Incentive Compensation what to evaluate from the transactions and how to match the results to the corresponding rate table. A simple input formula expression looks like this:
TRANSACTION_AMOUNT
For example, a company can establish that its sales force will be compensated based on transaction amount. The input expression evaluates transactions from the TRANSACTION_AMOUNT column of the CN_COMMISSION_HEADERS table.
This is an example of a rate table:
| Transaction Amount | Commission |
|---|---|
| $0 - $100 | 4% |
| $100 - $500 | 5% |
| $500 - $99,999 | 6% |
As transactions are sorted by through the input expression they are matched to the established rate table tiers. If a transaction is collected in Oracle Incentive Compensation with the following attributes:
-
Customer X
-
Transaction Amount $100
-
Product Z
Oracle Incentive Compensation, using the TRANSACTION_AMOUNT input expression, matches the above transaction of $100 with the rate table and determines that 5% will be paid on this order.
Output Expressions
Output expressions instruct the application how much to pay resources. The payment amount can either be tied to a rate table or not. This will be determined by the users.
Example of a typical output expression, which uses a rate table:
Rate Table Result * TRANSACTION_AMOUNT
Performance Measures
A performance measure is part of a plan element that captures an accumulation of transaction values by plan element and uses the data in reports that compare achievements to quota, goal and performance measure. Performance measures are not used to calculate compensation.
You can use a performance measure to track revenue. You select and define the columns where revenue information for transactions is held. Then, as transactions are entered and collected for the assigned plan element, the transaction values are accumulated. An example performance measure is:
TRANSACTION_AMOUNT
Note: Performance measures must use numeric expressions to work correctly. In a formula, if no performance measure is assigned, the application uses the first input expression. If that expression evaluates to string values, the calculation will fail. Therefore, it is important to assign a numeric performance measure when the first input expression is not numeric.
Defining Calculation Expressions
Calculation expressions define the flow of a formula. Input expressions bring the data into the formula and output expressions take the data out after the formula has run.
Depending on how an expression is defined, it is used as one of the following:
-
The input, output, or performance measure of a commission type formula which is applied to individual transactions
-
The input or output of a commission type formula which is applied to individual transactions
-
The output or performance measure of a formula of any type
-
The input of a bonus type formulas or a commission formula which is applied to a group of transactions
-
The input of a commission type formula which allows multiple inputs
-
The output of the forecast version of a formula
-
The input of the forecast version of a formula which allows multiple inputs
-
The tier expression of a dynamic dimension
-
As a forecast input or output expression
Navigation
Plan Administrator > Create Formula > Expressions
Notes
-
You can use operands, user created functions, and numeric constants or string values when building an expression.
-
You can use values from another plan element and plan element metrics.
-
After you save an expression, the status reads Valid if it has compiled properly. If an expression is not valid, it cannot be used. Fix the problem before attempting to validate the expression again.
-
The usage of the expression is also displayed once it is saved. The usage rules determine where the expression may be applied.
-
A Bonus calculation expression cannot include an element from the table cn_srp_period_quotas or any table that is mapped to this table. A Bonus calculation expression cannot be used as an embedded formula and cannot be mixed with a commission type formula. See Bonus Formulas for more information.
-
The six selections in the View H-grid represent groups of calculation elements. Only the calculation elements for that selection are displayed in the Calculation Values box.
-
Sales Compensation Elements: These include seeded and previously defined columns from the transaction headers and lines tables, as well as compensation plan related tables.
-
Expressions: Any previously defined expression can be used as part of another expression.
-
Formulas: Any previously defined non-cumulative commission formula can be used as part of an expression.
-
External Elements: For non-seeded tables or views to be available for expression building, they must be registered on the Tables page and mapping between them and seeded OIC tables should be defined on the External Table page.
-
SQL Functions: SQL Number, Group, and other functions can be added to an expression.
-
Others: Other elements, such as Rate Table Result and Forecast Amount, are listed here.
-
-
Selected columns are accessible for use in building formulas and performance measures.
-
The following Oracle Incentive Compensation tables are predefined in the system and can be used as calculation values in defining performance measures and formulas:
-
CN_COMMISSION_HEADERS: Contains information relating to the transaction, such as employee name and number. The 100 attributes defined on this page are descriptive flexfields. For more information on flexfields, see Oracle Incentive Compensation Implementation Guide, Appendix A, or the Oracle Applications Flexfields Guide.
-
CN_COMMISSION_LINES: Stores transactions created as part of calculation
-
CN_SRP_QUOTA_ASSIGNS: Stores resource plan element assignments
-
CN_SRP_PERIOD_QUOTAS: A multi-org view of quotas and achievements based on interval to date and period to date
-
CN_QUOTAS: Stores plan elements
-
Note: If you want columns to be hidden or added the Incentive Compensation Administrator must configure them under Tables and Columns.
-
-
A rate dimension calculation expression can only be defined from the following tables:
-
CN_SRP_PERIOD_QUOTAS: see above
-
CN_SRP_PLAN_ASSIGNS: Stores resource plan assignments
-
CN_SRP_QUOTA_ASSIGNS: see above
-
CN_SALESREPS: Stores resource personal data, such as name, salesrep-id, and email address.
-
-
Plan element metrics are stored for each resource in the database, and are not necessarily defined in the user interface. Most of the selections relate to accumulation of commission in a plan element over a period--period to date (PTD)--or an interval other than the period--interval to date (ITD). For example, a plan element can use a period of a month but also an interval of a quarter, and accumulation of commission for either interval or period can be used in another expression to calculate a bonus. This can be set on the Calculation Expressions page using the Plan Element field and the metrics drop-down list next to it.
Example of a User Defined Function
This is an example of a user defined function. Create a user defined function in SQL Plus in the APPS schema, and make sure it is valid. Then you can select it from the List of Values in the expression builder in the application. It is difficult to create a thresholding/cap function using the simple SQL elements supplied in Oracle Incentive Compensation. However, you can create a function in which if a given value is less than the threshold, the function returns to 0; if it is greater than the cap, the function returns the cap value; otherwise it returns the value itself.
In SQL Plus, the function is:
create or replace function
threshold_cap (value number, threshold number, cap number)
return number IS
begin
if value < threshold then
return 0;
elsif value > cap then
return cap;
else
return value;
end if;
end;
You can now build an expression that uses this function in the expression builder in Oracle Incentive Compensation:
threshold_cap(Commission Headers.Transaction Amount,1000,5000).
Warning: When creating user defined expressions, do not perform any updates of transaction related tables or perform any commits. This will potentially cause data corruption in the transaction tables. However, you are allowed to select any values from any table without causing data corruption.
Copying Calculation Expressions
You can create a copy of a calculation expression, that already exists in the operating unit. This way you need not create a new calculation expression, whose parameters are similar to an existing calculation expression. Oracle incentive compensation will create a copy, and then you change the parameters.
Steps:
-
Navigate: Plan Administrator > Maintain Component Library > Expressions
-
Search for the calculation expression, whose copy you want to create.
-
Click "Duplicate" icon.
Note: For more information on copying objects, see: Maintaining Compensation Plans (Copying Compensation Plans).
Export and Import Compensation Plans
As a Plan Administrator, you must modify or update existing compensation plans to conform to new sales directives. Oracle Incentive Compensation allows you to download details of a compensation plan you have modeled in a test environment, and upload it to the production environment. This approach allows you copy plans and plan components across different environments You can copy a compensation plan, and the following components: plan elements, formulas, expressions, rate tables, and rate dimensions.
The Export Setup Data function allows you to download the compensation plan and its components into your local system, as an XML document. After you have downloaded the file use the Import Setup Data function, to upload the XML file into a different environment. This allows you to migrate plans from one environment to another environment.
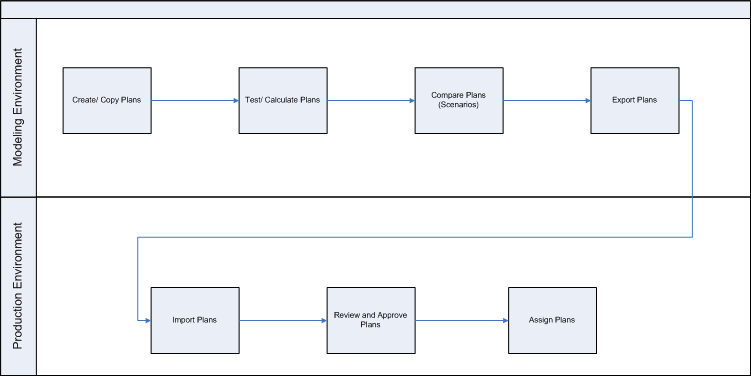
To accomplish copying plans from one environment to the other, you generally follow these steps:
-
Create a new plan or create copy of an existing plan.
-
Test the plans for correctness.
-
Compare the plans using Scenarios.
-
Create an Export request for the plan.
-
Import the plan to applicable environment.
-
Review and approve the plan.
-
Assign the plan.
Creating Export Requests
To export details of a compensation plans, you need to create an export request. An export request consists of a single compensation plan or multiple compensation plans. After you process an export request, Oracle Incentive Compensation saves details of the plans in an XML document, which you download to your local system. When you export a plan, application also exports the following element, within a plan:
-
Plan elements
-
Formulas
-
Rate tables
-
Rate dimensions
-
Expressions
Navigation
Plan Administrator > Export Setup Data > Create
Steps:
-
Enter Request Name.
-
Select Operating Unit.
-
Click Next. You will navigate to the Create Export Request: Choose Objects to Export page.
-
Click Add.
-
Search for a compensation plan and add it to the request.
Note: You can add multiple plans to the export request.
-
Click Submit.
Caution: After you have saved an export request, you can make changes to the plans listed in the request. You have rendered the plan incomplete, due to setup changes, or have deleted the plan; you can still submit the export request. In such a case, Oracle Incentive Compensation, will not process the export request, and it will not create any XML document.
Viewing Export Request
You use the Export Requests page to see details of a particular export request and also download the compensation plan export file. To view details of an export request, you must search for an export request. You can search for an export request using Request Name, Source Operating system, or Status. Oracle Incentive Compensation also provides for an Advanced Search feature. Using this feature, you can search for an export request using additional search criteria. Additionally, you can also click Views to personalize and save searches.
After you have searched for a particular export request, you can view details of the request, by clicking on either Request Id, Request Name, or View Log. If you click the Request Id link, then Oracle Incentive Compensation displays the parameters, notifications, and diagnostics details of the export request. If you click the Request Name link, then Oracle Incentive Compensation, displays plans that are included in the export request and you can download the plan details file, to your local drive.
Note: You can download the plan details file, only if the export request is in 'Complete' status.
Navigation:
Plan Administrator > Export Setup Data
Steps:
-
Enter Request Name.
-
Select Source Operating Unit
-
Click Go.
-
Click on applicable Request Name link.
When you click Download File in the Search Request page, or click Download in the request details page, then application dialog box, through which you can save the plan details file to a local system.
Creating Import Requests
To import a compensation plan, into a target operating unit, you need to create an import request. An import request consists of the request name, plan details file, that you had earlier downloaded using the export request process, and target operating unit name. It may or may not have a Prefix Text and Start and End Date.
When you import a compensation plan, into an operating unit, you may want to specify a default naming convention for the imported compensation plan and its sub-elements, to distinguish them from the objects that already exists. All the objects created in the target operating unit will derive their name using the Prefix Text. You may also want to specify start and/or end date for the imported compensation plans and its sub-elements.
Navigation
Plan Administrator > Import Setup Data > Create
Steps:
-
Enter Request Name.
-
Select Target Operating Unit.
-
Select Source Files.
Note: This is the same files you have downloaded to your system during the export process.
-
Optionally, enter Prefix Text.
-
Optionally, select Start and/or End Date.
-
Click Submit.
After you have submitted the export request, Oracle Incentive Compensation generates a Request Id. You can use this Request Id, to track the status of the import request.
Viewing Import Request
The View Import Requests page displays the details of a particular import request, including the source file name, target operating unit, object type, submission date, and status. You can search for an import request using Request Name, Target Operating Unit, and Status. Oracle Incentive Compensation also provides for an Advanced Search feature. Using this feature, you can search for an import request using additional search criteria. Additionally, you can also click Views to personalize and save searches.
After you have searched for a particular import request, you can view details of the request, by clicking on either Request Id, Request Name, or View Log. If you click the Request Id link, then Oracle Incentive Compensation displays the parameters, notifications, and diagnostics details of the export request. You can cancel the request if the status is "In Progress". When the request is complete or has failed, then the application does not provide an option to cancel the request.
If you click the Request Name link, then Oracle Incentive Compensation displays the status of the request, and the request options. You can view the import request report, as a Log file, which lists all the activities the import request has performed.
Navigation
Plan Administrator > Import Setup Data
Steps:
-
Enter Request Name.
-
Select Target Operating Unit.
-
Click Go.
-
Click on applicable Request Name link.
Import Examples
The following examples illustrates these scenarios:
-
Import Plan: Utilizing Object Reuse
-
Import Plan: Avoiding Object Reuse
Import Plans: Utilizing Object Reuse
This scenario explains the situation, when you import a plan, but do not want to create duplicate elements in the target operating unit.
Prerequisites
-
You have changed the names of modified plans and its sub-elements, in the source environment, to distinguish them from existing plans in the target environment.
-
You do not choose prefix text.
-
You have successfully exported plan and plan components.
Scenario: No Prefix Text and No Start/End Date
| Source Plan Details File | Elements in Target Operating Unit | Resulting Setup after Import Process |
|---|---|---|
Note: In XML source file, "Plan Element B" is reused across "Plan 1" and "Plan 2". |
Note: "Plan Element A" is reused across "Plan 3" and "Plan 4". |
Note: "Plan Element B" is reused across "Plan 1" and "Plan 2". "Plan Element A" is reused across "Plan 1", "Plan 2", "Plan 3", and "Plan 4". |
Import Plan: Avoiding Object Reuse
This scenario explains the situation, when you import a plan, without relying on reusing existing plan components.
Prerequisites
-
Plan and plan components haven been successfully exported to XML
-
Use Prefix Text.
Scenario: Prefix Text
You choose the following options when importing the XML, plan details, file:
-
Prefix text: 2008
-
No Start/End Date changes
| Source Plan Details Files | Elements Existing in Target Operating Unit | Resulting Setup after Import Process |
|---|---|---|
Note: In the plan details, XML, file, "Plan Element B" is reused across "Plan 1" and "Plan 2". |
Note: "Plan Element A" is reused across "Plan 3" and "Plan 4". |
Note: "2008: Plan Element B" is reused across "2008: Plan 1" and "2008: Plan 2". "Plan Element A" is reused across "Plan 3" and "Plan 4". |