Oracle Human Resources Management Systems Implementation Guide
Contents
Title and Copyright Information
- Getting Started with the Configuration Workbench
- Quick Start Implementation
- Quick Evaluation of Prototypes Using the Configuration Workbench
- Upgrade HR Foundation
- Full Implementation
- Configuration Workbench for Enterprise and Workforce Management
- Configuration Models for Your Enterprise Framework
- Defining Jobs in the Configuration Workbench
- Defining Positions in the Configuration Workbench
- Defining Grades in the Configuration Workbench
- Configuration Workbench for Compensation, Benefits, and Payroll
- Configuration Workbench for Payroll Process Management
- Defining Regional Jobs, Positions or Grades in the Configuration Workbench
- Converting Benefits Enrollments
- Overview
- Using the Spread Sheet Framework
- Create a Function and Download the Spread Sheet
- Upload and Download Spread Sheets
- Configuration Workbench for Data Conversion
- Configuration Workbench for HR Information Systems
- Configuration Workbench for Migrating Data
Implementation
Implementation Steps
Note: If you are implementing the Oracle HRMS Multi-Tenant functionality, you must refer to the Oracle HRMS Multi-Tenant Functionality white paper on My Oracle Support, Note ID: 760500.1
Before You Start
Before you begin implementing Oracle HRMS, you must ensure your legislation-specific startup data is installed. The installation is normally done by the MIS Manager. You need this startup data before you use Elements, Payment Methods or Legislation Specific Flexfield Structures.
See Oracle E-Business Suite Installation Guide: Using Rapid Install for more information.
Also, check to see whether there are any post installation steps you need to perform before you start to implement Oracle HRMS.
See: Post Install Steps.
Post Install Steps
There are two generic post install utilities for Oracle HRMS:
-
DataInstall enables you to specify all the legislations that you want to install for HR and Payroll, and HR only. This means that when you subsequently perform an installation or upgrade, you can install your legislations in a single operation. DataInstall provides a series of menus from which you can specify the legislation and product combinations.
-
AutoPatch (adpatch) applies the installation or upgrade combinations that you have previously specified in DataInstall.
Canada and USA
If you are installing Oracle Payroll (Canada and US) you also need to install Quantum, a third party taxation product, produced by Vertex, that Oracle Payroll (Canada and US) uses.
France
If you are installing a French localization, there are two additional post install steps for that must be completed for Oracle HR for France. These are:
-
Run the Seed French Data process
-
Create a new EUL (End User Layer) in Discoverer and enable user access to database tables and views by running the Grant HR Access to Discoverer process
US Federal HR
If you are installing the US Federal HR localization, there is one additional step to be able to produce bitmap reports.
To Run the DataInstall Utility (Required)
To specify legislations using DataInstall:
-
Run the DataInstall utility to select legislations using the command:
jre oracle.apps.per.DataInstall <APPS Username> <APPS password>
Note: In multiple ledger installs, supply the username and password of the first APPS account.
The DataInstall Main Menu is displayed.
-
Choose option 1. This displays a screen showing a list of product localization combinations that you can choose.
For each product or localization that already has legislation data on the database, the Action will be defaulted to upgrade. This cannot be changed.
-
Federal HR only: Choose both Oracle Federal HR and Oracle Human Resources from the list of product localizations.
-
Select any new installations that you want to implement. For example, if you wanted to install Canada Payroll, number 3, you would type 3I. This would also set the action on Canada Human Resources to Install as dependencies are maintained.
If you are installing an additional legislation, to correct a mistake use the Clear option. If you have selected to install an additional Payroll and HR legislation, clearing the Payroll legislation will clear the HR legislation also.
You cannot use Force Install for upgrades. You only need to use Force Install if you want to reapply steps in the Global Legislation Driver that have already been applied.
-
If you select a localization other than US or UK, you are returned to the main menu.
If you select a US or UK localization the DataInstall - College Data Option screen is displayed showing whether college data is currently installed for US and UK localizations. The install option is only available if you have no existing college data. If you have existing data then the localization will default to Upgrade, though this can be changed.
Choose Remain if you want to keep the existing data and not apply the upgrade, or choose Clear to set the action to null.
You cannot use Force Install at this point.
Press Return to display the main menu and make further changes or exit.
-
US and Canada only: If you have installed Oracle Payroll, select the JIT/Geocodes option from the DataInstall menu to load the latest JIT/Geocodes data.
This option is also available to Oracle HR customers who wish to validate US or Canadian addresses using Vertex Geocodes data and/or maintain employee tax data in Oracle HR. However, customers who do not have Oracle Payroll must obtain a license from Vertex before installing this data.
Press Return to display the main menu and make further changes or exit.
-
When you choose to exit the DataInstall Actions Confirmation screen is displayed.
Select Y to save your changes and exit, or select N to exit without saving your changes.
When you have exited, the DataInstall Actions Summary screen is displayed. This summarizes the actions that will be taken when the program exits, or when ADPATCH is run with the Global Legislation driver.
Run the Global Legislation Driver using AutoPatch (adpatch) (Required)
-
The Generic HR Post Install Driver delivers the generic entity horizon and all the selected localizations. To run it, type in the following commands:
$ cd $PER_TOP/patch/115/driver $ adpatch
Then apply the driver hrglobal.drv
-
After applying the Global Legislation Driver, examine the out file hrlegend.lst. This logs any localizations selected in the DataInstall utility but which have not been applied by this driver. Refer to the Installation Manual to ensure that everything has been applied correctly, or contact World-wide Support.
-
UK only: Examine the following out files:
-
pegbutcl.lst. This file logs the step that removes previously seeded user tables for the UK legislation before delivering the latest version. It may also show where seed data names have been changed between releases.
-
perleggb.lst. This file logs the housekeeping step that gets rid of redundant UK seed data after delivery of the latest version. It also records the new balance feeds that have been inserted following an upgrade from Oracle Human Resources to Oracle HRMS.
-
The log file produced by the FFXBCP formula compilation step. The name of the FFXBCP log follows the naming convention of the <request_id> log, and is included in the last section of the adpatch log.
These files are used by Oracle Support Services to diagnose problems with seed data following an upgrade. SQL errors indicate severe problems. Keep these files for reference in the event of any future problems with UK seed data.
-
Install Quantum for Oracle Payroll (Canada and US) (Conditionally Required)
-
Set up a directory structure to hold the Quantum product.
By default, Oracle Payroll looks for the Quantum product in the $PAY_TOP/vendor/quantum directory, however, you can choose where it is placed and override the default location.
Tip: You could create a $PAY_TOP/vendor/quantum_versions directory and a $PAY_TOP/vendor/quantum symbolic link pointing to the correct version of Quantum, since the Quantum products release cycle may be different from Oracle Payroll.
-
Unpack the Quantum Components from the CD.
Oracle Applications provide a CD on which will be a ZIP file called pyvendor.zip in a directory called pay. On the ZIP file will be one directory per operating system that is supported by Oracle Payroll (US). Uncompress the pyvendor.zip file and move the required version into the directory structure created in Step 1. For example, uncompress the file then do the following:
$ mv SOLARIS/2.2.4 $PAY_TOP/vendor/quantum_versions $ ln -s $PAY_TOP/vendor/quantum_versions/2.2.4 $PAY_TOP/vendor/quantum
The extraction from the compressed file will create a directory called (<operating system>/2.2.4) and two sub directories (lib and utils) along with a number of files in each directory. One of the files created is devenv, this devenv file is the same as the $FND_TOP/usrxit/devenv file except that some of the lines are uncommented. The uncommented lines relate to instructions on how the Oracle Payroll process PYUGEN should be linked. The lines that are uncommented are:
VND_VERTEX='$(PAY_TOP)/vendor/quantum' VND_LINK='$(VND_VERTEX)/lib/libvprt.a \ $(VND_VERTEX)/lib/libqutil.a \ $(VND_VERTEX)/libloc.a \ $(VND_VERTEX)/lib/libcb63.a' $ ln -s $PAY_TOP/vendor/quantum_versions/2.2.4 $PAY_TOP/vendor/quantum VNDPAYSL='$(PAY_TOP)/lib/py3c.o $(PAY_TOP)/lib/py3v.o $(VND_LINK)' VNDPAYPL='$(PAY_TOP)/lib/py3c.o $(PAY_TOP)/lib/py3v.o $(VND_LINK)' export VND_VERTEX VND_LINK VNDPAYPL VNDPAYSLNote: Some of these settings relate to the location of the Quantum product, thus if the Quantum product is not in $PAY_TOP/vendor/quantum this file needs to be edited.
If you have made any changes to your $FND_TOP/usrxit/devenv file, you must merge these differences into the file. If you have not already made any changes then you can simply copy 2.2.4/devenv to $FND_TOP_usrxit/devenv.
-
Relink the Oracle Payroll executable PYUGEN using adrelink.
$ adrelink force=y ranlib=y "pay PYUGEN"
Ensure that the adrelink completed successfully by checking the log file.
-
Build the Quantum product's data files.
To build Quantum's data files, firstly create a directory to hold the data files. Oracle Payroll assumes that these data files are in $PAY_TOP/vendor/quantum/data.
Secondly, run the utility dbcreate that is in the Quantum utils directory. This utility will show a menu of either Payroll or Geocoder. Choose the Payroll option and at the prompt "Enter the Payroll datasource name:" enter the directory into which the data files are to be placed, for example, /apps/pay/11.5/vendor/quantum/data. Once the processing is complete, the menu will reappear and the utility can be exited.
Note: Ensure that the file permissions of the data files are set to readable for all the relevant users. If this is not done then Oracle Payroll will not be able to access these files.
-
Populate the Quantum data files.
Once the data files have been created they need to be populated with taxation data. The taxation data is held in a file called qfpt.dat, which will be delivered in the pyvendor.zip file. Copy this file into the Quantum product area. Once this has been done the data file update utility can be run. This is located in the utils directory called vprtmupd. Select the Update Payroll Tax option from the menu, and answer the displayed questions. The first prompts for the datasource, this should be the location of the data files created in the previous step. The second is the location of the qfpt.dat file. For example:
Enter Datasource: /apps/[ay/11.5/vendor/quantum/data Enter the path of the update file: /apps/pay/11.5/vendor/quantum
Note: The update file supplied is a default file, it is not guaranteed to calculate taxes correctly. Its purpose is to allow you to perform testing prior to contacting Vertex to request the correct update file.
-
Register the Quantum Data Files location.
If the data files for Quantum have not been placed in the default location ($PAY_TOP/vendor/quantum/data), then the location of these files must be supplied to Oracle Payroll. This is performed by placing a row in the PAY_ACTION_PARAMETERS table:
SQL> insert into pay_action_parameters 2 values ('TAX_DATA', '/apps/quantum/data');
Run the Seed French Data process (France)
-
This process creates and populates some of the user defined tables used by the various French reports for the Business Group of the current responsibility. It also delivers the example data for the Bilan Social. It should be run for each Business Group that contains data for the French legislation.
For information on the user defined tables created by this process see: User Defined Tables Used by the Bilan Social, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide , and User Defined Tables, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Run the Seed French Data process in the Submit Requests window.
Create an EUL and Enable User Access to Database Tables and Views by Running the Grant HR Access to Discoverer process (France)
In order to use the supplied business area and Discoverer workbooks you must perform the following steps:
-
Create an EUL
If you do not have an existing Oracle Discoverer EUL you must create one before you can import the HR France - Bilan Social business area.
See: Oracle Discoverer Administration Guide for further information on creating an EUL.
-
Import the hrfrbsel.eex file
Once you have a suitable EUL you must import the hrfrbsel.eex file. This will deliver the HR France - Bilan Social business area. This file is contained in the Bilan Social Discoverer Components zip file that can be obtained from Oracle World Wide Support.
See: Oracle Discoverer Administration Guide for further information on importing files.
-
Run the Grant HR Access to Discoverer process
The EUL user must be given the correct permissions in order to access the tables and views in the database that are used by the Bilan Social. To do this, you must run Grant HR Access to Discoverer process in the Submit Requests window.
You will now be prompted to enter the following parameters:
-
the connect string for the database on which the Bilan Social data is stored
-
your EUL user name
-
your EUL password
Choose Submit. The process will now run and assign the appropriate permissions to your EUL user.
-
HR Print Reports (US Federal)
To be able to produce bitmap and postscript reports, you must relink ar60runb.
-
Chenv to the environment.
-
Make sure that FND_TOP and APPL_TOP are correct.
-
cd $FND_TOP/bin
-
adrelink.sh force=y "fnd ar60runb"
Implementation Checklist
Use the following checklists to record which parts of Oracle HRMS you want to use. Then refer to the implementation steps to see the high level steps you must complete for each business function you have chosen to implement.
 < Post Install Steps (Required)
< Post Install Steps (Required)
Refer to the Post Install Steps to see any steps you must perform before you implement Oracle HRMS.
 < Administration (Required)
< Administration (Required)
Includes key and descriptive flexfields, Extra Information Types (EITs), currencies, "View All" HRMS User, and lookups.
 < Enterprise and Workforce Management (Required)
< Enterprise and Workforce Management (Required)
Includes organizations, jobs, positions and position control, workflow for transactions, HR budgets, person types, and collective agreements.
 < Payroll Process Management (Optional)
< Payroll Process Management (Optional)
Includes payrolls, payment methods, and payslip information. For Canada, also includes Workers' Compensation, and provincial medical.
 < Compensation, Benefits, and Payroll (Optional)
< Compensation, Benefits, and Payroll (Optional)
Includes grades, grade related pay, benefits eligibility, life events, compensation objects, enrollment requirements, activity rates, elements, salary administration, leave and absence management, element sets, rate by criteria, and additional setup for payroll processing and health and welfare.
 < Benefits Implementation Without Total Compensation Setup Wizard (Optional)
< Benefits Implementation Without Total Compensation Setup Wizard (Optional)
Provides the full sequence of steps you follow to set up benefit plans manually.
 < Workforce Sourcing and Deployment (Required)
< Workforce Sourcing and Deployment (Required)
Includes recruitment, assignment statuses, contract statuses, assignment rate types for contingent workers, special personal information, global deployments, and requirements matching.
 < Talent Management (Optional)
< Talent Management (Optional)
Includes competencies, objectives (Workforce Performance Management), qualifications, and appraisals.
 < Workforce Intelligence (Optional)
< Workforce Intelligence (Optional)
Includes predefined Discoverer workbooks and a predefined Discoverer End User Layer based on HRMS transactional tables.
 < HR Information Systems (Optional)
< HR Information Systems (Optional)
Includes reports, letter generation, configuration, task flows, user security, audit requirements, Oracle Applications Help, and Web Applications Desktop Integrator (Web ADI).
Implementation Flowchart
Some of the steps outlined in this section are Required, and some are Optional. Required with Defaults means that the setup functionality comes with predefined, default values in the database; however, you should review those defaults and decide whether to change them to suit your business needs. If you want or need to change them, you should perform that setup step. You need to perform Optional steps only if you plan to use the related feature or complete certain business functions.
Administration

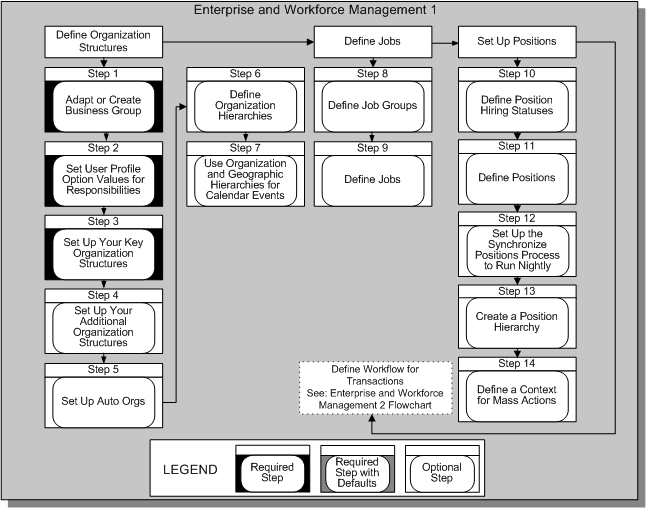
Enterprise and Workforce Management 1
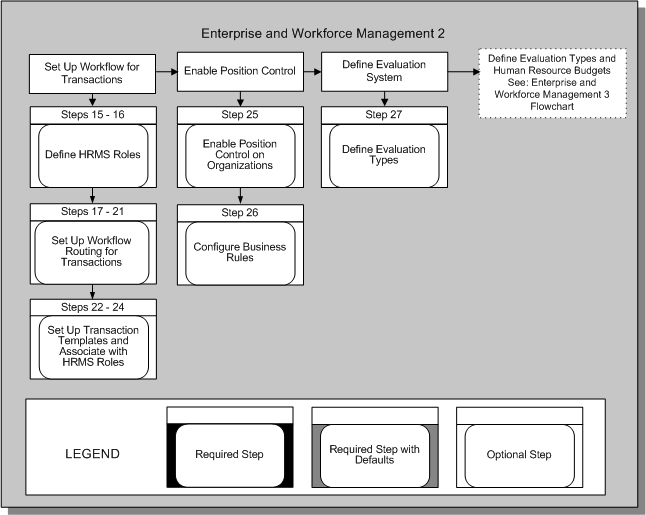
Enterprise and Workforce Management 2
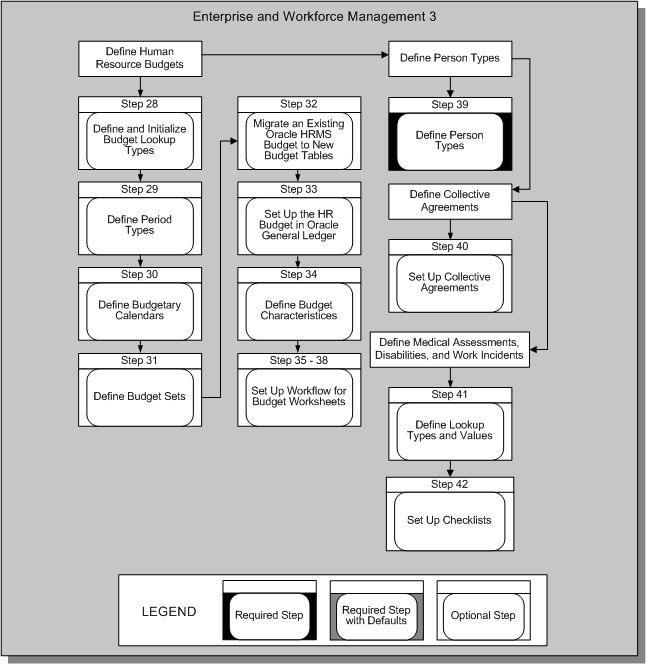
Enterprise and Workforce Management 3
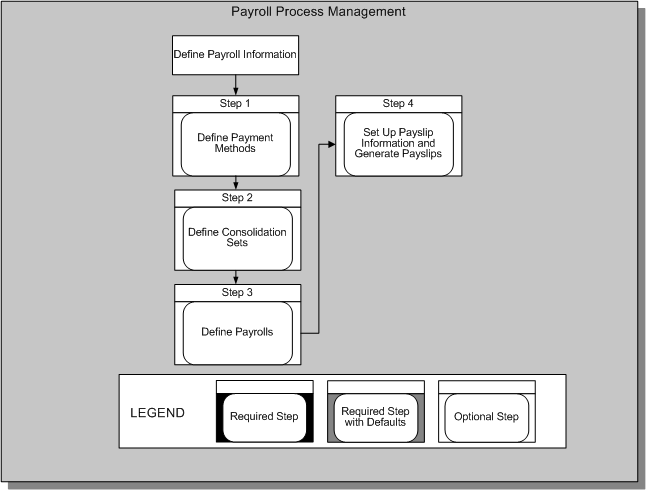
Payroll Process Management
Compensation, Benefits, and Payroll 1
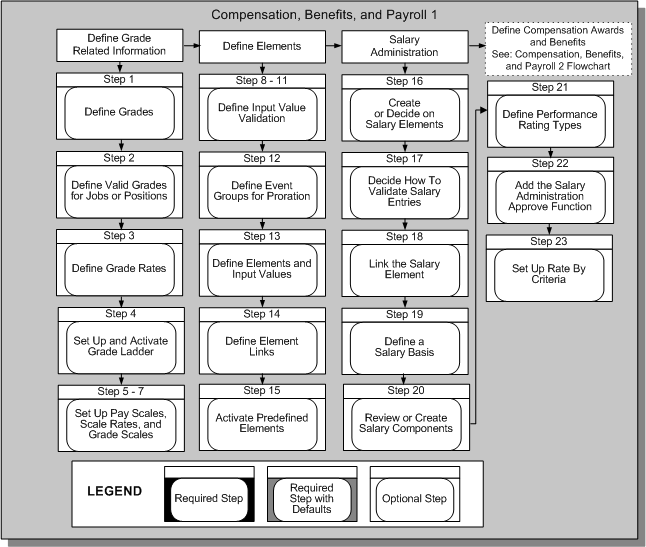
Compensation, Benefits, and Payroll 2
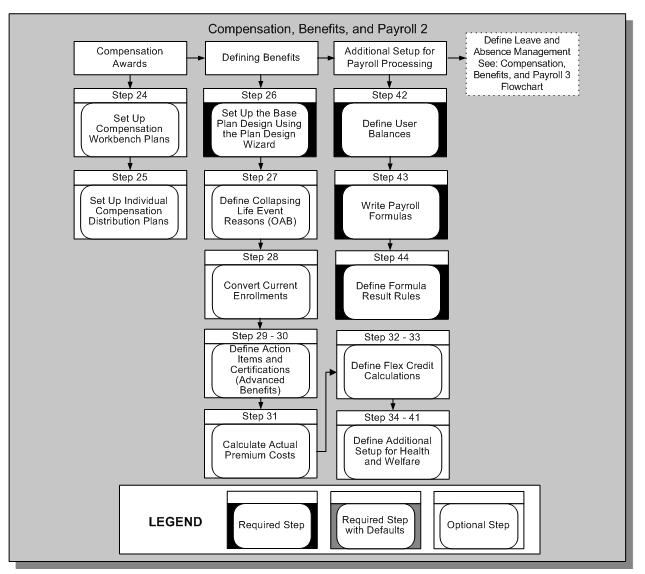
Compensation, Benefits, and Payroll 3
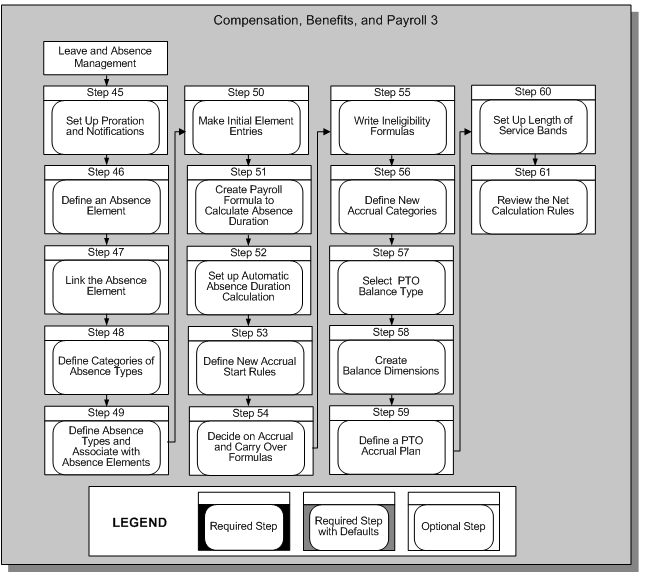
Statutory Absence Payments Setup (UK Only) 1

Statutory Absence Payments Setup (UK Only) 2

Element Sets and Batch Control Totals
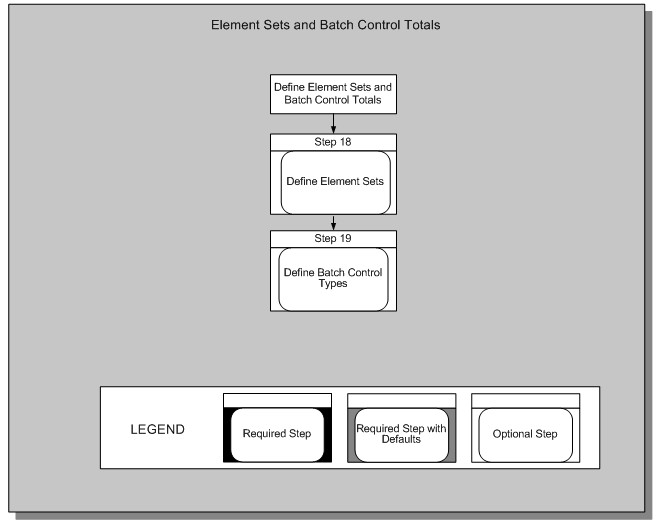
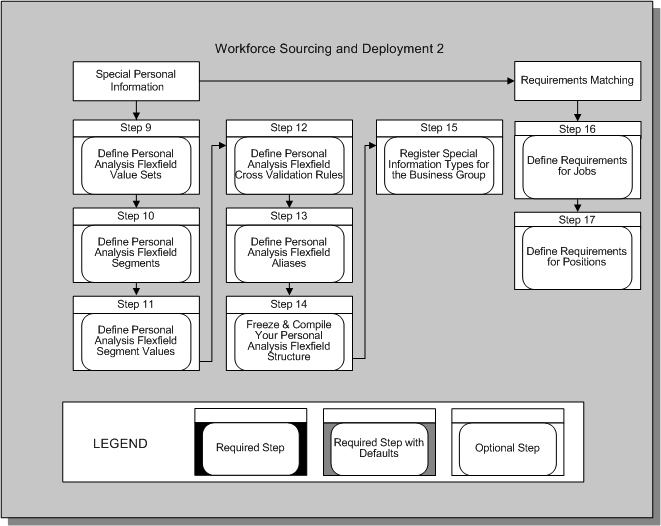
Workforce Sourcing and Deployment 1

Workforce Sourcing and Deployment 2
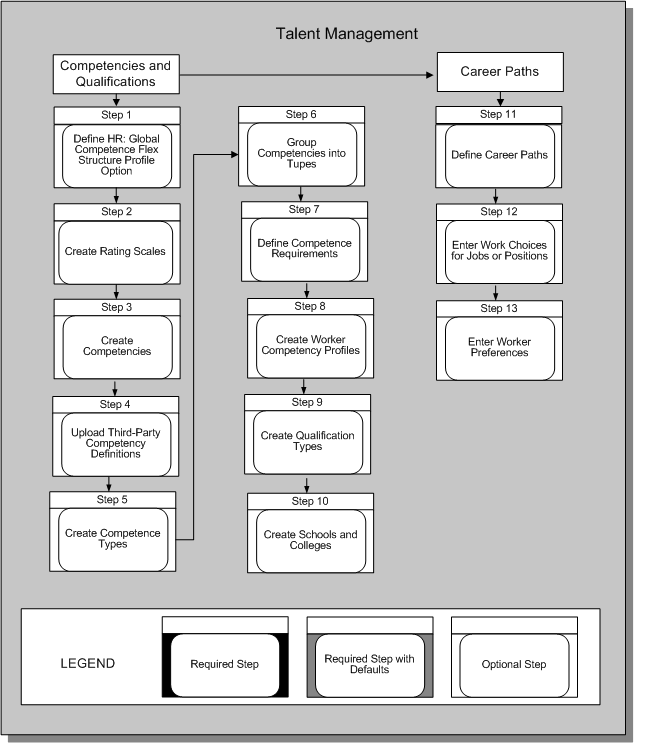
Talent Management
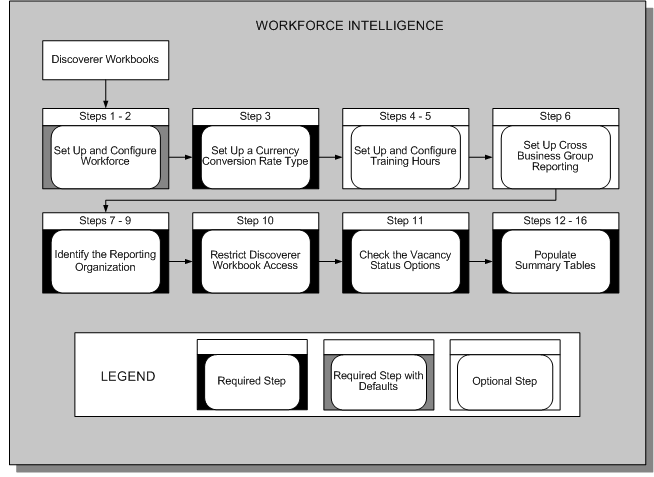
Workforce Intelligence
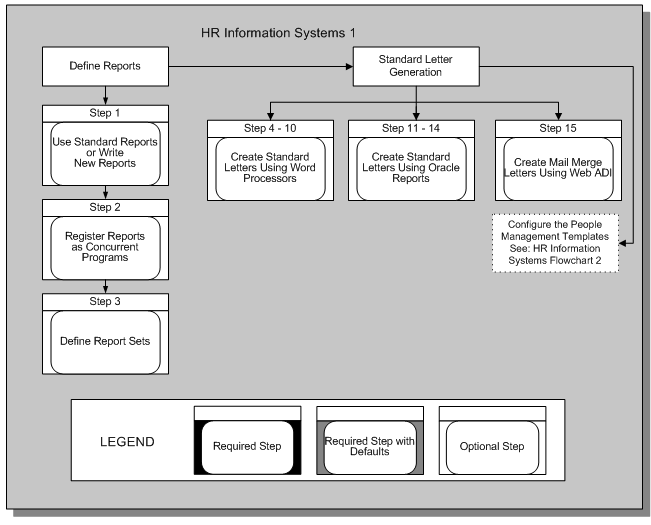
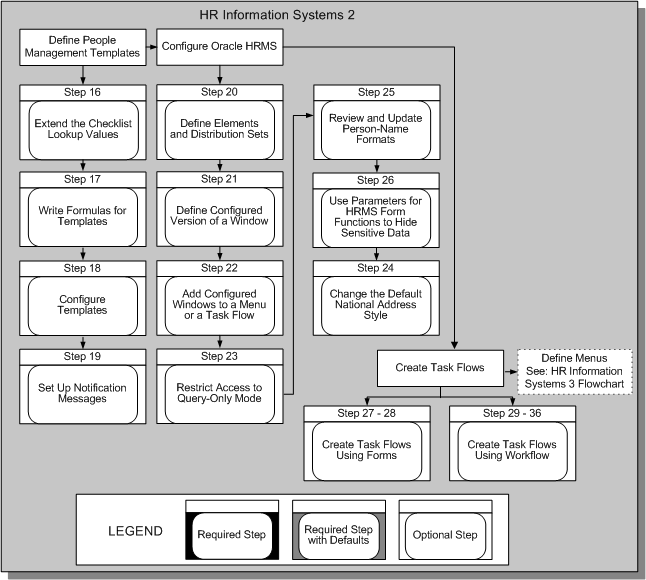
HR Information Systems 1
HR Information Systems 2
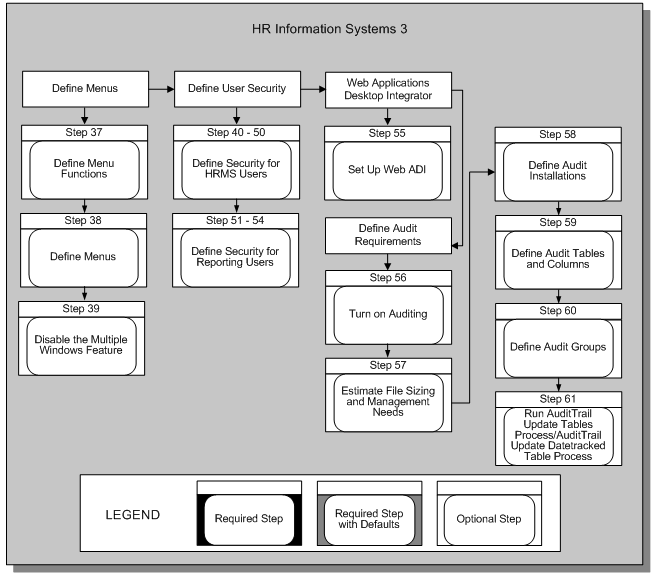
HR Information Systems 3
Administration
The administration steps are usually performed by the System Administrator. Sign on to the application using your System Administrator username and password. Contact your DBA if you do not know this information.
Key Flexfields
Before you can define a business group in Oracle HRMS you must define six Key Flexfield Structures:
-
Job
-
Position
-
Grade
-
People Group
-
Cost Allocation
-
Competence
You can also define the Collective Agreement Grades flexfield at this time, or you can do it after defining your business group.
Before you begin your implementation of these key flexfields you must clearly specify your requirements. This specification must include the following details for each key flexfield:
-
The Structure Name and the number of Segments
-
The Flexfield Segment Names, Order, Validation Options, and Qualifiers
-
The Flexfield Value Sets and any lists of values
After you have completed the definition of a key flexfield, you need to run the Create Key Flexfield Database Items process concurrent process to generate Database Items for the individual segments of the Flexfield. This applies to your Job, Position, Grade, Competence, and People Group Key Flexfields only.
Important: If you used the Configuration Workbench, you have already defined the structures for your Job, Position, and Grade key flexfields. You may want to add more validation, such as cross-validation. The Workbench created default structures for the other flexfields associated with a business group (People Group, Cost Allocation, and Competence). If you plan to use these flexfields in your implementation, you must update the default structures to display the segments you require.
Define Job Flexfield Optional Step s
After you have specified your requirements for recording and reporting Job information, follow this implementation sequence:
Step 1: Define Job Flexfield Value Sets
To validate the values which a user can enter for any segment, you must define a specific Value Set.
The attributes of the Value Set control the type of values that can be entered, and how many characters each segment can hold. The attributes of the Value Set will also control how the values are to be validated.
Value Sets can be shared by different segments of the same flexfield, or by segments of any other flexfield.
Use the Value Set window.
See: Defining Value Sets, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 2: Define Job Flexfield Segments
Define a structure for your Job Flexfield which contains the segments you want to use for your business group. You use this structure to create your unique Job Names in the Job window.
You must enter Yes in the Allow Dynamic Inserts field. If you enter No, you cannot create new job name combinations in the Job window.
Note: You do not need to use a Value Set to validate a segment. If you do not specify a Value Set then a user can enter any alphanumeric value up to a limit of 150 characters.
Use the Key Flexfield Segments window
See: Defining Key Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 3: Define Job Flexfield Segment Values
If you have chosen Independent or Dependent validation for a Value Set used by a Job Flexfield Segment, you must define your list of valid values for the Value Set.
Use the Segment Values window
See: Defining Segment Values, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 4: Define Job Flexfield Cross Validation Rules
Define any Cross Validation Rules you want to use to control the combinations of segment values which a user can enter.
You define Rules to Include or Exclude combinations of segment values. For each segment, you can define a Low to High range of values.
Use the Cross-Validation Rule window
See: Defining Cross-Validation Rules, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 5: Define Job Flexfield Aliases
Define Aliases for common combinations of segment values if you want to provide these as default options.
Use the Shorthand Aliases window
See: Defining Shorthand Aliases, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 6: Freeze and Compile Your Job Flexfield Structure
You are now ready to freeze your Job Flexfield definition. Navigate to the Key Flexfield Segments window. Enter Yes in the Freeze Flexfield Definition field and save your changes. The application now freezes and compiles your Job Flexfield definition. Compiling the flexfield definition enables the Job Flexfield window with the defaults, values and rules that you have defined.
Use the Key Flexfield Segments window
See: Defining Key Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 7: Run Create Key Flexfield Database Items Process
If you want to make use of the individual segments of the flexfield as separate Database Items you can run this concurrent process from the Submit a New Request window. The only parameter associated with this process is the Key Flexfield Name.
Use the Submit a New Request window
See: Submitting a Request, Oracle E-Business Suite User's Guide
Define Position Flexfield Optional Step s
After you have specified your requirements for recording and reporting Position information in your enterprise, follow this implementation sequence:
Step 8: Define Position Flexfield Value Sets
To validate the values a user can enter for any segment, you must define a specific Value Set.
The attributes of the Value Set control the type of values that can be entered, and how many characters each segment can hold. The attributes of the Value Set also control how the values are to be validated.
Value Sets can be shared by different segments of the same flexfield, or by segments of any other flexfield.
Use the Value Set window.
See: Defining Value Sets, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 9: Define Position Flexfield Segments
Define a structure for your Position Flexfield which contains the segments you want to use for your business group. You use this structure to create your unique Position Names in the Position window.
You must enter Yes in the Allow Dynamic Inserts field. If you enter No, you cannot create new position name combinations in the Position window.
Note: You do not need to use a Value Set to validate a segment. If you do not specify a Value Set then a user can enter any alphanumeric value up to a limit of 150 characters.
Use the Key Flexfield Segments window
See: Defining Key Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 10: Define Position Flexfield Segment Values
If you have chosen Independent or Dependent validation for a Value Set used by a Position Flexfield Segment, you must define your list of valid values for the Value Set.
Use the Define Segment Values window
See: Defining Segment Values, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 11: Define Position Flexfield Cross Validation Rules
Define any Cross Validation Rules you want to use to control the combinations of segment values which a user can enter.
You define Rules to Include or Exclude combinations of segment values. For each segment, you can define a Low to High range of values.
Use the Cross-Validation Rule window
See: Defining Cross-Validation Rules, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 12: Define Position Flexfield Aliases
Define Aliases for common combinations of segment values if you want to provide these as default options.
Use the Shorthand Aliases window
See: Defining Shorthand Aliases, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 13: Freeze and Compile Your Position Flexfield Structure
You are now ready to freeze your Position Flexfield definition. Navigate to the Key Flexfield Segments window. Enter Yes in the Freeze Flexfield Definition field and save your changes. The application now freezes and compiles your Position Flexfield definition. Compiling the flexfield definition enables the Position Flexfield window with the defaults, values, and rules that you have defined.
Use the Key Flexfield Segments window
See: Defining Key Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 14: Run Create Key Flexfield Database Items process
If you want to make use of the individual segments of the flexfield as separate Database Items you can run this concurrent process from the Submit a New Request window. The only parameter associated with this process is the Key Flexfield Name.
Use the Submit a New Request window
See: Submitting a Request, Oracle E-Business Suite User's Guide
Define Grade Flexfield Optional Step s
After you have specified your requirements for recording and reporting Grade information in your enterprise, follow this implementation sequence:
Step 15: Define Grade Flexfield Value Sets
To validate the values which a user can enter for any segment, you must define a specific Value Set.
The attributes of the Value Set control the type of values that can be entered, and how many characters each segment can hold. The attributes of the Value Set also control how the values are to be validated.
Value Sets can be shared by different segments of the same flexfield, or by segments of any other flexfield.
Use the Value Set window.
See: Defining Value Sets, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 16: Define Grade Flexfield Segments
Define a structure for your Grade Flexfield which contains the segments you want to use for your business group. You use this structure to create your unique Grade Names in the Grades window.
You must enter Yes in the Allow Dynamic Inserts field. If you enter No, you cannot create new grade name combinations in the Grades window.
Note: You do not need to use a Value Set to validate a segment. If you do not specify a Value Set then a user can enter any alphanumeric value up to a limit of 150 characters.
Use the Key Flexfield Segments window.
See: Defining Key Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 17: Define Grade Flexfield Segment Values
If you have chosen Independent or Dependent validation for a Value Set used by a Grade Flexfield Segment, you must define your list of valid values for the Value Set.
Use the Define Segment Values window
See: Defining Segment Values, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 18: Define Grade Flexfield Cross Validation Rules
Define any Cross Validation Rules you want to use to control the combinations of segment values a user can enter.
You define Rules to Include or Exclude combinations of segment values. For each segment, you can define a Low to High range of values.
Use the Cross-Validation Rule window
See: Defining Cross-Validation Rules, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 19: Define Grade Flexfield Aliases
Define Aliases for common combinations of segment values if you want to provide these as default options.
Use the Shorthand Aliases window
See: Defining Shorthand Aliases, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 20: Freeze and Compile Your Grade Flexfield Structure
You are now ready to freeze your Grade Flexfield definition. Navigate to the Key Flexfield Segments window. Enter Yes in the Freeze Flexfield Definition field and save your changes. The application now freezes and compiles your Grade Flexfield definition. Compiling the flexfield definition enables the Grade Flexfield window with the defaults, values, and rules that you have defined.
Use the Key Flexfield Segments window
See: Defining Key Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 21: Run Create Key Flexfield Database Items Process
If you want to make use of the individual segments of the flexfield as separate Database Items you can run this concurrent process from the Submit a New Request window. The only parameter associated with this process is the Key Flexfield Name.
Use the Submit a New Request window
See: Submitting a Request, Oracle E-Business Suite User's Guide
Define People Group Flexfield Required Step s
People Group information, associated with employee and contingent worker assignments, identifies special groups of people, such as members of a union or a working group.
Warning: In Oracle HRMS you must define at least one segment for the People Group Key Flexfield.
If you do not, you will not be able to use the Assignment window for employees, applicants, or contingent workers.
After you have specified your requirements for recording and reporting People Group information, follow this implementation sequence:
Step 22: Define People Group Flexfield Value Sets
To validate the values a user can enter for any segment, you must define a specific Value Set.
The attributes of the Value Set control the type of values that can be entered, and how many characters each segment can hold. The attributes of the Value Set also control how the values are to be validated.
Value Sets can be shared by different segments of the same flexfield, or by segments of any other flexfield.
Use the Value Set window.
See: Defining Value Sets, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 23: Define People Group Flexfield Segments
Define a structure for your People Group Flexfield that contains the segments you want to use for your business group. You use this structure to enter People Group details in the Assignment window.
You must enter Yes in the Allow Dynamic Inserts field. If you enter No, you cannot enter People Group information in the Assignment window.
Note: You do not need to use a Value Set to validate a segment. If you do not specify a Value Set then a user can enter any alphanumeric value up to a limit of 150 characters.
Use the Key Flexfield Segments window
See: Defining Key Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 24: Define People Group Flexfield Segment Values
If you have chosen Independent or Dependent validation for a Value Set used by a People Group Flexfield Segment, you must define your list of valid values for the Value Set.
Use the Define Segment Values window
See: Defining Segment Values, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 25: Define People Group Flexfield Cross Validation Rules
Define any Cross Validation Rules you want to use to control the combinations of segment values a user can enter.
You define Rules to Include or Exclude combinations of segment values. For each segment, you can define a Low to High range of values.
Use the Cross-Validation Rule window
See: Defining Cross-Validation Rules, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 26: Define People Group Flexfield Aliases
Define Aliases for common combinations of segment values if you want to provide these as default options.
Use the Shorthand Aliases window
See: Defining Shorthand Aliases, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 27: Freeze and Compile Your People Group Flexfield Structure
You are now ready to freeze your People Group Flexfield definition. Navigate to the Key Flexfield Segments window. Enter Yes in the Freeze Flexfield Definition field and save your changes. The application now freezes and compiles your People Group Flexfield definition. Compiling the flexfield definition enables the People Group Flexfield window with the defaults, values, and rules that you have defined.
Use the Key Flexfield Segments window.
See: Defining Key Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 28: Run Create Key Flexfield Database Items process
If you want to make use of the individual segments of the flexfield as separate Database Items you can run this concurrent process from the Submit a New Request window. The only parameter associated with this process is the Key Flexfield Name.
Use the Submit a New Request window.
See: Create Key Flexfield Database Items, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
See: Submitting a Request, Oracle E-Business Suite User's Guide
Define Cost Allocation Flexfield Required Step s
Cost Allocation information normally records the details of employee costing associated with payroll results. If you have installed Oracle Payroll, you can accumulate the costs associated with your payroll results and transfer these to your General Ledger system. If you have not installed Oracle Payroll you can use the costing flexfield to enter your cost allocation information.
After you have specified your requirements for recording and reporting costing information, follow this implementation sequence:
Warning: You must define at least one segment for the Cost Allocation Key Flexfield. If you do not, you will experience problems using windows with the flexfield window.
Step 29: Define Cost Allocation Flexfield Value Sets
To validate the values which a user can enter for any segment, you must define a specific Value Set.
The attributes of the Value Set control the type of values that can be entered, and how many characters each segment can hold. The attributes of the Value Set also control how the values are to be validated.
Value Sets can be shared by different segments of the same flexfield, or by segments of any other flexfield.
Use the Value Set window.
See: Defining Value Sets, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 30: Define Cost Allocation Flexfield Segments and Qualifiers
Define a structure for your Cost Allocation Flexfield which contains the segments you want to use for your business group. You use this structure to enter your payroll costing details.
You must enter Yes in the Allow Dynamic Inserts field. If you enter No, you cannot enter Costing details anywhere on the system.
Note: You do not need to use a Value Set to validate a segment. If you do not specify a Value Set then a user can enter any alphanumeric value up to a limit of 150 characters.
The Cost Allocation Flexfield is the only key flexfield in Oracle HRMS that makes use of Qualifiers. You use Segment Qualifiers to control the level at which costing information can be entered to the system. Each Qualifier determines the level at which costing information can be entered. The following table illustrates the six possible choices for each segment:
| Qualifier | Effect on window |
|---|---|
| Payroll | Enter segment values in the Payroll window. |
| Link | Enter segment values in the Element Link window. |
| Balancing | Enter balancing segment values in the Element Link window. |
| Organization | Enter segment values in the Costing Information window for the Organization. |
| Assignment | Enter segment values in the Costing window for the assignment. |
| Entry | Enter segment values in the Element Entries window. |
Use the Key Flexfield Segments window
See: Defining Key Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 31: Define Cost Allocation Flexfield Segment Values
If you have chosen Independent or Dependent validation for a Value Set used by a Cost Allocation Flexfield Segment, you must define your list of valid values for the Value Set.
Use the Define Segment Values window.
See: Defining Segment Values, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 32: Define Cost Allocation Flexfield Cross Validation Rules
Define any Cross Validation Rules you want to use to control the combinations of segment values a user can enter.
You define Rules to Include or Exclude combinations of segment values. For each segment, you can define a Low to High range of values.
Use the Cross-Validation Rule window
See: Defining Cross-Validation Rules, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 33: Define Cost Allocation Flexfield Aliases
Define Aliases for common combinations of segment values if you want to provide these as default options.
Use the Shorthand Aliases window
See: Defining Shorthand Aliases, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 34: Freeze and Compile Your Cost Allocation Flexfield Structure
You are now ready to freeze your Cost Allocation Flexfield definition. Navigate to the Key Flexfield Segments window. Enter Yes in the Freeze Flexfield Definition field and save your changes. Oracle HRMS now freezes and compiles your Cost Allocation Flexfield definition. Compiling the flexfield definition enables the Cost Allocation Flexfield window with the defaults, values, and rules that you have defined.
Use the Key Flexfield Segments window
See: Defining Key Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Define Competence Key Flexfield (Steps 35-40)
The Competence Key Flexfield records information about multi-level competencies. This enables you to record more details about a competence.
After you have specified your requirements for recording and reporting competence information, follow this implementation sequence:
Step 35: Define Competence Flexfield Value Sets
To validate the values that a user can enter for any segment, you must define a specific Value Set.
The attributes of the Value Set control the type of values that can be entered, and how many characters each segment can hold. The attributes of the Value Set also control how the values are to be validated.
Value Sets can be shared by different segments of the same flexfield, or by segments of any other flexfield.
Use the Value Set window.
See: Defining Value Sets, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 36: Define Competence Flexfield Segments
Define a structure for your Competence Flexfield that contains the segments you want to use. You use this structure to enter your competence details in the Competence window.
You must enter Yes in the Allow Dynamic Inserts field. If you enter No, you cannot enter new details in the Competence window.
You must specify one of the segments as the Default Attribute using the flexfield qualifier. You must also attach the Others flexfield qualifier to all other segments in the structure.
If you intend to upload SkillScape competencies you should try to ensure that you set up segment 1 to record the competence name as this is the segment into which the competence name is automatically uploaded. If you define another segment to hold the competence name you must alter the file $PER_TOP/patch/115/sql/peducomp.sql so that the reference to segment1 is changed to the segment in which you hold the name.
Note: You do not need to use a Value Set to validate a segment. If you do not specify a Value Set then a user can enter any alphanumeric value up to a limit of 150 characters.
Use the Key Flexfield Segments window.
See: Defining Key Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 37: Define Competence Flexfield Segments Values
If you have chosen Independent or Dependent validation for a Value Set used by a Competence Flexfield Segment, you must define your list of valid values for the Value Set.
Use the Segment Values window.
See: Defining Segment Values, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 38: Define Competence Flexfield Cross-Validation Rules
Define any Cross-Validation Rules you want to use to control the combinations of segment values a user can enter.
You define Rules to Include or Exclude combinations of segment values. For each segment, you can define a Low to High range of values.
Use the Cross-Validation Rule window.
See: Defining Cross-Validation Rules, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 39: Define Competence Flexfield Aliases
Define Aliases for common combinations of segment values if you want to provide these as default options.
Use the Define Shorthand Aliases window.
See: Defining Shorthand Aliases, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 40: Freeze and Compile Your Competence Flexfield Structure
You are now ready to freeze your Competence Flexfield definition. Navigate to the Define Key Flexfield Segments window. Enter Yes in the Freeze Flexfield Definition field and save your changes. The application now freezes and compiles your Competence Flexfield definition. Compiling the flexfield definition enables the flexfield window with the defaults, values, and rules that you have defined.
Use the Key Flexfield Segments window.
See: Defining Key Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Define Collective Agreement Grades Key Flexfield Optional Step s
The Collective Agreement Grades Key Flexfield records information about how an employee is graded or ranked in a collective agreement. The Collective Agreement Grades Key Flexfield enables you to specify any number of structures. Each grade structure is defined as a separate structure of the flexfield. You then link a specific structure to a collective agreement in the Agreement Grades window.
It is not mandatory to define your collective agreement grades key flexfield now. You can do it after you have defined your business groups.
Warning: If you are using the Italian legislation, do not create new structures for the Collective Agreement Grades Key Flexfield. You must use the predefined structure, IT_ CAGR and must not make changes to it.
After you have specified your requirements for recording and reporting agreement grade information, follow this implementation sequence:
Step 41: Design your Collective Agreement Grades Flexfield Structures
You need to design a Collective Agreement Grades Flexfield Structure for each Grade Structure you want the application to hold. For each structure you must include the following:
-
The Structure Title (the Grade Structure) and the number of Segments.
-
The Flexfield Segment Names (the Grade Factors), Order, and Validation Options.
-
The Flexfield Value Sets and any lists of values.
Note: Your system administrator performs this step.
Step 42: Define Collective Agreement Grades Flexfield Value Sets
To validate the values that a user can enter for any segment, you must define a specific Value Set.
The attributes of the Value Set control the type of values that can be entered, and how many characters each segment can hold. The attributes of the Value Set also control how the values are to be validated.
Value Sets can be shared by different segments of the same flexfield, or by segments of any other flexfield.
Use the Value Set window.
See: Defining Value Sets, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 43: Define Collective Agreement Grades Flexfield Segments
Define a structure for your Collective Agreement Grades Flexfield that contains the segments you want to use. You use this structure to create your Reference Grades in the Define Agreement Grades window.
You must enter Yes in the Allow Dynamic Inserts field. If you enter No, you cannot enter new details in the Define Agreement Grades window.
When you access the grades in the Assignment window they display in the numerical order defined in the Number column of the Segments Summary window.
Note: You do not need to use a Value Set to validate a segment. If you do not specify a Value Set then a user can enter any alphanumeric value up to a limit of 150 characters.
Use the Key Flexfield Segments window.
See: Defining Key Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 44: Define Collective Agreement Grades Flexfield Segments Values
If you have chosen Independent or Dependent validation for a Value Set used by a Collective Agreement Grades Flexfield Segment, you must define your list of valid values for the Value Set.
Use the Segment Values window.
See: Defining Segment Values, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 45: Define Collective Agreement Grades Flexfield Cross-Validation Rules
Define any Cross-Validation Rules you want to use to control the combinations of segment values a user can enter.
You define Rules to Include or Exclude combinations of segment values. For each segment, you can define a Low to High range of values.
Use the Cross-Validation Rule window.
See: Defining Cross-Validation Rules, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 46: Define Collective Agreement Grades Flexfield Aliases
Define Aliases for common combinations of segment values if you want to provide these as default options.
Use the Define Shorthand Aliases window.
See: Defining Shorthand Aliases, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 47: Freeze and Compile Your CollectiveAgreement Grades Flexfield Structure
You are now ready to freeze your Collective Agreement Grades Flexfield definition. Navigate to the Define Key Flexfield Segments window. Enter Yes in the Freeze Flexfield Definition field and save your changes. The application now freezes and compiles your Collective Agreement Grades Flexfield definition. Compiling the flexfield definition enables the flexfield window with the defaults, values, and rules that you have defined.
Use the Key Flexfield Segments window.
See: Defining Key Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Descriptive Flexfields
Use descriptive flexfields in Oracle HRMS to define your own additional fields to the standard windows. For example, if you want to record Driver's License Number for any person you can define a segment of the Additional Personal Details flexfield to record this additional information.
After this, you can enter a Driver's License Number in the Person window after the standard Personal details.
Note: Because the descriptive flexfield is defined at the level of the base-table, any window using the base-table displays the same descriptive flexfield segments. In this example, the Driver's License Number appears in the Contact window as well as the Person window.
Before you begin to implement any descriptive flexfield you must clearly specify your requirements. You must include the following details:
-
The Context and the number of Segments for each Context
-
The Flexfield Segment Names, Order and Validation Options
-
The Flexfield Value Sets and any lists of values
You can define two types of descriptive flexfield Segments:
-
Global Segments
Segments always appear in the flexfield window.
-
Context-Sensitive Segments
Segments appear only when a defined context exists. You can prompt a user to enter the context, or you can provide the context automatically from a reference field in the same region.
Note: Often you can choose between using a code, a "base-table" field, and a field that contains a meaning or description. You should always use base-table fields as reference fields for Context-Sensitive segments. These fields usually have the same name as the column in the base table.
Some of the Standard Reports supplied with the system include descriptive segment values. If you follow this suggestion, these reports will be able to use the prompts you define - otherwise they will apply a generic prompt to the data.
Note: If you want to include descriptive flexfield Segment Values in the Lookups list for DateTrack History, you need to modify the DateTrack History Views supplied in the application.
Define Descriptive Flexfields Optional Step s
Step 48: Register a Reference Field
You must use the Application Developer Responsibility to update the definition of the descriptive flexfield. From the Descriptive Flexfields window, navigate to the Reference Fields block and enter the name of the Reference Field you want to use.
Warning: Some descriptive flexfields are predefined and protected. These are used to deal with specific legislative and reporting needs of individual countries or industries.
Do not attempt to alter the definitions of these protected flexfields. These definitions are a fundamental part of Oracle HRMS. Any change to them may lead to errors in the operating of the application.
Oracle HRMS may use other segments of these flexfields in the future. Therefore, do not add segments to any protected flexfield. This can impair your ability to upgrade your system.
Use the Descriptive Flexfields window.
Step 49: Define Flexfield Value Sets
If you want to validate the values a user can enter for any segment you must define a specific Value Set.
-
The attributes of the Value Set control the type of values that can be entered, and how many characters each segment can hold.
-
The attributes of the Value Set also control how the values are to be validated.
Note: Value Sets can be shared by different segments of the same flexfield, or by segments of any other flexfield.
Use the Value Set window.
See: Defining Value Sets, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 50: Define Descriptive Flexfield Segments.
Define the segments of your descriptive flexfield for each Context.
You do not need to use a Value Set to validate a segment. If you do not specify a Value Set then a user can enter any alphanumeric value up to a limit of 150 characters.
-
Use Global Context to define any segments always appear in the flexfield window.
-
Enter your own Context Name to define segments which will appear only for that context.
-
Freeze and compile your descriptive flexfield definitions.
Warning: Any segment you define as "Required" is required for every record on the system. You can encounter two common problems:
-
If you define a "Required" segment after you have entered records: Existing records lack a value in this segment, causing the application to error when you query an existing record.
-
Some descriptive flexfields are used in more than one block. For example, any "Required" segments for Additional Personal Details must be entered for every Employee, Contingent Worker, Applicant, or Contact.
Use the Descriptive Flexfield Segments window.
-
See: Defining Descriptive Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 51: Define Flexfield Segment Values
If you have chosen Independent validation for a Value Set used by a descriptive flexfield Segment, you must define a list of valid values for the Value Set.
Use the Define Segment Values window.
See: Defining Segment Values, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 52: Run Create Descriptive Flexfields Database Items Process
When you have defined your descriptive flexfields you should run the Create Descriptive Flexfields Database Items process to create database items for your non-context-sensitive descriptive flexfield segments.
You should rerun this process whenever you create additional non-context-sensitive descriptive flexfield segments.
Note: If you require Database Items for Context Sensitive flexfield segments you should consult your Oracle Support Representative for full details of how to add other Database Items.
Use the Submit a New Request window
See: Submitting a Request, Oracle E-Business Suite User's Guide
Extra Information Types (EITs)
Extra Information Types are a type of descriptive flexfield that let you add an unlimited number of information types to six of the most important entities in Oracle HRMS.
For example, you might want to use the EIT on Assignment to hold information about project work within an assignment.
Note: With Organizations you can group the EITs by classification so that when a user selects a classification they see the EITs associated with the classification. You must undertake some additional steps to implement EITs for an Organization.
Define EITs (Excluding Organizations) Optional Step s
Step 53: Define Extra Information Types for Locations, Jobs, Positions, People and Assignments
Once you have decided which extra information types you require, you need to select the descriptive flexfield by title. Create a new record in the Context Field Values region and enter the name of your new Information Type in the Code field. Enter the segment values and compile the descriptive flexfield.
Use the Descriptive Flexfield Segments window.
See: Setting up Extra Information Types (Excluding Organization EITs), Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 54: Set Up Responsibility Access for Extra Information Types
EITs do not appear automatically in any responsibility. You must set up responsibility-level access for EITs. Alternatively, use CustomForm security to add individual EITs to a specific taskflow window. This level of security is usually defined later in the implementation when you need to restrict user access.
Note: This security does not apply to EITs on organizations.
Use the Information Types Security window.
See: Setting Up Extra Information Types against a Responsibility, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide.
Define EITs for Organization Optional Step s
EITs for organization classifications are set up differently from other EITs. When you define them you must also associate them with the classification of the organization. When a user selects the classification then the application displays the correct set of EITs.
Step 55: Define Organization Classification
Define a new organization classification if you want to group your EITs in this way. You do not need to do so if you intend to use an existing classification.
Tip: When you install Oracle HRMS you will find a predefined list of Organization Classifications. These values are defined for the Lookup Type ORG_CLASS, and provide options for all users of the Organization window.
You can disable the Lookup values you will not use in your implementation in the Application Utilities Lookups window.
Use the Application Utilities Lookups window.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 56: Set Up Extra Information Types for an Organization Classification
Define a new EIT and then enter a row into the HR_ORG_INFORMATION TYPES table. Then specify for which organization classifications this EIT is available.
See: Setting Up Extra Information Types for an Organization Classification, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
System Administration
These are tasks for your System Administrator.
Important: If you used the Configuration Workbench, you can skip these steps. The Workbench enables the currencies for the countries in which your enterprise operates, and creates a user called HRMS_USER for each business group.
Step 57: Enable Currencies
All major currencies are predefined with Oracle Applications. The codes used are the ISO standard codes for currencies. However, you must enable the specific currencies you want to use for your ledger currency, or for any compensation and benefit information.
The "ledger currency" is the default currency used by your business group.
Note: Oracle HRMS does not use extended precision. You can control the precision in any calculation using a formula.
Use the Currencies window
See: Enabling Currencies, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide.
Step 58: Define "View All" HRMS User Required Step
Before you can access any of the HRMS windows you must create a new Application User with access to one of the default Responsibilities supplied with the application.
Use the Users window.
See: Users Window, Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
Step 59: Define Lookup Types and Values Optional Step
Lookups supply many of the lists of values in Oracle HRMS. For example, both Title and Nationality in the Person window use Lookups.
You can add new Lookups Values at any time. You can set the Enable Flag for a Value to No, so that it will no longer appear in the list of values, or you can use the Start and End Dates to control when a value will appear in a list.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Enterprise and Workforce Management
Organization Structures
To begin modelling your enterprise, you set up the business groups, legal entities, and operating companies that comprise your organizational framework. You can define these organizations and locations yourself, or complete a configuration interview in the Configuration Workbench. The workbench creates the organizations and locations and places them in a hierarchy for you. The workbench creates a "View All" responsibility for each business group, and sets the required user profile options.
When the organizational framework is in place, you can extend it by creating additional internal and external organizations, and their locations, and by building the organizations into hierarchies.
If you use the Configuration Workbench, then you can skip steps 1, 2, and 3, although you can optionally perform step 2 to add user profile options to the responsibilities that the workbench creates. If you do not use the Configuration Workbench, then follow the steps below to configure your enterprise framework.
To find out what organization structures the workbench sets up see: Key Concepts for Representing Enterprises, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Note: If you are implementing the Oracle HRMS Multi-Tenant functionality, you must refer to the Oracle HRMS Multi-Tenant Functionality white paper on My Oracle Support, Note ID: 760500.1
Step 1: Set Up Your Business Groups Required Step
Use the predefined or seeded HR manager responsibility and the "Standard" Security Group selection. This gives you access to create your own business groups.
To find out how many business groups you require, see: Key Concepts for Representing Enterprises
Caution: When Oracle HR applications are installed they are 'always installed with ORGANIZATION_ID = 0 ' which is the 'Setup Business Group'. If the NAME of the 'Setup Business Group' is changed to a different value, the NAME value is changed back to 'Setup Business Group' value during an instance upgrade or during Oracle Human Resources patching. For additional information, refer to the following notes on My Oracle Support:
-
Setup Business Group Name Reverts Back To 'Setup Business Group' (Doc ID 815934.1)
-
Can Oracle Support Help Change the Name of the 'Setup Business Group'? (Doc ID 796593.1)
The Setup business group has a default legislation code of US and a default base currency of USD. If you intend to process payrolls in your business group, or you intend to implement legislation for another territory, then you must create a new business group with a valid legislation code and base currency. The system uses these values to copy in the predefined data it needs to comply with local legislative and processing requirements.
You cannot change these definitions after they have been saved.
-
Create a new Business Group.
See: Creating an Organization, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
-
Set up a responsibility for the business group in the Responsibilities window.
Step 2: Set User Profile Option Values for Responsibilities Required Step
Note: Use Standard HRMS security, rather than the Security Groups Enabled model during implementation. You can change to the Security Groups Enabled model later in your implementation. See: Security Models, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
Set the HR User Profile Options for any new responsibilities you create. You must set up the HR: User Type, HR: Security Profile and the HR: Business Group options, at responsibility level.
-
You can set also set up other User Profile Options for new responsibilities you created or the workbench generated.
See: System Profile Values Window, Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
See: User Profiles, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 3: Set Up Your Key Organization Structures Required Step
Create the legal entities and operating companies you require to represent your enterprise. The operating companies and legal entities are key organization structures that form your basic enterprise framework, to find out what they represent, see: Key Concepts for Representing Enterprises, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
To find out how many operating companies and legal entities you require, see: Configuration Models for Your Enterprise Framework
See: Setting up Organizations, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 4: Set Up Your Additional Organization Structures Optional Step
You can extend your basic enterprise structure by creating additional organizations and locations to represent internal divisions or departments, and external organizations for reporting or third-party payments.
See: Extending the Enterprise Framework, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
See: Setting Up Organizations, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
The Configuration Workbench creates legal entities for HR purposes only. If you want to integrate Oracle Payroll with Oracle Cash Management, see: the Oracle Cash Management User Guide
Step 5: Set Up Auto Orgs Optional Step
You can enable the automatic creation of HR organizations using the Auto Orgs functionality. If your enterprise has a close relationship between its financial structure and line management hierarchy, then this means you only have to maintain your financial structure in GL and the corresponding line manager hierarchy is automatically synchronized.
See: Implementing Automatic Company Cost Center Creation, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
For further information on setting up multiple organizations see Oracle Applications Multiple Organizations Implementation Guide.
Step 6: Define Organization Hierarchies Optional Step
You can represent your management or other reporting structures by arranging organizations into reporting hierarchies. An organization can belong to any number of hierarchies, but it can only appear once in any hierarchy.
Organization reporting lines change often and you can generate a new version of a hierarchy at any time with start and end dates. In this way, you can keep the history of your organizational changes, and you can also use this feature to help you plan future changes.
When you use DateTrack you see the "current" hierarchy for your effective date.
Important: Your primary reporting hierarchy will usually show your current management reporting structure. You can define other hierarchies for other reporting needs.
You can create organization hierarchies using the:
-
Organization Hierarchy Window
See: Creating Organization Hierarchies, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
-
Organization Hierarchy Diagrammers (they enable you to create your hierarchies graphically, and to make intuitive drag-and-drop changes).
See: Adding Organizations or Positions to a Hierarchy, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 7: Use Organization and Geographic Hierarchies for Calendar Events Optional Step
You use geographical and organizational hierarchies to identify the group of people you want a calendar event to apply. Calendar events represent important dates that affect the working time of your workforce such as a public holiday.
See: Setting Up Calendar Events, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
You can use organizational hierarchies when you define calendar events in your enterprise. If the calendar event applies to people in your organizations, you can select an organization hierarchy as the type of coverage for the event. For example, if you have a planned factory closure, you can define it as an organizational holiday and apply it to the factory organization in your hierarchy. The calendar event becomes applicable to the people in the factory organization who are scheduled to work at the time of the event.
See: Creating Organization Hierarchies, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
You use the geographical hierarchy as the type of coverage for calendar events that apply to a geographic entity, such as, a country, state, or region. For example, if you are an enterprise operating in multiple countries, you can define calendar events for the public holidays in those countries. The calendar event becomes applicable to people if they work in the country you include in the event.
See: Generic Hierarchies Overview, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Jobs
If you used the Configuration Workbench, you may already have loaded jobs from a spreadsheet in the Workbench. You can skip the Define Jobs step.
Step 8: Define Job Groups Optional Step
As part of a working relationship, a person can simultaneously perform a number of roles in addition to being an employee or contingent worker. These can range from initiatives defined by the enterprise, such as fire warden, to legislative defined roles such as Health and Safety Representative. In Oracle HRMS, these are know as supplementary roles. Supplementary roles are set up as jobs in the Job window
Each job is held in a Job Group. The Job Group is used to store jobs of a similar type together in one group. All standard jobs created in Oracle HRMS, that is, those jobs that define the role the person is employed to fulfil, must be stored in the default HR Job Group. This Job Group is automatically created for your business group.
If you want to set up supplementary roles you must set up additional job groups to store these roles.
Use the Job Groups window.
See: Creating a Job Group, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 9: Define Jobs Optional Step Optional Step
Jobs can be generic or specific roles within your enterprise. By definition they are independent of organization structures and are generally used where there is flexibility in working roles.
A "Job Name" is a unique combination of values in the segments of the job flexfield structure that you have linked to your business group.
As you define jobs add any additional information that is appropriate.
Note: If you are a German public sector type organization then you use jobs to enter functional descriptions for your work places.
See: Additional Implementation Steps for Germany
Use the Job window.
See: Defining a Job, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
See: Entering Additional Information about Jobs and Positions, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Positions
If you used the Configuration Workbench, you may already have loaded positions from a spreadsheet in the Workbench. You can skip the Define Positions step.
Note: If you are a German public sector type organization, then you do not use positions as described here.
Step 10: Define Position Hiring Statuses Optional Step
Each position must have a hiring status: Proposed, Active, Frozen, Eliminated or Deleted. You can create user names for these system hiring statuses, and define more than one user name for each system name, if required.
Use the User Types and Statuses window.
See: Defining Hiring Statuses, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 11: Define Positions Optional Step
In Oracle HRMS a position is a job within an organization. Positions are generally used where roles are fixed within a single organization. If you decide to use positions you may want to use jobs to identify the common job groups of individual positions.
A "Position Name" is a unique combination of values in the segments of the position flexfield structure that you have linked to your business group.
As you define positions add any additional information that is appropriate. To prevent position users from attaching a position to an existing control budget and entering budget data, set the form function parameter DISABLE_BUDGETS="Y" for the Position window (HRWSPSF).
HRMS provides Position Copy and Mass Position Update windows that enable you to automate the reorganization of your workforce. If you want to restrict the positions that appear in these windows to those falling within the user's security profile, you must attach secure versions of the forms to the menu. The secure versions of the function names are PQHWSCET1 (Position Copy) and PQHWSCET2 (Mass Position Update).
Use the Position window to define positions.
See: Defining a Position, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
See: Entering Additional Information about Jobs and Positions, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 12: Set Up the Synchronize Positions Process to Run Nightly Optional Step
Oracle HRMS uses the Synchronize Positions process to update the non-datetracked Positions table (PER_ALL_POSITIONS) with changes made to the datetracked table (HR_ALL_POSITIONS_F). When you run the process, any datetracked changes with an effective date on or before today are applied to the non-datetracked table. Hence, future dated changes are not applied until they become effective.
Running the Synchronize Positions process every night ensures that the system automatically updates the table with the position changes that become effective each day. If a power or computer failure disrupts this process, you can start it manually from the Submit a New Request window.
Warning: Ensure that the resubmission interval is set to run every night.
Use the Submit a New Request window.
See: Submitting a Request, Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Configuration
Step 13: Create a Position Hierarchy Optional Step
You can structure positions into hierarchies to show detailed position reporting structures. You can also use position hierarchies to define security profile groups within your enterprise, or to define career progression paths for positions.
You can create position hierarchies using the:
-
Position Hierarchy Window
See: Creating a Position Hierarchy, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
-
Position Hierarchy Diagrammers (they enable you to create your hierarchies graphically, and to make intuitive drag-and-drop changes).
See: Adding Organizations or Positions to a Hierarchy, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Define a Context for Mass Actions
The Contexts form determines what information you can view, enter, and change on the Mass Assignment Update and Position Copy forms. A predefined global Context form contains the default position and assignment attribution that appear on the forms. When you create a new Context, you can choose the attributes to display based on a user's Application, Legislation, and Responsibility.
Step 14: Set Up a New Context
Create a new context defining the Application, Legislation, and Responsibility. Define the attributes to include in the Display, Change List, and Criteria columns.
Use the Contexts window.
See: Defining a Context for Mass Actions, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
WorkFlow for Transactions
Define HRMS Roles
Step 15: Define Lookup Values for Role Types Optional Step
Define list of lookup values for Role Types: PQH_ROLE_TYPE.
Use the Applications Utilities Lookups window.
Step 16: Define HRMS Roles Optional Step
Define the HRMS roles that you are going to use in your enterprise for routing transactions and budget worksheets.
Use the Roles window.
See: Defining HRMS Roles for Transactions, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Set Up Workflow Routing for Transactions
Step 17: Define the Type of Routing Optional Step
When you set up workflow, you have a choice of how to route each transaction category (position transaction, budget worksheet, budget reallocation transaction). The routing types include:
-
routing list
-
position hierarchy
-
supervisory hierarchy
Choose one routing type for each transaction category.
Use the Transaction Type Wizard.
See: Transaction Type Wizard, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide .
Step 18: Define the Transaction Type Optional Step
Define the Post and Future update methods. Define the notification timeout.
Use the Transaction Type Wizard.
See: The Transaction Type Wizard, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide.
Step 19: Associate Roles with Users or Positions Optional Step
You associate roles to users, positions, or role templates, based on the routing type you selected for each transaction category.
-
Routing List
Assign role(s) to users, specifying the user's default role.
Use the Maintain Roles window.
See: Associating HRMS Roles with Users, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
-
Position hierarchy
Assign a role to each position in the position hierarchy.
Note: Before you can assign roles to the positions, you must define the positions and create a position hierarchy.
Use the Maintain Roles window.
See: Associating HRMS Roles with Positions, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
-
Supervisory hierarchy
Assign roles to users who initiate transactions or have transactions routed to them as supervisors.
Use the Roles window.
See: Associating HRMS Roles with Users, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 20: Define the Routing Sequence Optional Step
If you route transactions using:
-
Routing lists, create routing list(s) specifying the destinations on the list (roles and roles/users).
Use the Routing Lists window.
See: Defining Routing Lists for Transactions, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
-
Position hierarchies, include in the position hierarchy the users' primary assignment positions.
Use the Position Hierarchy window.
See: Creating Position Hierarchies, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
-
Supervisory hierarchy, verify that supervisors are entered in the Assignment window for those users who will initiate transactions or have transactions routed to them.
You don't define a supervisory hierarchy. When a user routes a transaction, the system automatically determines the user's supervisor (the one entered in the user's primary assignment) and routes to that person.
Use the Assignments window.
See: Entering an Assignment, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 21: Define Routing and Approval Rules Optional Step
You can define routing and approval rules that determine the routing sequence and identify valid approvers based on the values entered in the transaction.
Select attributes to use as the basis for defining the routing and approval rules, and then define the rules.
Use the Transaction Type Wizard.
See: Transaction Type Wizard, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide.
Set Up Transaction Templates and Associate with HRMS Roles
Step 22: Set up Role Templates Optional Step
Each role must have an associated role template which sets the maximum permissions for that role. The product includes a Basic Role template that you can assign to the roles you define in your organization. You have the option of defining new role templates and establishing permissions appropriate for each role.
Define role templates, specifying attributes as View or Edit.
Use the Roles window.
See: Setting Up Transaction Templates, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 23: Set Up Task Templates Optional Step
The product comes with two predefined task templates, a Create and Update template. You can define your own templates for those routine tasks where you wish to simplify or restrict data entry.
Define task templates, defining attributes as View, Edit, or Required.
Use the Templates window.
See: Setting Up Transaction Templates, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 24: Associate Roles and Templates Optional Step
Each role must have an associated template. You can assign each role the supplied Basic Role template or choose a role template that you have defined.
Use the Templates window.
See: Associating HRMS Roles with Transaction Templates, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Position Control
Step 25: Enable Position Control on Organizations Optional Step
Designate an organization hierarchy as the primary position control hierarchy. Designate the starting point (top node or subordinate level), and include/exclude subordinates (optional).
You can designate only one hierarchy for position control. Any versions you create of this hierarchy are also position controlled.
Note: Refer to Defining Budget Characteristics, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide for enabling position control on budgets for these organizations.
Use the Organization Hierarchy window.
See: Creating Organization Hierarchies, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 26: Configure Business Rules Optional Step
Review and where necessary configure the business rules (also called process rules) that validate assignment modifications, budgets, and budget reallocations. The predefined business rules are configured as warnings. You can change them to allow an action to proceed (ignore) or to prevent an action (error).
Use the Configurable Business Rules function.
See: Business Rules, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Evaluation Systems
Step 27: Define Evaluation Types Optional Step
With Oracle HRMS you can record summary evaluation information for Jobs, or Positions in the Evaluation window.
Define the name of your evaluation system as a value for the Lookup Type EVAL_SYSTEM.
To record detailed evaluation scores for the Hay System or any other system you can enable the Additional Evaluation Details descriptive flexfield to hold and validate this information.
You can also hold comment or review information for each evaluation you undertake.
Note: If you use more than one evaluation system you may want to define the segments as context sensitive to the System Name.
Use the Application Utilities Lookups window.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Human Resource Budgets
Step 28: Define and Initialize Budget Lookup Types and Values Optional Step
Oracle HRMS delivers the following seeded budget measurement units: Money, Hours, Headcount, Full Time Equivalent (FTE), and Percent Full Time Equivalent. You cannot extend the delivered budget measurement units, but you can copy and rename an existing measurement unit.
Define values for BUDGET_MEASUREMENT_TYPE.
Use the Application Utilities Lookups window.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
You can configure the application to recalculate and update Assignment Budget Values (ABV) for FTE automatically when determining factors (such as working hours or frequency) change. A related concurrent process (Calculate Assignment Budget Values) helps you initialize assignment records with budget values.
See: Recalculating Assignment Budget Values, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
See: Running the Calculate Assignment Budget Values Process, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 29: Define Period Types Optional Step
The most common period types are already predefined in Oracle HRMS. You can change the names of these predefined types but you cannot add any new types.
Use the Period Types window.
See: Renaming Period Types, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 30: Define Budgetary Calendars Optional Step
You use calendars to define the budget years for your staffing budgets.
Use the Budgetary Calendar window.
See: Defining Budgetary Calendars, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 31: Define Budget Sets Optional Step
A budget set is comprised of one or more elements. You define a budget set to record the money or hours or other budget measurement units in your budget. Oracle HRMS uses budget sets to track actual expenditures and commitments.
Use the Budget Set window.
See: Defining Budget Sets, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 32: Migrate an Existing Oracle HRMS Budget to the New Budget Tables Optional Step
If you created a budget in Oracle HRMS prior to Release 11i, you can use an existing budget as the basis for a new budget worksheet.
Run the Migrate Budget Data process from the Submit Requests window to migrate an existing budget to the new database tables for Budgets.
See: Migrating a Budget to Oracle HRMS, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 33: Set Up the HR Budget in Oracle General Ledger Optional Step
If you are transferring a budget from Oracle HRMS to Oracle General Ledger, you must first define the budget in Oracle General Ledger.
Use the Define Budget window in Oracle General Ledger to define the budget.
See: Setting Up an Oracle HRMS Budget for Transfer to Oracle General Ledger, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 34: Define Budget Characteristics Optional Step
You set up budget characteristics to define the Oracle HRMS work structure for which you are establishing a budget. The primary entities against which you can create a budget are job, position, grade, and organization. You can also create a budget for a combination of these entities.
Defining the characteristics of a budget also requires you to define the budget measurement units (Money or Headcount, for example). Optionally, you can select the elements that are used to process budget funding commitments during a budgetary period. For budgets that are transferred to Oracle General Ledger, you can map Oracle HRMS Costing Segments to GL Chart of Account Segments.
Use the Budget Characteristics window.
See: Defining Budget Characteristics, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Set Up Workflow for Budget Worksheets Optional Step s
If you use Oracle Workflow to delegate a budget worksheet through an organization hierarchy or to route a worksheet for approval, you must set up HRMS roles and routing for your budgeting personnel. A manager responsible for a budget can only delegate a budget worksheet to another manager in the organization hierarchy who has a valid HRMS role, and is a member of the applicable routing list or hierarchy.
Step 35: Define an Organization Hierarchy Optional Step
Create an organization hierarchy if needed. Organization hierarchies enable you to restrict the number of budget line items that appear in your budget, and delegate to other managers.
Use the Organization Hierarchy or the Global Organization Hierarchy window.
See: Creating Organization Hierarchies, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 36: Specify Starting Organization Optional Step
Specify the organization hierarchy and the organization within the hierarchy where the budget is effective. This action enables the budget in subordinate organizations as well.
Use the Budget Characteristics window.
See: Defining Budget Characteristics, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 37: Define HRMS Roles Optional Step
Define the roles that you are going to use in your enterprise for routing budget worksheets.
Use the Maintain Roles window.
See: Defining HRMS Roles for Transactions, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 38: Set Up Workflow Routing Optional Step
When you set up workflow, you have a choice of how to route each transaction type (position transaction, budget worksheet, budget reallocation transaction). The routing styles include:
-
routing list
-
position hierarchy
-
supervisory hierarchy
Choose one routing style for each transaction type.
Use the Transaction Type Wizard.
See: Transaction Type Wizard, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Person Types
Step 39: Define Person Types Required Step
You can define your own names to identify the "types" of people in your system.
Note: Person Type is a common option for Form Customization.
Use the Person Types window.
See: Defining Person Types, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Collective Agreements
A collective agreement is an agreement that defines the terms and conditions of employment for all employees that are covered by its terms. Agreements are typically negotiated and agreed by external bodies such as Trade Unions and Representatives of Employers.
Step 40: Setting Up Collective Agreements Optional Step
If your enterprise uses collective agreements, follow the steps in the referenced topic to enter a collective agreement, set up the eligibility criteria for the agreement, and to apply the values defined in the agreement to the eligible employees.
See: Setting Up a Collective Agreement, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Medical Assessments, Disabilities and Work Incidents
Step 41: Define Lookup Types and Values Optional Step
If you want to record medical assessments, disabilities, or work incidents for the people in your enterprise, you must define Lookup Values for the Lookup Types that are used in those windows.
See: User and Extensible Lookups, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Use the Application Utilities Lookups window.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 42: Set Up Checklist Templates Optional Step
If you want to use the Checklist functionality to automatically allocate checklists and tasks to people and assignments, you must first set up the checklist templates and tasks.
See: Checklists Overview, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Payroll Process Management
If you use Oracle Payroll, you must define payrolls and payment methods. You can also define these items for information and reporting in Oracle Human Resources.
You must include a payroll in the employee assignment before you can make nonrecurring entries to an element for an employee. Nonrecurring entries are only processed for one payroll period.
Define Payroll Information
Step 1: Define Payment Methods Optional Step
Standard categories of payment methods such as Direct Deposit are predefined with your system. You can define your own names for each of these methods, and if you have installed Oracle Payroll you can also use these methods to control payments to your employees.
When you define your payment method you can specify how you want to handle costing of payments. At implementation time you can choose whether your payment method should cost:
-
Cleared payments only
-
Uncleared payments only
-
A combination of cleared and uncleared payments
You enter this information in the Costing tab for your payment method. If the Costing tab is not enabled you can enable it by doing each of the following:
-
Update the PAY_LEGISLATIVE_FIELD_INFO table with the following entries
-
rule_mode = 'Y'
-
validation_type = 'TAB_PAGE_PROPERTY'
-
validation_name = 'DISPLAY'
-
field_name = 'COSTING_TAB'
-
target_list_item = 'PAYWSDPM'
-
legislation_code = 'LEGISLATION_CODE'
-
-
Add the Costing of Payment concurrent program (PAYMCOSTING) to your request set.
When you define your payment method, you can also specify whether you want costs to be transferred to General Ledger on completion of the Costing process.
Important: If you are defining payment methods for a European country that has adopted the Euro, we strongly recommend that you select the Euro payment methods provided.
Use the Organizational Payment Method window.
See: Defining a Payment Method, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 2: Define Consolidation Sets Optional Step
When you define your business group the system automatically generates a default Consolidation Set. If you have not installed Oracle Payroll you can skip this step.
Oracle Payroll uses consolidation sets to gather the results from different payroll runs into a single set for reporting or transfer to other systems. You can define any number of additional consolidation sets.
Use the Consolidation Sets window.
See: Defining Consolidation Sets, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 3: Define Payrolls Optional Step
You define your own payroll groups to meet your business needs for processing and payment. For example, you may have a monthly and a weekly payroll but you might want to manage and process your weekly payroll by plant location. In this case you could define one monthly payroll and two weekly payrolls, one for each plant.
Note: The payroll calendar is different from the budgetary calendar in Oracle HR. You define your budgetary calendar for headcount or staffing budgets.
Use the Payroll window.
See: Defining a Payroll, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 4: Set Up Payslip Information and Generate Payslips Optional Step
You can set up information to appear on your payslips, and generate a printed or online version for your employees.
See :Setting Up Payslip Information and Generating Payslips, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 5: Set up Element Set for Employee Claims Optional Step
Perform the following steps to enable employees to make claims using the self-service interface:
-
Create an element set with the elements for which you want to make a claim.
See: Defining an Element or Distribution Set, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
-
Associate the element set at the HR Organization level to enable the elements to appear in the Employee Claims interface.
See: Entering the Claims Element Set Information, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
-
Enter the claim details using the self service interface.
See: Employee Claims, Oracle E-Business Suite Self-Service Human Resources Deploy
Compensation, Benefits, and Payroll
Follow the implementation steps in this section to set up your compensation and benefits plans, including grade/step progression schemes and absence plans. This section includes the following implementation areas:
-
Grade Related Information: Set up grades to record the relative status of employee assignments
-
Elements: Define elements to represent a variety of earnings and deductions, as well as other employer liabilities
-
Salary Administration: Manage the basic remuneration that employees receive
-
Compensation Awards: Distribute one-time and recurring awards, such as stock options and bonuses, or set up voluntary employee contribution plans
-
Benefits: Set up health and welfare offerings
-
Additional Setup for Payroll Processing: If you use Oracle Payroll, you can set up user defined balances and write Payroll Formulas for elements that you process in payroll runs
-
Leave and Absence Management: Set up paid time off schemes to administer the vacation or sick leave rules of your enterprise
-
Statutory Absence Payments Setup (UK Only): Manage statutory absence payments according to legislative requirements
-
Element Sets and Batch Control Totals: Group elements together to restrict processing; set up batch controls to calculate numerical input values with Batch Element Entry
If you plan to load details of employee entry history you should consider using a fixed date, such as 01-JAN-1951, as a default for your initial setup definitions. This will simplify your data-entry.
Grade Related Information
Step 1: Define Grades Optional Step
Grades show the relative status of employees within an enterprise. Many enterprises use grades as the basis for eligibility to compensation and benefits.
The Grade Name is a unique combination of values in the segments of the grade flexfield structure that you have linked to your business group.
Use the Grades window.
See: Defining a Grade, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 2: Define Valid Grades for Jobs or Positions Optional Step
You can define Valid Grades for jobs or positions. Oracle HRMS checks that you assign employees to valid grades for their jobs or positions.
Use the Valid Grades window.
See: Entering Valid Grades for Jobs or Positions, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 3: Define Grade Rates Optional Step
You can use grade rates to show valid rates of pay for each grade. You can express the rate of pay as a fixed value, or a range of values.
When you define a grade rate you are setting up a table of values. You can use these values with an employee's grade to control, or compare, the salary of the employee.
-
You can use grade rate values in Element Input Validation formulas to validate the element entry values given to employees.
-
Oracle HRMS uses grade rates to calculate comparatio values in the View Employee Grade Comparatio window and in the Salary Administration window for salary validation.
Use the Grade Rate window.
See: Defining a Grade Rate, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Set Up Grade/Step Progression Optional Step s
If you want to relate pay to grades indirectly through a pay scale, you have a choice:
-
Use Grade/Step Progression if you want to progress large numbers of employees automatically from one grade, or grade step, to the next on a grade ladder. You can define progression rules for each grade ladder. You can also use criteria salary rates to vary employee pay depending on other details of their assignment, such as job, location, or bargaining unit. This approach is common in public sector enterprises and in highly-regulated organizations such as retail or those subject to collective bargaining.
-
Use Pay Scales and Scale Rates if you want to progress employees manually or using a process that supports a limited range of criteria for selecting the assignments to progress. Unlike Grade/Step Progression, this approach cannot automatically maintain salary values using element entries. To use this approach, skip this section and go to: Set Up Pay Scales, Scale Rates, and Grade Scales.
Step 4: Set Up and Activate Grade Ladder Optional Step
Set up the grade ladder, adding grades and steps to it and defining rules for progression and salary update.
Use the Total Compensation Setup Wizard.
See: Setting Up a Grade Ladder, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Set Up Pay Scales, Scale Rates, and Grade Scales Optional Step s
Follow these steps if you are not using Grade/Step Progression and you want to relate pay to grades indirectly using a pay scale.
Step 5: Define Pay Scales Optional Step
Pay scales are used commonly in government and regulated or unionized enterprises where actual values of pay are defined as a "pay scale", a "schedule", or a "spine".
In this environment it is common to find an automatic incrementing of employee pay based on length of service or on a fixed date. When you define the Pay Scale you define the points in the incrementing sequence you want to use.
A predefined incrementing process is supplied with Oracle HRMS. This will automatically increment step and point values for employees using a fixed date. You can specify the number of steps that you want a person to be incremented, on a specified pay scale.
Note: You can modify the process to meet your specific business rules for incrementing.
Use the Pay Scale window.
See: Defining a Pay Scale, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 6: Define Scale Rates Optional Step
You define a scale rate for each type of pay, such as salary, shift allowance, and overtime. You enter a value for each point on the pay scale. These values are datetracked.
Use the Scale Rate window.
See: Defining Scale Rates, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 7: Relate Grades to Progression Points Optional Step
Define the points from the pay scale that are valid for each grade as a numeric sequence of steps.
The auto-incrementing process uses these steps to increment an employee's grade point up to a ceiling that you can define for the grade.
Use the Grade Scale window.
See: Relating Grades to Progression Points, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Elements
Before you define any elements, you should make all of your decisions about the definitions and rules for eligibility. Review the template earnings and deductions available in the template library in Configuration Workbench for your localization. You may be able to use these elements as supplied or as a starting point for your own definitions. In some localizations you also have the option of generating certain earnings and deductions using the Element Design Wizard or template windows.
Define Input Value Validation Optional Step s
Step 8: Define Lookup Types and Values Optional Step
You define new Lookup Types to create additional lists of values to validate any element input value with a character datatype.
Note: You can also use Lookup Types to validate a flexfield segment. Use the Table Validation option for the Value Set and use the Lookups table as the source of your list.
You can add new Lookup Values at any time. You can set the Enable Flag for a Value to No, so that it will no longer appear in the list of values, or you can use the Start and End Dates to control when a value will appear in a list.
Use the Application Utilities Lookups window.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 9: Define User Tables Optional Step
With Oracle HRMS you can set up any number of User-Defined Tables. A user-defined table is a "matrix" of columns that hold different values for the same row. You can access this information using the GET_TABLE_VALUE function in any formula.
For example, you may want to set up a single table to hold union pay rates, deductions, and benefit levels for different job groups. Use the rows to hold "Job Group" and the columns to hold the specific values for each job group.
You can define exact row values or an inclusive range of values.
Use the Table Structure window.
See: Setting Up User Tables, Columns and Rows: , Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 10: Define Table Values Optional Step
You now need to define the table values.
Use the Table Values window.
See: Entering Table Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 11: Define Element Validation Formulas Optional Step
When you define input values you can use a formula to validate any entry to that input value.
Important: You must define the formula before you define the element input value. The type of formula is Element Input Validation.
Use the Formula window.
See: Writing Formulas for Validation, Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
Define Earnings, Deductions, and Other Elements Optional Step s
Step 12: Define Event Groups for Proration Optional Step
Perform this step if proration is enabled for your legislation, and you want earnings to be prorated when there are relevant changes to assignments and rates mid-period. The Event Group is a collection of events that trigger proration for one or more elements.
Important: You must create the Event Groups before you can create proration elements.
Use the Event Group window.
See: Defining Event Groups, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
For the complete proration setup process, see Setting Up Proration, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
Step 13: Define Elements and Input Values Optional Step
Elements are the basic components of all compensation and benefit types. You can also use elements to represent tangible items distributed to employees, such as tools or safety equipment.
Use the Element window.
See: Defining an Element, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
Note: UK Users: Oracle HRMS supplies templates for generating elements, formulas, and balances for certain earnings and deductions. Use the template windows or pages, rather than the Element window, Formula window, and Balance window to set up these earnings and deductions.
See: Setting Up Pension Schemes, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
See: Setting Up Vehicle Mileage Processing, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
See: Setting Up Union Deductions, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
See: Setting Up Professional Body Subscriptions, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Netherlands Users: Use the Pensions pages, rather than the Element window, Formula window, and Balance window to set up deductions for pensions and savings schemes.
See: Setting Up Pension Schemes, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Note: UK Users: If you want to calculate payments at the rate that existed when the work was done--rather than at current rates--enter extra information for your elements using the Element Attribution Information and Rate Type Information EITs.
See: Setting Up Historic Rates, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 14: Define Element Links Optional Step
You can give an entry to an employee only when they are eligible for that element. Employees are eligible for an element when their assignment details match the link details.
You can link an element to any combination of organization, group, grade, job, position, payroll, location, employment category or salary basis.
Use the Element Link window.
See: Defining Element Links, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 15: Activate Predefined Elements Optional Step
When you install Oracle HRMS a number of predefined elements are installed. These elements represent the legislative deductions that are processed in the payroll run.
If you have installed Oracle Payroll you will also have all of the formulas and balances you need for processing these deductions. If you have not installed Oracle Payroll, you can still use these elements to record information for transfer to your own payroll system.
To activate these predefined elements you need only define links for them.
Use the Element Link window.
See: Defining Element Links, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Note: UK Implementations only
Examples of elements representing legislative deductions in the UK are: PAYE, NI, PAYE, Court Orders, EAS Court Order (only applies in Scotland) and CMA Court Order (only applies in Scotland).
If you are a UK implementation and you want to use the employee Tax window to enter PAYE and NI details you should define a "Standard" link to all Payrolls for both the PAYE and NI elements.
When you define links for the PAYE and NI elements, specify some default input values. We suggest you use the following defaults:
-
Tax Code "BR"
-
Tax Basis "Cumulative"
-
NI Category "A" or "D" (Use category D if the majority of your employees are enrolled in a company pension scheme.)
Salary Administration
Use the Salary Administration function to manage basic remuneration for individual employees.
Step 16: Create or Decide on Salary Elements Optional Step
You need at least one salary element for each salary basis in your enterprise.
If predefined elements exist in your localization, you might decide to use these. If your localization does not include predefined elements, or if the predefined elements are insufficient or inappropriate, you must create new elements to store the salary value.
Note: Consider how many different elements you will need to define for the different salary bases you want to manage. Remember that you can administer the salary on an annual basis but store the value as a monthly value.
Use the Element window.
See: Creating a Salary Element, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 17: Decide How To Validate Salary Entries Optional Step
You can validate salary entries in one of two ways:
-
Warn users when they enter a salary proposal that is outside a valid range defined for an employee's grade. This approach uses grade rate ranges.
-
Prevent users from approving a salary that is outside a valid range, or that fails validation performed by a formula. Notice that this validation is not performed until you try to approve a salary proposal. This approach uses element input value validation.
See: Validating Salary Entries, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 18: Link the Salary Element Optional Step
Link the salary elements to components of employee assignments to establish employee eligibility for the elements.
Use the Element Link window.
See: Linking the Salary Element, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 19: Define a Salary Basis Optional Step
Define a salary basis for each salary element to be used for salary administration. This establishes the duration for which a salary is quoted, for example, hourly, monthly or annually.
Use the Salary Basis window.
See: Defining a Salary Basis, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 20: Review or Create Salary Components Optional Step
Review the salary components predefined as values for the Lookup Type PROPOSAL_REASON. If necessary, create your own salary components.
If you want your new components to be displayed in the Salary Management folder, you must also change a view.
See: Creating Salary Components, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Use the Application Utilities Lookups window.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 21: Define Performance Rating Types Optional Step
If you want to record performance ratings such as Outstanding, Superior and Average, enter them in the Application Utilities Lookups window for the Lookup Type PERFORMANCE_RATING.
Use the Application Utilities Lookups window.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 22: Add the Salary Administration Approve Function Optional Step
Add the function "Salary Administration Approve" to the menu of responsibilities that should be able to approve salary proposals.
Note: If this function does not exist for a Responsibility then a user can enter but not approve salary proposals.
Use the Menus window.
See: Defining Menus, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 23: Set Up Rate By Criteria Optional Step
To pay employees at varying rates according to a range of eligibility criteria, you must set up Rate By Criteria (RBC), including these three areas:
-
Create your own eligibility criteria (optional for RBC)
-
Define criteria rates
-
Create a rate matrix
See: Setting Up a Rate Matrix, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Compensation Awards
If you use SSHR, you can set up compensation plans to enable line managers to allocate compensation awards to the individuals who report to them. You can also set up plans to enable employees to enter voluntary contributions, such as savings plans, charitable organizations, and company perquisites.
Important: If you are licensed to use Compensation Workbench, you must set the HR: Self Service HR Licensed profile option to 'Yes' to avoid this error: 'You do not have permission to use this product', when attempting to use Compensation Workbench.
Step 24: Set Up Compensation Workbench Plans Optional Step
You can create multiple compensation plans to handle different compensation types--such as salary, stock, and bonuses--separately, or you can create a single plan and define each compensation type as an option so that managers allocate all the awards from the same worksheet. Alternatively, you can use options to identify different components of awards (such as merit or cost of living). If you operate across multiple business groups, you can link local plans to a global plan so that you can make a single budget allocation for a compensation type across your enterprise. To review the plan design options, see: Plan Design for Compensation Workbench, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
For the Compensation Workbench setup steps, see: Setting Up Compensation Workbench Plans, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
Step 25: Set Up Individual Compensation Distribution Plans Optional Step
Define Individual Compensation Distribution plans for any one-time or recurring awards, bonuses, and allowances that you want managers to allocate to employees through SSHR. If your enterprise offers a charitable contribution plan or a savings bond plan to which employees contribute at their own discretion, set up an ICD plan so that employees can enter their voluntary contributions through SSHR.
See: Setting Up Individual Compensation Distributions (ICD), Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
Benefits
This sequence of setup steps for Benefits assumes you are using the Total Compensation Setup Wizard, which is the recommended approach. If you prefer to set up your plan design using individual windows, follow the steps in Benefits Implementation Without Total Compensation Setup Wizard , Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guidethen skip to Additional Setup for Payroll Processing.
Total Compensation Setup Wizard is a guided configuration tool that provides a fast and easy way to set up compensation objects and other plan design data. You can rapidly implement flex and non-flex programs that include health and welfare plans, life insurance plans, and plans of other common plan types funded by employee and employer contributions. Advanced Benefit users may also configure default and life event-based enrollments. The Wizard also helps you to convert current enrollments from legacy and third-party systems.
You currently cannot use the Wizard to set up flex credits, premiums, communications, and primary care providers; there are separate windows to set these up. Similarly, if you require flexfields for your benefit plans, you must set these up in other windows. Some implementation steps are only relevant if you use Oracle Advanced Benefits. These implementation steps are indicated.
You can use the Plan Copy feature to copy programs and plans to provide a starting point for similar plans.
Step 26: Set Up the Base Plan Design Using the Total Compensation Setup Wizard Required Step
The Total Compensation Setup Wizard provides a step-by-step process for creating Health and Welfare programs and the business processing rules you associate with them. The Wizard guides you through the setup process, reducing the likelihood of implementation errors.
Your base plan design includes compensation objects (programs, plan types, plans, and options), enrollment periods, eligibility profiles, life event reasons, default enrollments, and activity rates. You complete the other components of your plan design using the relevant windows as described in the following steps.
See: Total Compensation Setup Wizard, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 27: Define Collapsing Life Event Reasons (OAB) Optional Step
You create a collapsing life event definition for those instances when a combination of two or more detected life events results in either a different life event or the voiding of the detected events.
Use the Collapsing Rules window.
See: Defining a Collapsing Life Event (Advanced Benefits), Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 28: Convert Current Enrollments Optional Step
You can use Total Compensation Setup Wizard to convert benefits enrollments from third-party and legacy systems.
See: Converting Benefits Enrollments
Action Items and Certifications (Advanced Benefits) Optional Step s
You can set up any certifications that a benefits participant must provide to satisfy the enrollment requirements for a compensation object. When a participant fails to provide the required certification, the application suspends the election pending the completion of the action item.
Step 29: Set Up Certifications for Compensation Objects Optional Step
Typical certifications include date of birth and proof of good health.
Use the Certifications window.
See: Defining Certifications for Enrollment in a Plan, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 30: Define Action Item Due Dates Optional Step
As part of implementation, you define the required completion date of each action item.
Use the Action Types window.
See: Defining an Action Item Due Date, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Actual Premiums Optional Step s
A premium is the amount paid by a plan sponsor to the supplier of the benefit. Typically, you calculate premiums on a per-participant basis, but the application also supports premium calculation based on total enrolled participants and total volume of elected coverage.
Step 31: Calculate Actual Premium Costs Optional Step
You maintain the criteria that the Premium Calculation Process uses to calculate the actual premium cost that a plan sponsor owes to a benefits supplier.
Use the Actual Premiums window.
See: Defining an Actual Premium, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Flex Credit Calculations (Advanced Benefits) Optional Step s
Step 32: Define Characteristics of Benefit Pools Optional Step
You define benefit pools to limit how a participant can spend flex credits and how excess flex credits can be rolled over, distributed as cash, or forfeited.
Use the Benefit Pools window.
See: Defining the General Characteristics of a Benefits Pool, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 33: Define Flex Credits Optional Step
You define a flex credit calculation and link the calculation with a compensation object. The compensation object to which you link a flex credit calculation must be part of a program regardless of the level at which you define flex credits.
Use the Flex Credit Definitions window.
See: Defining Flex Credits, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Additional Setup for Health and Welfare Optional Step s
Step 34: Define Reporting Groups Optional Step
You can define a reporting group that you link to one or more programs and plans. When you run a report for a reporting group, the report results are based on the programs and plans that you include in the reporting group.
You can also define the regulatory bodies and regulations govern a reporting group.
Use the Reporting Groups window.
See: Defining a Reporting Group, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 35: Define Reimbursable Goods and Service Types Optional Step
Define goods and services that you approve for reimbursement. You then associate one or more goods and services types with a reimbursement plan.
Use the Goods and Services window.
See: Defining Reimbursable Goods and Service Types, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 36: Define Reimbursement Plans Optional Step
Use reimbursement plans to define goods and services that eligible participants may purchase. The participant can submit a reimbursement claim for the cost of the good or service that was purchased out-of-pocket.
Use the Plan Reimbursement window.
See: Defining a Reimbursement Plan, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 37: Define Communications Optional Step
You define the communications you send to employees and other potential participants. You specify the conditions that trigger a communication and the delivery method and medium.
Use the Communication Types window.
See: Defining Communication Types, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 38: Define Benefit Balances Optional Step
Benefit balances are useful for transitioning legacy system data to Oracle HRMS. You define a benefit balance type and then assign a value to that type for a given person using the Person Benefit Balances window.
Use the Benefit Balances window.
See: Defining a Benefit Balance, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 39: Maintain Desktop Activities List Optional Step
The Maintain Online Activities window lets you define the functions and windows that are available from the Desktop Activities list of the Online Benefits Services windows.
Use the Maintain Online Activities window.
See: Maintaining Online Activities, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 40: Maintain Pop Up Messages Optional Step
You can configure messages to display in the Online Benefit Services window based on user events that you define. You create the message text in the Messages window
Use the Maintain Pop Up Messages window.
See: Maintaining Pop Up Messages, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 41: Set Up Primary Care Provider Access Optional Step
You can define restrictions on the selection of a primary care provider and set high-level configuration options for web-based PCP database searches through Oracle Self-Service Benefits.
Use the Maintain Plan Primary Care Providers window.
See: Maintaining Primary Care Providers for a Plan, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Additional Setup for Payroll Processing
These windows are available in your menus only if you are using a responsibility that includes Oracle Payroll. If you have not installed Oracle Payroll, skip these steps and go to the next section.
If you are using template earnings and deductions from the template library in Configuration Workbench, or if you generated your earnings and deductions using the Element Design Wizard or template windows, the required balances, formulas, and formulas result rules are already available for your elements. However you can follow these steps to review the generated components and ensure that they fully meet your needs.
Step 42: Define User Balances Required Step
Important: Oracle Payroll has many predefined balances installed with the system to support all your legislative requirements for calculation of gross to net balances. To protect the integrity of the payroll processes you cannot change any of these balances.
You can define other balances. For example, you might want to define a special balance to calculate a "Stop Rule" on a recurring deduction. You might also need to define a special balance for calculating retroactive payments.
When you define a payroll balance you must specify the feeds and the dimensions.
Use the Balance window.
See: Defining User Balances, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 43: Write Payroll Formulas Required Step
You write the formula for every element that you want to process in a payroll run. The formula type is "Oracle Payroll".
Warning: Remember that formula definitions are datetracked. After you have used a formula in a payroll calculation you should always update any changes to the formula.
This will keep the history of formulas for any re-calculation of retrospective earnings or deductions.
Use the Formula window.
See: Writing Payroll Formulas for Elements, Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
Step 44: Define Formula Result Rules Required Step
When you process an element in a payroll run the system will calculate the results using a formula. The results of the formula are the values you include in the Return statement to end the formula. The result rules define what will happen to each of the results produced by the formula.
You can calculate any number of different results in a single formula. The different types of result are:
-
Direct
-
Indirect
-
Message
-
Order Indirect
-
Stop Recurring
-
Update Recurring
There is normally at least one Direct result of a payroll calculation, which provides the Pay Value of the entry. You can create additional direct results.
Warning: If you allow users to enter the Pay Value of any earnings or deduction type, this value will override any formula calculation to provide the direct result for payment.
Use the Formula Result Rules window.
See: Defining Formula Processing and Result Rules, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Leave and Absence Management
You can set up as many plans as you need to permit employees to accrue PTO to use for vacation or sick leave. Each plan has the units of Hours or Days, and can have its own rules regarding accrual frequency, accrual bands, ceilings, carryover, start dates, entitlement of employees with different assignment statuses, and so on.
Set Up Absence Management
Step 45: Set Up Proration and Notifications Optional Step
If you want to associate recurring elements with absence types, you must set up proration and retro notifications. This ensures that absences that end in the middle of a payroll period are detected and processed by the payroll run, and that retrospective changes to absences are recorded in the Retro Notifications report.
Note: Proration is available to Oracle Payroll users in selected localizations only.
See: Setting Up Absence Management, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 46: Define an Absence Element Optional Step
For each of your accrual plans, or each type of absence you are tracking, you define a nonrecurring element and input value to hold the actual time taken for vacation or sick leave.
If you use Oracle Payroll and the proration functionality is available for your localization, you can use a recurring element instead. This enables you to begin processing a long term absence before you enter an end date, and to apportion time correctly over payroll periods.
Use the Element window.
See: Defining and Linking an Absence Element, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 47: Link the Absence Element Optional Step
Link each absence element to define who is eligible to take this kind of absence.
Use the Element Link window.
See: Defining Element Links, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 48: Define Categories of Absence Types Optional Step
Define categories of absence types as values for the Lookup Type ABSENCE_CATEGORY, and your absence reasons as values for the Lookup Type ABSENCE_REASON.
Use the Application Utilities Lookups window.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 49: Define Absence Types and Associate with Absence Elements Optional Step
If you expect to record absent time using the Absence Detail window, define absence types, associating each with an absence element.
Use the Absence Attendance Type window.
See: Defining an Absence Type, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 50: Make Initial Element Entries Optional Step
For an absence type with a decreasing balance, use the Element Entries window or the Element Entry API to make initial element entries for employees eligible for the type. You can also initialize a decreasing balance by entering a negative value using BEE. For example, if you enter -16 hours using BEE, a decreasing balance starts at 16 hours. However, be aware that using BEE creates an absence record that will show on employees' absence history.
If you want to make batch entries, see Making Batch Element Entries Using BEE, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide.
Step 51: Create Payroll Formula to Calculate Absence Duration Optional Step
If you defined a recurring element, create a payroll formula that handles proration to process the element and calculate the appropriate absence duration in each pay period (taking into account the number of days or hours in a month, working and shift patterns, public holidays, and so on).
See: Sample Payroll Formulas Enabled for Proration, Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
Step 52: Set Up Automatic Absence Duration Calculation Optional Step
If you want the application to automatically calculate the duration of an absence, then you can either set up schedules and calendar events or create a basic formula.
Define schedules and calendar events that are relevant to your enterprise and assign them to various levels in your work structures. The application uses the worker's schedule assigned to their primary assignment and their applicable calendar events to determine the duration of the absence. This ensures the people in your enterprise inherit work schedule information and the application can use this information to calculate the absence duration.
See: Setting Up Availability, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
If you do not want the application to use the schedules and calendar events information to calculate absence duration, then you can write a formula to calculate absence duration from the absence start and end dates, and set the profile option HR: Absence Duration Auto Overwrite to Yes.
See: Writing Formulas to Calculate Absence Duration, Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
Set Up Accrual Plans
After completing the absence management setup steps, follow these additional steps to set up a PTO accrual plan:
Step 53: Define New Accrual Start Rules Optional Step
There are three seeded start rules: Hire Date, Beginning of Calendar Year, and Six Months After Hire Date. If you need other rules, define them as values for the Lookup Type US_ACCRUAL_START_TYPE.
Use the Application Utilities Lookups window.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 54: Decide on Accrual and Carry Over Formulas Optional Step
Decide which Accrual and Carry Over formulas to use. You can use the seeded formulas, configure them, or write your own.
Use the Formula window.
See: Writing Formulas for Accrual Plans, Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
Step 55: Write Ineligibility Formula Optional Step
If your Accrual formula defines a period of ineligibility and you want to use Batch Element Entry (BEE) to enter absences against the accrual plan, define an Ineligibility formula. BEE calls this formula to check whether an employee is eligible to use accrued PTO.
Note: If you use the seeded Accrual formulas, you do not need to define an Ineligibility formula. They use a period of ineligibility entered on the Accrual Plan form, and BEE validation can use the same value.
Use the Formula window.
See: Writing Formulas for Accrual Plans, Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
Step 56: Define New Accrual Categories Optional Step
There are several seeded accrual categories. If you need additional categories, define them as values for the Lookup Type US_PTO_ACCRUAL.
Use the Application Utilities Lookups window.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 57: Select PTO Balance Type Optional Step
Oracle Payroll users: If you want to use a payroll balance to store gross accruals, decide whether the payroll run should update accruals as of the run's date earned (the date the payroll run uses to determine which element entries to process) or date paid (the date that appears on pay advices). Select your choice for the business group.
See: Business Groups: Selecting a PTO Balance Type, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 58: Create Balance Dimensions Optional Step
Oracle Payroll users: If you want to use a payroll balance to store gross accruals, consider whether you need to define a new balance dimension. Dimensions are predefined that reset the balance each year on 1 January, 1 June, or hire date anniversary. If you require your balance to accumulate over a different period of time, or reset at a different date, you must create your own balance dimension.
See: Balances in Oracle Payroll
Step 59: Define a PTO Accrual Plan Optional Step
Define the accrual plan, selecting the formulas and absence element it is to use.
Use the Accrual Plan window.
See: Defining a PTO Accrual Plan, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 60: Set Up Length of Service Bands Optional Step
Optionally, set up length of service bands for the plan.
Use the Accrual Bands window.
See: Setting Up Length of Service Bands, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 61: Review the Net Calculation Rules Optional Step
Review the net calculation rules for the plan. If necessary, create additional elements and associate them with the plan by selecting them in the Net Calculation Rules window.
See: Changing Net Accrual Calculations, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Statutory Absence Payments Setup (UK Only)
This section details the implementation steps you should perform to set up the Statutory Absence Payments feature, in the sequence that you should follow.
Statutory Absence Payments is a feature available to the UK users of Oracle HRMS. It offers you a flexible way of meeting your statutory absence payment obligations.
Basic Implementation Setup
As part of the basic implementation setup you need to perform the administration steps such as defining the appropriate Lookup values and descriptive flexfields relevant to the Statutory Absence Payments feature. These are usually performed by the System Administrator. Sign on to the system using your System Administrator username and password. Contact your DBA if you do not know this information.
See: Administration Implementation Steps for Oracle HRMS
You also need to perform the required Reporting, Security and Audit Setup to give your users appropriate access to the Statutory Absence Payment reports and functions and to audit the actions of your users
See: HR Information Systems Implementation Steps for Oracle HRMS
Step 62: Define Setup Menu
Oracle HRMS is supplied with a predefined menu that includes the specific functions for Statutory Absence Payments.
To implement this feature, you need to incorporate the predefined Statutory Absence Payments menu to an existing HR or Payroll responsibility so you can access the other specific HR and Payroll functions required to set up Statutory Absence Payments. At a later stage in the implementation, you need to define menus for your system users.
Note: After you have completed this step you can sign on and use the new menu to begin implementing Statutory Absence Payments. Where you need to change responsibility, instructions are given.
Use the Menus window.
See: Defining Menus, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Note: To add the predefined SSP menu to an existing HR or Payroll menu, in the Menus window select SSP Top in the Submenu field. You can enter a user-friendly, intuitive prompt your menu displays for this function, such as Statutory Absence Payments. You see this menu prompt in the hierarchy list of the Navigator window.
Basic SSP Setup
Step 63: Define Sickness Control Rule
You define a sickness control rule to specify whether employees must submit sickness evidence when they report a sickness absence. If your business rules specify that users must submit incapacity evidence, the application creates a stoppage for SSP payments automatically if sickness or incapacity evidence is not entered for a sickness absence.
Select the Business Group for your organization. Choose the Others button, select Sickness Control Rules and Select Yes or No in the Incapacity Evidence Required field.
Use the Organization window.
See: Business Groups: Entering Sickness Control Rules, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide.
Step 64: Define Time Units for SSP Qualifying Patterns
Qualifying days are the only days for which SSP can be paid. You define SSP qualifying patterns for all the employees in your company, so that qualifying days can be distinguished from non-qualifying days and their entitlements to SSP can be calculated.
You need to define all the component time periods you want to use for SSP qualifying patterns.
Use the Pattern Time Units window.
See: Defining Pattern Time Units, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 65: Define SSP Qualifying Patterns
The qualifying pattern is used to specify the sequence of Time Units. Each pattern represents a sequence of days which are qualifying or non-qualifying for SSP. For example, 1 non-qualifying day followed by 5 qualifying days and another single qualifying day would represent Sunday, the 5 week days and Saturday.
You need to name and define all the possible qualifying day patterns that have been agreed for use.
The most commonly used pattern should be assigned to the Business Group as the default, which can be overridden for individual employees.
Use the Patterns window.
See: Creating a Pattern, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 66: Define Links for Predefined SSP Elements
There are two predefined SSP elements. For more information about these, refer to Statutory Sick Pay Elements, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide. To activate the predefined SSP elements you need only define eligibility rules for them. This will link them to groups of employees.
Use the Element Link window.
See: Defining Element Links, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
Step 67: Define Sickness Absence Types
You can define all of the absence types your enterprise requires for recording and analyzing sickness absences.
Use the Absence Attendance Type window.
-
If you want to show running totals for absences, associate the absence types with a sickness balance element.
-
If you want to set up a PTO accrual plan for sickness absences, associate the absence types with a plan.
Important: Make sure that the Category is Sickness when you define the absence type. SSP only applies to this category of absence types.
See: Defining an Absence Type, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
Process SSP Payments Setup
Refer to Setup to Process Payments for SSP, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide for an overview of processing SSP payments.
Step 68: Define Additional SSP Elements
You can define additional SSP elements to hold the formula results from processing the Statutory Sick Pay element.
If you need to maintain the SSP Total balance, you should define an SSP Total element. You can report on the SSP Total balance element at the year end. This non-payment element will be fed an indirect result from the SSP element and pass that value to the SSP Total balance.
If you also want to pay SSP you need to define an SSP Paid element, with a Pay Value. You can feed this element as an indirect result from the Statutory Sick Pay element via a formula, or you can process this element separately in a payroll run, depending on your own business needs.
-
SSP payment elements are used for the payment, offsetting and costing of SSP payments, according to your business rules.
Note: If you are offsetting SSP payments from salary payments, you will not want to use the SSP Amount from the Statutory Sick Pay element as the Pay Value for the SSP Paid element. Use the Statutory Sick Pay formula to calculate the relative portion of SSP paid, depending on your business rules.
Use the Element window.
See: Defining an Element, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
Step 69: Define Links for Additional SSP Elements
Define links for SSP Total and SSP Paid elements if you have defined them.
Use the Element Link window.
See: Defining Element Links, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
Step 70: Write Formula for Calculating SSP Payment
Write the formula that is associated with the Statutory Sick Pay element to perform the payroll calculations for SSP payments. You should be conversant with your own business rules for the payment/offsetting of SSP payments.
Use the Formula window.
See: Writing Payroll Formulas for Elements, Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
Step 71: Define Formula Result Rules
Associate the formula with the Statutory Sick Pay element to specify what happens to the formula results for this element.
-
There is no Direct Result.
-
Amount is the Indirect Result for SSP Total.
-
Amount or a calculated value is the Indirect Result for SSP Paid.
Use the Formula Result Rules window.
See: Defining Formula Processing and Result Rules, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
Basic SMP, SAP, and SPP Setup
The basic implementation of SMP, SAP and SPP includes:
-
Defining links for the predefined elements
-
Defining maternity, paternity, and adoption absence types for analyzing and recording this information
-
Defining an assignment status for maternity and adoption absences.
Some of the steps are optional, depending on the requirements for your organization.
Step 72: Define Links for Predefined SMP, SAP, and SPP Elements
There are two predefined elements for each statutory payment. For more information about these elements, refer to Statutory Maternity, Paternity, and Adoption Pay Elements, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide. To activate the predefined elements you need only define their element links.
Use the Element Link window.
See: Defining Element Links, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
Step 73: Define Absence Types
You can define all of the absence types your enterprise requires for recording and analyzing maternity, paternity, and adoption absences.
Important: Make sure you select the appropriate Category--Maternity, Paternity, or Adoption--when you define the absence type.
Use the Absence Attendance Type window.
See: Defining an Absence Type, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
Step 74: Define Assignment Statuses for Maternity, Paternity, and Adoption
You can define assignment statuses as Maternity, Paternity, and Adoption.
You can use these assignment statuses:
-
For information, analysis, and reporting
-
To control processing of other earnings and deductions during maternity, paternity and adoption absences.
Use the Assignment Statuses window.
See: Defining Assignment Statuses, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide.
Process SMP, SAP, SPP Payments Setup
Refer to Setup to Process Payments for SMP, SAP, and SPP, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide for an overview of processing these statutory payments.
Step 75: Define Additional SMP, SAP, or SPP Elements
You can define additional SMP elements to hold the formula results from processing the Statutory Maternity Pay element. Similarly, you can define additional elements for SAP, SPP Birth, and SPP Adoption.
For example, if you need to maintain the predefined SMP Total balance, which can be reported on at year end, you should define an SMP Total element. This non-payment element will be fed an indirect result from the SMP element and pass that value to the SMP Total balance.
-
Define this element with a classification of SMP Non Payment and a Pay Value to feed the SSP Total balance.
-
Also, mark it as Indirect Results Only.
Similarly, you can define an SAP Total element, and SPP Birth Total Element, and an SPP Adoption Total element to feed the relevant predefined Total balances.
If you also want to pay SMP, you must define an SMP Paid element with a Pay Value. You can feed this element as an indirect result from the Statutory Maternity Pay element, or you can process this separately in a payroll run, depending on your own business needs.
-
SMP payment elements are used for the payment, offsetting, and costing of SMP payments, according to your business rules.
-
Define the SMP Paid element with a classification Earnings and a secondary classification of SMP Earnings and a Pay Value. Decide if the element should be marked as Indirect Results Only.
Note: If you are offsetting SMP payments from salary payments, you will not want to use the SMP Amount from the Statutory Maternity Pay element as the Pay Value for the SMP Paid element. Use the Statutory Maternity Pay formula to calculate the relative portion of SMP paid, depending on your business rules.
Similarly, you can define an SAP Paid element, and SPP Birth Paid Element, and an SPP Adoption Paid element to calculate the amount to appear on the payslip for each statutory payment.
Use the Element window.
See: Defining an Element, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
Step 76: Define Links for Additional SMP, SAP, and SPP Elements
Define links for SMP Total and SMP Paid elements--and the equivalent elements for SAP, SPP Birth, and SPP Adoption--if you have defined them.
Use the Element Link window.
See: Defining Element Links, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
Step 77: Write Formulas for Calculating SMP, SAP, and SPP Payments
Write the formula that is associated with the Statutory Maternity Pay element to perform the payroll calculations for SMP payments. You should be conversant with your own business rules for the payment/offsetting of SMP payments.
-
The formula type is Oracle Payroll.
-
'Inputs are...' statement must include Amount
-
'Return...' Amount for SMP Total
-
'Return...' Amount or a calculated value for SMP Paid
Similarly, write the formulas for the predefined SAP element, SPP Birth element, and SPP Adoption element to calculate the amount to appear on the payslip for each statutory payment.
Use the Formula window.
See: Writing Payroll Formulas for Elements, Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
Step 78: Define Formula Result Rules
Associate the formula with the Statutory Maternity Pay element to specify what happens to the formula results for this element.
-
There is no 'Direct' Result.
-
Amount is the Indirect Result for SMP Total
-
Amount or a calculated value is the Indirect Result for SMP Paid.
Similarly, create the formula processing rule and result rules for the Statutory Adoption Pay element, the Statutory Paternity Pay Birth element, and the Statutory Paternity Pay Adoption element.
Use the Formula Result Rules window.
See: Defining Formula Processing and Result Rules, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
Element Sets and Batch Control Totals
Step 79: Define Element Sets Optional Step
In Oracle HRMS you can define a set of elements to:
-
Restrict access to elements using Form Customization
-
Distribute costs across a Distribution Set of elements
-
Process a restricted set in a Payroll Run
-
Enter values for a restricted set using BEE (Batch Element Entry)
You define an element set as a named list of elements such as Salary, or Salary and Bonus. You can also define an element set using the classification. For example, you can restrict access to all elements in the classification Earnings.
Use the Element and Distribution Set window.
See: Defining an Element or Distribution Set , Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 80: Define Batch Control Types Optional Step
If you use Batch Element Entry, you can set up batch control types to sum the entries in any numerical input value. This enables users to validate a BEE batch against control totals to check for missing lines or miskeying of amounts.
Use the Application Utilities Lookups window.
See: Setting Up BEE Validation Using Control Totals, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Benefits Implementation Without Total Compensation Setup Wizard
The following implementation steps provide the full sequence of steps you follow to set up benefit plans manually. If you are using the Total Compensation Setup Wizard, note that the Wizard handles most of the steps in the following sections:
-
Benefits Eligibility
-
Life Events
-
Compensation Objects
-
Enrollment Requirements
-
Activity Rates and Coverage Calculations
See: Compensation, Benefits, and Payroll if you implement your benefit plans using the Total Compensation Setup Wizard, which is the recommended approach.
If you plan to load details of employee entry history you should consider using a fixed date, such as 01-JAN-1951, as a default for your initial setup definitions. This simplifies your data-entry.
Benefits Eligibility
You define participation eligibility profiles to determine eligibility for compensation and benefits. You can also use eligibility factors to determine variable contribution and distribution rates for a benefit.
Step 1: Define Benefits Groups Optional Step
You define a benefits group as a category of people who can be either included or excluded from receiving a benefit or a standard activity rate. A benefit group is one optional component of an eligibility profile or a variable rate profile.
Use the Benefits Groups window.
See: Defining Benefits Groups, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 2: Define Postal Code (ZIP) Ranges Optional Step
You define postal code (zip) ranges if you limit benefits eligibility based on a person's home address or if an activity rate varies based on a person's address.
Postal code ranges are also a component of service areas.
Use the Postal Zip Ranges window.
See: Defining Postal Zip Ranges, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 3: Define Service Areas Optional Step
You can define a service area to group people who live in a region by their postal codes. A service area is one optional component of an eligibility profile or a variable rate profile.
Use the Service Areas window.
See: Defining Service Areas, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 4: Define Regulations Optional Step
You define regulations as discrete rules, policies, or requirements that a governmental or policy making body defines regarding the administration of one or more benefits.
Use the Regulations window.
See: Defining Regulations, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 5: Create Your Own Eligibility Criteria Optional Step
You can create as many eligibility profile criteria as you need, in addition to the existing standard eligibility and derived factor criteria, to meet the particular requirements of your organization. You can use these criteria to determine employee eligibility for compensation, benefits, entitlements in collective agreements, personal actions, and so on.
Use the User Defined Eligibility Criteria window, which you can access from the Participation Eligibility Profiles window, or the Create Eligibility Criteria page.
See: Creating your own Eligibility Criteria., Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Define Derived Eligibility Factors
A derived factor is a system calculated value that you can use to determine eligibility for a benefit or to determine an activity rate.
Step 6: Define Derived Compensation Level Factors Optional Step
Define compensation level factors to determine how the system derives a person's compensation level based on a person's stated salary or a balance type that you specify.
Use the Derived Factors window.
See: Defining Derived Factors: Compensation Level, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 7: Define Derived Percent of Full Time Employment Factors Optional Step
Define percent of full time factors to determine how the system derives a person's percent of full time employment.
Use the Derived Factors window.
See: Defining Derived Factors: Percent of Full Time Employment, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 8: Define Derived Hours Worked in Period Factors Optional Step
Define hours worked in period factors to determine how the system derives the number of hours a person worked in a given period.
Use the Derived Factors window.
See: Defining Derived Factors: Hours Worked in Period, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 9: Define Age Factors Optional Step
Define age factors to determine how the system derives a person's age.
Use the Derived Factors window.
See: Defining Derived Factors: Age, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 10: Define Length of Service Factors Optional Step
Define length of service factors to determine how the system calculates a person's length of service.
Use the Derived Factors window.
See: Defining Derived Factors: Length of Service, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 11: Define Combination Age and Length of Service Factors Optional Step
Define combination age and length of service factors to combine an age factor and a length of service factor.
Use the Derived Factors window.
See: Defining Derived Factors: Combination Age and Length of Service, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Define Eligibility Profiles Optional Step s
Step 12: Define an Eligibility Profile Optional Step
Defining an eligibility profile is the primary way in which you implement eligibility requirements for a benefit. You link an eligibility profile with a compensation object (a benefit that you define) so that when eligibility processes run, only the persons meeting the eligibility profile requirements are eligible to receive the benefit.
Use the Participation Eligibility Profiles window.
See: Defining an Eligibility Profile, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 13: Define Dependent Coverage Eligibility Profiles Optional Step
You define dependent coverage eligibility profiles to enforce eligibility requirements for dependents.
Use the Dependent Coverage Eligibility Profiles window.
See: Defining a Dependent Coverage Eligibility Profile, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Life EventsLife Events (Advanced Benefits)
You define a life event as a change in a person's record that can potentially trigger an enrollment action. Life events can be external to work, such as a marriage or the birth of a dependent, or they can be internal, such as a job change. The application also handles scheduled enrollments as life events.
Step 14: Define Life Event Processing Optional Step
Define the life events that you use to control electability, activity rates and coverage levels, coverage dates, communications, and automatic and default enrollment processing.
Use the Life Event Reasons window.
See: Defining General Characteristics of Life Event Reasons, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 15: Define Person Changes Optional Step
You define the changes to a person's record that trigger a life event by specifying the value of the database field that indicates this person change has occurred.
Use the Person Changes window.
See: Defining Person Changes, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 16: Associate Person Changes with Life Events Optional Step
You associate the person change that triggers the life event for each life event that you define.
Use the Person Change Causes Life Event window.
See: Associating a Person Change with a Life Event, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 17: Define Related Person Changes Optional Step
You define the changes to a person's record that trigger a life event for a related person by specifying the value of the database field that indicates this related person change has occurred.
For example, you could define a termination life event to end benefits coverage for terminated employees. You would define a corresponding related person life event that ends coverage for the dependents of the primary participant when the primary participant is terminated.
Use the Related Person Changes window.
See: Defining Person Changes, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 18: Associate Related Person Changes with Life Events Optional Step
You associate a related person change with each related person life event that you define. A related person change is a change to the primary participant's HR record that may generate a life event for a person related to the primary participant.
Use the Related Person Change Causes Life Event window.
See: Associating a Person Change with a Life Event, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Compensation Objects
You define compensation objects as the benefits that you offer to your employees and other eligible participants.
Compensation objects are arranged according to the compensation object hierarchy:
-
Program
-
Plan Type
-
Plan
-
Option
Definitions that you set at the program level cascade to the plan types, plans, and options in that program unless you override the definition at a lower point in the hierarchy.
Step 19: Define Reimbursable Goods and Service Types Optional Step
Define goods and services that you approve for reimbursement. You then associate one or more goods and services types with a reimbursement plan.
Use the Goods and Services window.
See: Defining Reimbursable Goods and Service Types, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 20: Define a Program or Plan Year Period Optional Step
You define a program or plan year period to set the coverage boundaries for the duration of a benefit program or plan.
Use the Program/Plan Year window.
See: Defining a Program or Plan Year Period, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 21: Define Plan Types Optional Step
You define plan types to categorize common types of benefits, such as medical plans or savings plans.
Use the Plan Types window.
See: Defining Plan Types, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 22: Define Options Optional Step
You define options to indicate the coverage levels available under a plan or to define investment options for a savings plan.
Use the Options window.
See: Defining Options, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 23: Define Plans Optional Step
A plan is a benefit in which an eligible participant can enroll. Common plans include medical, group term life insurance, and stock purchase plans.
Use the Plans window.
See: Defining a Benefits Plan, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 24: Define Reimbursement Plans Optional Step
Use reimbursement plans to define goods and services that eligible participants may purchase. The participant can submit a reimbursement claim for the cost of the good or service that was purchased out-of-pocket.
Use the Plan Reimbursement window.
See: Defining a Reimbursement Plan, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 25: Define Programs Optional Step
You define a program to group together the benefits that you offer as a package. A program typically is comprised of plan types, plans, and options.
Use the Programs window.
See: Defining a Benefits Program, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Enrollment Requirements
You define enrollment requirements to control when an eligible person can enroll in a benefit.
Step 26: Define Program Enrollment Requirements Optional Step
Enrollment requirements determine how an eligible participant enrolls in a program.
In standard benefits, you define enrollment requirements based on the unrestricted enrollment type. Advanced Benefits customers can specify whether default or automatic enrollment rules apply for a program.
Use the Program Enrollment Requirements window.
See: Defining Enrollment Methods for a Program, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 27: Define Enrollment Requirements for a Plan Optional Step
You use the Plan Enrollment Requirements window to define enrollment requirements for a not in program plan or an option in plan. You also use this window to set up requirements for beneficiary designations.
Use the Plan Enrollment Requirements window.
See: Defining an Enrollment Method for a Plan, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Activity Rates and Coverage Calculations
Activity rate calculations determine the contribution rate necessary to purchase a benefit and the distribution rate for benefits that provide distributions.
Step 28: Calculate Variable Activity Rates Optional Step
You define variable activity rate calculations if an activity rate for a compensation object can vary by participant.
Use the Variable Rate Profiles window.
See: Defining General Information for a Variable Rate Profile, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 29: Calculate Coverages Optional Step
You define the amount of coverage available under a benefit plan for those plans that offer a range of coverage options. Your coverage calculation can include the minimum and maximum coverage level available regardless of the calculation result. For Advanced Benefits customers, coverage levels can vary based on life events.
Use the Coverages window.
See: Defining a Coverage Calculation, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 30: Define Across Plan Type Coverage Limits Optional Step
You can define the minimum and maximum coverage amount that a participant can elect across plan types in a program.
Use the Coverage Across Plan Types window.
See: Defining a Coverage Limit Across Plan Types, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 31: Calculate Imputed Income (US Only) Optional Step
You can define activity rates that calculate the amount of plan income that is considered a "fringe benefit" and subject to Section 79 of the US Internal Revenue Service code.
Note: You must have already created the corresponding elements.
Use the Imputed Income window.
See: Defining an Imputed Income Calculation, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 32: Calculate Actual Premium Costs Optional Step
You need to maintain the criteria used to calculate the actual premium cost that a plan sponsor owes to a benefits supplier.
Use the Actual Premiums window.
See: Defining an Actual Premium, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 33: Define Period-to-Date Limits Optional Step
You define period-to-date contribution limits for those plans or options in plan that restrict participant contribution levels in a year period. When you define a standard contribution, you can associate a period-to-date limit for those plans or options in plan that require contribution restrictions.
Use the Period-to-Date Limits window.
See: Defining Period-to-Date Limits, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 34: Define Activity Rates for Standard Contribution/Distribution Optional Step
You define a standard activity rate calculation to calculate a benefit's contribution or a distribution amount.
Note: You must have already created the corresponding elements.
Use the Standard Contributions/Distributions window.
See: Defining Activity Rates for a Standard Contribution/Distribution, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Flex Credit Calculations (Advanced Benefits) Optional Step s
Step 35: Define Characteristics of Benefit Pools Optional Step
You define benefit pools to limit how a participant can spend flex credits and how excess flex credits can be rolled over, distributed as cash, or forfeited.
Use the Benefit Pools window.
See: Defining the General Characteristics of a Benefits Pool, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 36: Define Flex Credits Optional Step
You define a flex credit calculation and link the calculation with a compensation object. The compensation object to which you link a flex credit calculation must be part of a program regardless of the level at which you define flex credits.
Use the Flex Credit Definitions window.
See: Defining Flex Credits, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Additional Setup for Health and Welfare
Step 37: Add the Benefits Tabbed Region to the People Window (US Only) Optional Step
A person with a responsibility of system administrator or application developer can use the Menus window to add the benefits alternate region to the People window.
-
Query the BEN_MANAGER menu in the Menu field.
-
Add a new line and select HR View Benefits in the Function field.
-
Save your work.
Use the Menus window.
See: Menus Window, Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
Step 38: Define a Monthly Payroll (US Only) Optional Step
You must define a monthly payroll for each business group you maintain. When you process employee terminations, a copy of the person's assignment record is created as a benefits assignment. Benefits assignments are used to maintain eligibility for continuing benefits, and always have a payroll with a monthly period.
Note: If you have already defined payroll information, including monthly payrolls for each Business Group, you can skip this step.
Use the Payroll window.
See: Defining a Default Monthly Payroll for a Business Group, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 39: Define Reporting Groups Optional Step
You can define a reporting group that you link to one or more programs and plans. When you run a report for a reporting group, the report results are based on the programs and plans that you include in the reporting group.
You can also define the regulatory bodies and regulations govern a reporting group.
Use the Reporting Groups window.
See: Defining a Reporting Group, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 40: Define Communications Optional Step
You define the communications you send to employees and other potential participants. You specify the conditions that trigger a communication and the delivery method and medium.
Use the Communication Types window.
See: Defining Communication Types, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 41: Define Benefit Balances Optional Step
Benefit balances are useful for transitioning legacy system data to Oracle HRMS. You define a benefit balance type and then assign a value to that type for a given person using the Person Benefit Balances window.
Use the Benefit Balances window.
See: Defining a Benefit Balance, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Define Online Benefits Services Optional Step s
You use the Online Benefit Services window to access a variety of benefits windows from a central location. You can configure the windows that are accessible from this window and you can define the pop up messages that display based on user events that you define.
Step 42: Maintain Desktop Activities List Optional Step
The Maintain Online Activities window lets you define the functions and windows that are available from the Desktop Activities list of the Online Benefits Services windows.
Use the Maintain Online Activities window.
See: Maintaining Online Activities, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 43: Maintain Pop Up Messages Optional Step
You can configure messages to display in the Online Benefit Services window based on user events that you define. You create the message text in the Messages window
Use the Maintain Pop Up Messages window.
See: Maintaining Pop Up Messages, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
For the next step in the implementation sequence, see: Additional Setup for Payroll Processing, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide .
Workforce Sourcing and Deployment
Oracle HRMS enables you to define your own names to identify the "types" of people in your system, and to identify the status of employees and contingent workers in each assignment using your own names.
Recruitment
Step 1: Define Assignment Statuses for Applicants Required Step
Assignment Statuses for applicants enable you to define the distinct stages of your own recruitment processes.
With Oracle HRMS you can use your own names to identify these stages. For example, you might want to define a special status to identify applicants who have been invited to a First Interview and applicants who have been Rejected on Application.
These user statuses enable you to track the recruitment circumstances of all your applicants.
Use the Assignment Statuses window.
See: Defining Assignment Statuses, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Setup for Employees and Contingent Workers
Step 2: Define Assignment Statuses for Employees and Contingent Workers Required Step
With Oracle HRMS you can identify the status of employees and contingent workers in each assignment using your own names. For example, you might want to define special statuses to identify assignments which have been Suspended while the employee or contingent worker is temporarily assigned to another role.
Use the Assignment Statuses window.
See: Defining Assignment Statuses, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 3: Create Contract Statuses Optional Step
Oracle HRMS enables you to create up to 250 different contract statuses to help track and identify employees.
See: Creating Contract Statuses, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 4: Create Contract Types and Values (UK Only) Optional Step
To enable Oracle Payroll to calculate Full Time Equivalent information correctly, you set up contract types and enter hours and periods information for each contract type.
Use the Table Structure and Table Values windows.
See: Setting Up Full Time Equivalent, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 5: Set Up Shift Patterns (UK Only) Optional Step
You can define any number of shift patterns. Oracle Payroll uses this information to calculate hours worked and payments such as overtime.
Use the Table Values window.
See: Setting Up Shifts and Shift Patterns, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 6: Select Assignment Rate Types for Contingent Workers Optional Step
This step applies only if you are not using Oracle Services Procurement to provide purchase order information for contingent workers.
Oracle HRMS enables you to record payment rate information for contingent workers. You select an assignment rate type (such as Standard Rate or Weekend Rate) and associate it with a rate basis (such as Hourly Rate or Weekly Rate). You can then associate this combination of rate type and basis with an assignment rate (a monetary value) for specific contingent worker assignments.
See: Defining a Combination of Assignment Rate Type and Basis, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
You can define additional rate basis values for your assignment rate types by adding to the existing lookup type RATE_BASIS.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 7: Set Up Availability Information Optional Step
Use the integrated features from Oracle HRMS and Common Application Components (CAC) to set up information such as shifts, schedules, and calendar events to help you determine a worker's availability.
See: Setting Up Availability, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 8: Set Up Global Deployments Optional Step
HR Professionals can use the Global Deployments function to transfer employees automatically between business groups. Some setup tasks are necessary for the Global Deployments function.
See: Setting Up Employee Transfers and Secondments, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Special Personal Information (Personal Analysis Key Flexfield Structures)
Use the Personal Analysis Key Flexfield to record special personal information that is not included as standard information. You define each type of information as a separate Structure of the flexfield. For example, you might set up a structure to hold medical information.
This flexfield is used in the following areas:
-
Special Information details for People
-
Matching requirements for Jobs and Positions
You need to design a Personal Analysis Flexfield Structure for each Special Information Type you want to hold in Oracle HRMS. For each structure you must include the following:
-
The Structure Name and the number of Segments.
-
The Flexfield Segment Names, Order and Validation Options.
-
The Flexfield Value Sets to be used and any lists of values.
Defining the Flexfield Structure is a task for your System Administrator.
Note: You cannot use the Create Key Flexfield Database Items process to create database items for the segments of your Personal Analysis Flexfield structures.
Step 9: Define Personal Analysis Flexfield Value Sets Optional Step
If you want to validate the values which a user can enter for any segment you must define a specific Value Set.
The attributes of the Value Set will control the type of values that can be entered, and how many characters each segment can hold. The attributes of the Value Set will also control how the values are to be validated.
Value Sets can be shared by different segments of the same flexfield, or by segments of any other flexfield.
Use the Value Set window.
See: Defining Value Sets, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 10: Define Personal Analysis Flexfield Segments Optional Step
Define a structure for your Personal Analysis Flexfield which contains the segments you want to use. You will use this structure to enter details in the Special Information Types window.
You must enter Yes in the Allow Dynamic Inserts field. If you enter No, you will not be able to enter new details in the Special Information Types window.
Note: You do not need to use a Value Set to validate a segment. If you do not specify a Value Set then a user can enter any alphanumeric value up to a limit of 150 characters.
Use the Key Flexfield Segments window.
See: Defining Key Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 11: Define Personal Analysis Flexfield Segment Values Optional Step
If you have chosen Independent or Dependent validation for a Value Set used by a Personal Analysis Flexfield Segment, you must define your list of valid values for the Value Set.
Use the Segment Values window.
See: Defining Segment Values, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 12: Define Personal Analysis Flexfield Cross Validation Rules Optional Step
Define any Cross Validation Rules you want to use to control the combinations of segment values which a user can enter.
You define Rules to Include or Exclude combinations of segment values. For each segment, you can define a Low to High range of values.
Use the Cross-Validation Rule window
See: Defining Cross-Validation Rules, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 13: Define Personal Analysis Flexfield Aliases Optional Step
Define Aliases for common combinations of segment values if you want to provide these as default options.
Use the Shorthand Aliases window
See: Defining Shorthand Aliases, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 14: Freeze and Compile Your Personal Analysis Flexfield Structure Optional Step
You are now ready to freeze your flexfield definition. Navigate to the Define Flexfield Segments window. Enter Yes in the Freeze Flexfield Definition field and save your changes. Oracle Human Resource Management Systems now freezes and compiles your Personal Analysis Flexfield definition. Compiling the flexfield definition enables the flexfield window with the defaults, values and rules that you have defined.
Use the Key Flexfield Segments window
See: Defining Key Flexfield Structures, Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide
Step 15: Register Special Information Types for the Business Group Optional Step
After you have defined your Personal Analysis Flexfield Structures you must link them to your business group.
You do this using your view-all responsibility.
-
Select each Information Type you want to use in this business group.
-
Select the categories for each type.
-
Job for Job Requirements
-
Position for Position Requirements
-
Skills for use with Oracle Training Administration
-
Other for use with Person Special Information
-
ADA for use only in the US, for special information types set up to record information about employees with disabilities.
-
OSHA for use only in the US, for a special information type set up to record information about employees' work-related injuries or illness.
Tip: If you do not check the Other category, you cannot use the type to hold information for a person. This means that you could also use the Special Information Types to hold any type of information for a Job or a Position only.
-
Use the Special Information Types window.
See: Enabling Special Information Types, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Requirements Matching
If you have decided to set up competencies, you can enter these as requirements for jobs and positions and match them against people's competence profiles.
If you have other job and position requirements that you want to record, but not define as competencies, you can set them up using the Personal Analysis key flexfield. You can set up each type of requirement as a Special Information Type, which is one instance of the flexfield.
For each Special Information Type, you can also choose whether to enable entry of information for people so that you can match people against the job or position requirements. A standard report (Skills Matching) has been provided to match the requirements of a job and the Special Information details of people in the system.
Important: US users: If you want to include essential job or position requirements in your ADA reporting, make sure you have entered these requirements for your jobs or positions.
Step 16: Define Requirements for Jobs Optional Step
You can define the attributes required by any employee who is assigned to a job. These attributes may be Essential or Desirable.
Definitions of requirements can use the same personal analysis flexfield structures and segments you have defined for special personal information.
Use the Job window.
See: Entering Job and Position Requirements, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 17: Define Requirements for Positions Optional Step
After you define positions in your enterprise, you can define the attributes required by any employee assigned to that position. These attributes may be Essential or Desirable. The requirements are based on the same personal analysis flexfield structures you have defined for special personal information.
Use the Position window.
See: Entering Job and Position Requirements, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Talent Management
Talent Management is the management of worker competencies and objectives to meet enterprise goals. Oracle HRMS, Oracle SSHR, and Oracle Learning Management (OLM) each supply key components of the Talent Management functionality. This topic describes the implementation process for the Oracle HRMS competencies, qualifications, and career path functions.
Oracle Performance Management is a separately licensed product. You must purchase a separate Oracle Performance Management license in addition to an Oracle Self-Service HR license to use the Appraisals, Questionnaire Administration, and Objectives Management self-service functions.
See: Oracle Performance Management Overview, Oracle Performance Management Implementation and User Guide
See: Implementing Oracle Performance Management, Oracle Performance Management Implementation and User Guide
Competencies
Competencies are measurable skills a workforce must acquire or possess to enable the enterprise to achieve its goals.
Step 1: Set HR:Global Competence Flex Structure Profile Option Optional Step
Each business group has a competence key flexfield structure. For global competencies, you can define an additional competence key flexfield or use an existing, business-group-specific structure. In either case, you identify the structure for creating global competencies on the HR:Global Competence Flex Structure Profile Option. Otherwise, you cannot create global competencies.
Use the System Profile Values window.
See: User Profiles, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 2: Create Proficiency Rating Scales Optional Step
You can use generic proficiency rating scales to assess competencies during an appraisal.
Use the Rating Scales window.
See: Creating a Rating Scale, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 3: Create Competencies Optional Step
Create definitions of competencies recognized and required by your enterprise to meet business goals.
Use the Competencies window.
See: Creating a Competency, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 4: Upload Third-Party Competency Definitions Optional Step
As an alternative or in addition to creating individual competencies, you can upload competencies supplied by third-parties, such as vendors who supply competency definitions for specific lines of business.
See: Uploading Third-Party Competency Information, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 5: Create Competency Types Optional Step
For ease of management and retrieval, you can group competencies into competency types. You define competency types using the lookup COMPETENCE_TYPE.
Use the Application Utilities Lookups window.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 6: Group Competencies into Types Optional Step
Associate individual competencies with one or more defined competency types.
Use the Competence Types window.
See: Grouping Competencies into Types, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 7: Define Competency Requirements Optional Step
You can define competency requirements for business groups, jobs, organizations, and positions. You can compare an individual's competencies with those required for a job or position, for example, to assist with promotion, training, or compensation plans.
Use the Competence Requirements window.
Defining Competency Requirements, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 8: Create Worker Competency Profiles Optional Step
A competency is a record of a worker's proficiency in competencies of interest to the enterprise. Users can compare worker competency profiles with the competency requirements of jobs or positions when searching for suitable candidates, for example.
See: Creating a Competency Profile, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management
Qualifications
For each worker, you can record qualifications achieved and educational establishments attended.
Step 9: Create Qualification Types Optional Step
You can define all qualification types your enterprise recognizes.
Use the Qualification Types window.
See: Creating Qualification Types, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 10: Create Schools and Colleges Optional Step
You can define all schools and colleges that deliver the qualifications your enterprise recognizes, so that users can select an educational establishment when recording a worker's qualifications. Alternatively, users can enter school and college names manually for each qualification.
Note: School and college definitions are available to all business groups; therefore, define them once only.
Use the Schools and Colleges window.
See: Creating Schools and Colleges, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Career Paths
Career Paths show the progression opportunities that are available to workers in your enterprise. You can define career paths based on either jobs or positions.
Step 11: Define Career Paths Optional Step
Define the career-progression routes available to workers in your enterprise.
Important: In the US, for AAP-Workforce Analysis reporting use the career path functionality to build the lines of progression for the jobs included in your AAP plans.
Use the Career Path Names and Map Career Paths windows.
See: Defining Career Paths, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 12: Enter Work Choices for Jobs or Positions Optional Step
You can record requirements, such as work location and work schedule, for jobs and positions.
Use the Work Choices window.
See: Entering Work Choices for a Job or Position, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 13: Enter Worker Preferences Optional Step
For each worker, you can enter work preferences, such as the preferred work location or working schedule. You can compare this information with job or position requirements when career planning or looking for candidates.
Use the Work Preferences window.
See: Entering Work Preferences, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Workforce Intelligence
These implementation steps are required to enable you to view data in the HRMS Discoverer business areas and workbooks. They assume that you already have installed Discoverer. For information on Discoverer installation, see: Discoverer Administration Guide.
Discoverer Workbooks
Follow the steps below to implement Workforce Intelligence Discoverer workbook reports. If you do not complete these steps, reports will be available to you, but they will not display data correctly. You need to perform some of these steps periodically, so that the reports reflect changes in your enterprise data. See: Programs to Populate Workforce Intelligence Discoverer Reports, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Set Up and Configure Workforce Required Step s
Workforce is not necessarily a count of the number of employees within your enterprise. Instead, it is a count based on employee assignments and budget measurement type. Calculations depend either on your budget measurement values for assignments, or they use a FastFormula..
Step 1: Set budget measurement values Optional Step
Set budget measurement values for each employee assignment within Oracle Human Resources. Reports and performance measures then calculate workforce using the budget values.
If you do not set a budget measurement value for an assignment, and a Business Group default does not exist, the reports and performance measures either calculate workforce using Oracle FastFormula, or they will not include the workforce for an assignment.
Use the Assignment Budget Values window.
See: Entering Assignment Budget Values, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 2: Setup the Workforce FastFormula Templates Optional Step
If you want to configure how workforce is counted do not set a budget measurement type and assignment measurement value for an assignment. The reports will then use Oracle FastFormula to calculate workforce.
HRMSi provides two predefined workforce formulas:
-
TEMPLATE_HEAD
-
TEMPLATE_FTE
Use the Formula window.
See: Configuring Workforce Calculations using Oracle FastFormula, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Set Up a Currency Conversion Rate Type Required Step s
Step 3: Enter a Currency Conversion Rate Type Required Step
Workforce Intelligence uses the conversion rates set up in the GL Daily Rate window. You can enter a specific conversion rate type for Workforce Intelligence, such as Corporate or Spot.
Use the Oracle Human Resources Table Values window.
See: Entering a Conversion Rate Type, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Set Up and Configure Training Hours Optional Step s
Within Oracle Training Administration OTA you can record the duration of a training event using a time period of your choice.
For example, rather than recording an event in hours you might record it in weeks or months. To enable the workbooks to display the number of hours of a training event, a predefined Oracle FastFormula, TEMPLATE_BIS_TRAINING_CONVERT_DURATION, converts your time periods into hours.
OTA is installed with four predefined time periods. If you record the duration of events using these predefined time periods the formula automatically converts them into the following hours:
-
D (Day) = 8 Hours
-
W (Week) = 40 Hours
-
M (Month) = 169 Hours
-
Y (Year) = 2028 Hours
Note: You set up time periods in Oracle Training Administration using the Lookup type FREQUENCY.
Step 4: Amend the Default Training Hours Optional Step
Amend the FastFormula TEMPLATE_BIS_TRAINING_CONVERT_DURATION if you have set up different time periods using the Lookup type FREQUENCY.
Use the Formula window.
See: Amending the Default Training Hours, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 5: Add Additional Training Time Periods Optional Step
Amend the FastFormula TEMPLATE_BIS_TRAINING_CONVERT_DURATION if the number of hours per time period does not match those of your enterprise.
Use the Formula window.
See: Adding Additional Training Time Periods, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Set up Cross Business Group Reporting Optional Step s
If users are using a local security profile they will only be able to see information in a specific business group. The business group is defined in the security profile attached to the responsibility.
For Discoverer reports, you may want to enable users to see data that spans business groups.
Step 6: Provide users with a global security profile Optional Step
If you want to enable cross business reporting, provide users with a global security profile. A global security profile provides cross business group reporting because it does not specify a business group.
Use the Global Security Profile window.
See: Defining a Security Profile, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Identify the Reporting Organization Required Step s
HRMS Discoverer workbooks will not run unless the application can identify an organization to report on. If a workbook cannot identify the reporting organization, it will fail to generate certain report parameter lists and will produce the following error message when displaying the report parameter page:
“No values were found for the parameter Organization whilst attempting to build the list of values. To run this report your system must have the parameter Organization set up. Please contact your system administrator.”
The application identifies an organization through a business group. You must therefore ensure that you assign a business group correctly to report users. How you assign the business group depends on which security model you implement and whether you are using a local or global security profile. See the options below.
Step 7: Set the Profile Option HR: Security Optional Step
If you have implemented the standard HRMS security model, with a local security profile, you must set the profile option HR: Security to the business group you want to report on.
The reports identify the business group through the profile option HR: Business Group. The application automatically sets this profile option to the value in the HR: Security profile option.
Set up the business group in the profile option HR: Security. Use the System Profile Values window.
See: System Profile Values Window , Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
Step 8: Set the Profile Option HR: Business Group Optional Step
If you have implemented the standard HRMS security model, with a global security profile, the HR: Business Group profile option is not set automatically.
Set the profile option HR: Business Group at responsibility level to the business group that you want to report on.
Use the System Profile Values window.
See: Defining Preferences with User Profile Options, Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
Step 9: Associate a Business Group with a Security Profile Optional Step
If you have implemented the Security Groups Enabled security model, the HR: Business Group profile option is not used. You associate a business group with a security profile.
Use the Assign Security Profile window.
See: Assigning Security Profiles, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Restrict Discoverer Workbook Access Required Step s
Step 10: Grant Access to Discoverer Business Areas Required Step
Grant access privileges to the Discoverer business area to determine which workbooks users can create or view.
Use Oracle Discoverer Administration Edition.
See: Grant Business Area Access, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Check the Vacancy Status Options Required Step s
Step 11: Check the Vacancy Status Options Required Step
To ensure the reports that cover vacancies return accurate results, you need to ensure that users close vacancies by using the status of CLOSED. You may have to obsolete an old vacancy status option that results in the status of C.
Use the Application Utilities Lookups window.
See: Check the Vacancy Status Options, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Populate Summary Tables Required Step s
To ensure your HRMS Discoverer workbooks run correctly and efficiently, you need to run concurrent programs to populate summary tables with your hierarchy data and workforce measurement values.
For a full discussion of these concurrent programs, and when you need to run them, see: Programs for Populating Workforce Intelligence Discoverer Reports, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 12: Populate the Organization Hierarchy Summary Table Required Step
All reports that use organization hierarchy gather information from the Organization Hierarchy Summary table. Populate this summary table with your organization hierarchy data. The table ensures that you are getting the best possible performance from your reports.
To populate the summary table, run the concurrent program HRI Load All Organization Hierarchy Versions.
Use the Submit Requests window.
See: Populating the Organization Hierarchy Summary Table, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 13: Populate the Supervisor Hierarchy History Table Required Step
All reports that use supervisor hierarchy gather information from the Supervisor Hierarchy Summary table. Populate this summary table with your supervisor hierarchy data. The table ensures that you are getting the best possible performance from your reports.
To populate the summary table, run the concurrent program HRI Load All Supervisor Hierarchies.
Use the Submit Requests window.
See: Populating the Supervisor Hierarchy History Table, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 14: Populate the Workforce Measurement Value History Table Required Step
Many reports use Workforce Measurement Values (WMVs). WMVs currently include headcount and full-time equivalent (FTE) assignment budget values.
Run the concurrent program HRI Load Workforce Measurement Value History to populate the Workforce Measurement Value History table with the WMVs used by your reports.
Use the Submit Requests window.
See: Populating the Workforce Measurement Value History Table, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 15: Populate the Generic Hierarchy Summary Table Required Step
Some US specific Discoverer workbooks use a 'Vets, EEO, AAP, OSHA, Multi Work Sites' hierarchy. They require information about the current generic hierarchy.
Run the concurrent program HRI Load All Generic Hierarchy Versions to calculate and collect the required data.
Use the Submit Requests window.
See: Populating the Generic Hierarchy Summary Table, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 16: Collect Organization Hierarchy Structures Optional Step
The Organization Rollup – Current folder in the Discoverer End User Layer uses organization hierarchies held in the HRI_ORG_PARAMS and HRI_ORG_PARAM_LIST tables. If you build Discoverer reports using the Organization Rollup – Current folder, you must populate these tables with your organization hierarchies.
To populate the tables, run the concurrent program BIS Load Organization Hierarchy Summary Table.
See: Collecting Organization Hierarchy Structures, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
HR Information Systems
Reports
Step 1: Use Standard Reports or Write New Reports Optional Step
A number of standard reports are supplied with Oracle HRMS. These reports have been written using Oracle Reports V.2 and registered as concurrent programs with the Standard Requests Submission (SRS) feature of Oracle Applications.
You can use these Standard Reports or write your own reports and register these as additional reports which users can request from the Submit a New Request window.
UK Payroll Implementation Only
In the UK, P45 and Pay Advice reports supplied with Oracle Payroll are designed for use with preprinted stationery. These reports use two special printer drivers to control the print format.
-
P45 - paygbp45.prt
-
Pay Advice -paygbsoe.prt
If your printer does not accept the same control characters as the DEC LN03 printer, you may need to modify the special SRW driver files.
When you install Oracle Payroll the two sample files are stored in the $PAY_TOP/srw directory. You should copy the files to $FND_TOP/$APPLREP and then register them using the Printer Drivers window.
Step 2: Register Reports as Concurrent Programs Optional Step
After you have written your new reports and saved them in the correct subdirectory, you must register the report as a concurrent program. You also register the parameters which can be submitted with the report. For example, you may have written a report to display personal details and you want to submit employee name to limit the output to include one person at a time.
Use the Concurrent Programs window.
See: Concurrent Programs Window, Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
Step 3: Define Report Sets Optional Step
You can define sets of Reports:
-
To restrict user access to specific reports.
A set of reports can be linked to a Responsibility.
-
To simplify requesting a report
You can run a report set in one request, rather than a request for each report.
Use the Request Set window.
Standard Letter Generation
You can use standard letters in HRMS to help you to manage your enterprise's recruitment or enrollments, for example. You do this by issuing standard letters to applicants or students, triggered by changes in assignment or enrollment status.
Oracle HRMS provides you with three different methods to create standard letters:
-
Method 3: Create Mail Merge Letters using Web ADI
Method 1 - Concurrent Processing using Word Processors
You can create standard letters using Multimate, WordPerfect or Microsoft Word.
Step 4: Plan Standard Letter Requirements Optional Step
You need to identify the database information to include in the letters.
See: Planning Standard Letter Requirements, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 5: Write a SQL*Plus Script Optional Step
Oracle HRMS supplies you with SQL*Plus scripts as templates for extracting database information for standard letters. You can copy the SQL*Plus script templates and modify them to create the standard letters you require.
See: Writing a SQL*Plus Script for MultiMate or WordPerfect, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
See: Writing a SQL*Plus Script for Microsoft Word, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 6: Register the SQL*Plus Script Optional Step
Register your SQL*Plus program with Oracle HRMS. You register your program so that you can run it as a concurrent program. Name the file PERWP*** (or OTAWP***). You must use this prefix for the system to recognize it as a type of letter.
Use the Concurrent Programs window.
See: Registering the SQL*Plus Script, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 7: Link the SQL*Plus Script to the Letter Optional Step
Link your SQL*Plus script with a letter and one or more statuses. In Oracle Human Resources, you can link one or more applicant assignment statuses with each recruitment letter. A request for the letter is then created automatically when an applicant is given an associated assignment status. For example, you can link your standard recruitment rejection letter to the status Rejected so that the letter is triggered when you set an applicant's assignment status to Rejected
Use the Letter window.
See: Linking the SQL*Plus Script with aLetter, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 8: Writing a Skeleton Letter Optional Step
Write a skeleton letter using your word processor. Include the appropriate merge codes from the data source for the word processor you are using.
See: Writing a Skeleton Letter, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 9: Requesting Letters Optional Step
When you, or other users, set the status for an applicant or enrollment that triggers your standard letters, Oracle HRMS creates a letter request automatically, with the status of Pending. It also adds the applicant's or student's name to the request. You can view the pending request and names through the Request Letter window.
Use the Request Letter window.
See: Requesting Letters/Running the Report, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 10: Merging the Data Files Optional Step
You now need to merge the data in the Data File with your skeleton letters.
See: Merging the Data File with the Standard Letter, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Method 2 - Concurrent Processing using Oracle Reports
You can create a report for each letter using Oracle Reports, or another tool of your choice. The report contains the skeleton letter text and Select statements specifying the data to be extracted from the Oracle database.
Step 11: Plan Standard Letter Requirements Optional Step
You need to identify the database information to include in the letters.
See: Planning Standard Letter Requirements, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 12: Write and Register the Report Optional Step
You now need to write and register the report.
See: Writing and Registering the Report, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 13: Link the Report with a Letter Optional Step
You need to link your report with a letter and one or more statuses. In Oracle Human Resources, you can link one or more applicant assignment statuses with each recruitment letter. A request for the letter is then created automatically when an applicant is given an associated assignment status. In Oracle Training Administration, you can link one or more enrollment statuses with each enrollment letter. A request for the letter is then created automatically when an enrollment is given an associated status.
Use the Letter window.
See: Linking the Report With a Letter, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 14: Run the Report Optional Step
When you, or other users, set the status for an applicant or enrollment that triggers your standard letters, Oracle HRMS creates a letter request automatically, with the status of Pending. It also adds the applicant's or student's name to the request. You can view the pending request and names through the Request Letter window.
Then, when you change the letter request from Pending to Requested, Oracle HRMS runs the report that you created.
Use the Request Letter window.
See: Registering Letters/Running the Report, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Method 3 Create Mail Merge Letters Using Web ADI
Step 15: Create Mail Merge Letters Optional Step
Define Web ADI integrators and layouts and set up template letters.
See Creating Mail Merge Letters Using Web ADI, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
People Management Templates
Step 16: Extend the Checklist Lookup Values Optional Step
You can add your own values to the supplied list of checklist items and statuses to be included in a template.
Define values for the CHECKLIST_ITEM and CHECKLIST_STATUS Lookup Types.
Define values for BUDGET_MEASUREMENT_TYPES
Use the Application Utilities Lookups window.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 17: Write Formulas for Templates Optional Step
You can use formulas to configure the people management templates in the following ways:
-
Template Validation Formula
-
Template Information Formula
-
People Management Message Formula for the Assignment Field
-
People Management Message Formula for the Message Tokens
Use the Formulas window.
See: Writing Formulas for Templates, Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
Step 18: Configure Templates Optional Step
You can use the People Management Configurator to create templates for your users to use. We recommend that you use one of the supplied templates as a basis for your configured version.
Use the People Management Configurator.
See: Using the People Management Configurator, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 19: Set up Notification Messages Optional Step
You can setup additional notification messages to be used with the people management templates.
Use Oracle Workflow
See: Notification Messages Issued from Templates Forms, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Oracle HRMS Configuration
Step 20: Define Elements and Distribution Sets Optional Step
Select element classifications or individual elements to define a set. There are three types of set:
-
Customization set
-
Run set
-
Distribution set
Use the Element and Distribution Set window.
See: Defining an Element or Distribution Set, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
Step 21: Define Configured Version of a Window Optional Step
Form Customization lets you restrict the types of information a user can access in a specific window.
You can define your own window titles for any window configuration option. Remember that the user guides and the online help use the default window names to identify windows.
You can call the configured window in two ways:
-
Define a customized node in a task flow
-
Add the customization as an argument to the menu function which calls the window
Use the Form Customization window.
See: Configuring a Window With Customform, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 22: Add Configured Window to a Menu or a Task flow Optional Step
You must add your configured windows to a menu or task flow.
See: Adding Configured Windows to a Menu or a Task Flow, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide.
Step 23: Restrict Access to Query-Only Mode Optional Step
You can restrict access to query-only mode for an individual form.
See: Restricting Access to Query-Only Mode, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide.
Step 24: Change the Default National Address Style Optional Step
The different national address styles are held and configured in the Personal Address Information descriptive flexfield using the Descriptive Flexfield Segments window. You can change the national address style for any country.
See: Changing Default National Address Styles, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 25: Review and Update Person-Name Formats Optional Step
HRMS supplies a format definition for a person's full name and other name definitions for use in custom code. You can change the supplied person-name format definitions and create additional format definitions to suit enterprise requirements.
See: Person-Name Formats, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 26: Use Parameters for HRMS Form Functions to Hide Sensitive Data Optional Step
You can prevent sensitive data from appearing on the Enter a person window by using parameters for HRMS window functions.
See: Using Parameters for HRMS Form Functions, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Task Flows
A task flow defines the selection of windows you want to use when performing a specific task. These can be arranged in sequence or as branched groups of Nodes, and you can include configured windows as nodes in your task flow.
Warning: Do not use apostrophes (') or percent (%) symbols in task flow names or task flow node names.
You can create task flows using:
Create Task Flows Using Forms
Step 27: Define Task Flow Nodes Optional Step
All of the task flow windows provided with Oracle HRMS have nodes predefined for them. You can define new task flow nodes to provide different versions of these windows. For example, if you wanted to use CustomForm on a specific node in a task flow.
Use the Define Task Flow Nodes window.
See: Defining Task Flow Nodes, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 28: Define Task Flows Optional Step
Arrange the nodes of your task flows in sequential or branched groups
Use the Task Flow window.
See: Defining Task Flows, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Create Task Flows Using Workflow
Step 29: Create a Top Level Process Optional Step
You must define a top level process for each task flow. The top level process can contain sub processes, but not any other top level processes.
You use the Process Diagrammers within Oracle Workflow to create your task flows. You do this by adding and connecting the windows you want to appear.
You must create a top level process, sub processes are optional.
See: Creating a Top Level Process, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 30: Create Sub Processes Optional Step
You can group a logical set of task flow windows into a sub process, which can then be used by several top level processes. This simplifies process modelling. Each sub process can contain other sub processes. There are two rules to note regarding sub processes:
-
A sub process cannot be defined as runnable.
-
When you use a sub process in another process, you must connect the sub process to the Top Node window.
See: Creating Sub Processes, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 31: Create Button Labels Optional Step
You can enter the label you want to appear on the task flowed windows, such as Photo (for the Picture window), and such. Each task flow window activity has an attribute called Button Label. Use this attribute to override the default button label for a window and to define an access key (or keyboard shortcut).
See: Creating Button Labels, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 32: Position Button Display Optional Step
You can position the display order of buttons on the window. For example, you might want the first button to display the Picture window.
See: Positioning Button Display, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 33: Identify Windows or Blocks to Display Optional Step
If you are creating task flows using the combined People and Assignment window, complete this step, otherwise skip this step.
For most task flow windows, you must display the first block of the window on entry. However, when you use the Combined People and Assignment window in a task flow, you must specify whether to display the People window (or block) or the Assignment window on entry.
See: Identifying Windows or Blocks to Display, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 34: Identify Configured Forms to Include in the Task Flow Optional Step
If you have created a configured version of a window, you can use it in the task flow. If not, you can skip this step.
See: Identifying Configured Forms to Include in the Task Flow, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 35: Verify and Save the Workflow Optional Step
When you have completed the task flow definition within Oracle Workflow, use the Workflow Verify function to check that your workflow conforms to Oracle Workflow modeling rules. When you have successfully verified the Workflow, save it to the HRMS database.
See: Verifying and Saving the Workflow, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 36: Generate a Task Flow From Oracle Workflow Optional Step
After modelling a task flow in Oracle Workflow and saving it to the database, you must generate task flow definitions.
Use the Define Task Flow window.
See: Generating a Task Flow From Oracle Workflow, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Menus
Step 37: Define Menu Functions Optional Step
Menus are composed of submenus and functions and all Oracle Applications are supplied with default functions and menus to give you access to all of the available windows.
Warning: You should not modify the default functions and menus supplied with the system. On upgrade, these defaults will be overwritten.
If you want to add window configuration options or task flows you should define your own menus.
Use the Form Functions window.
See: Defining Menu Functions, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 38: Define Menus Optional Step
The supplied menus give you access to all of the available submenus. However, a number of seeded functions are not enabled on these menus. You need to add them for the responsibilities that should have access to these functions:
Use the Menus window.
See: Defining Menus, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 39: Disable the Multiple Windows Feature Optional Step
In most Oracle Applications, you can open multiple windows from the Navigator window without closing the window you already have open. HRMS, however, does not support Multiform functionality.
Important: You must disable this feature on menu structures that access Oracle HRMS windows.
See: Disabling Multiple Windows, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
User Security
Any system that holds human resource and payroll information must be secured against unauthorized access. To reach employee information you need the correct security clearance.
The responsibility for defining and maintaining the internal security of your system is usually given to your system administrator.
Defining Security for HRMS Users
Defining the access limits of each user is a multi-stage process which defines which records a user can see and which forms and windows they can see and use.
There are two security models to enable you to set up the right type of security for your enterprise:
-
Standard HRMS security model
Set up standard security if your enterprise sets up a different responsibility for each business group.
-
Security Groups Enabled security model
Use Security Groups Enabled security if your enterprise wants to enable many business groups for one responsibility. This type of security is most commonly used by Service Centers.
See: Defining Security for HRMS Users
Defining Security for Reporting Users
You can also create reporting users who have read only access to data. This can be useful if you want to permit access to the data from another system.
See: Defining Security for Reporting Users
Defining Security for HRMS Users (Optional)
Step 40: Set up the Enable Security Groups option for your Security Model
-
If you are using Standard HRMS security, ensure that the Enable Security Groups profile option is set to No at site and application level.
-
If you are using Security Groups Enabled security, ensure that the Enable Security Groups profile option is set to Yes at the application level.
Important: Once you have changed to Security Groups Enabled Security you cannot revert to the Standard Security model.
Use the System Profiles Value window
See: System Profile Values Window, Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
Step 41: (Security Groups Enabled Model only) Run the Enable Multiple Security Group Process
If you are using the Security Groups Enabled model, you must run the Enable Multiple Security Group process to set up Oracle HRMS to use security groups.
Use the Submit a New Request window
See: Submitting a Request, Oracle E-Business Suite User's Guide
Step 42: Define a Security Profile
Use the Security Profile window (to give access to a single business group) or the Global Security Profile window (to allow users to access records from more than one business group).
See: Defining a Security Profile, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 43: Ensure Required Functions or Menus are Set Up
This is required for the responsibility. For menu functions calling configured forms or task flows, you must enter a parameter in the Parameter field of the Form Functions window.
See: Defining Menu Functions, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 44: Ensure Required Request Group is Set Up
You can define the groups of standard reports and processes that a user can run from the Submit a New Request window. Every responsibility can have access to one request group.
Use the Request Group window.
See: Defining Menu Functions, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
See: Request Groups Window, Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
Step 45: Define a Responsibility
You need to define a responsibility.
Use the Responsibilities window.
See: Responsibilities Window, Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
Step 46: Set the User Profile Option Values for Responsibility
Set the HR User Profile Options for the new responsibility.
You must set up the following:
-
HR: User Type
Use this profile option to limit field access on windows shared between Oracle Human Resources and Oracle Payroll.
-
HR:Cross Business Group
Set this profile option to Yes if you want users to be able to view some information across all business groups in your enterprise.
For details of the information you can make available to users across business groups, see User Profiles, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
HR: Security Profile
-
If you are using the Standard Security model, enter the security profile for the responsibility. This must be set up at responsibility level, otherwise the default view-all security profile is used. Using Standard HRMS security you can only set up one security profile for a responsibility.
-
If you are using the Security Groups Enabled security model, do not set up or amend the HR: Security Profile option using the System Profile Values window. To set up or change this profile option use the Assign Security Profile window.
You can set also set up other User Profile Options.
-
Use the System Profile Values window.
See: System Profile Values Window, Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
Step 47: Associate a Responsibility With a Set of Help Files
Oracle Applications Help for HRMS defaults to Global help, but you can associate a responsibility with a set of help files for a localization, such as Canada, US or UK, or for a verticalization such as Oracle Federal HRMS. You do this by setting the user profile Help_Localization_Code.
See: User Profiles, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
In addition to associating a responsibility with a localization or a verticalization you can also specify that a particular responsibility should have access to a configured subset of the localized or verticalized help files.
See: Customizing Oracle Applications Help, Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
Step 48: Create Usernames and Passwords
-
If you are using the Standard Security model, you need to create usernames and passwords and link responsibilities to users.
-
If you are using the Security Groups Enabled security model, you need to create usernames and passwords. Do not link responsibilities and security groups (business groups) to users in the Users window for HRMS; instead, use the HRMS Assign Security Profile window.
Important: If you do enter a responsibility and security group in this window when using Security Groups Enabled security, you still need to use the Assign Security Profile window, to link your user to a responsibility and security profile. If you do not use the Assign Security Profile window, the default view-all security profile is used and your user will be able to see all records in the business group.
Use the Users window.
See: Users Window, Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
Step 49: (Security Groups Enabled Model only) Assign Security Profiles
If you are using the Security Groups Enabled model, associate a security profile with a user, responsibility and business group.
Important: You cannot use the HRMS Assign Security Profile window to link responsibilities to users if you are setting up Standard Security.
Use the Assign Security Profile window.
See: Assigning Security Profiles, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 50: Run Security List Maintenance Process (PERSLM)
Oracle HRMS uses the Security List Maintenance process to generate the lists of organizations, positions, payrolls, employees, contingent workers, and applicants that each security profile can access.
Important: When you initiate the Security List Maintenance process you must enter the resubmission interval to run the process every night
You must do this so that the system will automatically update the lists with the data changes you make every day.
If a power or computer failure should disrupt this process, you can initiate it manually from the Submit a New Request window.
When this process has completed successfully you can sign on to the system using the new username and responsibility.
Use the Submit a New Request window
See: Submitting a Request, Oracle E-Business Suite User's Guide
Defining Security for Reporting Users (Optional)
Step 51: Create a New Reporting User Oracle ID
If you want reporting users to have the same restricted access to records as your online users, ask your ORACLE Database Administrator to create a new ORACLE User ID.
Reporting Users have read only access to data. This can be useful if you want to permit access to the data from another system.
Note: You need to inform Reporting Users of their Reporting Username and Password.
Step 52: Register the New Oracle ID
Register the new ORACLE ID with Application Object Library.
Use the Register window.
Step 53: Define a Security Profile
Using a view-all responsibility, you can define security profiles in the Security Profile window.
Use the Security Profile window.
See: Defining a Security Profile, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 54: Run Generate Secure User Process (SECGEN)
The Generate Secure User process will grant permissions to the new Reporting User ORACLE ID. Until you run this process, reporting users cannot access Oracle HRMS data using this security profile.
-
Select Generate Secure User.
-
In the Parameters window, enter the security profile you created for the ORACLE ID.
-
Submit your request.
A concurrent request ID appears in the ID field. You can check the progress of your request on the View Concurrent Requests window.
Use the Submit a New Request window
See: Submitting a Request, Oracle E-Business Suite User's Guide
Web Applications Desktop Integrator (Web ADI)
Step 55: Set Up Web ADI Optional Step
You can set up Web Applications Desktop Integrator (Web ADI) to export information from your Oracle HRMS database to desktop applications, for example, spreadsheets.
See Implementing Web ADI for Use with Oracle HRMS, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
See: Upgrade Information for Converting from ADE to Web ADI, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Audit Requirements
Step 56: Turn on Auditing Optional Step
To turn on Auditing, set the AuditTrail:Activate profile option to Yes at Site or Application level.
Use the System Profile Values window.
See: System Profile Values Window, Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
Turning Audit on has no noticeable effect on the performance of the system and users will not be aware of any extra delay in committing their transactions.
Step 57: Estimate File Sizing and Management Needs Optional Step
Whenever you choose to audit the actions of users of the system you are deciding to keep the details of all the transactions which take place. This will include before and after details as well as the details of who made the change and when.
Warning: In normal use the auditing of data can soon generate large volumes of audit data, which even when stored in a compressed format will continue to grow in size until you reach the limits imposed by your environment. If you reach the limits during active use then users will be unable to use the system until you remedy the problem.
You are strongly advised to consider the scope of your audit activities and how you will use the data you accumulate. Also you should consider how often you will report on the audit data, and when you will archive and purge your audit data.
If you need more advice on this you should contact your Oracle Support representative.
Step 58: Define Audit Installations Optional Step
If you have installed more than one Oracle Application you can audit across multiple installations. For Oracle HRMS you should enable auditing for the HR user and the APPLSYS user.
Use the Audit Installations window.
See: Audit Installations Window, Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
Step 59: Define Audit Tables and Columns Optional Step
With Oracle Applications you can define the level of detail you want to audit. You define the individual fields of each record that you want to audit.
-
Query the Table you want to audit
-
Enter the columns you want to audit for that table
Use the Audit Tables window.
See:Audit Tables Window, Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
Step 60: Define Audit Groups Optional Step
You can define one or more Audit Groups for your installation. You might find this useful if you have more than one Oracle Application installed.
Use the Audit Groups window.
See: Audit Groups Window, Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
Step 61: Run AuditTrail Update Tables Process and AuditTrail Update Datetracked Tables Process Optional Step
To start the AuditTrail activity you must submit the AuditTrail Update Tables Process for all tables, and the AuditTrail Update Datetracked Tables Process for all datetracked tables.
Use the Submit a New Request window.
See: Submitting a Request, Oracle E-Business Suite User's Guide
Additional Implementation Steps for French Legislations
If you are implementing Oracle HR for France you must also complete the following additional implementation steps.
Additional Implementation Steps
Populate User Defined Tables Required Step s
A number of user defined tables are used by the reports supplied with Oracle HR for France. These tables interpret the data held in the database and convert it into the format required by the particular report.
In order to ensure the tables contain the correct data for your enterprise you must perform the following step:
Step 1: Define the Values Required in the User Defined Tables
A number of tables have been supplied with empty columns that must have the relevant values for your enterprise entered. For details of the supplied tables:
See: User Defined Tables, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Use the Table Values window.
See: Entering Values Into Tables, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 2: Include Assignment Extra Information in the Navigator Optional Step
The Declaration Unique d'Embauche reports on information in the employee or applicant assignment, depending on whether it is run before or after the hire date. It also retrieves information entered in the Hiring Declaration assignment extra information type. On delivery, you can only access the Hiring Declaration assignment extra information type from the Assignment window, and therefore you can only enter information for employees. To enable your users to enter information in the Hiring Declaration assignment extra information type for applicants you should include it Navigator.
On selecting the assignment extra information from the navigator you can find the required person and assignment combination and enter details accordingly.
Use the Menus window.
See: Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator's Guide - Security
Set up the Bilan Social Required Step s
Before you can run the Bilan Social Report process you must first perform the following setup steps.
Step 3: Review and Modify Item Types
You must review the item types, and all the associated restriction and key types that have been supplied with Oracle HR for France. Where these do not meet the requirements of your enterprise you must copy and modify them accordingly.
Use the Setup window.
See: Reviewing and Modifying Calculations, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 4: Set up the Bilan Social Template
The template groups together all the item types that will be used when the Bilan Social Report process is run. It also defines the key types and restriction types that will apply for each item type. If the supplied Example Template does not meet your requirements you must either copy and amend it, or create a new template.
Use the Generic Summary Process window.
See: Creating the Bilan Social Template, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 5: Review and Modify the HR France - Bilan Social Business Area
If the folders that are supplied do not meet the requirements of your enterprise you must create new folders accordingly.
Use Oracle Discoverer.
See: Using Oracle Discoverer to View the Bilan Social, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 6: Review and Modify the Supplied Workbooks
If the workbooks that are supplied do not display the data required by your enterprise you must create new workbooks accordingly.
Use Oracle Discoverer.
See: Using Oracle Discoverer to View the Bilan Social, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 7: Configure the Supplied Worksheets
In order for a number of the supplied worksheets to work correctly you must amend them according to the values you have entered in you user defined tables. The worksheets that need to be modified are as follows:
-
C22: This worksheet has a condition set, Medical Examination Type = `Additional', that limits the records retrieved to those with a medical examination type that has a corresponding value of `Additional' in the FR_MEDICAL_EXAMINATION_TYPE user defined table. You must change the condition so that the value (i.e. `Additional) reflects the value in your FR_MEDICAL_EXAMINATION_TYPE user defined table.
-
R9: This worksheet uses a number of calculations that rely on the FR_EMPLOYEE_CATEGORY user defined table. The calculation R9:AVG(Ouvrier) includes all records with an employment category that has a corresponding value of `Ouvrier' in the FR_EMPLOYEE_CATEGORY user defined table. You must replace all occurrences of `Ouvrier' in the calculation with the required value from your FR_EMPLOYEE_CATEGORY user defined table.
The calculation R9-R10:AVG(Cadre) includes all records with an employment category that has a corresponding value of `Cadre' in the FR_EMPLOYEE_CATEGORY user defined table. You must replace all occurrences of `Cadre' in the calculation with the required value from your FR_EMPLOYEE_CATEGORY user defined table.
-
R10: This worksheet uses a number of calculations that rely on the FR_EMPLOYEE_CATEGORY user defined table. The calculation R10-AVG(Employee) includes all records with an employment category that has a corresponding value of `Employee' in the FR_EMPLOYEE_CATEGORY user defined table. You must replace all occurrences of `Employee' in the calculation with the required value from your FR_EMPLOYEE_CATEGORY user defined table.
Use Oracle Discoverer.
See: Oracle Discoverer User's Guide
Step 8: Customize MMO and D2 FastFormulas Required Step
The D2 and the Declaration Mensuelle Obligatoire des Mouvements de Main d'Oeuvre use Oracle FastFormula to define formulas that control some of the data that is retrieved. If the supplied formulas do not meet the requirements of you enterprise you must create new formulas.
Use the Formula window.
See: MMO and D2 FastFormulas, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 9: Public Sector-type Functionality Optional Step
You can set up a particular Business group for Commercial or Public Sector-type functionality.
See: Business Group: Setting Up Public Sector-type Functionality, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 10: Collective Agreement Entitlement Items Required Step
You need to associate the entitlement items you have created for accommodation, awards and decorations with the specific entitlements you have defined for your enterprise.
See: Setting Up Collective Agreement Entitlement Items, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 11: Salary Share Required Step
You need to associate the salary share with the appropriate physical share.
See: Setting Up Salary Share, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 12: Dependent Child Relationship Optional Step
You need to indicate which of your contact relationships should be treated as dependent child relationships by the application to calculate the number of dependent children.
See: Setting Up Dependent Child Relationship, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 13: Reasons and Subtypes for Statutory Situations Optional Step
You can add more reasons and subtypes for statutory situations to meet your business requirements.
See: Reasons and Subtypes for Statutory Situations, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide and Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide.
Step 14: Define a Default Normal Inactivity Statutory Situation Required Step
You must define a default Normal Inactivity statutory situation for a public sector type organization to select an employee as a Fonctionnaire in the specific public sector type organization.
See: Statutory Situations, Oracle HRMS for France Supplement and Entering Additional Personal Information (People Window, Oracle HRMS for France Supplement)
Step 15: Link Professional Activity to Public Sector Type Required Step
You must link the fields of professional activity to type of public sector before you associate a field of professional activity as the primary area of professional activity in a corps.
See: Linking Professional Activity to Public Sector Type, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 16: Extend the Types of Public Sector Optional Step
You can define types of public sector using the predefined value Other in the system lookup is FR_PQH_ORG_CATEGORY. For example, you can define Other as French Army to maintain and process the workforce details in the French army. The lookup has a DDF in the Further Information field to record whether the type of public sector allows incomplete employment time. The incomplete employment time details enable the HR Administrator to enter the agreed number of work hours and the frequency of work for the workforce.
See: Extending Types of Public Sector, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 17: French Workers Election Person Extra Information Type Required Step
Before you can run the Prod'hommale (Workers Election) Declaration process, you must enable the French Workers Election Person extra information type for your responsibility.
See: Setting Up Extra Information Types for a Responsibility, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 18: Set Up Element Group Names Required Step
When you define an element, you select a group name. All the elements allocated the same group name normally appear on one line of the pay advice against the group name, rather than the element reporting name. The exceptions are:
-
If the elements in the group use different rates, the bases are not summed; they appear on separate lines.
-
If the elements were prorated and the proration dates are different, they are listed on separate lines.
-
Some classifications behave differently. For example overtime and payments/deductions for absences show all elements separately.
Selecting a group name is required for most classifications. You set up as many group names as you require using the lookup FR_USER_ELENT_GROUP.
Step 19: Absence Payments Optional Step
If you want to process pay for sickness, maternity, paternity, or adoption absences, then you must perform some additional implementation.
See: Setting Up Sick Pay, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guid
See: Setting Up Maternity, Paternity, and Adoption Pay Processing, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 20: Setting up the Personnel Registry Report Optional Step
To customize the details displayed on the Personnel Registry report, you must complete several tasks.
See: Customizing XML Reports, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Use the predefined template RUP_TEMPLATE.rtf as a sample while creating your report template. See: Personnel Registry Report Template Tags, Oracle HRMS for France Supplement
Use the following details of the predefined template definition as a sample while creating a new template definition for your report template:
| Column Name | Column Value |
|---|---|
| Name | French RUP Report |
| Code | PERFRRUP |
| Application | Human Resources |
| Data Definition | French RUP Report |
| Type | RTF |
| Start Date | 01-Jan-1900 |
| Default File | RUP_TEMPLATE.rtf |
| End Date (not mandatory) | |
| Default File Language | English |
| Subtemplate (not mandatory) | |
| Default File Territory | United States |
| Description | French RUP Report |
While creating the template definition, you must specify the data definition as French RUP Report as Oracle XML Publisher associates your template definition with this predefined data definition.
While modifying the predefined template, you can add as new fields the values that are available in the lookup FR_RUP_XML_REPORT and HR tables such as PER_ALL_PEOPLE_F, PER_CONTRACTS_F, but not mapped with the predefined report template RUP_TEMPLATE.rtf. You must not add new fields that have no data source in either the FR_RUP_XML_REPORT lookup or HR tables.
Step 21: Setting up the Training Access Individual Report Optional Step
To customize the details displayed on the Training Access Individual report, you must complete several tasks.
See: Customizing XML Reports, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Use the predefined template BIAF2005.rtf as a sample while creating your report template. See: Training Access Individual Report Template Tags, Oracle HRMS for France Supplement
Use the following details of the predefined template definition as a sample while creating a new template definition for your report template:
| Column Name | Column Value |
|---|---|
| Name | BIAF |
| Code | BIAFXMLR |
| Application | Human Resource |
| Data Definition | BIAFXMLR |
| Type | RTF |
| Start Date | 01-Jan-1900 |
| Default File | BIAF2005.rtf |
| End Date (not mandatory) | |
| Subtemplate (not mandatory) | |
| Default File Language | English |
| Territory Description | United States |
While creating the template definition, you must specify the data definition as BIAFXMLR as Oracle XML Publisher associates your template definition with this predefined data definition.
You can modify the predefined rich text format template by:
-
Adding new fields in the predefined template to display the required details in the BIAF report. You can add Full Name, Birth Date (date of birth), and Maiden as new fields without changing the existing fields in the predefined template. The full name, date of birth, and maiden name fields are available in the lookup BIAF_LOOKUP_CODE but not mapped with the predefined report template BIAF.rtf. In order to use these field names, you must customize the rich text format template with these label form fields and the corresponding data form field. You cannot add new data form fields.
-
Changing the name of the existing labels in the template. To change the display name of the labels in the template, you must change the existing values in the lookup BIAF_LOOKUP_CODE.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 22: Setting up the DIF Statement Optional Step
To meet the training law requirements, Oracle HRMS enables you to print DIF statement for all your employees. You can print the statement using the sample DIF statement template, or you can change the layout to display details that meet your business requirements. To configure the details displayed on the DIF statement, you must complete several tasks. See: Customizing XML Reports, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
While configuring the statement details, you can:
-
Use the predefined template DIF_stmt_tmpl.rtf as a sample while creating your statement template. See: DIF Statement Template Tags, Oracle HRMS for France Supplement
-
Use the following details of the predefined template definition as a sample while creating a new template definition for your statement template:
Column Name Column Value Name DIF Statement Template Code DIFSTM Application Oracle Human Resources Data Definition FRDIFSTM Type RTF Start Date 01-Jan-1990 Default File DIF_stmt_tmpl.rtf End Date (not mandatory Subtemplate (not mandatory) Default File Language English Territory Description French Republic (comprises Metropolitan France, French Guiana, Guadeluope, Martinique, Reunion, Mayotte, Saint Pierre, Miquelon, French Polynesia, French Southern Territories, New Caldonia, and Wallis and Futuna) While creating the template definition, you must specify the data definition as FRDIFSTM as Oracle XML Publisher associates your template definition with this predefined data definition.
-
You can modify the predefined rich text format template by:
-
Adding new fields in the predefined template to display the required details in the DIF Statement. You can add new fields that are available in the DIF_STMT_LOOKUP_CODE lookup but not mapped with the predefined report template DIF_stmt_tmpl.rtf. You can also remove fields from the predefined template.
Note: Ensure you save the modified template with a different name to retain the predefined template as a sample for reference.
-
Changing the name of the existing labels in the template. To change the display name of the labels in the template, you must change the existing values in the lookup DIF_STMT_LOOKUP_CODE.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
Step 23: Create and Assign Fast Formula to Eligibility Profiles For Corps Required Step
Before you define eligibility profiles for the corps, use the predefined PL/SQL function PQH_FR_SPEED.chk_speed_length() to create the formula function and fast formula of type Participation and Rate Eligibility. This fast formula evaluates whether an employee satisfies the length of service required in the current step, current grade, or grade ladder depending upon the career path you defined at the step. You must assign this fast formula to the required participation eligibility profile. See: Setting Up Corps, Oracle HRMS for France Supplement
While creating the formula function, ensure the following:
-
The formula function definition matches the PL/SQL function PQH_FR_SPEED.chk_speed_length().
-
Click Context Usages and add Assignment_Id as context name with Number as data type and Date_Earned as context name with Date as data type.
See: Registering a Function, Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
While creating the fast formula, ensure that you select Participation and Rate Eligibility as type and return a variable with name ELIGIBLE. This is required as the calling Eligibility program expects a variable having the name "ELIGIBLE" and should return a value of either "Y" or "N". See: Writing or Editing a Formula, Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
Setting Up Web/ADI to Produce the Full Settlement Report Optional Step s
Web/ADI is the replacement for ADE. It allows a view to associated with a professional form. When the export button on the form is pressed the view is executed using the WHERE clause existing in the form to restrict the data. The output of the view is downloaded into either an Excel or Word document, and the system can be configured to automatically link this to become the source of a Word MailMerge.
See: Implementing Web ADI for use with Oracle HRMS, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Setting up Web/ADI to produce this behaviour requires the following steps:
Step 24: Adding Web/ADI responsibility to the user
The user should be given the responsibility Web ADI with the Standard security group.
Step 25: Create mapping between view and form
Enter the Web Adi responsibility and navigate to Create Document
-
Select Settings - click Next
-
Select Integrator - choose HR Integrator Setup - click Next
-
Select Content - click Next
-
Document Creation Review - click Create Document
-
Spreadsheet should be created - complete as follows
a. METADATA_TYPE = DOWNLOAD
b. APPLICATION_ID = 800
c. INTEGRATOR_USER_NAME = FR_TERMINATION
d. VIEW_NAME = HR_FR_TERMINATION_V
e. FORM_NAME = PERWSTEM
-
Choose Oracle -> Upload
-
In dialog window - click Upload
-
Close dialog and spreadsheet
-
From Web ADI responsibility choose "Define Layout"
-
Select Integrator - choose FR_TERMINATION - Go
-
Define Layout
a. Layout Name = FR_TERMINATION
b. Layout Key = FR_PERWSTEM
c. Field List = HR_FR_TERMINATION_V
-
Click Next
-
Define Layout - Select All, then deselect system values, i.e. Assignment ID etc. - Apply, Cancel
-
Add "Web ADI Create Document" function to FR_HRMS_NAV menu
-
In End Employment form query person. Use Export to download the information to a word document. Save as a temporary file.
-
Create Mail Merge Template document using the temporary download doc as the data source.
-
Add "HRMS ADI Document Manager Menu" submenu option to FR_HRMS_NAV
-
Upload the Mail Merge Temporary document from the Document Management menu option.
-
Alternatively use the following to upload the document :
FNDGFU apps/apps 0 Y PROGRAM_NAME=HRMS_ADI PROGRAM_TAG=TERMINATION LANGUAGE=US CONTENT_TYPE=application/msword {document}.docCheck if the document now exists following the upload using
select FILE_NAME
from fnd_lobs
where PROGRAM_NAME like 'HRMS_ADI';
-
Web/ADI -> Manage Document Links
-
Select Integrator - choose FR_TERMINATION - Go
-
Select Layout - FR_TERMINATION - Link a document - Go
-
In End Employment form query person. Use Export to download the information to a Word 2000.
-
Mail Merge occurs automatically.
Use the View -> List -> People Folder form (PERWSFPE) to produce the Full Settlement Report for multiple employees.
A new folder should be defined that only contains those employees who have been terminated. One possible way of doing this is to create a folder with the following additional WHERE clause:
1=1 and exists (select null from per_periods_of_service where person_id = per_people_v2.person_id and actual_termination_date is null)
Note: This additional WHERE clause returns all employees who have a period of service with an actual termination date. It may not be restrictive enough in which case an alternative restriction must be found.
Step 26: Run the Seed French Data Process Optional Step
This process creates and populates user defined tables using predefined lookup types and rows. It generates new columns in a user defined table that has the same name as the lookup type. There are no parameters to be completed for this report.
You run the 'Seed French Data' process from the Submit Requests window.
To Run the Seed French Data Process
-
Select Seed French Data in the Name field.
Choose the Submit button.
Additional Implementation Steps for Hong Kong
If you are implementing Oracle HRMS for Hong Kong, you must also complete the following additional implementation steps.
Set up MPF Processing
Step 1: Define MPF Information Element Link Required Step
For the purpose of administering MPF processing for your employees, you need only define one element link in Oracle Payroll. This link is for the element MPF Information. This element requires a scheme to be entered for all employees at the time of enrolment. The link for MPF Information must not be a Standard link, and is normally a link to all payrolls.
See: Defining Element Links, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 2: Create Balance Feeds for MPF Contributions Required Step
In order to process MPF contributions, you must create balance feeds for the following two balances:
-
MPF_RI (Relevant Income for MPF calculations)
-
MPF_BASIC (Basic Pay for MPF calculations)
See: Creating Balance Feeds for Individual Elements, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Report Retro MPF Liability by Pay Period
Oracle provides a new function to report the break up the Retro MPF Liability component amounts by payroll period rather than displaying as a consolidated amount within the MPF Remittance report.
Step 3: To report Retro MPF Liability by Pay Period Optional Step
Follow the steps given below to report the break up amounts by payroll periods:
-
Use the predefined non-recurring elements Retro MPF Liability for First Period and Retro MPF Liability for Second Period for displaying the break up amounts of Retro MPF Liability component for each pay period. The values for these elements are fed indirectly from MPF formula of MPF Information element
-
If you want to use the existing Retro MPF Liability element for balance adjustment, then feed the same values for the Retro MPF Liability for First Period.
-
If you want to use get_retro_mpf function, then add the following parameters to return value, date for different pay period.
-
l_er_liab_prd_fp
-
l_er_liab_prd_sp
-
l_er_start_date_fp
-
l_er_start_date_sp
-
l_er_end_date_fp
-
l_er_end_date_sp
-
-
If you are using a custom MPF formula, the formula results should add values into Retro MPF Liability for First Period and (or) Retro MPF Liability for Second Period elements.
Set up IR56 Balance Feeds
Step 4: Create Balance Feeds for IR56 Reporting Optional Step
You must create balance feeds for the following balances before you can run your IR56 reports:
-
IR56_A
-
IR56_B
-
IR56_C
-
IR56_D
-
IR56_E
-
IR56_F
-
IR56_G
-
IR56_H
-
IR56_I
-
IR56_J
-
IR56_K1
-
IR56_K2
-
IR56_K3
-
IR56_L
-
IR56_M
See: Create Balance Feeds for Individual Elements, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Set up Pay Leave Payments Based on Average Daily Wage Rate
If you plan to use the average daily wage rate based on salary earned in the last 12 months feature, then complete the following steps:
Step 5: Set up Pay Leave Payments Based on Average Daily Wage Rate Optional Step
Oracle HRMS provides seeded balance, formula and function to support 12-month Average Wage calculation.
-
Create a new balance or for an existing balance, feed all earnings elements that contribute to calculation of average pay rate.
-
Attach dimension _ASG_12MTHS_PREV to the balance to generate appropriate DB item, <Balance>_ASG_12_MTHS_PREV.
-
Using the DBI in custom fast formula, retrieve the total earnings in last 12 months. For custom formula, use the template formula HK_12MONTH_AVG_RATE as reference.
-
Calculate the number of days in last 12 months using the formula function HK_LAST_12_MNTH_DAYS ( ) and the DB item.
-
The application calculates the average daily wage rate = Last 12 months earnings sum/No of days in last 12 months
Set Up the Postscript Printer for Postscript Reports
There are five postscript reports produced for Oracle HRMS for Hong Kong.
-
IR56F - Employee Cessation Remaining in Hong Kong
-
IR56G - Employee Cessation departing Hong Kong
-
IR56E - Employers Return
-
IR56B - Annual Employers Return Hong Kong (Full)
-
IR56B - Annual Employers Return Hong Kong (Partial)
To print the postscript reports, you must install and configure the required fonts for your printer.
Step 6: To set up the postscript printer: Required Step
-
Make a note of the printer type specified at the concurrent program level, when you are submitting the postscript report.
-
Locate the directory $ORACLE_HOME/guicommon6/tk60/admin, and open the uiprint.txt file
-
Find the printer specified in step 1 while submitting the postscript report, and its corresponding generated .PPD file. Make a note of the file name and proceed to the next step.
-
Locate the directory $ORACLE_HOME/guicommon6/tk60/admin/PPD, open the .PPD file that was generated (Step 3), and search for the font type Courier-BoldItalic.
Note: If you do not have the Courier-BoldItalic font, download the appropriate PPD files. The application picks up this font while printing the report, only if the font entry exists in the .PPD file.
-
Edit the uiprint.txt file. Remove the dummy line at the end of the file, and create your entry. For example, FRED:PostScript:2:team_hpljet5:HPLJ5SI1.PPD
-
Save your file and exit.
-
Print the postscript report from the Oracle HRMS application.
Set Up Chinese Characters for IR56B Annual Employers Return Hong Kong Report
To ensure that the IR56B Annual Employers Return Hong Kong Report display the Chinese full name correctly, follow the steps given :
Step 7: To set up Chinese Characters Required Step
-
Login using the System Administrator responsibility to set environment variable IX_PRINTING
-
Run the Prints Environment Variable process. Check if the value is
/slot/ems2903/appmgr/apps/apps_st/appl/fnd/12.0.0/resource/ixlib.cfg
If the value returns NULL, see My Oracle Support Doc ID 415967.1 for the steps.
-
Ensure to backup the configuration file - ixlib.cfg file
cp ixlib.cfg ixlib.cfg.bkp
-
Modify the configuration file ixlib.cfg
vi ixlib.cfg
Comment the existing lines under section [AMERICAN,,,,,]
%Font.Times.Plain= printer:Times-Roman %Font.Times.Bold = printer:Times-Bold
Add the following two new lines:
Font.Times.Plain = <FND_TOP>/<APPLRSC>/ALBANWTT.ttf Font.Times.Bold = <FND_TOP>/<APPLRSC>/ALBANWTT.ttf
-
Restart all the services.
-
If concurrent manager is inactive, run the following command:
adcmctl.sh start apps/apps
-
Enter the full name in Chinese characters for employees.
See: Entering a New Person (People Window) , Oracle HRMS for Hong Kong Supplementand Entering Additional Personal Information, Oracle HRMS for Hong Kong Supplement.
-
Run the QuickPay.
See: Running the QuickPay Process, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
-
Run Prepayment processes.
See: Running the Prepayment Process, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
-
Run IR56B Annual Employers Return Archive process. See : Running the IR56B Annual Employers Return Archive process, Oracle HRMS for Hong Kong Supplement.
-
Run IR56B Annual Employers Return Hong Kong (Full) process. See: Running the IR56B Annual Employers Return Hong Kong (Full) process, Oracle HRMS for Hong Kong Supplement
Additional Implementation Steps for the Netherlands
If you are implementing Oracle HR for the Netherlands, you may also need to complete the following additional implementation steps.
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Configure the Title Field
If the Title field does not meet the requirements of your enterprise, you can add new values to the existing set of predefined lookup values.
-
Lookup Type: TITLE
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 2: Configure User Tables for Default Absence Actions
To use absence tracking, you must first set up a user table to store default re-integration actions for each absence category you want to use. As a minimum you must set up one user table for the absence category of Sickness.
The re-integration actions you set up here are displayed in the Absence Tracking pages for absence records with the relevant absence category. Using the Absence Tracking pages you can use these actions and update them, add more actions to the absence record or delete the actions from the record.
Note: Only the default re-integration actions you set up for an absence category using the user tables appear for the absence records. Any actions you add, update or delete to an absence record using the Absence Tracking pages appear only for that record.
Set up the default re-integration actions user tables as follows:
-
Name each user table: NL_ABS_ACTION_(category code). The absence category code relates to the relevant lookup code in the Absence Category Lookup Type. For example, the category code for Sickness is 'S'.
-
Set the match type as Match and the key units of measure as Text.
-
Set up the following four columns and values:
Column Name Required Values Example Values ROW_NUMBER NA This column uniquely identifies the ACTION. You can enter alpha and numercial values, for example 1, 1A, 1B etc. ACTION NA This column describes the re-integration action, for example Progression Plan. TIME_PERIOD NA This column describes the number of time units. For example, for the action Progression Plan, you set up a time period of 1 and a time unit of 'M' for months, this means you have one month to perform the action for the employee from the start of the absence record. TIME_UNITS 'D' for Days, 'W' for Weeks, 'M' for Months NA -
Set up row labels for each row in the Exact field, and set up the order you want the rows to appear in the table using the Sequence field. The number of rows you set up determines the number of values you can enter.
-
For every date effective row you set up in the user table, you must also set up a date effective value for each column. This is to ensure that when you use the Absence Tracking pages on a date that is on or later than the effective dates set up, then the user table displays the default actions and their values.
Note: If you use the Absence Tracking pages on a date that is earlier than the effective dates set up in the user table, an error message displays to indicate that the user table is incorrectly set up.
See: User and Extensible Lookups, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
See: Setting Up User Tables, Columns and Rows, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
See: Tracking Absences, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 3: Set Up Dutch Organizations for Social Insurance, Tax and the Law SAMEN
You must set up your organizations correctly to enable you to:
-
Record the correct tax and social insurance information for your employers and employees.
-
Process the tax deductions and social insurance contributions.
-
Run the Law SAMEN Reporting information correctly.
See: Setting up Tax, Social Insurance, and Private Health Insurance Organizations, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
See: Setting Up Social Insurance Days, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
See: Setting Up Information for the Law SAMEN Reports, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 4: Set up Statutory Deductions
If you are using Oracle Payroll, you must set up your statutory tax and social insurance deductions.
See: Setting up Tax and Social Insurance Deductions, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
To enable flat rate taxation in Oracle Payroll, you must set up elements and balances related to flat rate tax.
See: Setting Up Flat Rate Taxation, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 5: Set Up Pension Schemes
You can set up the pension schemes available to your employees. This enables you to process pension contributions in the payroll run. To review the functionality available, see: Savings and Retirement Overview, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide. For the setup steps, see: Setting Up Pension and Savings Schemes, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 6: Disable Full Name Formats Optional Step
You can disable full name formats that you do not wish to use in the User Types and Statuses window. The full name formats that you disable, do not appear in the Full Name Format field in the People window.
See: Disabling Full Name Formats, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
See: Entering Additional Personal Information (People Window), Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 7: Set Up Information for the Wage Report Required Step
Some setup tasks are necessary before you can run the Dutch Wage Report.
See: Setting Up the Dutch Wage Report, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 8: Link Predefined Elements Required Step
You must link the following predefined elements:
-
Labour Handicap Discount, which holds the calculated discount value for labor handicapped employees
-
Retro Labour Handicap Discount, which holds changes made retrospectively to the Labour Handicap Discount element
Note: You do not need to attach these elements to assignments eligible for labor handicap discount. The application checks for eligibility during SI processing and generates results for eligible elements. Ensure you link the elements for costing purposes.
You need to attach the predefined element, SI Override Days to assignments to enter override days manually. The application uses this information in case of the following:
-
For long-term unpaid leave
-
If an employee has more than three active assignments and a time gap exists between assignments, for example, the employee has one or more days between the payroll start date (or employee period of service start date if earlier than period start date) and payroll end date (or employee period of service end date if later than period start date) where no active assignment exists.
Note: You do not need to use this element if the assignments remain active throughout the payroll period and period of service.
Step 9: Set Up Information for Health and Disability Insurance Contributions Required Step
Some setup tasks are necessary before the payroll process can calculate health and disability insurance contributions.
See: Setting Up ZVW, WGA, IVA, and UFO Contributions, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 10: Set Up First Day Report Required Step
You need to set up the first day report for enabling you to electronically send the employee information to tax authorities.
See: Setting Up the First Day Report, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Additional Implementation Steps for Germany
If you are implementing Oracle HR for Germany you must also complete the following additional implementation steps.
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Define Element Links
You must define the element links for tax and social insurance.
You define the links in the Element Links window.
-
Select Social Insurance in the Element Name field.
-
Select an effective date that is prior to the system date, for example, 01 Jan 2001.
-
Save your work.
-
Repeat the above steps for the Tax Information and Tax Exemption Information elements.
Step 2: Specify a Preferred Organization Hierarchy
When you define your business group, you must specify which hierarchy is the preferred, or named, hierarchy. For example, you could choose the primary hierarchy or a different hierarchy. The named hierarchy defines how the additional information entered for your organizations is inherited by the child organizations.
You select the hierarchy in the Organization window.
See: Entering German Business Group Information, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide.
Additional Implementation Steps for Singapore
Additional Implementation Steps
If you are implementing Oracle HRMS for Singapore you must also complete the following additional implementation steps.
For information on the validations required to process IRAS processes accurately, see: Oracle HRMS Process to Report Employees' Yearly Remuneration, White Paper on My Oracle Support.
Step 1: Set Up the National Service In-Camp Training Computation Report
This report enables you to calculate the pay amount that can be claimed for an employee who is attending mandatory National Service In-Camp Training.
See: Setting up the National Service In-Camp Training Computation Report, Oracle HRMS for Singapore Supplement.
Step 2: Create Balance Feed for Community Chest/SHARE Contributions
In order to process voluntary Community Chest/SHARE contributions, you must create a balance feed for the Community Chest Withheld balance.
See: Creating Balance Feeds for Individual Elements, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 3: Create Balance Feed for CPF and SDL Contributions
A number of balances have been predefined, known collectively as Eligible Compensation Balances. These balances enable you to control which payments are considered for certain statutory deductions. When creating a new earnings element, you must manually enter the new element into the feeds of the appropriate Eligible Compensation balance.
Two Eligible Compensation balances are predefined for CPF contributions:
-
CPF Additional Earnings Eligible Comp
-
CPF Ordinary Earnings Eligible Comp
One Eligible Compensation balance is predefined for SDL contributions:
-
SDL Eligible Comp
See: Creating Balance Feeds for Individual Elements, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 4: Personalize the Address Region to Use Formatted Address Style within the SSHR Pages Optional Step
The SSHR Personal Information page supports the Singapore International address style. In order to use the Singapore Formatted Address Style, you can personalize the address region in the Person Information page as follows:
-
Navigate to Personal Information.
-
Click Add/Modify/Update of Main Address and/or Other Address.
-
Click Personalize Main Address or Personalize Other Address.
-
Scroll down to HrAddressFlex and click the pencil icon for personalization.
-
Navigate to the Segment List at the bottom of the page.
-
Update the Segment List field under the responsibility level with Singapore Formatted address style using the following segment list
SG|Block Number or Address Number|Apartment Unit Floor-Number|Street|Postal Code|Country|Telephone|Telephone2|Telephone3
Note: The Singapore Formatted address style context SG is followed by the segment list separated by pipe.
Tip: Refer the structure defined for SG context for Personal Address Information Developer Flexfield.
-
Click Apply.
-
You can now enter the Main Address and Other Address in Singapore Formatted address style.
-
You can also personalize Segment List in Personal Information (Overview) Page and Personal Information Review Page for Main Address and Other Address to view the address in Singapore local format.
Additional Implementation Steps for Oracle HRMS for South Africa
To implement Oracle HRMS for South Africa, you must perform additional legislative-specific implementation steps.
You perform these steps at the implementation stage indicated below. For example, you perform the South African Administration steps when you perform the global Administration steps that apply to all legislations.
See: Implementing Oracle HRMS for the global implementation steps.
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Define Occupational Categories and Levels
When defining your key flexfields, you must define Occupational Categories and Occupational Levels for your Grade, Position or Job Flexfield(s), depending on which key flexfield(s) you want to use to hold employment equity information.
Important: You must assign the predefined valuesets, PER_ZA_OCCUPATIONAL_CATEGORIES and PER_ZA_OCCUPATIONAL_LEVELS, on the Occupational Category and Occupational Level segments on the key flexfields that you choose.
See: Define Key Flexfields in the online help and Setting Up Employment Equity, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 2: Set Up Responsibility Access for Extra Information Types
You must set up responsibility-level access for the ZA_Tax_Information Assignment Extra Information Type (EIT).
See: Setting Up Extra Information Types Against a Responsibility in the online help.
You must set up responsibility-level access for the ZA_UIF_INFORMATION Assignment Extra Information Type (EIT).
See: Setting Up Extra Information Types Against a Responsibility in the online help.
Note: These EIT's should not be linked to any responsibilities that are used to administer Contingent Workers as the information stored on the EIT's is not relevant for Contingent Workers.
Step 3: Set Up Leave Reasons for Employment Equity and the UIF
You must enter the leave reasons for your enterprise into the LEAV_REAS lookup as part of the setup for the Employment Equity Reports and the Electronic UIF File.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 4: Set Up the User Table for NQF SETA and Skills Development Levy
You set up the NQF user table to record NQF SETA information and to run the skills development levy report.
See:Setting Up the User Table for NQF SETA and Skills Development Levy, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 5: Set Up User Tables for Employment Equity, UIF, and RSC
You must set up user tables for Employment Equity, UIF and RSC. Before you set up the Employment Equity and UIF tables, you must run the Termination Categories Setup Process.
-
Running the Termination Category Setup Process, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide and Setting Up User Tables, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide for the Employment Equity Report and the Electronic UIF File.
-
Setting Up User Tables for the RSC Levy Report, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 6: Define South African Organization Structures
When defining your organizations, you must set up South African-specific classifications and additional information for the following:
-
ACB Installation
-
NQF SETA
-
Tax File Creator
-
Employment Equity
-
ZA Tax
-
UIF File Creator
See: Entering Additional Information, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide for more information.
Step 7: Load CDV Bank Codes for ACB Payments
You must load CDV bank codes before you can run the ACB payroll processes.
See: Load CDV Bank Codes, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Note: You are unable to enter bank details when setting up Organizational and Personal Payment Methods until the CDV bank codes are loaded.
Step 8: Set Up Printers
To run South African reports in Oracle HRMS, you need to associate the predefined print styles with your printer driver.
See: Setting Up Your Printers, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide.
Step 9: Set up RetroPay Required Step
You need to set up the retropay information to process these payments correctly.
See: Setting Up Retro-Notification and RetroPay, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Additional Implementation Steps for Kuwait
If you are implementing Oracle HRMS for Kuwait, then you must also complete the following additional implementation steps.
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Set up the Social Insurance Calculations Required Step
To record and process the Public Institution for Social Security (PIFSS) social insurance schemes for employees, you must complete the setup for social insurance calculations. See: Calculating Social Insurance, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 2: Set up the Statement of Earnings Required Step
You need to set up the online statement of earnings before you can see the values correctly. See: Setting Up a Global Statement of Earnings, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Note: When entering SOE information at the Business Group level, select the predefined element sets KW_SOE_EARNINGS_ELEMENTS and KW_SOE_DEDUCTIONS_ELEMENTS and the predefined balance attribute KW_SOE_BALANCE_ATTRIBUTES.
Step 3: Set Up Electronic File Transfer Required Step
To process the electronic file transfer, you must complete several tasks. See: Setting Up Electronic File Transfer, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 4: Set up the Loan Process Required Step
To run the loan process, you must complete the following tasks:
-
Add the required loan types, such as car loan or house loan, as values to the lookup KW_Loan_Type. See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
Link the Loan Recovery element to the payroll. See: Defining Element Links, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Also see: Processing Loans, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Additional Implementation Steps for UAE
If you are implementing Oracle HRMS for UAE, then you must also complete the following additional implementation steps.
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Set up the Social Insurance Calculations Required Step
To record and process the GPSSA social insurance schemes for employees, you must complete the setup for social insurance calculations. See: Calculating Social Insurance, Oracle HRMS for United Arab Emirates Supplement
Step 2: Set up the Statement of Earnings Required Step
You need to set up the online statement of earnings before you can see the values correctly. See: Setting Up a Global Statement of Earnings, Oracle Payroll Processing Management Guide
Note: When entering SOE information at the Business Group level, select the predefined element sets AE_SOE_EARNINGS_ELEMENTS and AE_SOE_DEDUCTIONS_ELEMENTS and the predefined balance attribute AE_SOE_BALANCE_ATTRIBUTES.
Step 3: Set Up Electronic File Transfer Required Step
To process the electronic file transfer, you must complete several tasks. See: Setting Up Electronic File Transfer, Oracle HRMS for United Arab Emirates Supplement
Step 4: Set Up Gratuity Required Step
To process gratuity, you must complete several tasks. See: Calculating Gratuity, Oracle HRMS for United Arab Emirates Supplement
Step 5: Set up the Loan Process Required Step
To run the loan process, you must complete the following tasks:
-
Add the required loan types, such as car loan or house loan, as values to the lookup AE_Loan_Type. See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
Link the Loan Recovery element to the payroll. See: Defining Element Links, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Also see: Processing Loans, Oracle HRMS for United Arab Emirates Supplement
Additional Implementation Steps for Oracle HRMS for New Zealand
If you are implementing Oracle HRMS for New Zealand, you must also complete the following additional implementation steps.
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Set Up Leave and Leave Liability Required Step
Oracle HRMS for New Zealand allows you to enter leave absence information and leave payment details. In order to record an employee's leave payments and leave liability details, you must set up leave payments and leave liability.
Set Up Hourly Rate Formula
For leave liability processing, the implementation team must ensure that the hourly rate formula has been correctly set up. If an hourly rate formula has not been defined correctly, leave liability processing will not work.
See: Setting Up Leave Payments and Leave Liability, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide.
Step 2: Set Up Quarterly Employment Survey Reporting Required Step
The Quarterly Employment Survey has several balances that need to be set up.
See: Running the Quarterly Employment Survey Report, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 3: Set Up Responsibilities/Menus/Report Groups Required Step
When setting up Oracle HRMS for New Zealand, you must ensure that you set up the following;
-
the responsibility NZ HRMS Manager
-
the menu PER_NZ_HRMS_NAVIGATOR
-
the request group NZ HRMS Reports and Processes
See: Responsibilities, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 4: Create Other Bank File Formats Optional Step
Oracle HRMS for New Zealand supports the National Bank of New Zealand as the bank file format. To generate a custom bank file format, follow the steps given below to develop your own template.
-
Ensure that you have the XML Publisher Administrator responsibility.
-
Create an eText template for the bank file you want to generate. BI Publisher applies this template to an input XML data file to create an output text file.
-
You can also use the predefined XML for bank payments to build your eText template.
-
Use the XML Publisher Administrator responsibility to register the eText Outbound template.
-
Enter the template code as _EFT to indicate that the template is an electronic file transfer (EFT) file.
-
You must create a new lookup type within the Application Utilities Lookups window using the naming convention as %NZ_PYNZEFT%.You must enter the template code that you have defined for the eText template as the lookup code. You use the System Administrator responsibility to create the lookup type.
See: Adding Lookup Types and Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
Run the concurrent program Register BI Publisher Templates for Payroll to register the template as a bank file format.
See: Running the Register BI Publisher Templates for Payroll, Oracle HRMS for Payroll Processing Management Guide
Additional Implementation Steps for Hungary
If you are implementing Oracle HR for Hungary you must also complete the following additional implementation steps.
Please see the implementation section in Implementing Oracle HRMS for all other implementation steps that are not specific to Hungary.
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Set Up Language Skills
If your enterprise records information about the language skills held by its employees, you can set up a rating scale and competence to define this information, then assign the profile to an employee. You can configure the Additional Competence Element Details flexfield to hold the Certification Number. See: Setting Up Language Skills, Oracle HRMS for Hungary Supplement
Step 2: Set Up Shift Patterns
Set up work patterns to record shift details for your employees. See: Setting Up Shift and Shift Patterns, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 3: Set Up Pension Schemes
Set up pension schemes and enroll employees. See: Setting Up Pension Schemes, Oracle HRMS for Hungary Supplement
Step 4: Set Up the Employment Certification Report
Before you can run the Employment Certification Report, you must configure the report using Web ADI and then run the report generator. See: Setting Up the Employment Certificate Report, Oracle HRMS for Hungary Supplement
Step 5: Set Up the Hungarian Absence Report
Before you can run the Hungarian Absence Report, you must configure the report using Web ADI and then run the report generator. See: Setting Up the Hungarian Absence Report, Oracle HRMS for Hungary Supplement
Additional Implementation Steps for Spain
If you are implementing Oracle HRMS for Spain you must also complete the following additional implementation steps.
Please see the implementation section in Implementing Oracle HRMS for all other implementation steps that are not specific to Spain.
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Set Up Spanish Organizations
You must set up your organizations in a specific order to meet your business and reporting requirements.
See: Setting Up Spanish Organizations, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Step 2: Set Up Contract Key Relationship
You must set up the ES_CONTRACT_KEY_RELATION table to map the relationship between the contract key, status, type, subtype, and start reason.
See: Setting Up User Tables, Columns and Rows, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide and Setting Up the Contract Key Relation User Table, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 3: Set Up Termination Reasons
You must link your termination reason to the social security reasons for terminating employees.
See:Linking Termination Reasons to Social Security Reasons, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 4: Set Up Professional Category and Contribution Group Required Step
You must link the professional category to contribution groups to determine the monthly minimum and maximum social security contributions for employees.
See: Linking Professional Categories to Contribution Group, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 5: Set Up Shift Patterns
Set up work patterns to record shift details for your employees. See: Setting Up Shift and Shift Patterns, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 6: Set Up Statutory Reports
Before you can run the RED System : New Hires, Leavers, and Contract Changes Report and the Company Certificate Report, you must set up these reports to run the report generator and then run the data lock process.
See: Setting Up Statutory Reports, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 7: Set Up Tax and Social Security Information
You must define the following element links for recording the tax information accurately.
-
Tax Details
-
Tax Withholding Rates Overrides
You must define the following element links for recording the social security information accurately.
-
Social Security Details
-
Multiple Employment Details
You define the links in the Element Links window
-
Select Tax Details in the Element Name field
-
Select an effective date that is prior to the system date, for example, 01 Jan 2001.
-
Save your work.
-
Repeat the above steps for the Tax Withholding Rates Overrides, Social Security Details, Multiple Employment Details.
Step 8: Set Up Absence Information Required Step
You must set up the absence information to report the absences and the social security deductions accurately on the social security contribution reports (TC-1 and TC-2).
See: Setting Up Absences, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 9: Set Up Temporary Disability Absence Type
You must set up the Temporary Disability absence type to record the sickness leave. See:Setting Up Temporary Disability Absences, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 10: Set Up Historic Rates Required Step
You must set up Historic Rates if you want the option of calculating payments from the rates applicable when the work was done, rather than the later rates in effect at the time of calculation.
The Tax Withholding Rate process uses Historic Rates to calculate the Contractual Earnings. You must create a Rate Type called Contractual Earnings in the lookup, and attach this rate type to all elements that should be included in the employee's contractual earnings.
See: Setting Up Historic Rates, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 11: Set Up Net-to-Gross Information Optional Step
You need to set up net-to-gross information to process net-to-gross calculations.
See: Setting Up Net-to-Gross Calculation, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 12: Set Up Set Up Events for Proration and RetroPay Optional Step
You need to set up the proration and RetroPay information to make pro-rata payments and backdated payments
See: Setting Up Proration or Retro-Notification, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 13: Set Up Benefits in Kind Information Optional Step
You need to set up benefits in kind information to capture and calculate the applicable benefit information.
See: Setting Up Benefits in Kind, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 14: Set Up Court Order Information Optional Step
To calculate court order deductions you need to set up the court order information.
See: Setting Up Court Orders, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 15: Set Up Statutory Information Required Step
You must set up your statutory information to process the tax and social security deductions.
See: Setting Up Statutory Information, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 16: Set Up Partially Exempt Earnings Information Optional Step
To process the partially exempt earnings, you must set up the partially exempt element information.
See: Setting Up Partially Exempt Earnings, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 17: Set Up Tax Withholding Rate Information Optional Step
To compute the tax withholding rate you must set up the personal and economic information.
See: Setting Up Tax Withholding Information, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 18: Set Up Statement of Earnings Optional Step
You need to set up the online statement of earnings before you can see the values correctly.
See: Setting Up The Statement of Earnings, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 19: Set Up RetroPay Optional Step
You need to set up the RetroPay information to process backdated payments and corrections.
See: Setting Up Retro-Notification and RetroPay, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 20: Set Up Advance Pay Optional Step
You must set up the advance pay information to enable users to process the advance payments to employees.
See: Setting Up Advance Pay for Individual Assignments, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Additional Implementation Steps for Norway
If you are implementing Oracle HR for Norway you must also complete the following additional implementation steps.
See the implementation section in Implementing Oracle HRMS for all other implementation steps that are not specific to Norway.
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Upload the Postal Code File
You must upload the postal code file provided by the postal authority.
See: Uploading the Postal Code File, Oracle HRMS for Norway Supplement
Step 2: Set Up Norwegian Organizations
You must set up the following additional organizations to meet statutory Norwegian requirements.
See: Setting up Norwegian Organizations, Oracle HRMS for Norway Supplement
Step 3: Run Meta-Mapper
Run the meta-mapper process to support the uploading of tax cards. You run this process only once during implementation.
Step 4: Set Up Income Tax Information
You need to set up your tax information to calculate tax correctly.
See: Setting Up Income Tax Deduction, Oracle HRMS for Norway Supplement
Step 5: Upload Tax Card
You must upload the flat file, containing the employees' tax information, which you receive from the tax administration to calculate the tax deductions correctly.
See: Uploading the Tax Card, Oracle HRMS for Norway Supplement
Step 6: Set Up Proration
You need to set up the proration information to process these payments correctly.
See: Setting Up Proration or Retro-Notification, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 7: Set Up Retro-Notification and RetroPay
You need to set up the retro-notification and retropay information to process these payments correctly.
See: Setting Up Retro-Notification and RetroPay, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 8: Set Up Third-Party Payment Information
You need to set up the third-party payment information to capture the third-party payment details.
See: Setting Up Third-Party Payments, Oracle HRMS for Norway Supplement
Step 9: Set Up Support Order Information
You need to set up support order information to calculate support order wage attachments.
See: Setting Up Support Orders, Oracle HRMS for Norway Supplement
Step 10: Set Up Union Dues Information
You need to set up union dues information for the electronic payment of union dues to any trade union to which an employee belongs.
See: Setting Up Union Dues, Oracle HRMS for Norway Supplement
Step 11: Set Up Tax Levy Information
You need to set up tax levy information for the electronic payment of tax levies to the tax authority.
See: Setting Up Tax Levies, Oracle HRMS for Norway Supplement
Step 12: Set Up Employer Contributions
You need to set up the employer contributions calculation.
See: Setting Up Employer Contributions, Oracle HRMS for Norway Supplement
Step 13: Set Up Travel Expense Information
You need to set up travel expense information to capture the relevant details.
See: Setting Up Travel Expenses, Oracle HRMS for Norway Supplement
Step 14: Set Up Benefits in Kind Information
You need to set up benefits in kind information to capture and calculate the applicable benefit information.
See: Setting Up Benefits in Kind, Oracle HRMS for Norway Supplement
Step 15: Set Up Statement of Earnings
You need to set up the online statement of earnings before you can see the values correctly.
When entering SOE information at the Business Group level, select the predefined element sets NO_SOE_EARNINGS_ELEMENTS and NO_SOE_DEDUCTIONS_ELEMENT and the predefined balance attribute NO_SOE_BALANCE_ATTRIBUTES.
See: Setting Up a Global Statement of Earnings (SOE), Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Additional Implementation Steps for Finland
If you are implementing Oracle HRMS Payroll for Finland you must also complete the following additional implementation steps.
See the implementation section in Implementing Oracle HRMS for all other implementation steps that are not specific to Finland.
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Set Up Finnish Organizations
Set up the following organizations to meet your statutory Finnish requirements.
See: Setting Up Finnish Organizations, Oracle HRMS for Finland Supplement
Step 2: Link Place of Residence to Regional Membership
You must enter values into the FI_REGIONAL_MEMBERSHIP table to map the place of residence to any of the three regional memberships, Nordic, EU, or non-EU.
See: Setting Up User Tables, Columns and Rows, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide and Linking Place of Residence to Regional Membership, Oracle HRMS for Finland Supplement
Step 3: Run Meta-Mapper
Step 4: Set Up Income Tax Information
You need to set up your tax information to calculate tax correctly.
See: Setting Up Income Tax Deduction, Oracle HRMS for Finland Supplement
Step 5: Upload Tax Card
You must upload the flat file, containing the employees' tax information, that you receive from the tax administration to calculate the tax deductions correctly.
See: Uploading the Tax Card, Oracle HRMS for Finland Supplement
Step 6: Set Up Proration and RetroPay
You need to set up the proration and RetroPay information to process these payments correctly.
See: Setting Up Proration or Retro-Notification, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 7: Set Up Third Party Payment Information
You need to set up the third party payment information to capture the third party payment details.
See: Setting Up Third Party Payments, Oracle HRMS for Finland Supplement
Step 8: Set Up Pension Insurance Information
You need to set up pension insurance information to calculate pension insurance contributions.
See: Setting Up Pension Insurance Contribution, Oracle HRMS for Finland Supplement
Step 9: Set Up Insurance Premium Information
You need to set up insurance premium information to calculate accident insurance premium, unemployment insurance fee, and group life insurance premium.
See: Setting Up Insurance Premiums, Oracle HRMS for Finland Supplement
Step 10: Set Up Court Order Information
You need to set up court order information to calculate court order deductions.
See: Setting Up Court Orders, Oracle HRMS for Finland Supplement
Step 11: Set Up Union Dues
You need to set up trade union information to calculate union dues.
See: Setting Up Union Dues, Oracle HRMS for Finland Supplement
Step 12: Set Up Travel Expense Information
You need to set up travel expense information to capture the relevant details.
See: Setting Up Travel Expenses, Oracle HRMS for Finland Supplement
Step 13: Set Up Benefits in Kind Information
You need to set up benefits in kind information to capture and calculate the applicable benefit information.
See: Setting Up Benefits in Kind, Oracle HRMS for Finland Supplement
Step 14: Set Up Net-to-Gross Information
You need to set up net-to-gross information to process net-to-gross calculations.
See: Setting Up Net-to-Gross Calculation, Oracle HRMS for Finland Supplement
Step 15: Set Up Social Security Information
You need to set up social security information to calculate social security fees.
See: Setting Up Social Security Fee, Oracle HRMS for Finland Supplement
Step 16: Set Up Negative Payment Information
You need to set up negative payment information to process negative payments manually.
See: Setting Up Negative Payments, Oracle HRMS for Finland Supplement
Step 17: Set Up Electronic File Transfer
You need to set up the electronic file transfer information to make payments.
See: Setting Up Electronic File Transfer (EFT), Oracle HRMS for Finland Supplement
Step 18: Set Up Statement of Earnings
You need to set up the online statement of earnings before you can see the values correctly.
See: Setting Up a Global Statement of Earnings (SOE), Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 19: Set Up Postal Codes
If you do not use the Finnish postal code upload functionality, then you can enter postal codes and post offices manually.
See: Entering Postal Codes, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 20: Set Up User Tables to Capture Absences for Multiple Assignments
You create absence element entries for multiple assignments by setting up user tables that map absence categories and types to elements. For an employee with multiple assignments, you can change the absence details to suit each assignment better.
Use the FI_ABSENCE_CATEGORY_AND_DETAILS table to map the absence categories to the elements. Use the FI_ABSENCE_TYPE_AND_DETAILS table to map the absence types to the elements. There are two columns in both the tables, ELEMENT and ELEMENT_ENTRY_LOGIC. The ELEMENT_ENTRY_LOGIC column contains the logic for loading the element entries. You must ensure that all the procedures you configure for the absence element entry creation return the absence_attendance_id value in the CREATOR_ID input value.
Step 21: Set Up Holiday Pay
Before you can calculate holiday pay, you must set up Holiday Pay before processing the payroll.
See: Setting Up Holiday Pay, Oracle HRMS for Finland Supplement
Additional Implementation Steps for Denmark
If you are implementing Oracle HRMS for Denmark you must also complete the following additional implementation steps.
Please see the implementation section in Implementing Oracle HRMS for all other implementation steps that are not specific to Denmark.
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Set Up Danish Organizations
Set up additional organizations to meet statutory Danish requirements.
See: Setting up Danish Organizations, Oracle HRMS for Denmark Supplement
Step 2: Run Meta-Mapper
Run the meta-mapper process to support the uploading of postal codes and tax cards. You run this process only once during implementation.
Step 3: Set Up Withholding Tax
You need to set up your tax information to calculate tax correctly.
See: Setting Up Withholding Tax, Oracle HRMS for Denmark Supplement
Step 4: Upload Tax Card
You must upload the flat file, containing the employees' tax information, that you receive from the tax administration to calculate the tax deductions correctly.
See: Uploading the Tax Card, Oracle HRMS for Denmark Supplement
Step 5: Set Up Proration
You need to set up proration to process these payments correctly.
See: Setting Up Proration or Retro-Notification, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 6: Set Up RetroPay
You need to set up the RetroPay information to process these payments correctly.
See: Setting Up Retro-Notification and RetroPay, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 7: Setting Up Pension Information
You need to set up your pension contribution information to calculate the pre-tax deductions.
See: Setting Up Wage Earners Supplementary Pension Foundation (ATP) Contributions, Oracle HRMS for Denmark Supplement
See: Setting Up Other Pension Contributions, Oracle HRMS for Denmark Supplement
Step 8: Set Up Labor Market Contributions
You need to set up labor market contribution information to calculate the pre-tax deduction.
See: Setting Up Labor Market Contributions (AMB), Oracle HRMS for Denmark Supplement
Step 9: Set Up Court Order Information
Link the Court Order Deduction element, which you enter on employee assignments, to your payroll.
See: Defining Element Links, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Managment Guide
See: Making Manual Element Entries, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Managment Guide
Step 10: Set Up Benefits in Kind Information
You need to set up benefits in kind information to capture and calculate the applicable benefits information.
See: Setting Up Benefits in Kind, Oracle HRMS for Denmark Supplement
Step 11: Set Up G-Dage Pay Information
Link the Court Order Deduction element, which you enter on employee assignments, to your payroll.
See: Defining Element Links, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Managment Guide
See: Making Manual Element Entries, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Managment Guide
Step 12: Set Up Electronic File Transfer
You need to set up the electronic file transfer information to make payments.
See: Setting Up Electronic File Transfer (EFT), Oracle HRMS for Denmark Supplement
Step 13: Set Up Statement of Earnings
You need to set up the online statement of earnings before you can see the values correctly.
The predefined element sets are:
-
DK_SOE_EARNINGS_ELEMENTS
-
DK_SOE_DEDUCTIONS_ELEMENTS
-
DK_SOE_EMPLOYER_CHARGES_ELEMENTS
-
DK_SOE_INFORMATION_ELEMENTS
The predefined balance attribute is DK_SOE_BALANCE_ATTRIBUTES.
See: Setting Up a Global Statement of Earnings (SOE), Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 14: Upload Postal Code
You need to upload the file that contains the postal codes and corresponding post office names to view the data correctly in the application.
See: Uploading Postal Code, Oracle HRMS for Denmark Supplement
Step 15: Set Up Holiday Pay
To calculate holiday pay, you must set up Holiday Pay before processing the payroll.
See: Setting Up Holiday Pay, Oracle HRMS for Denmark Supplement
Step 16: Set Up Sick Pay
To calculate sickness pay, you must set up Sick Pay before processing the payroll.
See: Setting Up Sick Pay, Oracle HRMS for Denmark Supplement
Additional Implementation Steps for Russia
If you are implementing Oracle HRMS for Russia, you must also complete the following additional implementation steps.
Please see the implementation section in Implementing Oracle HRMS for all other implementation steps that are not specific to Russia.
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Set Up Values for the Grade Key Flexfield
You must enter the number of the Grade Code segment of the Grade Key Flexfield in the RU_FLEXFIELD_SEGMENT_MAPPINGS table. This value enables the application to pick the statutory grade code while generating some statutory reports. See: Entering Table Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 2: Set Up Education Details
To help you manage the development of your workforce, you can record education details such as the professional retraining course that a worker attends. The foreign language information you record for your employees is used for statutory reporting purposes. You must set up the education details by completing the following tasks:
-
Define the qualification types. The category of qualification types consists of values from the RU_EDUCATION_LEVELS and RU_ENTERPRISE_ EDUCATION lookups. In addition, the category comprises two other values, Qualification Improvement and Professional Retraining. See: Creating Qualification Types, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
Set up the foreign language information. See: Setting Up Foreign Language Information, Oracle HRMS for Russia Supplement
-
Set Up Values for the Competence Key Flexfield segments. You must enter the numbers of the Foreign Language Code and Foreign Language Name segments of the Competence Key Flexfield in the RU_FLEXFIELD_SEGMENT_MAPPINGS table. This enables the application to pick the statutory code and name of the foreign language in which an employee is competent while generating some statutory reports. See: Entering Table Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
Map the RU_EDUCATION_LEVELS and RU_ENTERPRISE_EDUCATION lookup values to the PER_CATEGORIES lookup values using the User Types and Statuses window. This mapping enables the application to pick up Russia specific codes while generating the statutory reports. See: Creating User Types and Statuses, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 3: Set Up Values for the Marital Status Lookup
Map the RU_MARITAL_STATUS lookup values to the MAR_STATUS lookup values using the User Types and Statuses window. This mapping enables the application to pick up Russia specific codes while generating the statutory reports. See: Creating User Types and Statuses, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Additional Implementation Steps for India
If you are implementing Oracle HRMS for India you must complete the following additional implementation steps.
Please see the following implementation sections in Implementing Oracle HRMS for all other implementation steps that are not specific to India.
See: Enterprise and Workforce Management
See: Payroll Process Management
See:Compensation, Benefits and Payroll
See: Workforce Sourcing and Deployment
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Set Up Indian Organization structures Required Step
You must set up your GRE/Legal Entity, Business Group and Registered Company organizations in order to:
-
Configure company information, statutory setup information, income tax details, income tax declaration information, professional tax details, and termination notice period details.
-
Record challan bank details, income tax challan information, and representative details.
-
Process statutory tax deductions, social insurance contributions and retirement benefits contributions.
In addition to the above, set up the following organizations to suit your organization structure:
-
Factory
-
Shops/Establishment
-
ESI Organization
-
Provident Fund Organization
-
Professional Tax Organization
-
Contractor
See: Organization Classifications, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide (India), Creating an Organization, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide, and Entering Additional Organization Information, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide (India)
Step 2: Create Allowances, Perquisites, Earnings, and Fringe Benefits Elements using the Element Design Wizard Required Step
If you are using Oracle payroll, you must set up Allowances, Perquisites, Earnings and Fringe Benefit Elements. Oracle HRMS for India supports the following:
| Element Classifications | Description |
|---|---|
| Allowances |
|
| Perquisites |
|
| Earnings | Leave Travel Concession |
| Fringe Benefits | Fringe Benefits such as:
|
| Termination Payments | Elements that represent employer payments in regard to employee termination from the services of company. |
Note: For Fringe Benefits Elements, set the Enable Advances flag to Yes
-
Allowances, See:Setting up Allowances, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
-
Perquisites, See:Setting up Perquisites, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
-
Earnings, See:Setting up Regular Earnings, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
-
Fringe Benefits, See:Setting up Fringe Benefits, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
-
Termination Payments, See:Termination Processing, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide (India)
Step 3: Set Up Statutory Earnings and Deductions information
If you are using Oracle payroll, you must set up your statutory tax and social insurance deductions. Oracle HRMS for India supports the following:
-
See: India Tax and Deductions Information, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
Income Tax, See:Setting up Income Tax Deductions, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
-
Employee State Insurance, See: Setting up Employee State Insurance, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
-
Professional Tax, See: Setting up Professional Tax Deduction, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
-
Provident Fund, See:Setting up Provident Fund, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
-
Gratuity, See: Setting up the Gratuity, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide (India)
-
Labor Welfare Fund, See: Setting Up Labor Welfare Fund, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
-
Setting up Scanned Signature for Form 16, See:
Setting up Scanned Signature for Form 16, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
-
Setting up Digital Signature for Form 16, See:
Setting up Digital Signature for Forma 16, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
Step 4: Set Up Discoverer for Payroll Register Reporting Optional Step
You can set up Discoverer to generate payroll run results workbooks. Ensure that you use the India Professional User Self Service Responsibility.
To set up Discoverer for Payroll Register Reporting, see: Workforce Intelligence
For information on the Payroll Register Workbook, see: Payroll Register Workbook, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
Step 5: Set Up Bonus Optional Step
You can set up your bonus elements using the Elements window. You can also process employer paid tax on your bonus element. See:Setting Up Bonus, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
Step 6: Set Up the Demand Draft and Pay Order Payment Types Required Step
To pay your employees by Demand Draft or Pay Order, you must set up the Demand Draft and Pay Order Payment types, and run the Bank or Post Office Payment Process.
See: Setting Up Demand Draft and Pay Order Payment Types, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
See: Running the Bank or Post Office Payment Process, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
Step 7: Set Up the Labor Welfare Fund Deduction Required Step
To process the Labor Welfare Fund contributions for your employees, you must define the LWF frequencies for your employees and employers at the business group.
See: Setting Up Labor Welfare Fund, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
Step 8: Generating Ad hoc Reports using Discoverer Required Step
You can use Discoverer to generate customized ad hoc reports. You must use the following folders in the Discoverer Business Area for creating your workbooks:
-
HRMS Administration - Oracle Human Resources (IN)
-
HRMS - Personal Information - Human Resources (IN)
-
HRMS - Organization Information - Human Resources (IN)
-
HRMS - Reports Information - Oracle Payroll (IN)
See: Discoverer End User Layer Business Area Descriptions, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Step 9: Setting Up Control File with Mail Server details Required Step
To enable employers to e-mail payslip to employees, you must set up the mail server details and e-mail structure:
-
Use the XML Publisher responsibility to configure the site value for Temporary Directory.
-
Create a new Data Definition with the code of the Data Definition as PAYINSOE
-
Attach the Control File to the new Data Definition created as the Bursting Control File.
Step 10: Personalize the Self-service Application to Display Voluntary Provident Fund (VPF) Optional Step
By default the region containing PF Information details is rendered False in self-service application. You must personalize it to render it True to enable employees to record the VPF information using the self-service interface.
See: Tax Declaration (India), Oracle Self-Service Human Resources Deploy Self-Service Capability Guide
Step 11: Set Up Exception Reporting Required Step
You can use Exception reporting to identify exceptions and variations in payroll balances early in the payroll cycle.
Ensure that the Payroll Exception Report is added to the request group IN HRMS Reports and Processes. You can view it under the submenu IN HRMS Other.
See: Running an Exception Report, or Exception Report Group, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide (India)
Additional Implementation Steps for Australia
If you are implementing Oracle HRMS for Australia, you must also complete the following additional implementation steps.
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Set Up Workplace Giving Deduction
You must set up Workplace Giving deduction to record an employee's Workplace Giving contribution.
See: Setting Up Workplace Giving Deduction, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 2: Set the profile to view absence accruals in SSHR Optional Step
To view the employee absence accrual information using the self service pages, use your self-service responsibility to set the profile Concurrent: Report Access Level to Responsibility at the Site level.
See: Defining Preferences with User Profile Options, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
See: Viewing Accrual Balances in SSHR, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 3: Set the profile value to generate the PDF/Excel reports Required Step
You use the profile option Concurrent: Report Access Level to control the display of the request ID of the reports in the list of values while generating the PDF/Excel reports. Use the System Administration responsibility to set the profile value.
Set the profile value to Responsibility or User to display the report requests submitted against the responsibility or the user in list of values. You must set this profile value to enable you to generate the following reports:
-
Generate Australian PDF Report
-
Generate Australian Excel Report
-
Self Printed Payment Summary PDF
For information on profiles, see: User Profiles, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Defining Preferences with User Profile Options, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
For information on generating the PDF or Excel reports, see: Running the Generate Australian PDF or Excel Reports, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 4: Create customized XML templates Optional Step
To create and use customized templates to generate the PDF and Excel output formats of the various Australian reports, you must use the following naming convention for the template code. You create templates from the Template Manager using the XML Publisher Responsibility.
For example, to generate a PDF output, the template code should include PDF as the last three characters, PAY_AU_PAYREC_SUMM_PDF.
To generate an Excel output, the template code should include EXC. For example, PAY_AU_PAYSUM_VALIDATION_EXC.
For information on how to create templates, See: Using the Template Manager, Oracle XML Publisher Guide
Step 5: Set up RetroPay Required Step
You need to set up the retropay information to process these payments correctly.
See: Setting Up Retro-Notification and RetroPay, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
See: Setting Up Elements for Retro Processing, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 6: Set up payroll purge information Optional Step
You must set up the payroll information and balances before you can purge the data.
See: Setting Up the Payroll Purge Process, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 7: Set the value for TFN for Superannuation Guarantee Information Required Step
Starting 1 July 2007, employees must provide their Tax File Number (TFN) to their Super Fund. Oracle defaulted the value of TFN for Superannuation as No, prior to 1 July 2007. To change the default value of TFN for Superannuation for existing employees, you must manually update the default value to Yes by performing the following steps:
-
Navigate to Total Compensation > Element Link
-
Query Superannuation Guarantee Information.
-
Change the value of the TFN For Superannuation from No to Yes.
-
Save as Correction.
-
Create a new entry.
Step 8: Run Maintain Payment Summary Allowance Balances Process (2008/09 Only) Required Step
Run the Maintain Payment Summary Allowance Balances process to identify existing Payment Summary Reportable Allowances and upgrade them to use the Balance Attribute and group level reporting. This process identifies the Allowance balances, which have not been enabled for assignment level run and group level run and Allowance balance(s) reported in the Payment Summary. The process adds _LE_YTD dimension to the allowance balances for group level reporting.
You run this process from the Submit Requests window.
-
In the Name field, select Maintain Payment Summary Allowance Balances to open the Parameters window.
-
Select the mode with the following options:
-
Validate – to validate and generate a list of Allowance Balances, dimensions, and error messages to be updated and to make corrections prior to running the Update mode.
-
Update – to generate a list of updated Allowance Balances.
-
-
Click Submit.
Step 9: Configure the Control Bursting File for Email Payment Summary Optional Step
You can configure the bursting file to ensure that the Payment Summary is accurately mailed to employees.
-
Specify the first two lines of the XML as header portions.
-
The third line contains the Select expression which divides the entire XML into individual XML for each employee. The tag “GR1” is the separating tag for each employee and the parent tag for all “GR1” tags is PYAUPSSP
"<xapi:request select="/PYAUPSSP/GR1>"
-
Configure the e-mail details of the email server, the port, and the To and From addresses accurately.
"<xapi:email server="internalmailrouter.oracle.com" port="25" from="John.Smith@oracle.com" replyto="John.Smith@oracle.com">"
-
The sixth line includes the header information about the e-mail and contains a message ID which is the user specific number. It includes the details to whom the email (the tag <EM>) must be sent to. Users cannot change this tag name but can configure the carbon copy email address. It also includes the Subject “Payment Summary for XXX for year ending 2014”. The tag <F2> corresponds to the Full name of the employee and this tag name cannot be changed. The tag <Y1> corresponds to the financial year tag in XML and cannot be changed. Users can use the tags generated in the XML output in the control file to meet their organizational requirements.
"<xapi:message id="123" to="${EM}" cc="John.Smith@oracle.oracle.com" attachment="true" contenttype="html/text" subject="Payment Summary of ${F2} for year ending ${Y1}">" -
Configure the seventh line the contains the tags for the email text.
<H6> Dear ${F2}, Please find payment summary for year ending ${Y1} attached with this email.</H6> </xapi:message>" -
The tenth line contains the file naming specification of the PDF file delivered. It includes the tags for full name and financial year that can be configured. The output type must be PDF only and the delivery ID mentioned in this line must match the message ID mentioned in Step 4 above. This is mandatory.
<xapi:document output="Payment_Summary_${F2}_${Y1}" outputtype="pdf" delivery="123"> -
The eleventh line is the template type. The template is the RTF template.
<xapi:template type="rtf">
-
The twelfth line contains the location of the RTF template for payment summary. Place the RTF template for the Payment Summary in the directory /tmp or any other directory which is accessible. Before placing the PYAUPSPDF6_en_US.rtf in /tmp folder, modify the template as follows:
-
Remove the tags <EM_IF> and <EM_EIF> tags in the latest template.
-
Provide the complete absolute path of the template on the server .
"location="/tmp/PYAUPSPDF6_en_US.rtf">"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xapi:requestset xmlns:xapi="http://xmlns.oracle.com/oxp/xapi"> <xapi:request select="/PYAUPSSP/GR1> <xapi:delivery> <xapi:email server="internal-mail-router.oracle.com" port="25" from="John.Smith@oracle.com" reply-to="John.smith@oracle.com"> <xapi:message id="123" to="${EM}" cc="John.Smith@oracle.com" attachment="true" contenttype="html/text" subject="Payment Summary of ${F2} for year ending ${Y1}"> <H6>Dear ${F2}, Please find payment summary for year ending ${Y1} attached with this email.</H6>Dear ${F2}, Please find payment summary for year ending ${Y1} attached with this email.> <xapi:email></xapi:email> </xapi:delivery> <xapi:document output="Payment_Summary_${F2}_${Y1}" output-type="pdf" delivery="123"> <xapi:template type="rtf" location="/tmp/PYAUPSPDF6_en_US.rtf> </xapi:template> </xapi:document> </xapi:request> </xapi:requestset>
-
Step 10: Setting up to Email Payment Summary File Required Step
To enable employers to e-mail payment summary to employees, you must set up the mail server details and e-mail structure:
-
Use the XML Publisher responsibility to configure the site value for Temporary Directory as /tmp.
-
Create a new data definition with the code of the Data Definition as PYAUPSRP. Ensure that the code is same as the short name for the concurrent program Produce Self Printed Payment Summary XML-PDF (Australia).
-
Attach the control file to the new data definition created as the bursting control file.
Step 11: Setting Up the Password for Accessing the Email Payment Summary Report Optional Step
To set up a password for the Email Payment Summary, follow the steps:
-
Download the template to the temporary folder to customize the template.
-
Click the Custom tab.
-
In the Name field, enter xdo-pdf-open-password.
-
In the Type field, select Text.
-
Enter the value {/PYAUPSSP/GR1/E7}.
-
Enter the Name: xdo-pdf-security
-
Select the Type: Text
-
Enter the Value: true
-
Move the modified the template file to the server directory indicated in the XML bursting configuration file.
Step 12: Setting up the STP Report Authorizing User Required Step
Employes must set up authorized user who will create and submit the Single Touch Payroll report to the ATO. If employers do not provide the name, then the Single Touch Payroll report cannot be submitted.
When you run the Single Touch Payroll report, the application will default the name of the user who will submit the report.
-
Navigate to the Application Utilities Lookup
Other > Applications Utilities Lookup
-
Query for PY_AU_STP_AUTH_USER.
-
Enter the name of the user who will create and submit the Single Touch Payroll Report to the ATO. This name will default in the Declared By field when you run the Single Touch Payroll Report.
-
Save your work.
Step 13: Setting up Sending Service Provider Required Step
Employers must define a valid list of sending service provider (SSPs) for their organization. The application uses this third party organization to submit the file to the ATO.
-
Navigate to the Application Utilities Lookup.
Other > Applications Utilities Lookup
-
Query for PY_AU_STP_SSP.
-
Enter the name of the third party organization that will act as the service provider. This value will be defaulted when you run the Single Touch Report.
-
Save your work.
Troubleshooting Memory Issues
Step 14: Increase the heap size to resolve memory issues Optional Step
You may encounter an exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError, while generating the PDF or Excel reports. This exception occurs due to insufficient memory as the heap size is set to 512 MB. To resolve the memory issue, you need increase the heap size to 1024 MB. You define the Java runtime memory setting for the concurrent program using the Concurrent Program definition
Add the parameter values to the concurrent program definition as follows:
-
Use the System Administrator Responsibility.
-
Navigate to Concurrent > Program > Define
-
Query the program that errors, for example, Self Printed Payment Summary PDF (Shortname: PYAUPSRP_PDF).
-
In the Options field, enter Xmx1024M to increase the heap size from 512MB to 1024MB.
-
Save the changes to the concurrent program definition.
-
Restart the Concurrent Manager.
Additional Implementation Steps for Ireland
If you are implementing Oracle HRMS for Ireland you must also complete the following additional implementation steps.
Please see the implementation section in Implementing Oracle HRMS for all other implementation steps that are not specific to Ireland.
Additional Implementation Step
Step 1: Define Organization Structures
When defining your organizations, you must set up Irish specific classifications and additional information for the following:
-
Ireland employer information, see: Entering Employer Information, Oracle HRMS for Ireland Supplement
-
Ireland PayPath Information, see: Business Groups: Entering PayPath Information, Oracle HRMS for Ireland Supplement
Related Topics
See: Entering Additional Information, Oracle HRMS for Ireland Supplement
Step 2: Set Up Multiple Employer PAYE References
You need to set up multiple employer PAYE References for reporting purposes.
See: Setting Up Multiple Employer PAYE References, Oracle HRMS for Ireland Supplement
Step 3: Set up Pay Related Social Insurance (PRSI) Contributions
To record and process the Pay Related Social Insurance (PRSI) Contributions for employees, you must complete the setup for social insurance calculations.
See: Pay Related Social Insurance (PRSI) Contributions, Oracle HRMS for Ireland Supplement
Step 4: Set Up the Termination Lump Sum Process
You need to set up the termination lump sum process to enable you to make a lump sum payment to an employee for redundancy or retirement.
See: Setting Up the Termination Lump Sum Process, Oracle HRMS for Ireland Supplement
Step 5: Set Up Payments After Termination
You need to perform setup steps to enable you to process payments after termination, in the current year or the previous year.
See: Setting Up Payments After Termination, Oracle HRMS for Ireland Supplement
Step 6: Set Up Benefits in Kind Information
You need to set up benefits in kind information to record and calculate the applicable benefit information.
See: Setting Up Benefits in Kind, Oracle HRMS for Ireland Supplement
Step 7: Set Up Court Order Information
To calculate Court Order deductions, you need to use the element IE Attachment of Earnings Order or IE Attachment of Earnings NTPP Element.
Step 8: Set Up Net-to-Gross Information
You need to set up net-to-gross information to process net-to-gross calculations.
See: Setting Up Net-to-Gross Calculation, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 9: Set Up Shift Patterns
Set up work patterns to record shift details for your employees, if you want to prorate by working days/hours.
See: Setting Up Shift and Shift Patterns, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Step 10: Set Up Proration and RetroPay
You need to set up the proration and retropay information to process these payments correctly.
See: Setting Up Proration or Retro-Notification, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 11: Set Up Statement of Earnings
You need to set up the online statement of earnings before you can see the values correctly.
See: Setting Up a Global Statement of Earnings, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Note: When entering SOE information at the Business Group level, select the predefined element sets IE_SOE_EARNINGS_ELEMENTS and IE_SOE_DEDUCTIONS_ELEMENTS and the predefined balance attribute IE_SOE_BALANCE_ATTRIBUTES.
Step 12: Set Up Continuous Calculation
You need to set up the continuous calculation information to enable you to distribute your payroll processing throughout a payroll period.
See: Setting Up Continuous Calculation, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 13: Set Up Advance Pay
You must set up the advance pay information to enable users to process the advance payments to employees. See: Setting Up Advance Pay for Individual Assignments, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 14: Set Up Exception Reporting
You need to set up the exception reporting information to identify and view variations within payroll to avoid retrospective corrections.
See: Setting Up Exception Reporting, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Additional Implementation Steps for Sweden
If you are implementing Oracle HRMS for Sweden you must also complete the following additional implementation steps.
Please see the implementation section in Implementing Oracle HRMS for all other implementation steps that are not specific to Sweden.
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Set Up Swedish Organizations
Set up local units and legal employers to meet statutory Swedish requirements. You can also create social security offices and enforcement offices for reporting.
See: Setting up Swedish Organizations, Oracle HRMS for Sweden Supplement
Step 2: Run Meta-Mapper
You must run the Meta-Mapper to support the Tax Card upload process.
Step 3: Define Tax and Tax Card Elements
You must define the element links for tax and tax card.
You define the links in the Element Links window.
-
Select Tax in the Element Name field.
-
Select an effective date that is prior to the system date, for example, 01 Jan 1951.
-
Save your work.
-
Repeat the above steps for the Tax Card element.
See: Defining Element Links, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 4: Set Up Income Tax Information
You need to set up your tax information to calculate tax correctly.
See: Setting Up Income Tax Deduction, Oracle HRMS for Sweden Supplement
Step 5: Upload Tax Card
You must upload the flat file, containing the employees' tax information, which you receive from the tax administration to calculate the tax deductions correctly.
See: Uploading the Tax Card, Oracle HRMS for Sweden Supplement
Step 6: Set Up Proration
You need to set up the proration and retro-notification information to process these payments correctly.
See: Setting Up Proration or Retro-Notification, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 7: Set Up Retro-Notification and RetroPay
You need to set up the retro-notification and retropay information to process these payments correctly.
See: Setting Up Retro-Notification and RetroPay, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 8: Set Up Third Party Payment Information
You need to set up the third party payment information to capture the third party payment details.
See: Setting Up Third Party Payments, Oracle HRMS for Sweden Supplement
Step 9: Set Up Court Order Information
You need to set up court order information to calculate court order deductions.
See: Setting Up Court Orders, Oracle HRMS for Sweden Supplement
Step 10: Set Up Travel Expense Information
You need to set up travel expense information to capture the relevant details.
See: Setting Up Travel Expenses, Oracle HRMS for Sweden Supplement
Step 11: Set Up Benefits in Kind Information
You need to set up benefits in kind information to capture and calculate the applicable benefit information.
See: Setting Up Benefits in Kind, Oracle HRMS for Sweden Supplement
Step 12: Set Up Net-to-Gross Information
You need to set up net-to-gross information to process net-to-gross calculations.
See: Setting Up Net-to-Gross Calculation, Oracle HRMS for Sweden Supplement
Step 13: Set Up Negative Payment Information
You need to set up negative payment information to process negative payments manually.
See: Setting Up Negative Payments, Oracle HRMS for Sweden Supplement
Step 14: Set Up Electronic File Transfer
You need to set up the electronic file transfer information to make payments.
See: Setting Up Electronic File Transfer (EFT), Oracle HRMS for Sweden Supplement
Step 15: Set Up Statement of Earnings
You need to set up the online statement of earnings before you can see the values correctly.
See: Setting Up a Global Statement of Earnings (SOE), Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Note: When entering SOE information at the Business Group level, select the predefined element sets SE_SOE_EARNINGS_ELEMENTS and SE_SOE_DEDUCTIONS_ELEMENT and the predefined balance attribute SE_SOE_BALANCE_ATTRIBUTES.
Step 16: Upload the Postal Code File
You need to upload the file that contains the postal codes and corresponding post office names to view the data correctly in the application.
See: Uploading Postal Code, Oracle HRMS for Sweden Supplement
Additional Implementation Steps for Poland
If you are implementing Oracle Payroll for Poland, you must complete the following additional implementation steps.
Please see the following implementation sections in Implementing Oracle HRMS for all other implementation steps that are not specific to Poland.
See: Enterprise and Workforce Management
See: Payroll Process Management
See: Compensation, Benefits and Payroll
See: Workforce Sourcing and Deployment
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Configure SII Insurance Codes
If you use SII insurance codes relevant to your enterprise, define those codes and related column values using the Table Structure window. You must attach the supplied PL_CONTRIBUTION_TYPE_FF FastFormula to each column you add. You must also add each new code and its description to the PL_EMP_SOCIAL_SECURITY_MEANING lookup.
Step 2: Define Contribution Types For New Codes
For new codes, you must define the relevant contribution types and their valid values, O, D, and N using the Table Values window.
Step 3: Set Up Statement of Earnings (SOE)
You use the new profile option PAY: PL Statement of Earnings Display Zero to control the display of earnings or deductions elements with a zero Pay Value. You can set the profile value to Yes to display earnings and deductions elements with a zero Pay Value processed in the payroll run on the Statement of Earnings page.
Note: Ensure that you restart the apache server after setting up this profile option.
Step 4: Set the Profile Option PL+PER_NI_UNIQUE_ERROR_WARN
HRMS can flag duplicate PESEL entries at the legal-employer level by issuing either an error or a warning message. By default, HRMS issues a warning message. To switch to an error or prevent validation, set the profile option to Error or None respectively.
See: User Profiles, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Additional Implementation Steps for China
If you are implementing Oracle Payroll for China, you must complete the following additional implementation steps.
Please see the following implementation sections in Implementing Oracle HRMS for all other implementation steps that are not specific to China.
See: Enterprise and Workforce Management
See: Payroll Process Management
See: Compensation, Benefits and Payroll
See: Workforce Sourcing and Deployment
Additional Implementation Steps
Step 1: Define Corporate and Employer Information Required Step
Define an organization in your organization hierarchy as a corporate and an employer. If your organization hierarchy does not contain an organization with corporate information or employer information , you cannot define an organization with employer information using the Employer Information window. Only organizations with employer information are displayed in the Employer field of the Statutory Info window.
See: Entering Employer Information, Oracle HRMS for China Supplement
See: Entering Corporate Information, Oracle HRMS for China Supplement
Step 2: Set up contribution areas and rates Required Step
Set up deduction rates for workers and employers before processing the pre-tax deductions. To process Public Housing and Social Insurances deductions, you must set up the contribution areas and rates.
See: Business Group: Setting Up Contribution Area Rates, Oracle HRMS for China Supplement
See: Setting Up Public Housing Fund and Social Insurance Deductions, Oracle HRMS for China Supplement
Step 3: Set Up Contribution Base Rules Required Step
Set up the method of calculating the contribution base for a contribution area and organization.
See: Setting Up Contribution Base Rules, Oracle HRMS for China Supplement
Step 4: Set Up Termination and Severance Payments Optional Step
Before you make a termination or a severance payment, you must set up the termination and severance elements and plans. You can process termination payments using elements within particular element classifications.
See: Setting Up Termination Payments, Oracle HRMS for China Supplement
See: Setting Up Severance Payments, Oracle HRMS for China Supplement
Step 5: Set up Special Payments Methods Required Step
You can create input values, balance feeds, formulas, and formula results for processing Special Payments
See: Entering Special Pay Tax Method, Oracle HRMS for China Supplement
See: Setting Up Special Payments Taxation Element, Oracle HRMS for China Supplement
Step 6: Set Up Enterprise Annuity deductions Required Step
To enable employees and employers to contribute towards Enterprise Annuity, you must set up the Enterprise Annuity deduction rates before processing these post-tax deductions. Contributions due from both employer and employee are calculated using a percentage or fixed rate.
See: Setting up Values for the China Enterprise Annuity Contribution Rate User Table, Oracle HRMS for China Supplement
See: Setting Up Enterprise Annuity Deductions, Oracle HRMS for China Supplement
Step 7: Set Up Income Tax Information Required Step
Set up income tax information to calculate an employee's individual income tax and deduct the appropriate sums from an employee earnings.
See: Setting Up Income Tax for Employees in Specific Industries, Oracle HRMS for China Supplement
Step 8: Set Up Proration and RetroPay Optional Step
Set up the proration and RetroPay information to process these payments correctly.
See: Setting Up Proration or Retro-Notification, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Step 9: Set Up RetroPay and RetroPay Notification Report Optional Step
Set up the retro-notification and retropay information to process backdated payments and corrections. See: Setting Up Retro-Notification and RetroPay, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
Step 10: Set Up Statement of Earnings Optional Step
Set up the online statement of earnings before you can see the values correctly.
See: Setting Up The Statement of Earnings, Oracle HRMS Payroll Processing Management Guide
When entering SOE information at the Business Group level, select the predefined element sets CN_SOE_EARNINGS_ELEMENTS and CN_SOE_DEDUCTIONS_ELEMENTS and the predefined balance attribute CN_SOE_BALANCE_ATTRIBUTES.
Step 11: Set Up Discoverer Reports Optional Step
To enable you to view data in the HRMS Discoverer business areas and workbooks for China, you must set up the Discoverer functionality so that the reports reflect changes in your enterprise data.
You can find full instructions on developing the Discoverer EUL and creating and maintaining Discoverer workbooks in the Oracle Discoverer Plus User's Guide and the Oracle Discoverer Plus Administrator's Guide
See: Workforce Intelligence, Oracle Discoverer Plus User's Guide
Step 12: Set Up China Accounting Software Interface Information Required Step
Set up the China Accounting Software Interface to enable the entities to file their financial and accounting information in XML format.
See: Setting Up for Exporting Payroll Information for China Accounting Software Data Interface Standard, Oracle HRMS for China Supplement
Additional Implementation Steps for Korea
Step 1: Set up Custom Templates for YEA Reports Optional Step
Oracle HRMS for Korea provides you the ability to use custom templates for the Year End Adjustment reports. If you do not require custom templates, you can use the predefined template based on the report type selected on the Reports tab of the Year End Adjustment SSHR.
Follow the steps below to complete the setup of the custom templates for the YEA Tax Reclaim Sheet, YEA Tax Receipt and YEA Ledger Reports.
-
Use the XML Publisher Administrator responsibility.
-
Open Template Page from the XML Publisher Administrator responsibility.
-
Search for the Code as 'PAYKRYRS'.
-
Download the predefined template PAYKRYRS.rtf to your local machine.
-
Click Export Translation to download the translations for the template.
-
Modify the template PAYKRYRS.rtf, to suit your business requirements and rename it to custom template name. (For eg. PAYKRYRS_CUSTOM.rtf)
-
Click Create Template to create a new template.
-
Create the new template as:
-
Name: Custom Name
-
Application: Payroll
-
Code: PAYKRYRS_CUSTOM
-
Data Definition: KR YEA Reclaim Sheet
-
Type: RTF
-
Start Date: 01-Jan-1900
-
-
Save the information.
-
Save the file.
-
Search for your newly created template (For eg. PAYKRYRS_CUSTOM).
-
Click Upload Translation and upload the xlf file downloaded from the Seeded Template window.
-
Enable the template name check box and click Enable to enable the translation.
-
Repeat the steps if you want to create the templates for YEA Tax Receipt and YEA Ledger reports specifying PAYKRYTR and PAYKRYLG as Code.
-
Navigate to Work Structures > Organization > Description.
-
Search for business group.
-
Enter the custom template names into the YEA Report Template.
-
Save the information.
-
Run the YEA reports from SSHR.
-
The application picks the custom template specified at the business group.
Implementation
Further Implementation Steps
Step 1: Technical Essays Optional Step
This section includes technical essays for Oracle HRMS.
DateTrack
Batch Element Entry
Payroll Processes
FastFormula
Flexfields
Security
APIs
DataPump
SQL Trace
Backfeed
GB Branch Sort Code Validation in Oracle HRMS
Grade/Step Progression and the Total Compensation Data Model
XML Output for Payment Processes
- Oracle HR Foundation
- Requirements
- APIs Available for HR Foundation Users
- Menus Available for HR Foundation Users
- Enter Person
- Recording Employment Termination and Rehiring Ex-employees
- Viewing Person Information
- Defining a Position (non-HRMS users)
- Entering and Maintaining Contingent Worker Information (HR Foundation)