Employment Agreements and Legal Compliance
Employment Agreements and Legal Compliance Overview
In your enterprise, you may have employment agreements that govern employment terms and conditions. These agreements may cover a few, many, or all of your workforce and the terms that they define could vary, depending on the particular situation of an employee. For example, the employment terms and conditions such as pay, work schedules, vacations, termination notice, maternity leave, and deductions from wages may vary for an employee or groups of employees. The employer and the representatives of the employees, for example union representatives, negotiate the working terms and conditions specified in the employment agreements.
Apart from adhering to the employment agreements, an employer has to submit several reports to government authorities to ensure legal compliance. These reports measure the extent the employer complies with legal requirements such as employment standards, pay equity, labor relations (for unionized employees), health and safety protection at work for the employees.
Oracle HRMS enables you to represent the employment agreements with your employees and fulfill your statutory reporting requirements.
Representing Employment Agreements Using Oracle HRMS
In Oracle HRMS, you represent an employment agreement as a collective agreement. Using Oracle HRMS, you can:
-
Set up the collective agreement to contain the employment terms and conditions that apply to everyone covered by it
-
Specify the values your workforce receives for performing specific roles or at specific locations
-
Define the rules which ensure eligible workforce receive specific values such as one month of annual vacation that an employee completing minimum six months of employment in your enterprise receives
-
Automatically assign values to your eligible workforce, when they are eligible for multiple values, by calculating the most beneficial value for them
For more information about representing employment agreements using Oracle HRMS, see: Collective Agreements
Recording Occupational Health and Safety Details Using Oracle HRMS
-
Record occupational health and safety measures such as medical assessments, disability information, and injuries at work (work incidents) for the people in your enterprise
-
specify the disability concessions such as tax reduction and special consideration in work schedules such as part-time work
-
record multiple medical assessments such as recruitment medical assessment or annual medical assessment
Oracle HRMS enables you to link this information together. For example, if a medical assessment is required as the result of a work accident, and that assessment then diagnoses a disability in the person, you can connect these records to one another.
Reporting for Legal Compliance
Oracle HRMS and Oracle HRMSi provide support for several countries to enable employers to fulfill their statutory reporting requirements. For example, Oracle HRMS enables:
-
US users to generate ADA, IPEDS, OSHA, VETS, and EEO reports.
-
French users to generate the Bilan Social report.
-
Saudi users to generate the Saudi Disabled Employee report.
-
German users to generate the Work Incidents report.
-
South African users to generate the Employment Equity Workforce Profile report.
Oracle HRMSi offers, for example, the establishment and organization worksheets to report about employee equal opportunities by job. To work with Oracle HRMSi reports, you must purchase the appropriate license from Oracle. For information on licenses, contact your Oracle sales representative.
For more information, see Employee Agreements and Legal Compliance Reports, Oracle HRMS Window Navigation and Reports Guide
Key Concepts
To effectively use Oracle HRMS for employee agreements and legal compliance, see:
Collective Agreement Setup
Collective Agreements
A collective agreement is an agreement that defines the terms and conditions of employment for all employees that are covered by its terms. Agreements are typically negotiated and agreed by external bodies such as Trade Unions and Representatives of Employers.
The following sections describe the components you can use to represent the terms of a collective agreement in Oracle HRMS and to apply the correct entitlements to the primary assignments of eligible employees.
Entitlement Items
An entitlement item forms the basis for any entitlement that can be given to an employee as part of a collective agreement. For example, probation period, annual holiday, and car allowance are all entitlement items. For any entitlement you need to provide as part of a collective agreement, you must create an entitlement item.
You can create two types of entitlement item. These are:
-
An entitlement item that produces a value that is written to an employee's record.
-
An entitlement item that produces a value that is not written to an employee's record, but is held as part of the collective agreement results for that person. You could set up other areas of the application to reference this information if required.
For example, you could set up an item type called Paternity Leave Allowed that indicated whether an employee is eligible to take paternity leave. This would not be written to the employee's record, but could be seen in the collective agreement results for that person.
Eligibility Profiles
Use eligibility profiles to define the criteria that an employee must meet in order to receive a particular entitlement. The criteria that you can include in an eligibility profile are grouped into five factors:
-
Personal Factors
-
Employment Factors
-
Derived Factors
-
Related Coverages
-
Other Factors
Each factor contains a variety of criteria from which you select one or more criteria values.
For example, if a collective agreement states that people working in California should receive an extra allowance, you could define an eligibility profile using the Employment Factor criteria of Work Location. The value for the Work Location criterion would be California, (You need to define this work location using the Locations window). A person must meet this criterion in order to be given the associated allowance.
Eligibility profiles can be used in benefits plans, collective agreements, or both. The information you can enter against a profile differs slightly depending on whether you have accessed this window from the total compensation or collective agreements area of the application.
In addition to the eligibility profiles you define, there is a Default profile that you can select when defining entitlement values. You can use this to define a value to apply to everyone not eligible to receive something more beneficial.
Derived Factors
As part of the criteria for an eligibility profile you can set up derived factors. These are eligibility factors that are calculated by the application and can change over time. See: Derived Factors, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide for more information.
Collective Agreement Details
For each collective agreement recognized by your enterprise you can record information such as a name, number, and whether it is active. You can also indicate the parties by whom it has been agreed. You set these parties up using the organization classifications Employer and Bargaining Association.
Collective Agreement Entitlement Values
For each entitlement item to be included in a collective agreement you must select which eligibility profiles to use, and enter the values that employees who satisfy the criteria receive.
For some example setups of entitlements see: Example Entitlement Setups
Evaluation and Application of Collective Agreement Entitlement Values
To indicate which people are covered by the terms of a collective agreement you select the agreement as part of their primary assignment.
Note: You can select collective agreements as part of other assignments, but the evaluate and apply processes only calculate values for the primary assignment.
Once this has been done the application has to calculate what values the employee is eligible for and apply them to their record. How this is done depends on the settings of the following user profiles:
-
HR:Auto Apply Entitlements
-
HR:Auto Evaluate Entitlements
If the HR:Auto Evaluate Entitlements profile is set to Yes, then the values that an employee is entitled to are calculated as soon as the collective agreement is saved to their assignment. If it is set to No then you must run the evaluation process manually from the Collective Agreement Results window.
Note: If the HR:Auto Evaluate Entitlements profile is set to No, then the apply process will not run automatically, even if the HR:Auto Apply Entitlements is set to Yes
If the HR:Auto Apply Entitlements is set to Yes, then the values calculated for a person during the evaluation process are automatically applied to an employee's record. For any entitlements where the employee is entitled to more than one value but the application cannot determine which is most beneficial to the employee, you have to make a choice manually. If it is set to No you have to select and apply all values manually in the Collective Agreement Results window.
There is also a concurrent process called Collective Agreement Entitlement Evaluation that you can run from the Submit Request window to evaluate and apply an employee's entitlement values.
Value Sets for Collective Agreements
As part of the setup of your collective agreement entitlement items you may need to use value sets in order for your entitlement items to perform correctly.
Item Value Sets
If you are creating an entitlement item that populates one of the fields on the assignment included in the table below you need to select the corresponding item value set. This is so that when the entitlement item is selected in the Collective Agreement Entitlements window the values field displays a drop-down list of valid values.
The following table describes the fields on the assignment and the corresponding item value set:
| Field | Value Set |
|---|---|
| Bargaining Unit | CAGR_BARGAINING_UNIT |
| Employee Category | CAGR_EMPLOYEE_CATEGORY |
| Employment Category | CAGR_EMPLOYMENT_CATEGORY |
| Grade | CAGR_GRADES |
| Job | CAGR_JOBS |
| Organization | CAGR_ORGANIZATIONS |
| Payroll | CAGR_PAYROLL |
| Salary Basis | CAGR_SALARY_BASIS |
In addition to these a CAGR_YES_NO value set is provided to be used where the valid value for a field is Yes or No, or the field uses a check box, for example Union Member.
You can also use these supplied value sets as examples to set up your own should you need to. For example, if you want to create a value set to write a value to a descriptive flexfield column, you can define a value set that enforces the same validation that is used by the descriptive flexfield.
Beneficial Rule Value Sets
For entitlement items where the most beneficial value cannot be determined from the value itself, but can be determined from some other value associated with it, you can define a value set to enable the application to do this. An example of this would be grades where you can use the sequence number associated with a grade to determine which is most beneficial. This is presuming that you have set up your grades so that the higher the sequence number, the better the grade.
An example value set, CAGR_BR_GRADE has been supplied for you to use as a template for creating your own value sets.
Setups for Collective Agreement Value Sets
In order for the value set to work correctly with the collective agreement, it must conform to the following rules:
-
The item value set name must begin with CAGR_
-
The beneficial rule value set name must begin with CAGR_BR
-
The value set must be defined with a validation type of Table.
-
The value set must return two values, one ID and one value or description.
-
The following syntax is to be used if business_group_id is required in the sql. This example is for grades:
Where business_group_id = $PROFILES$.PER_BUSINESS_GROUP_ID AND GRADE_ID in ()
The important part of this syntax is that the ID column is restricted to a set of values that are inserted within the brackets. If the brackets are not there, the value set will not work.
Example Entitlement Setups
The following give an example setup for each of the categories supported in Oracle HRMS.
Assignment Category Example
Imagine that the notice period for employees is based on their employee category as shown in the following table:
| Employee Category | Notice Period |
|---|---|
| Default | 1 month |
| Blue Collar | 2 months |
| White Collar | 3 months |
To represent these collective agreement terms in Oracle HRMS you must complete the following steps:
1. Create an entitlement item called Notice Period and associate it with the Notice Period field.
2. Create two eligibility profiles based on the employment factor of Employee Category. In one select the employee category of Blue Collar and in the other select the employee category of White Collar.
3. Assuming you have already created your collective agreement, select the Notice Period entitlement item in the Collective Agreement Entitlements window and define the values for each of the eligibility profiles. Against White Collar, enter 3, and against Blue Collar, enter 2. Use the Default profile name to define the notice period of one month for all other employees.
Pay Scales Example
Imagine your enterprise uses the salary scale shown in the following table where employees' salary is based on their job and grade:
| Job | Grade | Point | Salary |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manager | M1 | 1.1 | 40000 |
| Manager | M1 | 1.2 | 45000 |
| Manager | M1 | 1.3 | 47500 |
| Manager | M2 | 2.1 | 50000 |
| Manager | M2 | 2.2 | 55000 |
| Executive | E1 | 3.1 | 65000 |
| Executive | E1 | 3.2 | 75000 |
To represent these collective agreement terms in Oracle HRMS you must complete the following steps:
1. Define jobs called Manager and Executive.
2. Define the grades M1, M2 and E2
3. Define a pay scale with points 1.1 through to 3.2.
4. Define a scale rate to associate the correct salary value with each point for the pay scale.
5. Define a grade scale to associate each grade to the correct points.
6. Create an entitlement item called Pay Scale and associate it with the Spinal Point field.
7. Create two eligibility profiles based on the employment factor of Job. In one select the job of Manager and in the other select the job of Executive.
8. Assuming you have already created your collective agreement, select the Pay Scale entitlement item in the Collective Agreement Entitlements window.
For each of the rows in the table you define a row in the Pay Scales tab. For the first row you would select the Manager eligibility profile, the grade M1, and the step 1.1.
Payroll Example
Imagine your enterprise uses the hourly rates shown in the following table where employees' rates are based on their grade:
| Grade | Standard Hourly Rate | Overtime Hourly Rate |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | 7.50 | 9.00 |
| A2 | 8.20 | 9.90 |
| A3 | 9.60 | 11.00 |
To represent these collective agreement terms in Oracle HRMS you must complete the following steps:
1. Define the grades A1 through to A3
2. Ensure the input values, element links and element entries have been defined for the Basic Salary Rate and Overtime elements.
3. Create two entitlement items, one called Standard Hourly Rate associated with the Basic Salary Rate element, and another called Overtime Hourly Rate associated with the Overtime element.
4. Create three eligibility profiles based on the employment factor of Grade. Select A1 in the first, A2 in the second, and A3 in the third.
5. Assuming you have already created your collective agreement, select the Standard Hourly Rate entitlement item in the Collective Agreement Entitlements window.
For each of the rows in the table you define a row in the values tabbed region. For the first row you would select the A1 Grade eligibility profile and enter the value of 7.50.
6. Select the Overtime Hourly Rate entitlement item in the Collective Agreement Entitlements window.
For each of the rows in the table you define a row in the values tabbed region. For the first row you would select the A1 Grade eligibility profile and enter the value of 9.00.
Setting Up a Collective Agreement
Follow these steps to enter a collective agreement, set up the eligibility criteria for the agreement, and to apply the values defined in the agreement to the eligible employees.
Note: Not all legislations utilise all the collective agreements functionality.
To set up a collective agreement
-
Define the entitlement items for your agreement.
See: Defining an Entitlement Item for a Collective Agreement
-
Define the eligibility profiles to be used with your collective agreement.
-
Create organizations to represent the two parties who have negotiated the agreement if required. Use the Employer and Bargaining Association organization classifications.
-
Create the collective agreement.
-
Define the entitlements for your collective agreement.
-
Assign the collective agreement to all employees who are covered by its terms.
See: Entering an Assignment, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
Select and apply the entitlement values to be applied to an employee.
See: Selecting and Applying Collective Agreement Entitlement Values
Defining an Entitlement Item for a Collective Agreement
You create entitlement items using the Entitlement Item Definition window.
To define an entitlement item to generate values to be written to an employee's record:
-
Enter a name for your entitlement item. This must be unique within the category.
-
Select the category for your entitlement item. The category you select here determines the values you see in the Field Name field. For example, if you select a category of Assignment, you will only be able to select field names that relate to assignments.
If you select the Payroll category, then you can select an element name, rather than a field, to associate with the entitlement item.
Note: The category of Absence does not have any field names associated with it in the current release so therefore does not have any effect on current absence processing.
-
If you have selected the Payroll category, then you must select the element to which the entitlement item is associated. For example, if this item is to generate values for a person's salary you should select the Regular Salary element.
If the element has been defined to allow multiple entries, then you must indicate whether the value calculated using this item should be applied to all entries within the pay period or not. If you do not select this check box and there are multiple entries for the element then the collective agreement apply process will error.
If there are no element entries for an assignment to which the entitlement item applies, then select the Automatically Create Entries check box. This enables the Collective Agreement Entitlement Evaluation process to create the required element entries while processing and applying collective agreement entitlement results.
Note: You must select the Automatically Create Entries check box while defining new entitlement items as you cannot update this information for existing entitlement items.
You must also select an input value for the element. Once an element and input value combination has been associated with an entitlement item, it cannot be used again.
-
If you have selected any other entitlement category then you must select a field name and, if the field you select requires it, a unit of measure. This defines which field in the application will be populated with the value generated by this entitlement item. You can only associate each field with one entitlement item.
Defining a Beneficial Rule
-
Select the rule that defines which value is most beneficial for this entitlement item. For example, if the item was Holiday Allowance, then the beneficial rule should be Highest. The application will use this rule when an entitlement item produces multiple valid values for an employee.
If it is not possible for you to define a beneficial rule or the application cannot determine what is the most beneficial value then you are required to manually select a value if multiple values are returned.
-
Select an item value set for your entitlement item, if required.
For information on which entitlement items require item values sets see: Value Sets for Collective Agreements
-
Select a beneficial value set if your entitlement item requires a value set to determine the most beneficial value.
For information on setting up value sets for collective agreements see: Value Sets for Collective Agreements
-
Save your work.
To define an entitlement item to generate values held in the collective agreement results for an employee:
-
Enter a name for your entitlement item. This must be unique within the category.
-
Select a beneficial rule and value set if required.
-
Select a category and unit of measure for your entitlement item.
-
Save your work.
Defining an Eligibility Profile
You use the Participation Eligibility Profiles window to define an eligibility profile with an effective start date of your choice. Before defining the profile, define any derived factors (such as length of service or compensation level), or your own eligibility criteria, that you plan to use as eligibility criteria.
If you want to create your own criteria to include in the eligibility profile, click User Defined Eligibility Criteria and create new criteria, see: Creating your own Eligibility Criteria., Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide To access these criteria, choose the Other tabbed region, and select User Defined Criteria from the list
You can use eligibility profiles to determine:
-
employee eligibility for compensation and benefits plans
-
entitlements in collective agreements
-
eligibility for grade/step progression
-
eligibility for various work schedules, and so on
The information you can enter differs slightly depending on whether you have accessed this window from the Total Compensation or Collective Agreements area of the application.
Note: If you use the Total Compensation Setup Wizard to set up grade ladders, programs and plans, and Total Compensation Statements, you can create or update eligibility profiles while you are working in the Wizard.
To define an eligibility profile
-
Enter the Name of the eligibility profile you are defining.
-
Enter a Description of this eligibility profile.
-
Select an Assignment Type to which this eligibility profile applies.
For example, you can define an eligibility profile for employee assignments if this profile is only used for employees.
Note: You can only select Employee Assignment Only for profiles to be used with collective agreements.
-
Select the profile Status.
Pending: This eligibility profile is currently proposed, but not active.
Active: This eligibility profile is in use.
Inactive: This eligibility profile is in use but cannot be associated with any new programs, plans, or options.
Closed: This eligibility profile was once Active or Pending, but is no longer in use.
-
Select whether this eligibility profile applies to benefits or collective agreements. If you are defining an eligibility profile for work schedules or grade step progression, then select benefits.
Choose the tabbed region that contains a criteria element that you want to include in your eligibility profile. Choose from:
-
Personal
-
Employment
-
Derived Factors
-
Related Coverages (Not applicable to collective agreements)
-
Other
-
-
Select a criteria element.
For example, you could choose Person Type as one of several eligibility criteria of the Personal type.
Note: When you define more than one value for a criterion, at least one of the values must be present in the person's record for them to be eligible. However, when you use multiple criteria in an eligibility profile (for example, a Work Location and an Organization), the person must meet at least one value for each criterion.
If you use a FastFormula eligibility rule as part of your eligibility profile, the participant must meet the criteria of the rule and one value from any other criteria that you include in the eligibility profile. If you use more than one FastFormula rule, by default the participant must meet the criteria of all the rules. If you change the user profile option BEN:Eligible Profile Rule from AND to OR, the participant need only meet the criteria of one rule.
-
Enter a Seq (sequence) number specifying the order the system processes this criteria element relative to any other criteria in this eligibility profile.
Note: You must assign a sequence number of a higher priority to all criteria that are used to exclude eligibility.
-
Select one or more values for the criteria element you have selected.
-
Check the Exclude field if a person becomes ineligible to participate in the compensation object, or to receive the collective agreement entitlement you associate with this eligibility profile if they meet this criterion.
You typically check the Exclude field when it is easier or faster to define which persons are excluded from eligibility, as opposed to defining which person are eligible.
If you are defining an eligibility profile for a grade ladder, and you want to rank your employees to determine the most eligible person to progress, enter an eligibility Score for this criteria.
The application calculates the eligibility rank based on the total score for all criteria that the person satisfies.
-
For grade ladders, you can also enter an eligibility Weight for a criteria.
The application multiplies the weight by the criteria value. You can only use weights with criteria that contain numeric values. If you enter a score and a weight for a criteria, the application adds the person's score to the weight to arrive at the final number.
-
Repeat steps 6 to 12 for each criteria element that you include in your eligibility profile.
-
Choose the Display All tabbed region to view the criteria elements in this eligibility profile.
-
Save your work.
Defining Derived Factors: Compensation Level
You can define a compensation level factor as part of an eligibility profile (to be used in determining benefits participation or collective agreement entitlements) or a variable rate profile. A compensation level factor can be based on either stated salary, balance type, or benefits balance type.
You define compensation level factors in the Derived Factors window. The values you can select in some of the fields depend on whether you have accessed the Derived Factors window from the Total Compensation or Collective Agreements area of the application.
To define a compensation level factor:
-
Enter a Name for this compensation level factor.
-
Select the Unit Of Measure for this compensation level factor.
Select the Source of the compensation level factor.
-
Select the Defined Balance for this compensation level factor if you selected a source of balance type.
-
Select a Benefits Balance Type if you selected a source of benefits balance type.
-
Select the compensation periodicity in the Stated Comp Periodicity field if you selected a source of stated compensation.
Note: If you have installed the Oracle Incentive Compensation patch 4409180 you can select either Oracle Incentive Compensation - Amount Earned or Oracle Incentive Compensation - Amount Paid as the source. If you select any of these sources, then the Incentive Compensation Information region displays, where you can enter the Start and End Dates, and select the Prorate if date range differs from OIC range check box
In the Values block:
-
-
Enter the Minimum amount under which the system does not calculate this compensation level factor.
-
Check the No Minimum field if there is no minimum compensation amount under which the system excludes participants when determining participation eligibility and activity rates.
-
-
Enter the Maximum amount above which the system does not calculate this compensation level factor.
-
Check the No Maximum Compensation field if there is no maximum compensation amount above which the system excludes participants when determining participation eligibility and activity rates.
-
-
Select a Determination Code or Rule to define when the system determines a participant's compensation level.
-
Choose a Rounding Code or Rounding Rule to specify the level to which the system rounds the results of this compensation level factor.
-
Save your work.
Defining Derived Factors: Percent of Full Time Employment
A percent full time factor derives an employee's percent of full time employment. The application uses this information to calculate activity rates, coverage amounts, or to determine participation eligibility for either benefits or collective agreement entitlements.
For example, you could define the 100% percent full-time factor to identify those employees who work 100% full-time (40 hours per week) and thus qualify for most benefits or entitlements.
You define percent full time factors in the Derived Factors window. The values you can select in some of the fields depend on whether you have accessed the Derived Factors window from the Total Compensation or Collective Agreements area of the application.
To define a percent full time factor:
-
Enter a Name for this percent full time factor.
-
Check the No Minimum field if there is no minimum percentage of full-time employment under which the application excludes employees when determining participation eligibility and activity rates.
-
Or, enter a Minimum Percent Value to define the minimum percentage of full-time employment to be used in this calculation.
-
-
Check the No Maximum field if there is no maximum percent of full-time employment beyond which the application excludes employees when determining participation eligibility and activity rates.
-
Or, enter a Maximum Percent Value to define the maximum percent of full-time employment to be used in this calculation.
-
-
Check the Use Primary Assignment Only field to specify that the application considers only an employee's primary assignment when determining percent of full time employment.
-
Check the Use Sum of All Assignments field to specify that the application considers all active assignments when determining percent of full-time employment.
-
Select a Rounding Code or Rule to specify the level to which the application rounds the results of this calculation.
-
Save your work.
Defining Derived Factors: Hours Worked In Period
An hours worked in period factor derives the number of hours a given employee has worked over a given period of time. The application uses this information to determine participation eligibility for either benefits or collective agreement entitlements, activity rates, and coverage amounts.
You define hours worked in period factors in the Derived Factors window. The values you can select in some of the fields depend on whether you have accessed the Derived Factors window from the Total Compensation or Collective Agreements area of the application.
To define an hours worked in period factor:
-
Enter a Name for this hours worked in period factor.
-
Select the calculation source for this hours worked in period factor in the Source field.
Balance Type: The application retrieves hours worked information from a balance.
Benefits Balance Type: The application retrieves hours worked information from a benefits balance.
-
Specify when the application calculates this hours worked in period factor in the Once or Continuing field.
Once: The application only calculates this hours worked in period factor following a life event or for open enrollment.
Continuing: The application calculates this hours worked in period factor each time you run the Participation batch process.
-
Select the Defined Balance for this compensation level factor if you selected a calculation source of balance type.
-
Select a Benefits Balance Type if you selected a calculation source of benefits balance type.
-
Check the No Minimum field if there is no minimum number of hours worked in period under which the application excludes employees when determining participation eligibility and activity rates.
-
Or, enter the Minimum hours worked in period under which the application does not calculate this hours worked in period factor.
-
-
Check the No Maximum field if there is no maximum hours worked in period above which the application excludes employees when determining participation eligibility and activity rates.
-
Or, enter the Maximum hours worked in period beyond which the application does not calculate this hours worked in period factor.
-
-
Select an hours worked Determination Code or Rule that defines how to calculate the hours worked in period.
-
Select a Rounding Code or Rule to specify the level to which the application rounds the results of this hours worked in period factor.
-
Save your work.
Defining Derived Factors: Age
An age factor derives a person's age in order to determine participation eligibility for either benefits or collective agreement entitlements, activity rates, and coverage amounts.
For example, you could define the Retire 65 age factor to identify those employees who are at least 65 years of age and thus qualify for a maximum benefit under your corporation's retirement plan. For collective agreements you could define the Age Less Than 21 age factor to identify those employees who are less than 21 and thus should be placed on a particular grade.
You define age factors in the Derived Factors window. The values you can select in some of the fields depend on whether you have accessed the Derived Factors window from the Total Compensation or Collective Agreements area of the application.
To define an age factor:
-
Enter a Name for this age factor.
-
Select the UOM to specify the unit of measure for this age factor.
-
Select an Age to Use code to indicate the kind of person, such as the participant or the participant's child, for whom you are defining a derived age factor.
Note: Derived factors to be used with collective agreements can only use the employee's age.
-
Select an Age Determination Code or Rule to specify the date the application uses to calculate age.
-
Check the No Minimum Age field if there is no minimum age under which the application excludes employees when determining participation eligibility and activity rates.
-
Or, enter the Minimum age beyond which the application does not calculate this age factor.
-
-
Check the No Maximum Age field if there is no maximum age beyond which the application excludes employees when determining participation eligibility and activity rates.
-
Or, enter the Maximum age beyond which the application does not calculate this age factor.
-
-
Select a Rounding Code or Rule to specify the level to which the application rounds the results of this age factor calculation.
-
Save your work.
Defining Derived Factors: Length of Service
A length of service factor derives the length of service for a given worker in order to determine participation eligibility for either benefits or collective agreement entitlements, activity rates, and coverage amounts.
You define length of service factors in the Derived Factors window. The values you can select in some of the fields depend on whether you have accessed the Derived Factors window from the Total Compensation or Collective Agreements area of the application.
To define a length of service factor:
-
Enter a Name for this length of service factor.
-
Select the unit of measure in the UOM field by which you are defining the length of service factor.
-
Select a Determination Code or Rule that defines how the system calculates an employee's length of service.
-
Check the No Minimum Applies field if there is no minimum length of service under which the system excludes employees when determining participation eligibility and activity rates.
-
Or, enter the Minimum length of service under which the system does not calculate this length of service factor.
-
-
Check the No Maximum Applies field if there is no maximum length of service above which the system excludes employees when determining participation eligibility and activity rates.
-
Or, enter the Maximum length of service beyond which the system does not calculate this length of service factor.
-
-
Select a length of service Date to Use Code or Rule to specify the date from which the system calculates the employee's length of service.
Hire Date: The system always uses the employee's hire date as the start date when calculating length of service.
Adjusted Service Date: The system first uses the employee's adjusted service date if one exists. If there is no adjusted service date, the system uses the employee's hire date.
-
Check the Use Override Service Date field to indicate that the system should override the person's service date when determining eligibility.
Note: You enter the Override Service Date for a person in the Participation Overrides window.
-
Select a Rounding Code or Rule to specify the level to which the system rounds the results of this length of service factor.
-
Save your work.
Defining Derived Factors: Combination Age and Length of Service
A combination age and length of service factor associates two factors you have already defined: an age factor and a length of service factor.
You define combination age and length of service factors in the Derived Factors window. The values you can select in some of the fields depend on whether you have accessed the Derived Factors window from the Total Compensation or Collective Agreements area of the application.
To define a combination age and length of service factor:
-
Enter a Name for the combination age and length of service factor you are defining.
-
Select an Age Factor.
-
Select a Length of Service Factor.
-
Enter the Minimum value for the combination of age and length of service that qualifies a person as eligible for the benefit, collective agreement entitlement, or activity rate with which this factor is associated.
-
Enter the Maximum value for the combination of age and length of service that qualifies a person as eligible for the benefit, collective agreement entitlement, or activity rate with which this factor is associated.
-
Enter an Order Number to specify the order in which the application processes and displays combined age and length of service records.
-
Save your work.
Entering a Collective Agreement
Use the Collective Agreements window to enter information about collective agreements used by your enterprise.
To enter a collective agreement:
-
Enter the name of the collective agreement. This must be unique to allow a collective agreement to be referenced across your business group.
-
Select a status for the collective agreement. Although you can still apply inactive collective agreements to employees, no values are calculated for it until you set it to Active.
-
Enter the number of the collective agreement.
-
Enter the start date of the collective agreement and enter its jurisdiction.
Note: An end date should only be entered once the collective agreement is no longer applicable to your enterprise. After the end date the collective agreement can no longer be applied to an assignment.
-
Select the employer and bargaining unit who have negotiated the collective agreement. These are defined using the employer classification and bargaining association classification in the Organization window. Enter the name of the signatory for each party.
-
Enter the name of the authorizing body and the date on which the collective agreement was authorized.
-
Save your changes.
What Next?
You can now define the entitlement values for the collective agreement using the entitlement items and eligibility profiles you have created. You do this in the Collective Agreement Entitlements window.
Defining Collective Agreement Entitlements
Use the Collective Agreement Entitlements window to define the values associated with all the entitlement items in your collective agreement. These are the values that employees covered by the terms of the collective agreement receive if they meet the criteria defined by the eligibility profile. Each value is held in an entitlement line.
Note: The Message Level, Range To, Range From, Non-Updateable, From Step, and To Step fields are to be used in future releases and are not currently active.
The following give an example setup for each of the categories supported in Oracle HRMS.
Assignment Category Example
Imagine that the notice period for employees is based on their employee category as shown in the following table:
| Employee Category | Notice Period |
|---|---|
| Default | 1 month |
| Blue Collar | 2 months |
| White Collar | 3 months |
To represent these collective agreement terms in Oracle HRMS you must complete the following steps:
-
Create an entitlement item called Notice Period and associate it with the Notice Period field.
-
Create two eligibility profiles based on the employment factor of Employee Category. In one select the employee category of Blue Collar and in the other select the employee category of White Collar.
-
Assuming you have already created your collective agreement, select the Notice Period entitlement item in the Collective Agreement Entitlements window and define the values for each of the eligibility profiles. Against White Collar, enter 3, and against Blue Collar, enter 2. Use the Default profile name to define the notice period of one month for all other employees.
Pay Scales Example
Imagine your enterprise uses the salary scale shown in the following table where employees' salary is based on their job and grade:
| Job | Grade | Point | Salary |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manager | M1 | 1.1 | 40000 |
| Manager | M1 | 1.2 | 45000 |
| Manager | M1 | 1.3 | 47500 |
| Manager | M2 | 2.1 | 50000 |
| Manager | M2 | 2.2 | 55000 |
| Executive | E1 | 3.1 | 65000 |
| Executive | E1 | 3.2 | 75000 |
To represent these collective agreement terms in Oracle HRMS you must complete the following steps:
-
Define jobs called Manager and Executive.
-
Define the grades M1, M2 and E2.
-
Define a pay scale with points 1.1 through to 3.2.
-
Define a scale rate to associate the correct salary value with each point for the pay scale.
-
Define a grade scale to associate each grade to the correct points.
-
Create an entitlement item called Pay Scale and associate it with the Spinal Point field.
-
Create two eligibility profiles based on the employment factor of Job. In one select the job of Manager and in the other select the job of Executive.
-
Assuming you have already created your collective agreement, select the Pay Scale entitlement item in the Collective Agreement Entitlements window.
For each of the rows in the table you define a row in the Pay Scales tab. For the first row you would select the Manager eligibility profile, the grade M1, and the step 1.1.
Payroll Example
Imagine your enterprise uses the hourly rates shown in the following table where employees' rates are based on their grade:
| Grade | Standard Hourly Rate | Overtime Hourly Rate |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | 7.50 | 9.00 |
| A2 | 8.20 | 9.90 |
| A3 | 9.60 | 11.00 |
To represent these collective agreement terms in Oracle HRMS you must complete the following steps:
-
Define the grades A1 through to A3.
-
Ensure the input values, element links and element entries have been defined for the Basic Salary Rate and Overtime elements.
-
Create two entitlement items, one called Standard Hourly Rate associated with the Basic Salary Rate element, and another called Overtime Hourly Rate associated with the Overtime element.
-
Create three eligibility profiles based on the employment factor of Grade. Select A1 in the first, A2 in the second, and A3 in the third.
-
Assuming you have already created your collective agreement, select the Standard Hourly Rate entitlement item in the Collective Agreement Entitlements window.
For each of the rows in the table you define a row in the values tabbed region. For the first row you would select the A1 Grade eligibility profile and enter the value of 7.50.
-
Select the Overtime Hourly Rate entitlement item in the Collective Agreement Entitlements window.
For each of the rows in the table you define a row in the values tabbed region. For the first row you would select the A1 Grade eligibility profile and enter the value of 9.00.
To define entitlements for a collective agreement
-
Select the category for the entitlement you are creating. Only entitlement items with this category can be selected in the Entitlement region.
Note: If you are defining entitlements for a payroll item type, then check that the following definitions have been entered:
-
The element and its input values
-
The element links
-
The element entries for all eligible employees
-
-
Select the entitlement item for which you want to create values. The remaining fields display the entries defined for the entitlement item in the Collective Agreement Entitlement Items window.
-
If you want to use a formula to calculate the value for this entitlement, then choose the Formula radio button and select the formula. If you want to define criteria to calculate the value, then ensure the Criteria radio button is selected.
Defining Entitlement Lines
-
Select the eligibility profile for which you want to define a value.
Note: In addition to the eligibility profiles you have created there is a DEFAULT profile. If you set up a value using this profile, then it is applied to all employees on the collective agreement, unless they are eligible for a more beneficial value.
-
Select whether this value is active. Inactive lines are ignored when calculating collective agreement values for an employee.
-
Do one of the following:
-
If you are entering values for a pay scale, then select the grade, and the step to be applied to employees that satisfy the criteria for this line. The pay scale for the grade is displayed automatically. The grade is used in association with the eligibility profile to determine the eligibility for pay scale entitlement items. To be eligible to be placed on the specified step, an employee must satisfy both the eligibility profile and be on the selected grade.
For example, if your eligibility profile is Age Less than 21, and you have selected grade SE01, then an employee must be less than 21 and be on grade SE01 to be placed on the step defined by this line.
-
Otherwise, enter the value to be applied to employees that satisfy this eligibility profile.
-
-
Add further entitlement lines until you have created all the required values for this entitlement, then save your work.
Setting up Collective Agreement Grades
Collective agreement grades enable you to define how an employee is graded or ranked in a collective agreement. A collective agreement grade is defined by a combination of values that you enter using grade factors. A grade factor is a user-defined field that you set up as part of the grade structure in the Collective Agreement Grades (CAGR) key flexfield. The grades that you predefine for a collective agreement are known as reference grades. To set up collective agreement grades:
To setup collective agreement grades:
-
Set up the Collective Agreement Grades key flexfield to define a grade structure and grade factors.
See: User-Definable Key Flexfields , Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Note: If you are in Italy, do not set up this flexfield. You must use the predefined IT_CAGR flexfield structure.
-
Enter collective agreement grades. to link a grade structure to a collective agreement, and to define a set of reference grades.
What Next?
You can now define a collective agreement grade for an assignment using the Employment Terms tabbed region on the Assignment form.
See: Entering Additional Assignment Details, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Entering Collective Agreement Grades
You enter collective agreement grades to link a collective agreement to a grade structure and to define a set of reference grades that can be used in that collective agreement.
You enter this information using the Agreement Grades window.
To enter a collective agreement grade:
-
Query the collective agreement and select the grade structure. The reference grades entered will be recorded against the combination of collective agreement and grade structure selected.
-
Check the Override Allowed check box if you want to enable users to enter any combination of values for the selected grade structure in the Assignment window. If you leave the check box unchecked users will be forced to select a predefined reference grade.
-
Insert a sequence number and click the Name field. Enter values for the grade factors that are displayed. Each combination of values represents a reference grade.
-
Enter as many reference grades as required.
-
Save your changes.
You can now use the Assignment window to define the assignment's collective agreement grade.
See: Entering Additional Assignment Details, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
Collective Agreement Administration
Collective Agreement Administration
After you set up the collective agreements in your enterprise, you need to evaluate and apply it for your required employees. Oracle HRMS provides you the evaluate and apply processes to enable your employees to receive the entitlements specified in the collective agreement.
To evaluate and apply, you must:
-
Indicate the people covered by a collective agreement by selecting the agreement as part of their primary assignment.
-
Set the HR:Auto Apply Entitlements and HR:Auto Evaluate Entitlements user profiles to calculate what values the employee is eligible for and apply them to their record.
If you set the HR:Auto Evaluate Entitlements profile to Yes, then the application calculates the values that an employee is entitled to as soon as the collective agreement is saved to their assignment. If you set it to No, then you must run the evaluation process manually from the Collective Agreement Results window.
Note: If you set the HR:Auto Evaluate Entitlements profile to No, then the apply process will not run automatically, even if you set the HR:Auto Apply Entitlements to Yes.
If you set the HR:Auto Apply Entitlements to Yes, then the application applies the values calculated for a person during the evaluation process automatically to the employee's record. For any entitlements where the employee is entitled to more than one value but the application cannot determine which is most beneficial to the employee, you have to make a choice manually. If you set it to No, then you have to select and apply all values manually in the Collective Agreement Results window.
There is also a concurrent process called Collective Agreement Entitlement Evaluation that you can run from the Submit Request window to evaluate and apply an employee's entitlement values.
Administering Retained Rights
Oracle HRMS enables an employee to continue to receive a specific entitlement item after an event makes the employee ineligible for the entitlement item. For example, if by changing the role an employee plays in your enterprise, the employee becomes ineligible for an education allowance, you can define it as a retained right if you still want them to receive it. The employee will continue to receive the allowance for the period you define in this window.
Selecting and Applying Collective Agreement Entitlement Values
How you use the Collective Agreement Results window depends on the settings of the profile options associated with collective agreements:
-
Setup A: If both HR: Auto Evaluate Entitlements and HR: Auto Apply Entitlements are set to No, then you use the Collective Agreement Results window to evaluate and manually select which of the generated values to apply to the employee.
-
Setup B: If HR: Auto Evaluate Entitlements is set to Yes, but HR: Auto Apply Entitlements is set to No, then the evaluation is done automatically once a collective agreement is selected for an employee. In this instance, you use the Collective Agreement Results window to manually select which of the generated values to apply to the employee.
If you set up your application like this you may experience a slight delay when saving an assignment record after selecting a collective agreement.
-
Setup C: If both profiles are set to Yes, then you use the Collective Agreement Results window to check that the application has applied the correct values, and also to manually select a value where the application cannot determine which is the most beneficial for the employee.
If you set up your application like this you may experience a delay when saving an assignment record after selecting a collective agreement.
Warning: Ensure that you have set up your collective agreement and associated information correctly before using this setup. Oracle recommends applying values generated by your collective agreements manually until you are sure that your setup works correctly.
The following procedures describe the behavior of the application following the selection of a collective agreement for the first time.
To select and apply entitlement values for setups A and B:
-
If your setup corresponds to Setup A, then in the Collective Agreement Results window, choose the Refresh Entitlements button. The Collective Agreement Evaluation process is run and the results are displayed.
If your setup corresponds to Setup B, then this evaluation will have been done automatically once you saved the collective agreement against the employee.
-
Choose the View Log button to look at the log file and ensure that the evaluation process has run correctly.
-
Use the category field to limit the entitlement items displayed in the Name fields by category if required. The results for the selected item are shown in the Entitlement Results region.
-
Choose which value to apply to the employee for each item by checking the Chosen check box. You must still check the Chosen check box even if only one value is displayed.
Where no values are displayed for an item then the employee is not eligible for that item.
Where the application has been able to calculate which of the values for an item is most beneficial to the employee, the Suggested check box is checked to show this. You must still check the Chosen check box for these values in order for them to be applied to the employee.
Any values that are included because they are retained rights are shown by a check in the Retained check box.
-
Save your work once you have chosen the value you want to apply to the employee for a particular item.
-
Repeat steps 3 to 5 until you have chosen values for all the entitlement items for which the employee is eligible.
-
Choose the Apply button to apply the values to the employee's record.
-
Choose the View Log button to look at the log and ensure that the values have been applied successfully. Any errors or warnings are shown in the Apply Process Log section.
Note: Every time you run the Apply process, a new Apply Process Log section is added to the end of the log, so ensure you are looking at the correct section.
-
Close the Collective Agreement Results window and requery the assignment in the Assignment window. The values applied from the collective agreement are displayed.
To select and apply entitlement values for setup C:
-
Choose the View Log button in the Collective Agreement Results window to look at the log file and ensure that the evaluation and apply processes have been run correctly.
-
Do one of the following to identify for which of the entitlement items the application has not been able to determine the most beneficial value for the employee:
-
Look through the log and check that the entry for each entitlement item that satisfies more than one eligibility profile contains the line Beneficial value is: You will have to choose a value manually for each of those that do not.
-
Navigate through the entitlement items in the Name fields. You will need to choose a value manually for each entitlement item that does not have the Suggested check box checked for one of its values.
-
-
Choose which value to apply to the employee for each item that has not been processed automatically by checking the Chosen check box. You must still check the Chosen check box even if only one value is displayed.
Note: If you want to override any of the values the application has applied, then you can still check the Chosen check box for items that have a suggested value.
-
Once you have chosen all the required values, then choose the Apply button to apply the values to the employee's record.
-
Choose the View Log button to look at the log and ensure that the values have been applied successfully. Any errors or warnings are shown in the Apply Process Log section.
Note: Every time you run the Apply process, a new Apply Process Log section is added to the end of the log, so ensure you are looking at the correct section.
-
Close the Collective Agreement Results window and requery the assignment in the Assignment window. The values applied from the collective agreement are displayed.
What Next?
If you make any changes to a person's employment record that may impact their entitlements, or you make changes to a collective agreement that may impact the entitlements of the employees covered by its terms, you must do one of the following:
-
Use the Collective Agreement Entitlement Evaluation process to re-evaluate and reapply the required values to each affected employee:
See: Running the Collective Agreement Entitlement Evaluation Process
-
Use the Collective Agreements Results window to re-evaluate and reapply the required values for each employee effected. Choose the Refresh Entitlements button to re-evaluate the entitlements the employee should receive and proceed as described in the procedure for setups A and B above.
Defining Retained Rights
Use the Collective Agreement Retained Rights window to define rights that an employee can still receive, even if they are no longer eligible for them. For example, if by transferring from a location an employee becomes ineligible for a location allowance, you can define it as a retained right if you still want them to receive it. The employee will continue to receive the allowance for the period you define in this window.
To define a retained right
-
Use the Category and Name fields to select the entitlement item that you want to retain for the employee.
-
Check the Retained check box for the value you want to retain.
-
Check the Freeze check box if you want to freeze the value of the entitlement. This means that even if the value of the entitlement item changes in the future due to a change in the collective agreement, the employee will still receive the value as it is now.
For example, if an employee receives a retained location allowance of $2000 that is frozen, even if the terms of the collective agreement increase the location allowance to $3000, then employee still receives $2000.
-
Enter the date from which the entitlement item is retained, and if required, enter the date when the item is no longer retained.
-
Save your work.
Running the Collective Agreement Entitlement Evaluation Process
The Collective Agreement Entitlement Evaluation process enables you to evaluate and apply collective agreement entitlements for an employee using the Submit Request window.
To run the Collective Agreement Entitlement Evaluation process:
-
Select the Collective Agreement Entitlement Evaluation process in the name field.
-
Click in the Parameters field to display the Parameters window, if it does not automatically open.
-
Select the date on which you want to run the process. This defaults to the system date.
-
Select the process mode. The options are:
-
Evaluate Only: Only the evaluation of possible results is performed.
-
Evaluate and Apply: Evaluate the possible results and apply them to the employee's record.
-
Apply Only: Apply the results already generated by the previous evaluation.
-
-
Select the processing level. The options are:
-
Single Assignment: Run the process for a single person.
-
Single Collective Agreement: Run the process for all people on a single collective agreement.
-
Single Entitlement: Run the process for a single entitlement item across all collective agreements.
-
Single Entitlement for Single Assignment: Run the process for a particular entitlement for a single person. You can use this option for employees with multiple entitlements. If there is change to the eligibility of a specific entitlement for which an evaluation is required, then select this option.
-
-
Select the validation mode. The options are:
-
No Commit - Database Not Updated: The selected process runs and produces a log file indicating any errors that have occurred but does not save any information on the database. This enables you to run the Apply process without actually applying the results to your employee's record. This means you can correct any problems that may occur prior to amending any values.
-
Commit - Database Updated: The selected process runs and saves the information on the database.
-
-
Do one of the following:
-
If you have selected a processing level of Single Assignment, then select the person for whom you want to run the process.
-
If you have selected a processing level of Single Collective Agreement, then select the agreement for which you want to run the process.
-
If you have selected a processing level of Single Entitlement, then select the entitlement item for which you want to run the process.
-
If you have selected a process level of Single Entitlement for Single Assignment, then select the person and the entitlement item for which you want to run the process.
Any changes that are made as a result of this process are made to the person's primary assignment.
-
-
Choose OK to return to the Submit Request window and choose Submit to run the report. You can view the log file generated from the Requests window. Use this file to identify any problems that have occurred during the running of the process.
Occupational Health
Occupational Health: Medical Assessments, Disabilities and Work Incidents
Oracle HRMS enables you to record medical assessments, disability information, and work incidents for the people in your enterprise. It also enables you to link this information together. For example, if a medical assessment is required as the result of a work accident, and that assessment then diagnoses a disability in the person, you could relate these records to one another.
Note: The Medical assessments, disabilities and work incidents functionality may not be used by your localization.
Medical Assessments
The Medical Assessment window enables you to enter information about the medical assessments (consultations) provided to the people in your enterprise. For example, you can record:
-
When the assessment took place, and the organization and person who performed it.
-
The result of the assessment, for example, if a disability was identified.
-
If the purpose of the assessment is to evaluate a particular disability, whether the person is considered fit for work.
-
Any work incident that was the reason for this assessment.
A person can have multiple medical assessment records. For example, a person may have a recruitment medical and several annual medicals.
Disabilities
Using the datetracked Disabilities window, you can enter information about a person's disabilities. For example, you can record:
-
The nature and severity of the disability
-
The full-time equivalent that this person represents towards your enterprise's quota of disabled employees
-
The details of the registration of this disability with an official organization
-
Any work incident that was the cause of this disability
-
The medical assessment that first identified this disability.
A person can have multiple disability records. Each disability can be linked to one work incident and to one medical assessment that diagnosed (or identified) the condition. Once a disability has been diagnosed and recorded, you can link it to multiple assessments that evaluate the disability.
Work Incidents
Oracle HRMS enables you to record work incidents, for example, accidents, that involve the people in your enterprise. Work incidents are incidents that occur:
-
at work
-
on the way to or from work
-
in other circumstances that are defined as work-related by your enterprise.
Using the Work Incidents window, you can record:
-
The details of the incident, for example, when and where it occurred.
-
The health and safety official and/or representative body that were notified of the incident
-
Medical details, such as any injury occurred, treatment given, and medical organizations involved
-
Whether any compensation was paid
-
Whether this person was absent as a result of the incident
-
The job the person was doing when the incident occurred
A person can have multiple work incident records.
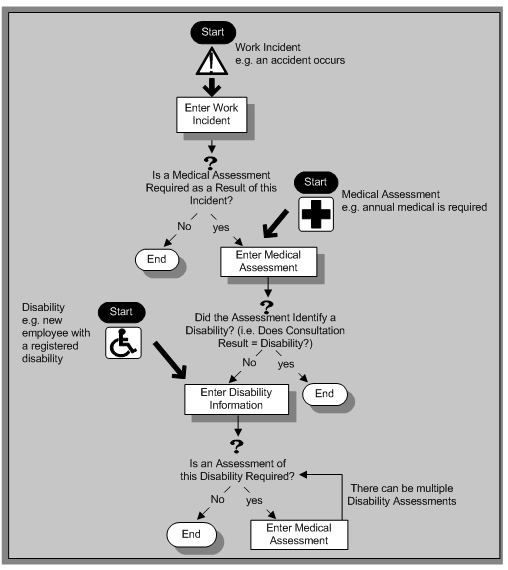
The graphic illustrates the relationship between the medical assessment, disability and work incident tasks. It shows the full process that you could follow if you wanted to record:
-
A work incident that occurred
-
The medical assessment that was required as a result of the work incident
-
The disability record that was required as a result of a "Disability" result in the medical assessment
-
The subsequent "Disability type" medical assessments that were required to evaluate the disability on a regular basis
The "Start" boxes show the points at which you can start the process, depending on the task you need to perform.
Recording a Disability
Entering Work Incident Information
You use the Work Incidents window to enter information about the work incident in which a person was involved.
To enter work incident information
-
Enter information about the incident:
-
Enter a unique reference number for this incident.
-
Enter the date on which the incident occurred.
-
If the incident occurred over time, enter the date on which the incident was identified or reported.
-
Select the type of incident that occurred.
-
Enter the time at which the incident occurred, if known.
-
Check the check box if the incident occurred over a period of time. For example, check this box if the incident was a gas leak.
-
Select the circumstances of the incident in the Activity field. For example, you can specify if the incident occurred en route to work.
For Russian users only: Activity is not required in Russia, so this field is not available to Russian users. Select the primary and secondary reasons for the incident. For example, you can select violation of industrial discipline as the primary reason and extreme temperatures as the secondary reason.
-
Enter the date on which the incident was reported.
-
Enter the reference number for a related work incident. The list is limited to incidents that involved this person and that occurred on or before the date of this incident.
-
Incident Description
-
Choose the Incident Description tab.
-
Enter more detail about the incident:
-
Select the main cause of the incident in the Hazard field.
-
Enter the location of this incident, for example, if the incident occurred in the workplace, identify the room and building.
-
Enter a further description of the incident, if required.
-
Incident Reporting
-
Choose the Incident Reporting tab.
-
Enter the reporting details:
-
Select the name of the person who reported this incident. You can only select a person who is on the system and who is in the same Business Group.
-
Select the method used to report this incident, for example, a voicemail.
-
Enter the date and time when the incident was reported. This cannot be earlier than the date and time recorded for the incident.
Note: You must select the name of the person who reported this incident before you can enter the date and time.
-
Enter the organization to whom the incident was reported, for example, the local fire station or police.
-
Enter contact details for anyone who witnessed the incident.
Note: For Russian users:The Incident Reporting tab is not applicable.
-
Official Notifications
-
Choose the Official Notifications tab.
-
Enter the official notification details:
-
Select the name of your organization's health and safety representative and enter the date on which they were notified of the incident
-
Describe any remedial action that was taken (or is planned) as a result of this incident.
-
Select the organization and person that are the representative body for this person and enter the date on which they were notified of the incident
Note: You must select the representative body organization before you can enter the person and reporting date.
-
Medical Details
-
Choose the Medical Details tab.
-
Enter any medical details:
-
Select the type of injury and/or disease caused by the incident.
-
Enter any further description of the injury or disease.
-
Check the box if the person received medical attention as a result of this incident. Then enter the name of the physician and/or the contact details for the hospital that was consulted or that provided treatment.
Note: If treatment was provided by an internal organization or person, for example, an occupational health organization or a first-aid officer, enter the details into the Hospital Details field.
Note: For Russian users:The Medical Details tab is not applicable.
-
Other Information
-
Choose the Other tab.
-
Enter other information about this incident:
-
If compensation was awarded for this incident, enter the amount. Then select the currency for the compensation amount. The Business Group's currency is shown as the default.
Note: If you enter a compensation amount, the Currency field cannot be left blank.
-
Enter the date on which the compensation was given.
-
Enter the job the person was doing at the time of the incident. The list is limited to jobs with effective start dates before the incident and effective end dates, if any, after the incident.
-
Enter the time the worker began work on the day of the incident.
See:Defining a Job, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Note: If the person was involved in this incident prior to joining your enterprise, leave the Job field blank.
-
Check the Resulted in Absence? check box if the person was absent from work as a result of this incident.
-
-
Enter further information about this work incident in the Further Information field if it has been set up by your Oracle localization team.
For Russian users only, see: Entering Work Incident Information
For Mexican users only: Select the type of risk from the available list-of-values.
-
Save your changes.
What Next?
If a medical assessment is required as a result of this incident, you can choose the Medical Assessment button to open the Medical Assessment window and to enter the details of the assessment. If you enter a medical assessment in this way, its type is Occupational Assessment and it is automatically linked to this incident.
Entering Medical Assessments
Use the Medical Assessments window to record information about the medical examinations performed for the people in your enterprise.
To enter a medical assessment:
-
Enter the date on which the medical assessment was held.
-
Select the type of assessment, for example, Annual Medical Assessment.
-
If you opened the Medical Assessment window via the Disability window, the assessment type is Disability and cannot be changed.
-
If you opened the Medical Assessment window via the Work Incidents window, the assessment type is Occupational Assessment and cannot be changed.
-
-
Select the result of the assessment.
Note: If the assessment type is Disability Assessment, you can only select Unfit for Work or Fit for Work. You cannot select a Disability result for a Disability Assessment.
-
Select the name of the examiner and the name of the organization that performed the assessment.
If the organization is not listed, create the organization and select the Medical Service Provider classification.
See: Entering Organizations and Entering Organization Classifications.
-
Enter the date on which the next assessment is planned.
-
Select the work incident to which this assessment is related, if any. After you choose an incident, the date on which it occurred is automatically displayed.
You can only link an assessment to an incident if the assessment type is Occupational Assessment.
Note: If you have saved the assessment date, the list of incidents is limited to those that occurred before the assessment date. Otherwise, all incidents for that person are listed.
To enter a work incident for this person, see Entering Work Incidents.
-
Enter a description of the assessment.
-
Enter further details in the Further Information field if it has been set up by your Oracle localization team.
-
Save your work.
What Next?
If, as a result of this assessment, a disability was identified, you can enter the details of that disability and link it to this assessment.
See: Entering Disability Information
Note: Once a medical assessment is referenced in a disability record, you cannot change its result from Disability.
Entering Disability Information
HRMS enables you to enter detailed disability information for the people in your enterprise.
You use the Disability window to enter this information.
Note: If you want to record that a person is registered as disabled, but you do not need to hold information about that disability, you can just check the Registered Disabled check box on the Personal tab in the Person window.
See: Entering a New Person (People Window), Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
To enter disability information
-
Set your effective date early enough to handle any historical disability information that you want to enter.
Note: If you want to associate this disability record with an existing medical assessment or work incident, your current effective date must be later than the assessment and incident dates. Ask your system administrator to enable the Work Incidents and Medical Assessments windows if they are not available.
-
Select the category of disability, for example, Severely Disabled.
-
Enter into the FTE field the full-time equivalent that this person represents towards your enterprise's quota of disabled employees. If no quota scheme exists, then leave the default value as 1.00.
Note: You can enter a number that is greater than 1.00, depending on the level of disability.
The actual figure will normally be provided by the official disability organization.
-
Select the status of this disability information.
-
Active: This information will be included in reports. You cannot enter an Active status if the record has an end date.
-
Inactive: This information will not be included in reports.
-
Pending: This information is not yet complete because you entered it before you entered the medical assessment confirming this disability (where the consultation result was Disability.)
-
Closed: This information has an end date because the person no longer has this disability.
For Russian users only: Disability status is not applicable in Russia, so the Status field is not available to Russian users. Instead, select the type of disability. You can find this information in the disability certificate provided by the Office of Medical Examination. The application uses this information to calculate any tax benefits and deductions for the employee.
-
-
Select the reason for the disability, for example, Occupational Incident. If the disability was diagnosed as the result of a medical assessment, select Occupational Assessment.
-
Enter the percentage of disability as determined by the official assessment of this disability.
For Hungarian and Spanish users only: The degree of disability depends on the category of disability. For example, if the person's disability category states that the disability decreases the work capacity by 50%, enter 50 as the percentage.
-
Select the incident that is related to, or caused, this disability. The list of incidents is limited to incidents that occurred before the current effective date of this disability. When you select an incident, its date is displayed automatically.
-
Select the medical assessment that recorded this disability.
The list of assessments is limited to assessments that:
-
have a result of Disability
-
have a consultation date that is earlier than the current effective date of the disability
-
are not already linked to a disability record for this person
-
were linked to any incident that you selected in the previous step
To link an incident to an assessment, see: Entering Medical Assessments
This field is not datetracked.
-
Entering Disability Registration Information
-
Choose the Registration tabbed region to enter the disability registration details.
-
Enter into the ID field the registration number assigned by the disability organization.
-
Select the name of the official disability organization with whom the person's disability is registered.
You create disability organizations in the Organization window, selecting the Disability Organization classification.
-
Enter the date on which the employee was registered as disabled with the disability organization and the date on which this registration expires.
Japanese users only: Select the confirmation method by which the disability was confirmed (by the employer).
Entering Additional Disability Information
-
Choose the Other tabbed region to enter additional details about this disability.
-
Enter a description of the disability.
For Russian users only: Disability description is not applicable in Russia. Instead, enter the job conditions under which the disabled employee can work. You can find this information in the disability certificate provided by the Office of Medical Examination. You can use this information to identify suitable assignments for the disabled employee.
-
Enter information about the work restrictions that the employee is subject to as a result of their disability.
-
Enter further information about this disability if the Further Information field has been set up by your Oracle localization team.
For Hungarian users only: Record if the employee is blind. The application uses this information to calculate any additional holiday or tax benefit for the employee.
For Indian users only: Indicate if the employee has provided proof of disability, for claiming disability benefits.
For Korea users only: Specify the following:
-
Disability grade
-
Effective date of the disability
-
If a certificate of disability is available or not.
-
Disabled type
You require this information when the employee is eligible for disable exemption.
For Mexican users only: Specify the following:
-
Disability ID of any related disabilities
The list-of-values displays all previous disabilities for your employee.
-
Number of disability days subsidized by the social security agencies
-
Type of disability
Valid values are:
-
General Disease
-
Maternity
-
Risk Incident
-
-
Result of the disability
The Consequence field provides the following options:
-
None
-
Temporary Disability
-
Provisional Initial Assessment
-
Definitive Initial Assessment
-
Death
-
Relapse
-
Assessment after start date
-
Provisional re-assessment
-
Relapse without medical discharge
-
Definitive re-assessment
-
-
Disability control
For Spanish users only: Record if the employee or dependent contact has a condition with reduced mobility. This information affects the employee's tax withholding rate.
For UAE users only: Indicate if the employee's disability will impact their social insurance contribution. Only one disability can be considered for calculating the social insurance contribution.
For Japanese users only: Specify the following:
You require the following information to submit the disability reports to the authorities for statutory purposes.
-
Degree/Grade - select the degree if the employee is intellectually disabled and the grade if physically disabled.
-
Confirmation Method - select the confirmation method by which the disability was confirmed by the employer.
-
Severely Disabled - select Yes if the employee has severe physical disability or severe intellectual disability and must be counted as 2 disabled persons for reporting purposes.
-
Part-time Worker - select Yes if the employee is a part-timer for reporting purposes.
The following information is required for the worker insurance report if the employee is disabled or injured as a result of work accident.
-
Wa Insurance Disability Grade - select the grade for work insurance purposes.
-
Insurance Injury and Sickness - select the values for the work insurance purposes.
-
-
Save your work.
What Next?
To set up an assessment to evaluate this disability, choose the Medical Asse. (Assessment) button.
See: Entering a Medical Assessment for more information.
Maintaining Disability Information
You can make changes to the disability information that you saved previously, but if your disability record includes either incident or medical assessment information, you cannot change or delete this information once you have saved it.
Reporting Categories and Statuses
Reporting Categories and Statuses
Some reports place no restrictions on the employment category or assignment status of the employees to be included. However, other reports, such as VETS-4212 and ADA, must include only non-temporary, full-time or part-time employees with a non-terminated assignment status.
To identify these employees, you register for the business group as Reporting Categories those employment categories that include non-temporary, full-time or part-time employees. You register as Reporting Statuses those assignment statuses that include non-terminated employees.
Registration of Reporting Categories and Statuses
You must limit the coverage of VETS-4212 and ADA reports to employees who work either full or part time but are not temporary workers, and who have a non-terminated employment status as of the end date of the reporting period.
To establish the employment categories and assignment statuses of the employees that VETS-4212 and ADA reporting must cover, you register Reporting Categories and Reporting Statuses for the Business Group:
-
Reporting Categories are the employment categories including employees who work full or part time on a non-temporary basis.
-
Reporting Statuses are the assignment statuses applicable to employees at a non-terminated status.
Start the registration of Reporting Categories and Statuses from the Organization window.
Registering Reporting Categories
Reporting Categories are employment categories that cover non-temporary, full-time, or part-time work. The categories you select here control which employees appear in the EEO-1 and VETS-4212 reports.
To register reporting categories for the Business Group
-
In the Organization window, query the Business Group if it does not already appear there. With the cursor on Business Group in the Organization Classification region, choose the Others button. Select Reporting Categories.
-
Click in the first blank field in the Additional Information window to open the Reporting Categories window. Select an employment category to register employees who are non-temporary, full time or part time workers. Choose OK to transfer your selection to the Additional Information window.
-
To register another employment category, repeat step one.
-
When you finish registering categories, save your work. Choose OK to close the Reporting Categories window and the Additional Information window.
Registering Reporting Statuses
Reporting Statuses are those assignment statuses that cover non-terminated statuses. The statuses you select here control which employees appear in the EEO-1 and VETS-4212 reports.
To register reporting statuses for the Business Group
-
In the Organization window, query the Business Group if it does not already appear there. With the cursor on Business Group in the Organization Classification region, choose the Others button. Select Reporting Statuses.
-
Click in the first blank field in the Additional Information window to open the Reporting Statuses window. Register a status that covers employees at a non-terminated status. Choose OK to transfer your selection to the Additional Information window.
-
To register another assignment status, repeat step one.
-
When you finish registering statuses, save your work. Choose OK to close the Reporting Statuses window and the Additional Information window.
ADA, AAP, and OSHA Reporting Setup
Reporting Organizations
You often must issue separate reporting for each GRE in your Business Group. Sometimes you must further break down data for a GRE by the establishments (hiring locations, units, or work sites) where its employees are based. A GRE can include employees working in several different establishments, and conversely, a given establishment can include employees in several different GREs.
For reporting purposes, an establishment may be a single physical location, a complex of work sites in a locality, or even all the sites included in a relatively large geographic area. For OSHA reporting, there may be two or more separate establishments at one physical work location if distinctly different types of operations are carried out at the location. To represent establishments for reporting, you give organizations the classification Reporting Establishment.
A GRE whose employees all work at the same establishment is simultaneously a GRE and a Reporting Establishment. For GREs with employees at different establishments you define a number of separate Reporting Establishments. To identify the establishment serving as the headquarters organization, you give a Reporting Establishment the additional classification of Corporate Headquarters.
AAP reporting requires breakdowns of employees by the affirmative action plans covering them, instead of breakdowns by establishment. To meet this requirement, you give organizations the classification AAP Organization, to represent individual affirmative action plans.
Establishment Hierarchies
To determine for reporting purposes which employees belong to a particular GRE and reporting organization, you construct establishment hierarchies, and supply them as parameters to the processes that produce particular reports.
A typical establishment hierarchy has a GRE at the top, Reporting Establishments at the next level, and HR Organizations subordinate to the Reporting Establishments. Report processes normally count employees as belonging to the Reporting Establishment to which their HR Organizations are subordinate in an establishment hierarchy.
Example Establishment Hierarchy
Looking at the example establishment hierarchy above, a report process with this hierarchy as a parameter counts the employees in the HR Organizations subordinate to the Thurbco Mfg. Reporting Establishment as based at that establishment, and those in HR Organizations subordinate to Thurbco Denver as based at that establishment.
Establishment Overrides
Report processes using establishment hierarchies can take exceptional cases into account. You can enter an override Reporting Establishment for any employee. When a process finds an override, it counts the employee as part of the override Reporting Establishment.
For example, if reports should include an employee in the count for Thurbco Denver, even though he is currently assigned to an organization subordinate to Thurbco Mfg, you simply enter Thurbco Denver as his override establishment.
Note: The establishment override functionality does not apply to AAP reporting. This is because the fundamental units of AAP reporting are affirmative action plans, not Reporting Establishments.
Varieties of Establishment Hierarchies
For most government-mandated HR reporting, you set up for a given GRE either a single-establishment hierarchy, or multiple-establishment hierarchies. If you have multiple establishments, you may also need a headquarters hierarchy for the establishment representing your enterprise headquarters.
The same basic rule applies to all the establishment hierarchies you build (but not to the AAP hierarchies used for AAP reporting). This rule is:
In a non-AAP establishment hierarchy, an organization classified as a Reporting Establishment can never be subordinate to another organization classified as a Reporting Establishment.
This means that in an establishment hierarchy, a GRE/Reporting Establishment can be the top organization, or Reporting Establishments can be subordinate to a GRE (and optionally to HR Organizations). But a Reporting Establishment cannot be subordinate to another Reporting Establishment.
AAP Establishment Hierarchies
Establishment hierarchies constructed for AAP reporting are exceptional because this reporting is based on the affirmative action plans existing within a GRE. This means that in AAP establishment hierarchies:
-
establishments appear as subordinates of AAP Organizations representing the affirmative action plans
-
AAP Organizations (which may also be Reporting Establishments) can appear at various levels in the hierarchy, and can be subordinate to other AAP Organizations (which may also be Reporting Establishments).
The Single-Establishment Hierarchy
In some cases, all the employees of a Business Group/GRE or a GRE work at, or from, a single establishment, and you use a single-establishment hierarchy as a parameter for production of an establishment report:
Example Single Establishment Hierarchy
The top organization of this type of hierarchy can be either a Business Group/GRE or a GRE, but must also be classified as a Reporting Establishment.
Multi-Establishment Hierarchies
For complex enterprises with multiple GREs and Reporting Establishments, you build multi-establishment hierarchies. For certain types of reporting you also require a special headquarters hierarchy, to cover the employees working in the Reporting Establishment that constitutes the enterprise headquarters. This section discusses multi-establishment hierarchies; the one following discusses headquarters hierarchies.
The top organization in a multi-establishment hierarchy can be either a Business Group/GRE or a GRE.
Note: For reporting that requires a separate report on your headquarters establishment, the top organization of a multi-establishment hierarchy must not be the headquarters organization. A headquarters organization always belongs in a special headquarters hierarchy.
An already existing organization classed as a GRE may be suitable for use as the top organization of a multi-establishment hierarchy. Alternatively, you can create a GRE for reporting purpose only, with a name similar to that of an operational GRE, and the same IRS identification number as the operational GRE.
Counting Establishment Employees
A report process can count of the number of employees in a particular Reporting Establishment, and alter its treatment of the establishment depending on the results of this count. For example, EEO-1 and VETS-4212 reporting for establishments with fewer than 50 employees is different from that for larger establishments.
Looking at the example hierarchy above for MS Distributors, report processes with this hierarchy as a parameter are able to determine that the MS Distributors Detroit Reporting Establishment has fewer than 50 employees, and to produce the appropriate reporting for this establishment.
Preparing for Government-Mandated HR Reporting
In preparation for running the VETS-4212 and ADA reports, you must register Reporting Categories and Reporting Statuses for the Business Group.
In preparation for all government-mandated HR reporting, you must set up one or more types of reporting organizations. These include:
-
Reporting Establishments
-
Corporate Headquarters
-
AAP Organizations
After setting up the reporting organizations you need, you can build establishment hierarchies and AAP establishment hierarchies that include these reporting organizations.
Before running EEO-1, VETS-4212, ADA, or OSHA reports, you enter establishment overrides for individual employees as necessary.
Setting Up Reporting Organizations
A reporting organization is an organization that has, in addition to any other classifications, one or more of these classifications:
-
Reporting Establishment
-
Corporate Headquarters
-
AAP Organization
Before defining reporting organizations, determine the establishment hierarchies your enterprise needs for government-mandated HR reporting. This will in turn determine the particular reporting organizations you must set up.
See: Varieties of Establishment Hierarchies
Reporting organizations that do not have the classification Corporate Headquarters may be subordinate to other organizations in establishment hierarchies. You can quickly place a subordinate reporting organization in a hierarchy by entering its parent organization as additional information for its classification.
Note: When a reporting organization is the top organization in an establishment hierarchy, you always place it in the hierarchy when creating the hierarchy in the Organization Hierarchy window.
Example Multi-Establishment Hierarchies
Example Multi-Establishment Hierarchies
For examples of multi-establishment hierarchies, we can look at the hypothetical corporation Swanson Inc. Its Business Group includes two GREs, the parent company Swanson Inc. and a subsidiary, MS Distributors Detroit. The enterprise employs workers at four separate establishments:
-
Company headquarters in Cleveland, Ohio.
-
One factory in a Cleveland suburb and another in Dayton, Ohio.
-
The MS Distributors warehouse and shipping center in Detroit, Michigan.
This table summarizes the distribution of the 4,000 employees of Swanson Inc., by GRE and Reporting Establishment:
| Reporting Establishment | Swanson Inc. GRE | MS Distributors Detroit GRE |
|---|---|---|
| Swanson Inc. Headquarters | 500 | |
| Swanson Mfg. | 1,500 | |
| MS Distributors Detroit | 955 | |
| Swanson Dayton | 1,000 | 45 |
For reporting purposes, this enterprise needs two multi-establishment hierarchies, and requires a headquarters hierarchy. The multi-establishment hierarchies required are these:
When you run a report giving one of these hierarchies as a parameter, the report process includes as belonging in a particular Reporting Establishment, any employees assigned to that establishment, plus all the employees assigned to the HR Organizations subordinate to that establishment. The only employees in these organizations that are not covered are any that have establishment overrides entered for the other Reporting Establishment in the hierarchy.
Setting Up ADA, APP, and OSHA Reporting
Setup Steps for AAP Reporting
Because AAP reports cover individual affirmative action plans rather than establishments, the Reporting Establishment override functionality available for EEO-1 and VETS-4212 reporting does not apply to AAP reporting.
To set up AAP reporting
-
Ensure that each employee has an gender and ethnic origin on record, and has an assignment to a GRE and a job.
-
Determine salary codes for your jobs by selecting a grade to represent each salary code. If necessary, define grades to use as salary codes.
See: Defining Grades, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
-
Define lines of progression for the jobs your affirmative action plans cover.
-
Determine the job groups that the jobs in your affirmative action plans belong to, and enter the job group names for the QuickCode type US_JOB_GROUPS.
A job group consists of jobs with similar levels of responsibility, compensation, and opportunities for advancement.
See:
Adding QuickCode Values, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
Associate each job your affirmative action plans cover with an EEO category, if they are not already so associated. Also associate these jobs with a salary code, line of progression, and job group.
See:
-
Define an AAP Organization to represent each of your affirmative action plans.
-
Determine the AAP hierarchies you require, and build them.
See:
-
Run the AAP report processes.
Setup Steps for ADA Reporting
-
Ensure that Reporting Categories and Statuses are registered for your Business Group.
-
Ensure that registration of employees as disabled, and that entry of information about disability types and requests for disability accommodation, is complete. Registration of someone as disabled is accomplished by checking the Disabled box when you enter personal information about him or her.
See:
Entering a New Person (step 9), Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
Ensure that each employee who is registered as disabled, who has provided information about a disability type, or who has requested a disability accommodation has an assignment to a GRE, a job or position, and an employment category.
See:
Entering a New Assignment, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
Identify the establishments within each GRE that you need for ADA reporting, and ensure that they are defined as Reporting Establishments.
-
Determine and build, if necessary, the establishment hierarchies you need to obtain ADA reporting.
-
To include information about essential job or position requirements in ADA reporting, ensure that you have entered these requirements for your jobs or positions.
-
Manually enter any necessary establishment overrides for employees.
-
Run the ADA report process.
Setup Steps for OSHA Reporting
-
Ensure that entry of information on each incident of work-related injury or illness is complete.
See: Entering Information about Work-Related Injury or Illness
-
Identify the establishments within each GRE that you need for OSHA reporting, and ensure that they are defined as Reporting Establishments.
See: OSHA Data and Reporting and Setting Up Reporting Establishments
-
Determine and build, if necessary, the establishment hierarchies you need to obtain OSHA reporting.
-
Manually enter any necessary establishment overrides for employees.
-
Run the OSHA report processes.
Define Reporting Establishments to Represent Corporate Headquarters
When using multi-establishment hierarchies for reporting purposes, you may need to identify a particular Reporting Establishment as the headquarters establishment of your enterprise. To do this you set up a Corporate Headquarters organization, for use as the top organization in a headquarters hierarchy.
You normally classify only one reporting organization within a Business Group as the Corporate Headquarters organization.
Note: An organization classified as a Corporate Headquarters should also have the classifications GRE and Reporting Establishment. It can have other classifications as well.
See: The Headquarters Hierarchy
To define a corporate headquarters
-
Using the Organization window, query the organization to be classified as a corporate headquarters, if it does not already appear there.
Note: This organization always has other classifications as well, for which entry of additional information is necessary
-
In the Organization Classifications region, select the classification Corporate Headquarters for the organization and enable it.
There is no additional information to add for the Corporate Headquarters classification. The Corporate Headquarters organization is always at the top of a headquarters hierarchy, so you place it in this hierarchy when defining the hierarchy.
Entering OSHA Specific Parent Entity Data for Electronic Reports
Use the OSHA Specific Details window to enter data for the organization that you have identified as the parent entity. These details are required to generate the Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Report in CSV format for electronic filing. See Running OSHA Electronic Reports for more information.
To enter OSHA specific parent entity data:
-
In the Organization window, search for the organization.
-
In the Organization Classifications region, select Parent Entity, choose Others, and select OSHA Specific Details.
-
Click in the Additional Information window to display the OSHA Specific Details window. The following fields are available in this EIT:
-
Annual Average Employees: Enter the annual average number of employees. This value must be:
-
Above zero
-
A number
-
Below 25,000
-
-
Size: Enter the size of the establishment based on the maximum number of employees who worked there at any point in the year for which you are submitting data:
-
Enter 1 if the establishment has more than 20 employees
-
Enter 2 if the establishment has between 20 to 249 employees
-
Enter 3 if the establishment has 250+ employees
-
-
Total Hours Worked: Enter the total hours worked by all employees in the last year (reporting period). This value must be:
-
Above zero
-
A number
-
Below 8760 (total_hours_worked divided by annual_average_employees)
-
Above 500 (total_hours_worked divided by annual_average_employees)
-
Note that you must manually populate this EIT information before submitting the Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Report concurrent process. This EIT can also be set for the parent entity of an organization. See Entering OSHA Specific Parent Entity Data for Electronic Reports for more information. The values set for the location always take precedence over the values set at the parent entity level. If the location level EIT is not set up, then the process will look at the parent entity setup.
-
-
Save your work.
Setup Steps for Electronic OSHA Reports
Complete the following setup steps to generate the magnetic (electronic) output file in CSV format for OSHA electronic filing. See OSHA Data for information about the electronic reports.
To set up electronic OSHA reporting
-
Ensure that entry of information on each incident of work-related injury or illness is complete.
See: Entering Information about Work-Related Injury or Illness
-
Identify the establishments within each GRE that you need for OSHA reporting, and ensure that they are defined as Reporting Establishments.
See: OSHA Data and Reporting and Setting Up Reporting Establishments
-
Determine and build, if necessary, the establishment hierarchies you need to obtain OSHA reporting.
-
Manually enter any necessary establishment overrides for employees.
-
If your enterprise uses the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS), then enter the NAICS number in the EEO1/VETS Establishment Data window. See Entering EEO-1/VETS Establishment Data for Parent Entities for more information.
-
Manually enter OSHA specific details for an organization either at the location level or at the parent entity level. The values set for the location always take precedence over the values set at the parent entity level. If the location level details are not set up, then the process will look at the parent entity setup.
See Location Extra Information Types and Entering OSHA Specific Parent Entity Data for Electronic Reports
-
Generate electronic OSHA reports. See Running OSHA Electronic Reports for more information.
Set Up Establishment Hierarchies
Establishment hierarchies include:
-
single-establishment hierarchies
-
multi-establishment hierarchies
-
headquarters hierarchies
-
AAP establishment hierarchies.
Single-Establishment Hierarchies
To create a single-establishment hierarchy
-
Determine the top organization of the hierarchy. It must be a GRE and a Reporting Establishment. It may be a Business Group/GRE.
-
Build the hierarchy by placing all the HR Organizations in the Business Group/GRE or GRE at the second and lower levels under the top organization.
Multi-Establishment Hierarchies
To create a multi-establishment hierarchy
-
Determine the top organization of the hierarchy. It can be a Business Group/GRE or a GRE. It cannot be a Reporting Establishment or an HR Organization, and should not have the classification Corporate Headquarters.
-
Build the hierarchy by placing the appropriate establishments and the HR Organizations subordinate to the establishments at lower levels.
Headquarters Hierarchies
To create a headquarters hierarchy
-
The top organization is that classified as Corporate Headquarters. It must also have the classifications GRE and Reporting Establishment.
-
Build the hierarchy by placing all the HR Organizations in the headquarters organization at the second and lower levels under the top organization.
Placing Subordinate Reporting Organizations in Hierarchies
Reporting organizations with the classification Reporting Establishment and/or AAP Organization may exist in subordinate positions in establishment hierarchies. There is a convenient way to place these organizations in hierarchies when you set them up. You can name the hierarchies and parent organizations of the reporting organization in the Parent Organization window, accessible from the Organization window.
See: Setting Up Establishment Hierarchies
To put a reporting organization in a hierarchy
-
In the Organization window, query the reporting organization if it does not already appear there. Select Reporting Establishment or AAP Organization in the Organization Classifications region, choose the Others button, and select Parent Organization to open the Parent Organization window.
-
Select the hierarchy name.
-
Select the name of the parent organization to which the reporting organization is subordinate in this hierarchy.
-
To place the reporting organization in another hierarchy, repeat steps 2 and 3.
-
Save your work.
Enter Establishment Overrides
Use establishment overrides when employees who would normally be counted in one Reporting Establishment, should actually be counted as belonging to another in the same establishment hierarchy. Report processes with establishment hierarchies as parameters check whether Reporting Establishment overrides exist for the employees the hierarchies cover. If it finds overrides, it counts the employees as belonging to the override Reporting Establishments.
Note: Because the basic unit of AAP reporting within a GRE is its affirmative action plans (AAP Organizations), not its Reporting Establishments, you cannot enter establishment overrides for AAP reporting.
To enter an establishment override for an employee
-
Select the override establishment in the Establishment field.
Define Lines of Progression for Jobs
To define a line of progression for a series of jobs, you build entities called career paths in Oracle HRMS. Career paths are also useful for Building a line of progression, or career path, involves these two steps:
-
entering the name of the line of progression into the system as a career path name, using the Career Path Names window
-
entering the jobs comprising the line of progression, starting from the job with highest status and remuneration and working down, using the Map Career Path window.
A job can appear only once in any line of progression.
To define lines of progression
-
In the Career Path Names window, enter and save the names of the lines of progression you have determined for your enterprise.
-
Open the Map Career Path window. In the Name field, select the top job in a line of progression.
-
In the Career Path Name field, select the name of this line of progression.
-
In the Job Progression From block, select the job that is one level down from the job appearing in the Name field. Check the Down box. The window redisplays with the selected job now appearing in the Name field.
-
Repeat Step 4 until you have entered all the jobs in the line of progression.
To move back up the line of jobs, check the Up box.
-
Save your work.
EEO, VETS, and IPEDS Reporting Setup
Establishment Hierarchies
The U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) defines an establishment as an economic unit, such as a factory, office, store, or mine, that produces goods or services. Typically, the establishment is at a single physical location and is engaged in predominantly one type of economic activity. For many EEO-related reports, you must organize employment data by establishment.
In Oracle HRMS, an establishment is a location, and you record establishment information in location EITs. For example, in the location EIT "EEO-1 Specific Data," you record the EEO-1 reporting name and unit number of the establishment. Using the Oracle HRMS generic hierarchies functionality, you can define a hierarchy of one or more establishments to represent your enterprise for reporting purposes. The establishment hierarchy is especially useful when you need to run reports for multiple establishments, as a single request can produce reports for multiple establishments. The establishment hierarchy you define is reusable: you can run various government-mandated reports, such as the EO Survey report, the EEO-1 reports, and the VETS-4212 reports for the same establishment hierarchy.
Components of the Establishment Hierarchy
In the Maintain Hierarchy Content page, you enter a name for your establishment hierarchy, and select the hierarchy type "VETS, EEO, AAP, OSHA, Multi Work Sites." For this hierarchy type, you select an organization with the classification parent entity as the top node in the hierarchy. You record some of the data required by U.S. government reports against the organization that is the parent entity. For example, you specify default data for establishments in the hierarchy in the EEO-1/VETS Establishment Data record of the parent entity.
To define your establishment hierarchy, you identify child nodes of the parent entity node. Immediate child nodes of the parent entity are establishment nodes. If all employees in your enterprise work from a single establishment, you define an establishment hierarchy with one parent entity and one establishment node. Alternatively, if your employees work from multiple establishments, you define multiple establishment nodes as child nodes of the parent entity. In a multi-establishment hierarchy, you identify one of the establishments as the headquarters establishment by updating the location EIT "EEO-1/VETS Generic Data."
If any establishment in your hierarchy comprises more than one location, you define location nodes as child nodes of the establishment node. For example, you may group multiple small locations under a single establishment in your enterprise. When you run a report for the hierarchy, information from the locations (such as employee assignments associated with the location) appears in the establishment report. However, this third level of nodes (the location level) is not usually required.
Single-Establishment Hierarchy
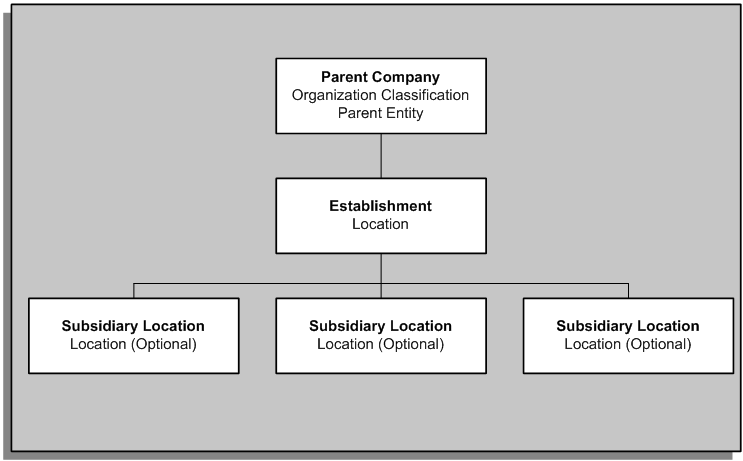
This figure shows an establishment hierarchy comprising a parent entity with one establishment node. This establishment has three subsidiary locations that are included in reports for the establishment.
Multi-Establishment Hierarchy
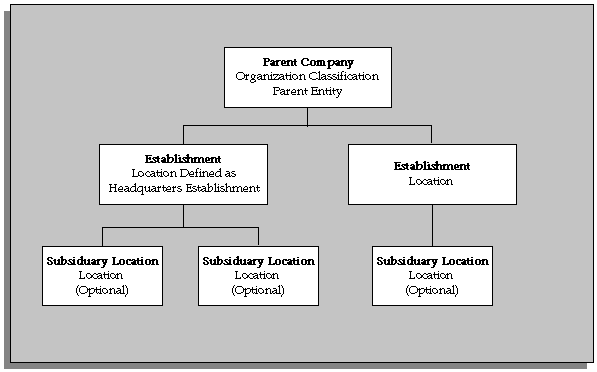
This figure shows an establishment hierarchy comprising a parent entity with two establishment nodes, one of which has been identified as the headquarters establishment. Both establishments have subsidiary locations.
This hierarchy of node types, where location is a child node of the establishment node, and the establishment node is a child node of the parent entity, is enforced by the hierarchy type "Vets, EEO, AAP, OSHA, Multi Work Sites."
In most cases, there is a one-to-one relationship between an establishment and a location. In some cases, there are many locations to one establishment. You can also associate a single location with multiple establishments. If different subsidiary companies of your enterprise (for example, a sales company and a maintenance company) that you want to report on separately are based at the same physical location, you can create multiple location records with identical address data but different establishment information in the location EITs. You include these establishments in the hierarchy in the usual way so that they appear as separate establishment nodes in the establishment hierarchy.
Data for EEO Reporting
For EEO and EO Survey reporting, you must maintain specific personal and job-related information for employees.
Employee Gender and Ethnic Origin
For EEO and EO Survey reporting, you must record both the gender and the ethnic origin of your employees.
The ethnic origin categories for the EO Survey Report are:
-
White (not Hispanic or Latino)
-
Black or African American (not Hispanic or Latino)
-
Hispanic or Latino
-
Asian (not Hispanic or Latino)
-
Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander (not Hispanic or Latino)
-
American Indian or Alaskan Native (not Hispanic or Latino)
-
Two or More Races (not Hispanic or Latino)
The ethnic origin categories for EEO reporting are:
-
White (Not of Hispanic Origin)
-
Black (Not of Hispanic Origin)
-
Hispanic
-
Asian or Pacific Islander
-
American Indian or Alaskan Native
When you select an employee's ethnic origin, Oracle HRMS displays the seven ethnic origin categories required by the EO Survey Report. Oracle HRMS automatically consolidates employee ethnic origin values into the five categories required for EEO reporting.
Note: The EEOC mandated all the ethnicity codes, but some agencies do not recognize all codes. When you select Two or More Races, you must fill out an additional ethnic category in the extra information type Additional Ethnic Category on the Person window. This allows you to report Two or More Races to the EEOC, and a lower level category to other agencies if needed.
EEO-1 Job Categories
To be included in EEO and EO Survey reports, employees must have assignments to jobs, and each job must be associated with an EEO-1 job category.
The following are the current EEO-1 Job Categories:
| First/Mid Level Officials and Managers |
| Executive/Senior Level Officials and Managers |
| Professionals |
| Technicians |
| Sales Workers |
| Administrative Support Workers |
| Craft Workers |
| Operatives |
| Laborers and Helpers |
| Service Workers |
Employment Categories and Assignment Statuses
Each employee to be included in an EEO-1 (or VETS-4212) report must have an employment category and assignment status that match those defined as reporting categories and statuses.
This requirement does not apply for the EO Survey Report.
Additional Requirements for EO Survey Reporting
For an employee to be included in the EO Survey Report, you must ensure that:
-
Their primary assignment status is one of: Active Assignment, Terminate Assignment, Suspend Assignment, Active Application, and Accepted.
-
You record their hire date and working hours.
-
You manage their salary using Oracle Payroll.
Additional Requirements for EEO-4 and EEO-5 Reporting
For an employee to be included in EEO-4 and EEO-5 reports, you must ensure that:
-
Their primary assignment status is not Terminate Assignment.
-
An EEO function is selected (for EEO-4).
-
A salary is specified (for EEO-4).
-
Their assignment category is either Full Time - Regular or Parttime - Regular.
Setting Up EEO, VETS, and IPEDS Reporting
Entering EEO-1/VETS Establishment Data for Parent Entities
Oracle HRMS uses EEO-1 and VETS establishment data in the production of EEO, EO Survey, and VETS-4212 reports. You specify default data for establishments beneath the parent entity in an establishment hierarchy in the EEO1/VETS Establishment Data window. This approach enables you to enter data that is common to your establishments once only, rather than entering it for each establishment individually. You can still override these default values at the location level.
To enter EEO-1 and VETS establishment data
-
Enter the Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) number and, if your enterprise uses the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS), enter the NAICS number.
-
Select a Government Reporting Entity (GRE).
-
Enter the Dun and Bradstreet (DUNS) number, if appropriate.
-
In the Government Contractor field, select Yes if most or all establishments in the hierarchy are government contractors. The EEOC defines an establishment as a government contractor if it is a prime government contractor or first-tier subcontractor and has a contract, subcontract, or purchase order for more than $50,000, or if it is a depository of government funds.
-
Indicate whether the establishments employ apprentices.
-
In the Main Activities fields, enter brief descriptions of the major business activities of the establishments in the hierarchy, as advised by your EEOC office.
-
Choose OK.
-
Save your work.
Entering EEO-1 Parent Entity Data
Enter EEO-1 parent entity data in the EEO1 Parent Entity Data window. This information is required for the EEO-1 and EO Survey reports.
To enter EEO-1 parent entity data
-
Enter the parent entity's reporting name and company number (FEIN).
-
Select Yes in the Affiliated field if the parent entity:
-
Employs fewer than 100 employees, and
-
Is affiliated with another company, or is subject to centralized ownership or management, resulting in a single enterprise employing 100 or more employees
-
-
Enter the user ID furnished by NORC. This user ID is required for the Upload Data file generated by the EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data concurrent request. See Running the EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report for information about output files.
-
Click OK.
-
Save your work.
Entering Multiple Worksite Report Parent Entity Data
Use this organization information type to record information about your parent entity that is used by the Multiple Worksite report.
To enter Multiple Worksite report parent entity data
-
Enter the legal name. This will be reported if it is different from the trade name entered against the establishment in the Location window.
For example, ABC Enterprises could have a subsidiary division called Bay Restaurant. ABC Enterprises would be considered as the legal name and Bay Restaurant would be a trade name.
-
Save your work.
Entering VETS Parent Entity Data
Use this organization information type to record information about your parent entity that is used by the VETS-4212 reports.
To enter VETS parent entity data
-
Enter the reporting name to be used for this parent entity.
-
Enter the company number that the US Department of Labor has provided to identify this parent entity.
-
Select the type of reporting organization appropriate for this parent entity.
-
Save your work.
Setting Up EEO-1 Reporting
-
Register reporting categories for your business group. Reporting categories are those employment categories that apply to nontemporary, full-time or part-time work.
-
Register reporting statuses for your business group. Reporting statuses are those assignment statuses that describe nonterminated assignments.
-
Specify the type of EEO report your business group runs. This selection determines the contents of the job categories list.
-
Associate each job in your enterprise with an EEO job category.
-
Ensure that each employee has:
-
Their gender and ethnic origin on record
-
A job linked to an EEO-1 job category
-
A location in the establishment hierarchy
-
An assignment status that matches a reporting status
-
An employment category that matches a reporting category
-
-
Define an organization with the classification of parent entity to represent the parent company in the establishment hierarchy.
See: Creating an Organization and Entering Organization Classifications
-
Enter EEO-1 parent entity data for the organization you have identified as the parent entity.
-
Enter default establishment data for the establishments in the hierarchy.
See: Entering EEO-1 and VETS Establishment Data for Parent Entities
-
For each location to be identified as an establishment in the hierarchy, enter EEO-1 specific data.
-
If your enterprise requires a headquarters report, identify one of the establishments in the hierarchy as the headquarters establishment.
-
Define your establishment hierarchy.
-
Run the EEO-1 reports for your enterprise.
Setting Up EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Reporting
See Running the EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report for more information.
Complete the following steps to set up EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data reporting.
-
In the NORC User ID field of the EEO1 Parent Entity Data window, for each organization, enter the user ID furnished by NORC. See Entering EEO-1 Parent Entity Data for more information.
-
Populate the Establishment Not Exempt or Prime Contractor field for the applicable locations using the EEO1 Specific Data location extra information. This field stores the answer to Question D2 which is required to be reported in the 14th column in the Upload Data file. See Location Extra Information Types for more information.
-
Populate the "EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data" person extra information type (EIT) if you are a US HR only customer.
This step must be performed if you are a US HR only customer, that is, you do not use Oracle EBS US Payroll but instead use a third-party product to process your payroll. This means the payroll component data required for the Component 2 EEO -1 Upload File does not reside within the EBS HRMS application. To populate the required payroll data, use the "EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data" person extra information type (EIT). Any employees who are missing this data in the Person EIT will not be included in the report output or the report counts, and instead will be reported as exceptions in a separate exception report output file. This EIT stores the W-2 Box 1 earnings and total hours worked for each employee for each reporting year. This information is necessary to report the correct data into the 'AnnualSalary' and 'TotalHours' columns of the Component 2 EEO -1 Upload File. See Running the EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report for information about the output files.
This EIT contains the following fields and enables you to enter multiple records, one for each reporting year.
-
Reporting Year
-
Total Hours Worked
-
W-2 Box 1 Earnings
To populate the EIT for employees:
-
You can manually populate the EIT fields for an employee using the Extra Person Information window.
-
For higher volumes of employee data that need to be populated, the total hours and W-2 Box 1 earnings data must be collected from the third-party payroll system into a spreadsheet. That data can then be loaded into the Oracle E-Business Suite HRMS database using one of the two methods:
-
Creating a custom WEB ADI upload integrator
-
Running a PL/SQL script to call the HR API hr_person_extra_info_api.create_person_extra_info
For information about loading data, refer to the My Oracle Support document note ID 2584353.1, Oracle E-Business Suite US HRMS: EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report - A Functional Overview for Release 12.1 and 12.2 Customer.
-
Information for US Payroll customers:
It is not necessary to populate the Person EIT details. This is because the report will derive the W-2 Box 1 Earnings and Hours Worked from the employee's Year End Preprocess archived data (A_WAGES and A_REGULAR_HOURS_WORKED archived items respectively). However, if the EIT details are populated, these values will be used for reporting instead of the employee's archived data.
-
If A_WAGES, that is, the employee's archived W-2 Box 1 wages from the Year End Preprocess archived data is not available or is zero, then the employee will not be included in the report counts and will be reported as an exception in a separate exception output file.
-
If A_REGULAR_HOURS_WORKED, that is, the employee's archived hours worked value from the Year End Preprocess archived data is not available or is zero, the Employee Hours Worked will be reported as 40 hours per week for Full Time Regular Employees and 20 hours per week for Part Time Regular Employees.
The following formula function is used by the report:
IF Employee_FullTime_Regular THEN Hours_Worked = (Days_Between Employee_Start_Date/Reporting_Year_Start_Date and Employee_Termination_Date/Reporting_Year_End_Date) / 7 * 40 ELSIF Employee_PartTime_Regular THEN Hours_Worked = (Days_Between Employee_Start_Date/Reporting_Year_Start_Date and Employee_Termination_Date/Reporting_Year_End_Date) / 7 * 20
-
Setting Up EO Survey Reporting
This process identifies tasks you perform to set up and run your EO Survey Report. You may have performed some of these tasks already for other mandatory reports, such as the EEO or IPEDS reports.
-
Define an organization with the classification Parent Entity to represent the parent organization in the establishment hierarchy. The organization must also have the classifications Business Group and GRE / Legal Entity.
-
Enter EEO-1 parent entity data for the organization you have identified as the parent entity. This step establishes the reporting name that appears in your EO Survey Report.
-
Enter default information for the establishments you will include in the establishment hierarchy. This step identifies the Government Reporting Entity (GRE), which provides the FEIN value in the EO Survey Report.
See: Entering EEO-1/VETS Establishment Data for Parent Entities
-
For each location to be included as an establishment in the hierarchy, enter EEO-1 Specific Data. This step provides the reporting name that appears in your EO Survey Report. If you omit this step, the name you enter for the parent entity (in Step 2) appears in the report.
See: Location Extra Information Types
See: Setting Up Locations
-
For each location to be included as an establishment in the hierarchy, enter EEO1/VETS Generic Data. This step identifies the Government Reporting Entity (GRE), which provides the FEIN value in the EO Survey Report. If you omit this step, the name you enter for the parent entity (in Step 3) appears in the report.
See: Location Extra Information Types
See: Setting Up Locations
-
Define your establishment hierarchy using the type VETS, EEO, AAP, OSHA, Multi Work Sites.
-
Specify the type of EEO report your business group runs. This step ensures that EEO-1 job categories appear in the job categories list when you define a job.
-
Ensure each job in your enterprise has an EEO-1 job category.
-
Ensure each person record includes the person's gender, ethnic origin, and hire date.
See: Entering a New Person (People Window), Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
See: Entering Additional Personal Information (People Window), Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
Ensure each person's assignment record includes their job, location, working hours, and a valid assignment status (Active Assignment, Terminate Assignment, Suspend Assignment, Active Application, or Accepted).
See: Entering an Assignment, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
See: Entering Additional Assignment Details (Assignment Window), Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
Ensure that whenever a person's assignment changes as a result of a promotion enter Promotion in the reason field on the Miscellaneous tab on the assignment window.
See: Entering Additional Assignment Details (Assignment Window), Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
The supplied balance EO Regular Salary Year to Date has three seeded salary feeds, which are Regular Salary, Regular Wages, and Time Entry Wages. If you use different salary elements, update the definition of the balance EO Regular Salary Year to Date to include your salary elements.
See: Defining User Balances, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
-
Run the EO Survey Report for your establishment or establishment hierarchy.
Setting Up EEO4 and EEO5 Reporting
To set up EEO4 and EEO5 reporting
-
Specify the type of EEO report your business group runs.
-
For the EEO5 report, create any annexes for your school district as locations. Details of these annexes appear on the header page of the report. In the EEO5 report, the annex count is a count of the locations associated with assignments in the business group. The school count is a count of the organizations in the business group.
Note: If you have multiple business groups, you must enter the annexes in the report manually, as locations are not specific to the business group.
See: Setting Up Locations
-
Associate each job in your enterprise with an EEO job category.
-
Ensure required personal information is captured.
-
Set up employment categories for each business group.
See: Writing Formulas for EEO Employment Categories, Oracle HRMS FastFormula User Guide
-
Submit the report.
Setting Up Data to Generate VETS-4212 Reports
This topic provides information about the necessary data setup to generate the VETS-4212 reports.
For an overview, see VETS-4212 Reporting.
To set up data to generate the VETS-4212 reports:
-
Define your establishment hierarchy.
-
Set up an organization with the classification of Parent Entity to represent your parent company.
-
Define one of the locations as the headquarters if a headquarters report is required.
-
Enter EEO1/VETS Generic Data for each location to be included as an establishment in the hierarchy.
-
Enter VETS Specific Data for each location to be included as an establishment in the hierarchy.
-
Define data for the VETS reports in the EEO-1 Specific Data location extra information type. Do this for each location that is included as an establishment for the report.
-
Enter data in the VETS Parent Entity Data additional information type for the organization that you have classified as parent entity.
-
Enter the information that you want to appear by default in the EEO-1/VETS Establishment Data additional information type.
See: Entering EEO-1 and VETS Establishment Data for Parent Entities
-
Specify the EEO Report Details required for your business group. In the EEO Report Details additional information window, select EEO1 in the Report Details field.
-
Enter the employer identification number using the Employer Identification additional information window.
-
Ensure that Reporting Categories and Statuses are registered for your business group. Reporting Categories are those employment categories that cover non-temporary, full-time or part-time work. Reporting Statuses are those assignment statuses that cover non-terminated statuses.
-
Ensure that EEO job categories are on record for your jobs.
-
Ensure that all employees qualifying as Special Disabled Veterans or Veterans of the Vietnam Era have a veteran status, an assignment to a job, and an employment category. Ensure that for such an employee, a Vets 100A value is recorded in the Employment tab of the People window. The employee counts reported in the VETS-4212 reports are derived based on the Vets 100A value in an employee's person record.
See: Entering a New Person, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide (US)
See: Entering an Assignment, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide (US)
See: Entering Additional Personal Information (People Window), Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide (US)
-
Run the VETS-4212 reports.
See: VETS-4212 Reporting.
Setting Up Information for the IPEDS Reports
To run the Integrated Post-secondary Education Data System (IPEDS) reports correctly you must ensure you complete the following setup steps:
To set up the information for the IPEDS reports
-
Enter IPED Report Details for your business group.
See: Business Groups: Entering EEO Report Details
The report you select here determines which job categories appear in the Job Further Information flexfield.
-
Ensure you enter an Institution Type of Medical or Non-Medical for all your HR Organizations.
See: HR Organizations: Entering IPEDS Institution Type Information
-
Select an IPED job category in the Job Further Information flexfield.
See: Defining a Job
The job categories that appear here depend on the type of report you select for your business group.
-
Select the gender of your employees.
See: Entering a New Person, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
Select the race/ethnicity of your employees.
See: Entering Additional Personal Information, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
Select full-time or part-time information for your employees in the Employee Category field.
See: Entering an Assignment, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
Enter non resident alien information in the Visa Details extra person information type.
See: Person Extra Information Types, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
Select the tenure status for your employees.
See: Person Extra Information Types, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
Select the academic rank of your employees.
See: Person Extra Information Types, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
Enter the contract length of your employees.
See: Entering Contracts, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
Ensure you have a salary basis and an annual salary defined for your employees.
See: Defining a Salary Basis, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
See: Entrering Salary for a New Employee, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
Employees are reported on the interval the salary falls under, this is called the salary class interval.
-
Run the IPEDS reports.
Associating Jobs with EEO Job Categories
For EEO, EO Survey, AAP, and VETS reporting, you must associate each job in your enterprise with an EEO job category.
To associate a job with an EEO category, start from the Job window.
To associate a job with an EEO job category
-
Query the job in the Name field if it does not already appear there. Click in the Further Information field to open the Further Job Information window.
Note: The type of report you select in your business group determines which categories appear.
-
In the EEO Category field, select the category for this job.
-
If your report is EEO4, select the EEO Function for this job.
-
Save your work.
EEO and IPEDS Reporting
Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO-1) Reporting
Most private employers in the U.S. must provide EEO-1 reports to the Joint Reporting Committee in accordance with the Civil Rights Act of 1964, as amended by the Equal Employment Opportunity Act of 1972.
Under Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) rules, an establishment for EEO reporting is an economic unit, such as an office, factory, store, or mine, that produces goods or services at a single physical location. Establishments are permanent locations from which you supervise employees or from where they operate.
The EEO-1 reports you must submit to the EEOC depend on whether you are a single-establishment or multi-establishment employer.
EEO-1 Suite of Reports
You can run the whole suite of EEO-1 reports at one time, or you can run individual reports. Oracle recommends that you run the whole suite of EEO-1 reports because the application automatically creates the appropriate single-establishment or multi-establishment reports for you from the hierarchy structure you identify.
For single-establishment employers, the application generates an EEO Individual Establishment Report.
For multi-establishment employers, the application generates the following reports:
-
EEO Consolidated Report: Uses the results of the Individual Establishment reports to summarize EEO information for all employees in the enterprise.
-
EEO Individual Establishment Report: For each job category, this report lists provides a total of employees according to sex and ethnicity. For business organizations with multiple locations, it provides a total for all locations. Required for each establishment that has 50 or more employees.
-
EEO Headquarters Report: Reports the sex and ethnicity of employees operating in a headquarters establishment, sorted by job category. Required for the establishment identified as the headquarters of the enterprise.
Note: For multi-establishment employers that have only one establishment located in the U.S., with the parent company being outside the U.S., in order to produce an EEO Headquarters Report, you must create a placeholder establishment to represent the headquarters. This establishment must have a GRE and a location and must be in a hierarchy.
The EEO Headquarters Report has the same header as the EEO Individual Establishment Report.
-
EEO Establishment Employment Listing: Shows the name, address, total employment, and major activity of any establishment with fewer than 50 employees.
You can submit EEO-1 reports formatted for magnetic media or as computer printouts, provided they conform exactly to EEOC formatting standards. If you are a multi-establishment employer who submits EEO-1 reports as computer printouts, you must submit the EEO Consolidated Report on Standard Form 100. This requirement does not apply if you submit EEO-1 reports formatted for magnetic media.
EEO-1 Exception Report
The EEO-1 Exception Report reports on:
-
Missing employees
It provides details of those employees, listed by location, whom you did not include in other EEO-1 reports. It shows the employee name, employee number, gender, job, EEO category, ethnic origin, and employment category of all employees excluded from the EEO-1 suite of reports. The EEO-1 Exception Report also explains why you did not include those employees in the EEO-1 suite of reports.
-
Missing locations
It reports on locations that have unpopulated fields in EEO1 Specific Information and EEO1/VETS Generic Information and on those locations that should be in the hierarchy but are not.
Oracle HRMS produces the EEO-1 Exception Report separately from the other EEO-1 reports, with its own header and details. See Running the EEO-1 Reports for more information.
EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report
The U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) collects workforce data from private employers with 100 or more employees, federal contractors, and subcontractors. To comply with EEOC reporting requirements, employers are required to submit to the EEOC “Component 2 Compensation data” if they have 100 or more employees during the workforce snapshot period. The workforce snapshot period is an employer-selected pay period between October 1 and December 31 of the reporting year. For further information about the EEOC Component 2 Compensation data requirements, visit the EEO-1 Survey website at https://www.eeoc.gov/employers/eeo1survey/index.cfm.
Oracle provides the EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report concurrent request to enable you to generate the necessary CSV output file according to the EEOC's Component 2 EEO -1 Upload File Layout specifications or to generate the paper forms to assist with manual data entry. This report collects the number of employees and the hours worked by job category, salary pay band, gender, and race or ethnicity data. For information about this report, visit the Component 2 EEO-1 Online Filing System website at https://eeoccomp2.norc.org/.
Important: Complete the additional setup steps prior to running this report. You must run the EEO-1 Exception Report prior to running the EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report. The EEO-1 Exception Report identifies employees with incorrect or incomplete setup. You must correct these setup issues. Otherwise, any employees reported by the EEO-1 Exception Report will neither be included in the EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report nor reported in the exception report.
See:
Running the EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report
Electronic EEO-1 Exception Report
When you run the Electronic EEO-1 Report and encounter missing or incorrect setup such as an incomplete address for one of the HR establishments, the program ends in error and displays the establishment name and reason that caused the error in the report request log.
Following are potential scenarios that can cause the Electronic EEO-1 Report to end in error:
-
Company Number of Parent Organization is missing in the EEO1 Parent Entity Data window. See Entering EEO-1 Parent Entity Data for more information.
-
Unit Name and Location Street Address are missing for any establishment inside the reporting hierarchy. For Unit Name, see "EEO-1 Specific Data" section in Location Extra Information Types.
-
City, County, State, and Zip code are missing from the address of any establishment inside the reporting hierarchy.
-
Unit Name is less than two characters for any establishment inside the reporting hierarchy.
-
The location's street address is less than four characters for any establishment inside the reporting hierarchy.
-
NAICS codes are entered for any establishment which is either designated as the headquarters or government-affiliated or has more than 100 employees (Parent Entity level).
-
Contact information of Certifying Officer is entered for a business group which is designated as the headquarters or government-affiliated or has more than 100 employees (Parent Entity level).
To minimize the effort required to resolve these errors and complete the EEO-1 report, run the Electronic EEO-1 Exception Report concurrent program. This program reports all the missing or incorrect setup in one place.
Important: As a best practice, run the Electronic EEO-1 Exception report before running the Electronic EEO-1 report to resolve any errors due to incomplete or incorrect setup ahead of time.
See Running the EEO-1 Reports for more information.
Submitting EEO Reports
You can submit EEO reports to the EEOC either formatted for magnetic media or as computer printouts.
Submitting Reports as Computer Printouts
You can submit the following reports as computer printouts:
-
EEO Headquarters Report
-
EEO Individual Establishment Report
-
EEO Establishment Employment Listing
-
EEO-1 Exception Report
-
Electronic EEO-1 Exception Report
-
EEO4 Reporting
-
EEO5 Reporting
Note: You must submit the EEO Consolidated Report on Standard Form 100; you cannot submit it as a computer printout.
The printouts comply with the current formatting rules of the EEOC. However, the EEOC requires submission of test printouts for review and written verification of acceptability.
Direct questions about computerized EEO-1, EEO-4, and EEO-5 reports to the appropriate coordinator:
The EEO-1 Coordinator:
EEO-1 Joint Reporting Committee
PRINTSRP
PO Box 19100
Washington, DC 20036-9100
The EEO-4 Coordinator:
Survey Management and Analysis Branch
Program Research and Surveys Division (OPO-ORPP)
FAX: 202-663-7130
Telephone: 202-663-4930
EEOC-Surveys
1801 L Street, N.W.
Washington, D.C. 20507
The EEO-5 Coordinator:
Survey Management and Analysis Branch
Program Research and Surveys Division (OPO-ORPP)
FAX: 202-663-7130
Telephone: 202-663-4952
EEOC-Surveys
1801 L Street, N.W.
Washington, D.C. 20507
Submitting Reports Formatted for Magnetic Media
You can submit the following reports formatted for magnetic media:
-
EEO Consolidated Report
-
EEO Headquarters Report
-
EEO Individual Establishment Report
-
EEO Establishment Employment Listing
When you submit a request for the Electronic EEO-1 Report, the application generates the appropriate reports from this list for your establishment hierarchy and formats them for submission to the EEOC on magnetic media. You can upload the formatted file to the EEOC using the EEO-1 Web Application.
IPEDS (Integrated Post-Secondary Education Data System) Reporting
Oracle HRMS enables you to record information required by the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). The National Center for Educational Statistics (NCES) collects and supplies information on employee affirmative action reporting to the EEOC.
The information on employee affirmative action reporting produced by the reports is used to determine federal program needs and eligibility.
The reports required by the NCES are:
-
IPEDS Report - Degree Granting Institutes - Part A
This report lists the count of full-time instructional staff by tenure, academic rank, gender, race or ethnicity, and medical school status of degree granting institutes. The breakup on tenure and race or ethnicity is based on the selected report parameter values.
-
IPEDS Report - Degree Granting Institutes - Part B
This report lists the count of full-time non instructional staff by tenure, occupational category, gender, race/ethnicity and medical school status of degree granting institutes. The breakup on tenure and race or ethnicity is based the selected parameter values.
-
IPEDS Report - Degree Granting Institutes - Part D
This report lists the count of part-time non instructional staff by occupational category, gender and race or ethnicity of degree granting institutes. The breakup on race or ethnicity is based on the selected report parameter values.
-
IPEDS Report - Degree Granting Institutes - Part E
IPEDS Report - Degree Granting Institutes - Part GThis report lists the count of part-time non instructional staff by tenure, medical school status and occupational category of degree granting institutes. The breakup of the tenure is based on the selected report parameter values.
-
IPEDS Report - Degree Granting Institutes - Part G
This report lists the salary outlays of the 9, 10,11, and 12 month contract of full-time employees of degree granting institutes.
-
IPEDS Report - Degree Granting Institutes - Part H
This report lists the count of number of new hire full-time staff based on tenure (only for instructional staff), occupational category (only for non-instructional staff), gender, race/ethnicity and medical school status of degree granting institutes. The breakup on tenure and race or ethnicity is based on the selected report parameter values.
-
IPEDS Report - Non Degree Granting Institutes
This report lists the count of new hire full-time or part time staff based on occupational category, gender, race/ethnicity and medical school status for non-degree granting institutes. The breakup on race or ethnicity is based on report parameter values selected.
For information on setting up information for IPEDS reports, see: Setting Up Information for the IPEDS Reports
Running the EEO-1 Reports
You can run the whole suite of EEO-1 reports at one time, or you can run individual reports. When you run the whole suite of EEO-1 reports, the application automatically creates the appropriate single-establishment or multi-establishment reports for you from the establishment hierarchy you identify.
The Electronic EEO-1 Report program generates the electronic EEO-1 report file with Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN) of each establishment. If an establishment has multiple locations at a common address and has the same NAICS code, then the Electronic EEO-1 Report consolidates the employee counts into a single record instead of reporting the employee counts separately for each establishment.
See: Equal Employment Opportunity Reporting (EEO-1)
You can generate the suite of EEO-1 reports as computer printouts or formatted for magnetic media. When formatted for magnetic media, the suite of EEO-1 reports does not include the EEO-1 Exception Report. You cannot format individual reports for magnetic media.
You submit all requests to run EEO-1 reports, including those for the suite of EEO-1 reports, as single requests from the Submit Request window. You can request the following EEO-1 reports:
-
EEO-1 Suite of Reports (computer printouts)
-
Electronic EEO-1 Report (magnetic media)
-
EEO Individual Establishment Report
-
EEO Consolidated Report
-
EEO Establishment Employment Listing
-
EEO-1 Exception Report
Note: As a best practice, run the Electronic EEO-1 Exception Report before running the Electronic EEO-1 report to resolve any errors due to incomplete or incorrect setup ahead of time.
-
Electronic EEO-1 Exception Report
To run an EEO-1 report
-
Select one of the following values in the Name field:
-
EEO-1 Suite of Reports
-
Electronic EEO-1 Report
-
EEO Individual Establishment Report
-
EEO Consolidated Report
-
EEO Establishment Employment Listing
-
EEO-1 Exception Report
-
Electronic EEO-1 Exception Report
-
-
If the Parameters window does not open automatically, click in the Parameters field.
-
Select the name and version of the establishment hierarchy to use for this report.
-
Enter the start and end dates of the report period. Choose any date between July 1 and September 30, and the start date can be the same as the end date.
-
This step does not apply to the following reports:
-
EEO Establishment Employment Listing
-
EEO-1 Exception Report
-
Electronic EEO-1 Exception Report
-
-
Select a report mode, if required. The report mode can be F (Final) or D (Draft).
-
Select final mode only when you are ready to submit the report to the EEOC. When you run a report in final mode, the employment data totals from the report are stored so that they can be included in next year's report in the PREVIOUS REPORTED TOTAL line.
-
Draft is the default mode. When you run a report in draft mode, the employment data totals are not recorded. You can run a report in draft mode as often as necessary.
Note: Avoid rerunning a report in final mode after you submit it successfully to the EEOC. If you rerun a report in these circumstances, the application may update the stored employment data totals. Therefore, when you run the report in the following year, the figures in the PREVIOUS REPORTED TOTAL line could differ from those you submitted to the EEOC during the year in question. Any discrepancy between the two sets of figures could cause the EEOC to question the data.
The Report Mode parameter is not applicable to the following reports:
-
EEO Establishment Employment Listing
-
EEO-1 Exception Report
-
Electronic EEO-1 Exception Report
-
-
Choose OK, then Submit.
To generate a PDF format output report
You can convert your EEO-1 report output into PDFs. Creating PDF reports involves running the XML Report Publisher report. Before you can perform this operation, you must configure your reports to generate the necessary XML files.
-
From the Submit Request window, select XML Report Publisher in the Name field.
-
Select the EEO-1 report you want to translate into PDF.
-
Select the XML Publisher template you want to use.
-
Select the language set you want to use.
-
Make sure the output format is PDF.
-
Click OK, then Submit.
This report generates your PDF output.
To reprint an EEO-1 report
You reprint a report by selecting Reprint from the Tools menu in the Find Requests window and entering its concurrent request ID.
To find the concurrent request ID of a single-establishment report use the Location window. To find the concurrent request ID of a multi-establishment report use the Organization window.
To reprint a single-establishment EEO report
-
Query the location for which you want to obtain the reprint and choose Extra Information.
-
In the Extra Location Information window, select the EEO1 Individual Establishment Archive Data type and click in the Details field.
-
Make a note of the concurrent request ID for the appropriate year's report.
To reprint a multi-establishment EEO report
-
Query the business group for which you want to obtain the reprint and select the Parent Entity organization classification.
-
Choose Others.
-
In the Additional Organization Information window, select EEO1 Consolidated Archive Data.
-
Click in the EEO1 Consolidated Archive Data field to display the data.
-
Make a note of the concurrent request ID for the appropriate year's report.
Running the EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report
The U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) collects workforce data from private employers with 100 or more employees, federal contractors, and subcontractors. To comply with EEOC reporting requirements, employers are required to submit to the EEOC “Component 2 Compensation data” if they have 100 or more employees during the workforce snapshot period. The workforce snapshot period is an employer-selected pay period between October 1 and December 31 of the reporting year.
Run the EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report concurrent request to generate the necessary CSV output file according to the EEOC's Component 2 EEO -1 Upload File Layout specifications or to generate the paper forms to assist with manual data entry. The report collects the number of employees and the hours worked by job category, salary pay band, gender, and race or ethnicity data. See EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report for details.
See:
Running the EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report
Run the report from the Submit Request window.
Prerequisites
- Complete the additional setup steps prior to running this report. You must run the EEO-1 Exception Report prior to running the EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report. The EEO-1 Exception Report identifies employees with incorrect or incomplete setup. You must correct these setup issues. Otherwise, any employees reported by the EEO-1 Exception Report will neither be included in the EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report nor reported in the exception report.
To run the EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report:
-
In the Name field, enter EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report.
-
Enter the following parameters:
Parameter Mandatory or Optional Description Reporting Period Start Date Mandatory Enter the start date of the pay period to be used for reporting. Reporting Period End Date Mandatory Enter the end date of the pay period to be used for reporting. Hierarchy Name Mandatory Select the applicable establishment hierarchy name. Hierarchy Version Mandatory Select the applicable establishment hierarchy version Create Employee Details Report Optional Set to Yes to provide an employee audit detail report. It is created using CSV format so that it can be easily uploaded into a spreadsheet for further reconciliation. By default, it is set to No. Create Paper Report Optional The value defaults to "Yes" but can optionally be changed to "No" to prevent the paper or PDF report output from being generated. Setting this parameter to No will be useful for customers with a large number of establishments and who are encountering performance issues. Note that when the report is run with Create Paper Report parameter set to No, then the Paper Report (PDF) output file displays the message "Paper Report details not generated, as Input Parameter 'Create Paper Report' is No." -
Submit the request.
Viewing Report Output Files
When the EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data Report is run, it generates the following output files.
-
Upload Data File
Upload Data file (CSV format): This is the CSV output file containing the EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data according to the required EEOC File Upload specifications that is to be uploaded to the Component 2 EEO-1 Online Filing System (https://eeoccomp2.norc.org/).
The file name format is UploadFileYYYYCCCCCCCC_DDHH24MI_5_P.eft.
Important Note: You must rename this output file to "UploadFileYYYYCCCCCCCC.csv" where:
-
YYYY is the Reporting Year
-
CCCCCCCC is the NORC User ID
-
DDHH24MI represents the Date (DD) and Time the report was run: HH24 = Hours (in 24 hours format) and MI = Minutes. But this part of the file name should be removed as neither the report run date nor run time should be included the Upload File name.
-
-
Paper Report File
Paper Report file (PDF Format): This file is the actual EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data according to the Online Filing tabular form and can be used to fill in the online form manually. The file name format is UploadFileYYYYCCCCCCCC_DDHH24MI_1_P.pdf.
-
Certifying Details File
Certifying Details file (CSV format): This file includes the details that are required for completing the Certification step (Additional Reporting Requirement to Certify Uploaded Files) once the Upload Data file is uploaded to the Component 2 EEO-1 Online Filing System or the data has been entered manually into the Online Form. The file name format is UploadFileYYYYCCCCCCCC_DDHH24MI_4_P.eft.
-
Base XML File
Base XML file: This is the base XML file based on which the other output files are generated. The file name format is UploadFileYYYYCCCCCCCC_DDHH24MI.xml.
-
Employee Details File
Employee Details file (CSV format): This is an audit file that contains the details of each individual employee included in the report. This output file will only be generated if the report input parameter “Create Employee Details Report” is set to 'Yes'. The file name format is UploadFileYYYYCCCCCCCC_DDHH24MI_2_P.eft.
-
Exception Employee File
Exception Employee file (CSV format): This report contains the details of employees who are not included in the report counts due to the following possible reasons.
-
EEO-1 Component 2 Compensation Data EIT is missing details
-
Year End Pre Process Archive Data is not available
-
W-2 Box 1 Earnings are zero
-
Total Hours Worked are zero
The file name format is UploadFileYYYYCCCCCCCC_DDHH24MI_3_P.eft.
-
Running the EEO4 Report
This report is a requirement for state and local governments. It provides information about employees that satisfies federal agencies' legal requirements. The EEO4 report provides information about functional areas, EEO job categories, race and ethnic category, and gender.
Run the EEO4 report from the Submit Requests window.
To run the EEO4 Report
-
In the name field, select EEO4 Reporting.
The Parameters window appears.
-
Enter the year for which you want to run the report.
-
Enter any additional message data.
This information is optional and appears in the top right corner of the report.
-
Click Submit.
Running the EEO5 Report
This report is a requirement for K -12 school systems or districts. It is an aggregate report for the entire school system or district. EEO5 covers EEO job category (assignment classification), race and ethnic category, and gender.
Run the EEO5 report from the Submit Requests window
To run the EEO5 Report
-
In the name field, select EEO5 Reporting.
The Parameters window appears.
-
Enter the year for which you want to run the report.
-
Enter the agency type.
-
Enter the enrollment figure for the reporting year.
This number indicates the total number of students enrolled in the reporting year.
-
Click Submit.
Running the IPEDS Reports
The following reports are a requirement for the National Center for Educational Statistics (NCES). The type of institution you choose determines which reports you must run.
You can run both IPEDS and EEO1 reports in a single business group, provided you have selected the report type IPEDS and EEO1 for the business group. You run all the reports from the Submit Request window.
-
IPEDS Report - Degree Granting Institutes - Part A
-
IPEDS Report - Degree Granting Institutes - Part B
-
IPEDS Report - Degree Granting Institutes - Part D
-
IPEDS Report - Degree Granting Institutes - Part E
-
IPEDS Report - Degree Granting Institutes - Part G
-
IPEDS Report - Degree Granting Institutes - Part H
-
IPEDS Report - Non Degree Granting Institutes
To run the reports
-
Query the IPEDS Report in the Name field.
-
Enter the Reporting Year. This is the date on which you want the report to be run.
-
Degree Granting Institutes:
For degree granting institutes, select the following parameters:
-
Reporting Date
-
Tenured (Yes/No)
-
With Race/Ethnicity (Yes/No)
The reports will provide the necessary data based upon the parameter values selected. The reports for degree granting institutes are according to the specifications outlined in the following documents that are available at https://surveys.nces.ed.gov/ipeds/visresults.aspx:
-
-
Non Degree Granting Institutes:
For non degree granting institutes, the applicable IPEDS report can be run with or without Race/Ethnicity data along with effective date. The reports can be run with the following parameters:
-
Report Date
-
Report Type (Part A/Part B)
-
With Race/Ethnicity (Yes/No)
The parameter values selected will determine the data that is produced in the report. The reports for non degree granting institutes are according to the specifications outlined in the following documents that are available at https://surveys.nces.ed.gov/ipeds/visresults.aspx:
-
-
-
Choose Submit.
Setting up Information for the EEO4A Reports
Complete the following steps to setup information for the EEO4A Report (XML) and EEO4A Exception Report:
-
Select the applicable value for an employee from the EIT 'US EEO-4A Ethnic Origin (Hawaii Only)'.
-
Navigate to People > Enter and Maintain > Other > Extra Information.
-
For the EIT 'US EEO-4A Ethnic Origin (Hawaii Only)', select the appropriate value for applicable employees.
This EIT is also accessible to both managers and employees in the Manager and Employee Self Service responsibility, Extra Information menu option.
-
-
Run the EEO4 A Report (XML) first and then the EEO4A Exception Report using the Submit Request window.
Running the EEO4A Report (XML)
This report supports the EEO-4A reporting requirements for state and local government EEO reporting in the state of Hawaii. This is an XML-based report that produces PDF output.
Prerequisites: Before you run the EEO4A Report (XML) report, you must complete certain setup steps. See: Setting up Information for the EEO4A Reports
Run the EEO4A Report (XML) report from the Submit Requests window.
To run the EEO4A Report (XML) Report
-
In the name field, select EEO4A Report (XML). The Parameters window appears.
-
Enter the year for which you want to run the report.
-
Click Submit.
Running the EEO4A Exception Report
This report lists all employees who were not included in the EEO4A Report (XML) report due to an exception. An employee will be included in the EEO-4A Exception report if one of the following conditions is met:
-
EEO4A Ethnic Origin (EIT) information is missing.
-
No individual race field is set to yes in EEO4A Ethnic Origin (EIT).
-
More than one individual race field is set to yes in EEO4A Ethnic Origin (EIT).
-
Job information is missing or is not of EEO-4 category.
-
Assignment Category information is missing.
-
EEO Function is missing in Job information.
-
Both EEO4 Ethnic Origin and EEO4A Ethnic Origin (EIT) information exist for the employee. An employee can only have one type of ethnic origin: either EEO4 or EEO4A.
Prerequisites: Before you run the EEO4A Exception Report, you must complete certain setup steps and also must have run the EEO4A Report (XML) report.
See: Running the EEO4A Report (XML)
Run the EEO-4A Exception Report from the Submit Requests window.
To run the EEO-4A Exception Report
-
In the name field, select EEO-4A Exception Report. The Parameters window appears.
-
Enter the year for which you want to run the report.
-
Click Submit.
EO Survey Reporting
Equal Opportunity (EO) Survey Reporting
The U.S. Office of Federal Contract Compliance Programs (OFCCP) requires government contractors with 50 or more employees and who satisfy other criteria regarding the business they transact to submit an Equal Opportunity (EO) Survey Report. Oracle HRMS can generate an EO Survey Report, which is in three parts:
-
Part A of the report shows the employer identification number (FEIN) and the reporting name of the establishment.
-
Part B of the report shows, for full-time positions in a 12-month period, numbers of applicants, hires, promotions, and terminations. It also shows the number of full-time employees on the last day of the reporting period. Oracle HRMS organizes the information in Part B by gender, ethnic category, and EEO-1 job category.
-
Part C of the report shows annual monetary compensation and tenure data for those who are full-time employees on the last day of the reporting period. Oracle HRMS presents this information, organized by EEO-1 job category, for minority males, minority females, nonminority males, and nonminority females.
The Reporting Establishment
You can run the EO Survey Report for either an establishment hierarchy or a single establishment in an establishment hierarchy. The location definition of an establishment supplies the reporting name and FEIN for Part A of the report. If the location definition does not include this information, equivalent information from the parent entity (the organization) appears in the report.
The Reporting Period
The EO Survey Report applies to a 12-month period. You can run the report for:
-
Your most recently concluded Affirmative Action Program (AAP) year
-
The last complete calendar year
People Included in the Report
Oracle HRMS includes in the EO Survey Report applicants, employees, and ex-employees whose:
-
Assignment record includes a location belonging to the establishment or establishment hierarchy for which you run the report.
-
Assignment record includes a job that is associated with an EEO-1 job category.
-
Assignment status is one of: Active Assignment, Terminate Assignment, Suspend Assignment, Active Application, and Accepted.
-
Ethnic category is known. Oracle HRMS includes in the 'Race missing or unknown' column of the report applicants whose ethnic category is unknown, but excludes from the report employees and ex-employees whose ethnic category is unknown.
Applicants
An applicant is a person whose application for full-time employment you receive in the reporting period, who has the assignment status Active Application or Accepted, and who has any of the following system person types:
-
Applicant
-
Applicant and Ex-Applicant
-
Employee and Applicant
-
Ex-Employee and Applicant
-
Contingent Worker and Applicant
-
Ex-Contingent Worker and Applicant
Oracle HRMS includes:
-
In both the Applicants and Employees counts an employee whose system person type is Employee and Applicant
-
In both the Hires and Applicants counts an employee who is a new hire in the reporting period and, later in the same period, an applicant in another group
-
In the Applicants, Hires, and Terminations counts a person who applies for a full-time job, is hired, and is terminated, all within the reporting period
Hires
A new hire is a full-time employee whose hire date is in the reporting period and whose system person type is either Employee or Employee and Applicant.
Oracle HRMS includes:
-
In both the Hires and Applicants counts an employee who is a new hire in the reporting period and, later in the same period, an applicant in another group
-
In the Applicants, Hires, and Terminations counts a person who applies for a full-time job, is hired, and is terminated, all within the reporting period
Promotions
Oracle HRMS includes in the Promotions count any full-time employee who changes assignment during the reporting period and whose assignment change reason is Promotion. The new job or position must be full time. When a person is promoted, the user should enter Promotion in the reason field on the Miscellaneous tab on the assignment window.
Terminations
Oracle HRMS includes full-time employees in the Terminations count if their assignment status is Terminate Assignment or Suspend Assignment and their actual termination date is in the reporting period.
Oracle HRMS includes in the Applicants, Hires, and Terminations counts a person who applies for a full-time job, is hired, and is terminated, all within the reporting period.
Full-Time Employees
Employees are full time if their annual working hours are greater than or equal to the number of hours you specify on input to the EO Survey Report. On the final day of the reporting period, an employee's assignment status must be Active Assignment and their system person type must be Employee or Employee and Applicant.
Oracle HRMS includes in both the Applicants and Employees counts an employee whose system person type is Employee and Applicant.
Annual Monetary Compensation
To calculate annual monetary compensation, Oracle HRMS provides a new balance, EO Regular Salary Year to Date, for the balance dimension Assignment Year to Date. Three seeded salary elements feed this balance:
-
Regular Salary
-
Regular Wages
-
Time Entry Wages
If you use different salary elements, you must update the definition of the balance EO Regular Salary Year to Date to include your salary elements.
The records of full-time employees who have been paid at least once in the reporting period contribute to Part C of the EO Survey Report.
Tenure Data
A full-time employee's tenure is the difference between their hire date and the end date of the reporting period. Oracle HRMS rounds to a whole month a period of more than 15 days but less than 1 month and ignores periods of 15 or fewer days. Tenure includes breaks in service.
Running the EO Survey Report
Run the EO Survey Report from the Submit Request Set window.
To run the EO Survey Report
-
In the Request Set field of the Submit Request Set window, select EO Survey Report.
-
In the Submit Request Set window, click in the EO Survey Report's Parameters field.
The Parameters window appears.
-
Enter the end date of the 12-month period on which you are reporting. You can run the report for:
-
Your last complete Affirmative Action Program (AAP) year
-
The last complete calendar year
For example, if your latest AAP year ended on 31st May 2004, enter 31-MAY-2004 to run the report for that year. To run the report for the calendar year 2003, enter 31-DEC-2003.
If you enter no date, Oracle HRMS uses the current effective date.
-
-
Select the name and version of the establishment hierarchy on which you are reporting.
-
To report on a single establishment in the selected hierarchy, select the establishment name.
-
Enter the minimum hours a full-time employee works in a year. For example, if your full-time employees work a minimum of 30 hours each week for 45 weeks each year, enter 1350 in the Minimum Hours field. In this example, the EO Survey Report excludes any employee who works fewer than 1350 hours each year.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Submit.
The application displays the concurrent request ID.
EVS Reporting
Employee Verification Service (EVS) Reporting
Employee names and social security numbers that you include in your Internal Revenue Service Forms W-2 (Wage and Tax Statement) must match Social Security Administration (SSA) office records so that the SSA can credit your employees' earnings records correctly. The SSA offers a free employee verification service, which you can use to validate your employee records at any time prior to submitting your W-2 statements.
To enable you to take advantage of this service, Oracle HRMS provides the Electronic Employee Verification Service (EVS) Report. The EVS report is a list of the employees in one or more Government Reporting Entities (GREs) showing their social security number, full name, gender, and date of birth. The report, which is in social security number order, can include:
-
People employed at any time in a specified period.
-
Employees whose hire date is in a specified period.
Oracle HRMS records in the report log the number of employees in the report and the number of employees in each GRE in the report. The report does not include contingent workers or applicants.
The SSA office compares your employee records with its own and returns a report showing a verification code for each employee record. A blank verification code indicates that your record matches the SSA record. A nonblank verification code indicates a mismatch that you must correct before submitting your W-2 statements. The SSA's instructions define the meaning of each verification code.
Requester Identification Code
Before you can submit an electronic EVS report to the SSA office, you must register your intention. When you register, the SSA office sends you a Requester Identification Code, which you must include in your report. To do this, you record the code in the EVS filing information for the GRE.
Submitting the EVS Report to the SSA
Oracle HRMS formats the EVS report for diskette according to the SSA's instructions. Oracle HRMS writes the first 11,000 employee records to file EVSREQ2K and subsequent batches of 11,000 records to files EVSREQ2K1, EVSREQ2K2, and so on. Oracle HRMS inserts the suffix number of the second and subsequent files in the final 3 characters of each employee record in the file. Before you write each file to diskette, rename it EVSREQ2K.
If you choose to submit your report on CD-ROM, Oracle HRMS produces a single file of employee records called EVSREQ2K, regardless of the number of records you have to verify.
Note: You are recommended to confirm with your SSA office that you can use CD-ROM before you run the report.
Running the Electronic Employee Verification Service (EVS) Report
Run the Electronic Employee Verification Service (EVS) Report from the Submit Request window.
To run the EVS report
-
In the Name field, select Electronic Employee Verification Service (EVS) Report.
-
Enter start and end dates. The end date can be the same as the start date. By default, the start date is the effective date, and the end date is 31st December of the year of the effective date.
The effect of these dates depends on the report category you select in Step 4. If you select the report category:
-
All Employees, the report includes people employed at any time in the specified period
-
Retirees, the report includes retirees whose retirement date is in the specified period
-
New Hires only, the report includes employees whose hire date is in the specified period
-
Employees and Retirees, the report includes people employed at any time in the specified period and retirees whose retirement date is in the specified period
Note: In all cases, the report includes only those employee records your security profile enables you to access.
-
-
Select the Government Reporting Entity (GRE) to which the report applies. If you leave this field blank, the report applies to all GREs in the business group.
-
Select a report category. By default, the report includes new hires only.
Available options are Employees Only, New Hires Only, Retirees, and Employees and Retirees.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Submit.
The application displays the concurrent request ID of the report.
Oracle HRMS writes to the report log the number of employee records in the report and the number of employee records in each GRE included in the report.
AAP Reporting
AAP (Affirmative Action Plan) Reporting
The US Federal Executive Order 11246 requires enterprises who are government contractors or subcontractors and have 50 or more employees, to establish affirmative action plans (AAPs) for women and ethnic minorities. The Office of Federal Contract Compliance Programs (OFCCP) of the US Labor Department, responsible for enforcing affirmative action laws, requires these enterprises to measure the effectiveness of their affirmative action plans by implementation of internal reporting.
To assist you with affirmative action reporting, Oracle HR provides two reports for your AAP plans:
-
AAP-Workforce Analysis
-
AAP-Job Group Analysis
These reports both display for each job an affirmative action plan covers, the EEO job category and a salary code indicating the job's relative compensation level. Also the reports display for each job, the number and percentage of employees in the job by gender and by ethnicity (White / Black / Asian / Native American / Hispanic).
Workforce Analysis Report
This report shows by their line of progression, the jobs in the organizations an affirmative action plan covers. A line of progression is a set of related jobs, ordered from the lowest to the highest paid. This is an example line of progression for jobs in Sales:
Sales Assistant -> Salesperson -> Sales Team Leader -> Sales District Manager -> Sales Regional Manager -> Vice-president of Sales
The Workforce Analysis report displays the current totals of all employees and of ethnic minorities for each organization and for the entire affirmative action plan. It also shows the totals for each organization as a percentage of the plan totals.
Job Group Analysis Report
This report organizes the jobs an affirmative action plan covers by their job groups. A job group is a set of jobs related by virtue of similar levels of responsibility, compensation and opportunities for advancement. For example, the Regional Manager Job Group could include these jobs:
Sales Regional Manager - Regional Director, Human Resources - Regional Head, Finance - Production Manager - MIS Regional Manager
For each job group, the report displays the current totals of all employees and of ethnic minorities in its jobs. It also displays these totals for the entire affirmative action plan, and shows the jobs, and shows each job group's totals as percentages of the plan totals.
AAP Organizations
AAP reporting differs from other types of government-mandated HR reporting in that the reports are issued for each affirmative action plan within a GRE, instead of the establishments within a GRE. While it can happen that an affirmative action plan covers all employees in one or several Reporting Establishments, plan coverage does not necessarily follow these boundaries.
For example, a plan may cover employees based in many different Reporting Establishments who all work in the same functional area, such as customer service or human resources. Another plan may cover a variety of employees based at different sites who all have the same job classification, such as Registered Nurse, Technician, or Machinist.
To represent the affirmative action plans in your enterprise, you set up organizations classified as AAP Organizations, entering for each the name of its plan. An AAP Organization can also be (but is not necessarily) a GRE, Reporting Establishment, and HR Organization. After defining AAP Organizations you place them in AAP establishment hierarchies.
AAP Hierarchies
AAP hierarchies differ from other establishment hierarchies in one important respect. Whereas in other establishment hierarchies one Reporting Establishment cannot be subordinate to another, in AAP hierarchies an AAP Organization, which can also be a Reporting Establishment, can occur at any level.
In other words, AAP Organizations can appear below other AAP Organizations in an AAP establishment hierarchy when this represents the reality of your enterprise, even if both organizations are also Reporting Establishments.
To obtain the AAP reporting for one of these plans, you supply the hierarchy name and the particular plan name as report parameters.
Data for AAP Reporting
For this reporting you maintain the same information as that required for EEO-1 reports:
-
employee gender and ethnic type
-
EEO job categories for jobs
Additionally, for AAP reporting you jobs must have:
-
salary codes, for which you use pay grades
-
lines of progression. You determine and set up your lines of progression, and then associate the appropriate jobs with them.
-
job groups. You determine your job group names, set them up, and then associate each job with its group.
Example AAP Hierarchy
Example AAP Hierarchy
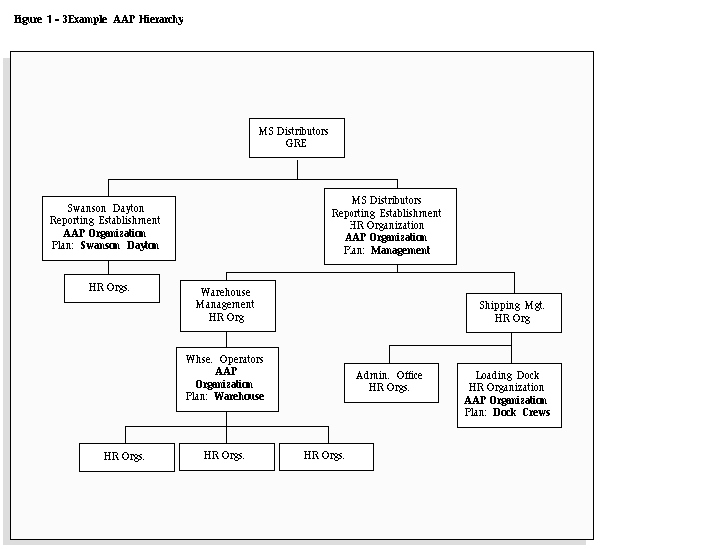
The following diagram is an example AAP Hierarchy.
This example AAP hierarchy includes these affirmative action plans:
-
the Swanson Dayton plan, covering all the employees who work in the Swanson Dayton factory
-
the Management plan, covering the employees who work in MS Distributors, Warehouse Management, Shipping Management, and Shipping's administration
-
The Warehouse plan, covering the employees in warehouse organizations below the management level
-
The Dock Crews plan, covering the laborers that work on the loading docks.
Set Up AAP Organizations
The hierarchies you build for AAP reporting must include AAP Organizations, to represent the affirmative action plans in effect in your enterprise.
See: AAP Organizations
To define an AAP organization
-
Using the Organization window, either query an existing internal organization or create an internal organization with the appropriate name and location for this AAP Organization.
-
In the Organization Classifications region, select the classification AAP Organization for the organization and enable it. Save your work.
-
Select the classification AAP organization in the Organization Classifications region. Choose the Others button and select AAP Organization. Click in the Additional Organization Information field to open the AAP Organization window. Enter the name of the affirmative action plan this organization represents.
Note: The organization can have other classifications as well. If it does, add information for these classifications as necessary.
-
Save your work. If this AAP Organization occurs as a subordinate organization in one or more AAP establishment hierarchies, place it in these hierarchies using the Parent Organization window.
See: Putting Subordinate Reporting Organizations in Hierarchies
Create AAP Establishment Hierarchies
To create an AAP establishment hierarchy
-
Determine how best to place in the hierarchy your affirmative action plans, represented by AAP Organizations, and the organizations under each plan.
If the hierarchy is for one affirmative action plan only, the AAP Organization representing this plan should be the top organization. If the hierarchy covers two or more plans, the AAP Organizations for these plans can appear at any level of the hierarchy.
-
Build the hierarchy by placing all the organizations with jobs covered by an affirmative action plan, below the AAP Organization representing that plan
Associate Jobs with AAP Reporting Information
To associate your jobs with salary codes, lines of progression, and job groups, define all the jobs covered by your affirmative action plans.
See: Defining Jobs
To associate jobs with AAP reporting information
-
In the Job window, query the job in the Name field if it does not already appear there. Click in the Further Information field to open the Further Job Information window.
-
Select for this job its job group name, line of progression, and grade used for its salary code, in the Job Group, Line of Progression, and Salary Code fields, respectively.
See Also
Obtain AAP Reports
Run report requests from the Submit Requests window.
To run the AAP-Workforce Analysis report
-
Select AAP-Workforce Analysis Report in the Request Name field. Click in the Parameters field if the Parameters window does not automatically open.
-
Enter the effective date of the report. This date defaults to your session date.
-
Select the name of the affirmative action plan on which to report, and the AAP hierarchy to use.
-
For the report to cover only one organization, select its name in the Organization field.
-
For the report to cover only one line of progression, select its name in the Line of Progression field.
-
Choose Submit.
To run the AAP-Job Group Analysis report
-
Select AAP-Job Group Analysis Report in the Request Name field. Click in the Parameters field if the Parameters window does not open automatically.
-
Enter the effective date of the report. This date defaults to your session date.
-
Select the name of the affirmative action plan on which to report, and the AAP hierarchy to use.
-
For the report to cover the jobs and employees in just one job group, enter its name in the Job Group field.
-
Choose Submit.
See Also
AAP (Affirmative Action Plan) Reporting
VETS-4212 Reporting
VETS-4212 Reporting
Each year, federal contractors and subcontractors whose contracts are of a specified value must file a Federal Contractor Veterans Employment Report. Effective August 1, 2015, the Veterans Employee and Training Service (VETS) administration mandates that federal contractors file their VETS reports using the VETS-4212 form, which replaces the VETS-100 and VETS-100A reports. The VETS-4212 form requires federal contractors to report aggregate data on the number of protected veterans that were newly hired and the number they employed.
VETS-4212 Reports
To accommodate the VETS-4212 reporting requirements, Oracle US HR provides the following concurrent programs to generate the VETS-4212 reports:
-
Electronic VETS-4212 Report: Use the Electronic VETS-4212 Report program to produce a magnetic file that contains all of the individual VETS-4212 reports that you can submit electronically.
-
VETS-4212 Suite Of Reports: Use this program to generate a VETS-4212 PDF-based report. This program launches the following programs:
-
VETS-4212 Consolidated Veterans Employment Report
-
VETS-4212 Veterans Employment Report
-
VETS-4212 Employment Listing
-
See:
You can generate all of the VETS-4212A reports for your enterprise by running a single program or by running each program individually according to your business requirements. The application automatically creates single-establishment or multiple-establishment reports based on the hierarchy structure selected.
Note: The Oracle US HR VETS-4212 reports are designed to comply with current formatting standards. However, Oracle recommends that you refer to the VETS-4212 website at https://www.dol.gov/vets/vets4212.htm for the latest reporting requirements.
Set Up Data to Generate VETS-4212 Reports
See Setting Up Data to Generate VETS-4212 Reports for information about setting up data to run the VETS-4212 reports.
The employee counts reported in the VETS-4212 reports are derived based on the VETS-100A value in an employee's person record. An HR professional selects the VETS-100A value for an employee in the Employment tab of the People window in the professional UI. If an employee uses the Disclose Veteran Status Employee Self-Service function to record their VETS-100A information, then the application captures the VETS-100A value and this value is visible in the Employment tab of the People window in the professional UI.
The following table maps each VETS-100A value to the Protected Veteran column in each VETS-4212 report:
| VETS-100A Value | Protected Veteran? |
|---|---|
| Armed Forces Service Medal (AFSM) Veteran | Yes |
| Disabled, AFSM Veteran | Yes |
| Disabled, Other Protected, AFSM Veteran | Yes |
| Recently Separated, AFSM Veteran | Yes |
| Disabled, Recently Separated, AFSM Veteran | Yes |
| Disabled Vet, Other Protected, AFSM, Recently Separated | Yes |
| Other Protected Veteran, AFSM, Recently Separated | Yes |
| Other Protected, AFSM Veteran | Yes |
| Not a Protected Veteran | No |
| Not a Veteran | No |
| Recently Separated Veteran | Yes |
| Disabled, Recently Separated Veteran | Yes |
| Recently Separated, Disabled, Other Protected Veteran | Yes |
| Other Protected, Recently Separated Veteran | Yes |
| Disabled, Other Protected Veteran | Yes |
| Other Protected Veteran | Yes |
| Veteran (Not used for legislative reporting) | No |
| Disabled Veteran | Yes |
| Protected Veteran, but not to Self-Identify Classifications | Yes |
Running the Electronic VETS-4212 Report
Run the Electronic VETS-4212 Report program to generate magnetic files in CSV format. These files are used for VETS-4212 electronic filing according to the specification provided by the US Department of Labor's website.
For an overview, see VETS-4212 Reporting.
Run the Electronic VETS-4212 Report from the Submit Request window.
To run the Electronic VETS-4212 Report
-
Select Electronic VETS-4212 Report in the Name field.
-
Enter the end date for the twelve month reporting period for which the report is being run. Only employees who were hired on or before this date are reported. If an employee was hired within 12 months prior to this date, then the employee is reported as a new hire. A recently separated veteran is considered protected if the period between their Military Discharge Date and the period end date is less than three years.
-
Select the name of the establishment hierarchy to use for this report. Only employees with assignment locations belonging to this hierarchy are reported.
-
Select the correct version number from the list for the chosen hierarchy. If an error occurs, then check that the hierarchy status is set correctly. The Hierarchy Version field is enabled only when a valid value is entered in the Hierarchy Name field.
-
Select Yes or No in the Consolidate Under 50 field. If you select Yes, then the report consolidates the employee count across locations within one state and displays the count as a single count. If you select No, then the employee count is displayed separately for each location in each state.
-
Submit the request.
Running the VETS-4212 Suite of Reports
Use the VETS-4212 Suite Of Reports program to generate a VETS 4212 PDF-based report. This program launches the following concurrent programs:
-
VETS-4212 Consolidated Veterans Employment. See: Running the VETS4212 Consolidated Veterans Employment Report
-
VETS-4212 Veterans Employment Report. See: Running the VETS-4212 Veterans Employment Report
-
VETS-4212 Employment Listing. See: Running the VETS-4212 Employment Listing Report
You can produce all of the VETS-4212A reports for your enterprise by running a single program or by running each program individually according to your requirements. The application automatically creates single-establishment or multi-establishment reports based on the hierarchy structure selected.
For an overview, see VETS-4212 Reporting.
Run the VETS-4212 Suite Of Reports from the Submit Request window.
To run the VETS-4212 Suite Of Reports
-
Select VETS-4212 Suite Of Reports in the Name field.
-
Select the name of the establishment hierarchy to use for this report. Only employees with assignment locations belonging to this hierarchy are reported.
-
Select the correct version number from the list for the chosen hierarchy. If an error occurs, then check that the hierarchy status is set correctly. The Hierarchy Version field is enabled only when a valid value is entered in the Hierarchy Name field.
-
Enter the end date for the twelve month reporting period for which the report is being run. Only employees who were hired on or before this date are reported. If an employee was hired within 12 months prior to this date, then the employee is reported as a new hire. A recently separated veteran is considered protected if the period between their Military Discharge Date and the period end date is less than three years.
-
Select the state for which you want to run the report. This is an optional field that restricts the count reported to a specific state.
-
Select Yes or No to control whether to display the new hire count under columns (C) and (D) of the VETS-4212 Reports.
-
Select Yes or No to control whether to display the total employee count in the last row, TOTAL EMPLOYEES, of the VETS-4212 Reports.
-
Select Yes or No to control whether to generate the audit files (.a03).
-
Submit the request.
Running the VETS-4212 Consolidated Veterans Employment Report
Run the VETS-4212 Consolidated Veterans Employment Report to generate the RTF or PDF output to report the employee count for establishments with less than 50 employees. This report lists state-wise details of hiring locations with fewer than 50 employees.
For an overview, see VETS-4212 Reporting.
Run the VETS-4212 Consolidated Veterans Employment Report from the Submit Request window.
To run the VETS-4212 Consolidated Veterans Employment Report
-
Select VETS-4212 Consolidated Veterans Employment Report in the Name field.
-
Select the name of the establishment hierarchy to use for this report. Only employees with assignment locations belonging to this hierarchy are reported.
-
Select the correct version number from the list for the chosen hierarchy. If an error occurs, then check that the hierarchy status is set correctly. The Hierarchy Version field is enabled only when a valid value is entered in the Hierarchy Name field.
-
Enter the end date for the twelve month reporting period for which the report is being run. Only employees who were hired on or before this date are reported. If an employee was hired within 12 months prior to this date, then the employee is reported as a new hire. A recently separated veteran is considered protected if the period between their Military Discharge Date and the period end date is less than three years.
-
Select the state for which you want to run the report. This is an optional field that restricts the count reported to a specific state.
-
Select Yes or No to control whether to display the new hire count under columns (C) and (D) of the VETS-4212 Reports.
-
Select Yes or No to control whether to display the total employee count in the last row, TOTAL EMPLOYEES, of the VETS-4212 Reports.
-
Select Yes or No to control whether to generate the audit files (.a03).
-
Submit the request.
Running the VETS-4212 Veterans Employment Report
Run the VETS-4212 Veterans Employment Report program to generate the RTF or PDF output to report the employee count for establishments with 50 or more employees.
For an overview, see VETS-4212 Reporting.
Run the VETS-4212 Veterans Employment Report from the Submit Request window.
To run the VETS-4212 Veterans Employment Report
-
Select VETS-4212 Veterans Employment Report in the Name field.
-
Select the name of the establishment hierarchy to use for this report. Only employees with assignment locations belonging to this hierarchy are reported.
-
Select the correct version number from the list for the chosen hierarchy. If an error occurs, then check that the hierarchy status is set correctly. The Hierarchy Version field is enabled only when a valid value is entered in Hierarchy Name field.
-
Enter the end date for the twelve month reporting period for which the report is being run. Only employees who were hired on or before this date are reported. If an employee was hired within 12 months prior to this date, then the employee is reported as a new hire. A recently separated veteran is considered protected if the period between their Military Discharge Date and the period end date is less than three years.
-
Select Yes or No to control whether to display the new hire count under columns (C) and (D) of the VETS-4212 Reports.
-
Select Yes or No to control whether to display the total employee count in the last row, TOTAL EMPLOYEES, of the VETS-4212 Reports.
-
Select Yes or No to control whether to generate the audit files (.a03).
-
Submit the request.
Running the VETS-4212 Employment Listing Report
Run the VETS-4212 Employment Listing program to generate the RTF or PDF output to report the establishments listed in the VETS-4212 Consolidated Veterans Employment Report. This report lists establishment in each state and provides details of hiring locations with fewer than 50 employees.
For an overview, see VETS-4212 Reporting.
Run the VETS-4212 Employment Listing from the Submit Request window.
To run the VETS-4212 Employment Listing report
-
Select VETS-4212 Employment Listing in the Name field.
-
Select the name of the establishment hierarchy to use for this report. Only employees with assignment locations belonging to this hierarchy are reported.
-
Select the correct version number from the list for the chosen hierarchy. If an error occurs, then check that the hierarchy status is set correctly. The Hierarchy Version field is enabled only when a valid value is entered in the Hierarchy Name field.
-
Enter the end date for the twelve month reporting period for which the report is being run. Only employees who were hired on or before this date are reported. If an employee was hired within 12 months prior to this date, then the employee is reported as a new hire. A recently separated veteran is considered protected if the period between their Military Discharge Date and the period end date is less than three years.
-
Select Yes or No to control whether to generate the audit files (.a03).
-
Submit the request.
ADA Reporting
Registering Employees as Disabled
When employees request registration as disabled, effect this registration by checking the Disabled box in the Person window when entering them in the system. They will then be listed on the ADA Report.
ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) Reporting
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) became law on 26 July 1990. It prohibits employers from discriminating against employees or applicants with disabilities who can perform the essential functions of a job with reasonable accommodation. Under ADA, people with disabilities are those:
-
who have a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more major life activities, or
-
who have a record of such an impairment, or
-
who are regarded as having such an impairment.
The ADA Report shows how your enterprise is responding to the requests of employees with disabilities for reasonable accommodations to permit them to carry out the essential functions of their jobs, without undue hardship to you as their employer.
Report Coverage
The ADA report covers those employees in each of your establishments who work on a non-temporary, full or part time basis, have a non-terminated assignment status as of the report period end date, and have taken one or more of the following actions:
-
requested registration as a disabled person.
-
provided information about a type of disability they have.
-
requested accommodation for a disability.
To determine which of your employment categories cover non-temporary full time or part time workers, and which assignment statuses count as non-terminated, you use the Reporting Categories and Reporting Statuses registered for your Business Group.
Information for ADA Reporting
The report provides basic information (name, number, organization and job) about employees who have identified themselves as having a disability. You can register employees as disabled when entering other basic personal information about them.
When employees submit information about particular types of disabilities, you maintain this information using the ADA Disabilities window. The report presents this information, including any information in the form of comments.
Requests for Accommodations
Because the Americans with Disabilities Act encourages employers to make reasonable accommodations permitting employers with disabilities to work, Oracle HR provides the Disabilities Accommodations window for recording information about employees' requests for such accommodations.
The ADA Report lists these requests with their request dates, reviewers, review dates and status (requested, approved, or denied). It also lists the cost of each approved accommodation, and the total cost of approved accommodations for each establishment.
Essential Functions of Jobs or Positions
The report can optionally display for each employee with a disability, the essential requirements of his or her job or position, providing that you maintain these requirements in the database.
See: Entering Job and Position Skill Requirements
Enter Information about Disabilities
When employees provide information about a type of disability they have, enter this information in the ADA Disabilities window. Start this entry from the Person window.
To enter information about a person's disability type
-
Query the person in the Person window if he or she does not already appear there. Choose the Special Info button to open the Special Information window.
-
In the Name field, select Disabilities. In the Details block, click in the Detail field to open the Disabilities window.
-
In the Type field, enter a brief description of the nature of the disability.
-
Optionally, enter more detailed information, such as the expected duration of the disability or the results of medical reviews, in the Comments window. To open this window, click on the paper clip icon in the toolbar.
-
Choose the OK button when you complete the entry, and save your work.
On the ADA Report, the information entered for employees appears under the heading Disability. Any comments entered also appear on the report.
Enter Requests for Disability Accommodation
When employees with disabilities request accommodations to help them perform the essential functions of their jobs, enter information about these requests in the Disability Accommodations window. Start this entry from the Person window.
To enter information about accommodation requests
-
Query the person in the Person window if he or she does not already appear there. Choose the Others button, and select Special Info to open the Special Information window.
-
In the Name field, select ADA Disability Accommodations. In the Details block, click in the Detail field to open the ADA Disability Accommodations window.
-
In the Description field, briefly enter the accommodation requested, for example, Wheelchair ramp or Widened door. The Date Requested field defaults to the effective date.
-
In the Status field, select Requested, Approved or Denied to track the request status.
-
Optionally, enter the name of the reviewer of the request, and the date reviewed, in the Confirmed By and Date Confirmed fields.
-
For approved requests, enter the date of providing the accommodation, and its cost.
-
Optionally, add comments regarding the request using the Comments window. Click on the paper clip icon to open this window.
-
Choose the OK button when you complete data entry, and save your work. The information entered for employees, including any comments, appears on the ADA Report.
See Also
Obtain ADA Reports
As ADA reporting is for your own use, there are no required formatting standards.
To run an ADA report
-
Select ADA Report in the Request Name field. Click in the Parameters field if the Parameters window does not open automatically.
-
. The effective date will be the date of the report.
-
For the Organization Hierarchy parameter, select the name of the establishment hierarchy to use for this report.
-
To obtain the report for a particular employee, select his or her name or employee number.
-
To obtain the report for employees in a particular job and/or location, select the job or location name, or both.
-
Select Yes for the report to include a listing of the essential requirements for the jobs or positions of employees with disabilities.
-
Select Yes for the View Registered Disabled Only parameter for the report to include only those employees with disabilities whose personal information includes registration as disabled.
-
For the Sort By parameter, select Employee to sort by employee last name. Select Assignment to sort by job name, location, grade, position and employee name, in that order.
-
Choose OK, then Submit.
See Also
ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) Reporting
OSHA Reporting
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Act) Reporting
The Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 and Title 29 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Part 1904 (29CFR Part 1904) require employers in certain industries to record and report on employees' work-related injuries and illnesses. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) administers this record keeping and reporting, often in cooperation with state agencies. Employers must consult with these agencies to determine if they are subject to additional state-level recording and reporting obligations.
Employers in relatively high-risk industries such as construction, manufacturing, and health services, must keep OSHA records for each individual establishment on an ongoing basis, if they have a combined total of 11 or more employees working at one or more establishments.
Employers in other industries that normally are not required to keep OSHA records must maintain these records when selected to participate in the Annual Survey of Occupational Injuries and Illnesses. This survey produces national estimates of occupational injuries and illnesses for all employers.
For a full list of industries required to maintain and report on OSHA information, and detailed instructions about OHSA record keeping, consult the document A Brief Guide to Recordkeeping Requirements for Occupational Injuries and Illnesses. To obtain copies of this publication, contact your regional office of the Bureau of Labor Statistics or write to:
Bureau of Labor Statistics
Division of Management Systems (1220-0029)
Washington, DC 20212
OSHA Data
Information needed for OSHA reporting includes a description of each work-related injury or illness and the date, place and circumstances of its occurrence or onset, as well as information on its physical effects and its outcome. For a nonfatal incident, you also maintain data showing its effects on the employee's ability to work.
OSHA 300, 300A, and 301 Reports
The OSHA 300 Log report and OSHA 300A Summary report record information about work-related injuries and illnesses during the year, and present a summary of these injuries and illnesses at year end. An additional report, OSHA 301 Incident Report, provides further information about the cases you record. The OSHA reports are XML-based and produce PDF output.
See Running OSHA Reports for more information.
Electronic OSHA Reports
To enable employers to electronically submit OSHA data according to statutory requirements, the following reports are available:
-
Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Exception Report: Produces exception reporting data, which is useful for resolving any errors ahead of time due to incomplete or incorrect setup. Important: It is recommended that this report be run before running the Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Report.
-
Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Report: Generates the required electronic format (CSV Interface).
See Running OSHA Electronic Reports for more information.
OSHA Establishments
GREs with more than one establishment must maintain separate sets of OSHA records and reporting for each establishment. To represent these establishments and the employees within them, you use Reporting Establishments and establishment hierarchies.
Notice that for OSHA record keeping and reporting, clearly separate activities performed at the same physical location require treatment as separate Reporting Establishments. For example, if an enterprise has manufacturing facilities and sales offices in the same building, each activity constitutes a distinct establishment.
OSHA Categories of Illness
OSHA recognizes these categories of occupational injury or illness:
-
Injury: Examples are back strain, bone breaks, and head injury.
-
Skin diseases or disorders: Examples are eczema, oil acne, chrome ulcers, and chemical burns.
-
Respiratory conditions: Examples are pneumonitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis, acute congestion due to chemicals, dusts, and gases or fumes.
-
Poisoning (systemic effects of toxic materials): Examples are poisoning by lead, mercury, cadmium, arsenic or other metals; by carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide or other gases; by benzol, carbon tetrachloride or other organic solvents; by insecticide sprays; by other chemicals such as formaldehyde, plastics, and resins.
-
All other illnesses: Examples are anthrax, brucellosis, infectious hepatitis, malignant and benign tumors, food poisoning, and histoplasmosis.
Entering Information about Work-related Injury or Illness
When employees suffer work-related injuries or illnesses, you record information about these incidents in the Work Incidents window. You begin this entry from the Person window.
To enter data on an OSHA-reportable incident
-
In the Person window query the employee suffering the injury or illness, if he or she does not already appear here.
-
Choose the Others button.
-
Select Work Incidents/OSHA.
-
For incidents of work-related injury, you must select the category Injury in the Incident Category field. Otherwise select the category appropriate for a work-related illness.
-
If the employee has an existing incident record related to the new incident you are recording you can select a corresponding reference number in the Related Incident Ref field.
-
Enter the Incident date.
-
Enter the time the incident occurred.
-
If you want the incident to appear on your OSHA reports, choose the OSHA Recordable check box.
Incident Description
-
Choose the Description tab.
-
In the Activity at time of incident field, describe what the employee was doing when injured or taken ill.
-
In the Objects/Substances Involved field, list any tools, equipment, or materials being used or handled.
-
If the incident caused the employee to miss work or restricted the employee's activities, enter the number of days missed or restricted.
Do not include the day of injury or onset of illness, or days the employee would not have worked in any case. For employees without regular work schedules, estimate the number of missed days.
-
Indicate if the incident caused the termination or permanent transfer of the employee.
-
Select a hazard relative to the injury if appropriate.
-
Enter the location where the incident took place.
-
Enter a brief description of the incident.
-
Enter any additional incident details.
Reporting Information
-
Choose the Reporting tab.
Note: The information recorded in the Reporting tabbed region is not used by the OSHA reports.
-
Enter a report date. The date you enter must be a date on or before the incident date.
-
Enter a report time.
-
Enter brief details of who the incident was reported to.
-
. Briefly detail any witness accounts of the incident.
-
. Enter a name, title, and telephone number for the person responsible for the report.
Official Notifications
-
Choose the Official Notifications tab.
Note: This tabbed region is optional. The information recorded in this region is not used by the OSHA reports.
-
Select a health and safety representative name.
-
Enter a notification date for the health and safety representative.
Note: You must enter a health and safety representative name before you can enter the Date Notified field.
-
Briefly describe any remedial action taken as a direct result of the incident.
-
Select the representative body notified of the incident.
-
Select a representative name for the representative body.
Note: You must enter a representative body before you can enter a representative name.
-
Enter the date that the representative name was notified of the incident.
Note: You must enter a representative name before you can enter a notification date.
Medical Details
-
Choose the Medical Details tab.
-
If the employee was hospitalized as a result of the incident choose the Hospitalized check box.
-
If the employee required emergency treatment as a result of the incident choose the Emergency Room check box.
-
If the employee sustained an injury as a result of the incident select the injury sustained.
-
If the employee contracted a disease as a result of the incident select the disease contracted.
-
In the Body Parts Affected field, enter the injury or illness and the body part, for example, Fracture of ribs; Dermatitis of left hand; Lead poisoning.
-
Enter the name and address of the physician attending the employee, and if he or she was hospitalized, the name and address of the hospital.
Other Important Information
-
Choose the Other tab.
-
Enter the work start time of the employee.
-
If you do not want the employee to be identified on the OSHA reports choose the Privacy Issue check box.
-
If the injury or illness caused the employee's death, you must enter the date of death. Entry of a date in the Date of Death field signals that the injury or illness was fatal, and must be reported as such.
-
Enter compensation details of amount, currency and the date compensation was awarded.
-
Select the employee's job at the time of the incident.
-
If the incident resulted in an absence from work check the Resulted in Absence check box.
-
Save your work.
When you run the OSHA 300 and OSHA 301 reports, information entered in this window appears on one or both of these reports.
Note: The Case Number field populates when you save your work.
-
-
-
-
-
Running OSHA Reports
Computer-generated versions of OSHA 300, OSHA 300A, and OSHA 301 are acceptable, so long as they contain the same information and are as readable and comprehensible as the OSHA forms. The BLS advises employers using computer-generated forms to submit a sample report for review, to ensure compliance with BLS regulations.
Oracle delivers the following OSHA reports that are XML-based and produce PDF output. These reports replace the existing text-based reports:
-
OSHA 300 Log Report
-
OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Report
-
OSHA 301 Incident Report
Run report requests from the Submit Requests window.
See: Setup Steps for OSHA Reporting
To run OSHA 300, 300A, or 301 Reports
-
Select OSHA 300 Log Report, OSHA 300A Summary Report, or OSHA 301 Incident Report in the Request Name field. Click in the Parameters field if the Parameters window does not open automatically.
-
Enter the start and end dates of the period this report covers.
The period end date is the date that appears on the report.
-
Select the name of the establishment hierarchy to use for the report.
-
Select a location for the report.
-
Select sort orders for the report in the Order by fields.
-
Choose the Submit button to run the report. The OSHA reports produce output in PDF format.
See Running OSHA Electronic Reports for more information
Running OSHA Electronic Reports
To enable employers to electronically submit OSHA data according to statutory requirements, the following reports are available:
-
Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Exception Report: Produces exception reporting data, which is useful for resolving any errors ahead of time due to incomplete or incorrect setup. It is recommended that you run this report first before running the Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet report.
-
Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Report: Generates the required electronic format (CSV Interface).
Run the reports from the Submit Request window.
Prerequisites
- Complete the setup to generate electronic OSHA reports. See Setup Steps for Electronic OSHA Reports for more information.
Running the Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Exception Report
When the Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Report is run and encounters missing or incorrect setup such as fields not being populated in the “OSHA Specific Details” EIT, the process will error out and display the establishment name and reason that caused the error in the report request log. There are two potential scenarios that can cause the Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Report to error out:
-
Missing setup in the OSHA Specific Details (Annual Average Employees, Size and Total Hours Worked) at the location or the parent entity level.
-
Missing NAICS Number
To minimize the effort required to resolve these errors and complete the Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Report, run the Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Exception Report, which will report all the missing or incorrect setup in one place.
To run the Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Exception Report:
-
In the Name field, enter Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Exception Report.
-
In the Hierarchy Version field, select the name of the establishment hierarchy to use for the report and then submit.
Running the Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Report
This concurrent program generates the magnetic (electronic) output file in CSV format for OSHA electronic filing according to the specifications provided by the US Department of Labor's website.
To run the Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Report:
-
In the Name field, enter Electronic OSHA 300A Summary Worksheet Report.
-
Enter the following parameters.
-
Reporting Year: Enter the reporting year for which you want the report to be run.
-
Hierarchy Version: Select the name of the establishment hierarchy to use for the report.
-
-
Submit the concurrent request.
US OFCCP Disability/VEVRAA Audit Reporting
Setting Up the US OFCCP Disability/VEVRAA Audit Report
The US OFCCP Disability/VEVRAA Audit Report enables you to generate an audit report containing employee disability and veteran status information in the event of a compliance audit by the Office of Federal Contract Compliance Programs (OFCCP).
Before you run the US OFCCP Disability/VEVRAA Audit Report, complete the following steps:
-
Add the US OFCCP/VEVRAA functions to the applicable menu.
The following functions are not available by default with the seeded Employee Self-Service menu (HR_EMPLOYEE_DIRECT_ACCESS_V4.0):
-
US OFCCP Disability
-
US VEVRAA
Function Name Technical Name Prompt Description US OFCCP Disability PER_US_DISABILITY Disclose Disability Status Provides the Disclose Disability Status page. US VEVRAA PER_US_VEVRAA Disclose Veteran Status Provides the Disclose Veteran Status page. To enable employees to provide their disability and veteran status information using the self-service pages, you must manually add these functions to the Employee Self-Service menu or any applicable menu that you use. Once you add these functions, the Disclose Disability Status and Disclose Veteran Status pages will be available to the employees to provide information.
-
-
Ensure that employees have provided their disability and veteran status information using the following Employee Self-Service pages:
-
Disclose Disability Status page: Consists of an enterable PDF form that reproduces Form CC 305 where the self service user can optionally make selections disclosing their disability status.
-
Disclose Veteran Status page: Consists of an enterable PDF form where the self service user can optionally make a selection disclosing their veteran status.
-
See:
Entering Disability and Veteran Status Details to Comply with OFCCP, Oracle Self-Service Human Resources Deploy Self-Service Capability Guide
Running the US OFCCP Disability/VEVRAA Audit Report
Running the US OFCCP Disability/VEVRAA Audit Report
Run this report to generate an audit data containing employee disability and veteran status information in the event of a compliance audit by the Office of Federal Contract Compliance Programs (OFCCP). This report provides audit details for employees only. It does not report on the applicant data. Depending on the report type selected by the user, the report generates either CC 305 (Disability Status) PDF or Veteran Status PDF output containing the corresponding data entered or submitted by employees. The PDF output generated is read-only and reflects the most recently submitted employee data. This means that for the CC 305 PDF (Disability Status) output, the Today's Date field in the form will reflect the date when the employee last submitted their disability status data. The report output essentially replicates the PDF form as it was submitted by the employee and can therefore act as a physical audit copy for employers.
If you have implemented Oracle iRecruitment, then you can run the iRecruitment US OFCCP Disability/VEVRAA Audit report to generate OFCCP and veteran external applicant data for compliance audit. See: Oracle iRecruitment Implementation and User Guide
You can run the US OFCCP Disability/VEVRAA Audit report from the Submit Request window.
Prerequisites
To run the US OFCCP Disability/VEVRAA Audit Report
-
Select US OFCCP Disability/VEVRAA Audit Report in the Name field.
-
Enter the following parameters:
-
Report Type: Select either Disability Status Data or Veteran Status Data. Selecting Disability Status Data will generate an audit report containing CC 305 form data. Selecting Veteran Status Data will generate an audit report containing veteran status data (VEVRAA audit information).
-
Government Reporting Entity: Select the GRE to determine the employees to be included in the report. All employees whose primary assignment is assigned to this GRE will be picked up by the report.
-
Organization: This is an optional parameter. Select the HR organization to further filter the employee population to be included in the report.
-
Employee Name: This is an optional parameter and can be used in the event that the report needs to be generated for a single employee only. Optionally select a single employee to be included n the report. This parameter is dependent on both the GRE and Organization selected. Therefore it will be enabled once the organization is selected.
-
Effective Date: Enter the date on which you want to run the report.
-
-
Click OK and then Submit.
Workforce Intelligence for Employment Agreements and Legal Compliance
Discoverer Reports for Employment Agreements and Legal Compliance (US)
Additional Information: See also My Oracle Support Knowledge Document 2277369.1, Oracle E-Business Suite Support Implications for Discoverer 11gR1.
Compliance (United States Specific) Detail Workbook
This workbook provides US-specific compliance information. It enables you to:
-
View OSHA incident details.
-
View organization-wide disability information.
-
View details of accommodations made for disabilities across the organization.
-
View special information associated with people in the organization.
Parameters
This wookbook has no parameters.
Worksheets
This workbook has the following worksheets:
-
OSHA Incidents
-
Disabilities
-
Disability Accommodations
-
Detailed Special Information
OSHA Incidents Worksheet
This worksheet enables you to view details associated with recorded OSHA incidents within your organization.
Business Questions
What OSHA incidents have occurred?
Disabilities Worksheet
This worksheet enables you to view special information concerning employees with disabilities within your organization.
Business Questions
Which employees are disabled and in what way?
Disability Accommodations Worksheet
This worksheet enables you to view details about accommodations made for employees with disabilities across your organization.
Business Questions
What accommodations have been for disabled people?
Detailed Special Information Worksheet
This worksheet enables you to view special employee information for employees within your organization. The worksheet includes only current employees.
Business Questions
Show me the special information held against my employees.
Employee Equal Opportunity Exceptions (United States Specific) Detail Workbook
This workbook is provided to aid Ethnic Origin reporting requirements in the United States. It can be used to highlight the exceptions to employee data in your HRMS system that require action before you can produce legislative reports.
Worksheets
This workbook has the following worksheets:
-
Employees Outside an Establishment Hierarchy
-
Employees Without a Location
-
Employees With Missing Equal Opportunity Data
Employees Outside an Establishment Hierarchy Worksheet
The Employees Outside an Establishment Hierarchy worksheet enables you to analyze which employees are at a location that is not in a defined Reporting Establishment Hierarchy, on a given effective date.
Business Questions
Which employees are outside the establishment hierarchy?
Parameters
You must specify a value for the following parameter:
-
Effective Date
The report includes employees who have an assignment on the selected effective date.
Employees Without a LocationWorksheet
The Employees Without a Location Worksheet enables you to analyze which employee primary assignments are not assigned a location on a given effective date.
Business Questions
Which employees have no location specified for them?
Parameters
You must specify a value for the following parameter:
-
Effective Date
The report includes employees who have an assignment on the selected effective date, and who are not associated with a location.
Employees With Missing Equal Opportunity DataWorksheet
This worksheet enables your organization to discover which employee primary assignments have missing Ethnic Origin information on a given effective date.
For example, the report will show if an employee is missing data for employment category or ethnic origin.
Business Questions
Which employees have missing equal opportunity information?
Parameters
-
Establishment Hierarchy
-
Top Establishment
-
Effective Date
The report includes employees who have a primary assignment within the selected establishment hierarchy on the selected effective date.
Employee Equal Opportunity for New Hires (United States Specific) Detail Workbook
This workbook enables you to list new employee hires within a given period. The workbook output includes the employee primary assignment details, job name, employee number, ethnic origin, hire date, and age at hire date, hired annual salary and current annual salary.
Worksheets
This workbook has the following worksheets:
-
By Establishment Hierarchy
-
By Organization Hierarchy
By Establishment Hierarchy Worksheet
This worksheet enables you to list employee new hires within a given period. The worksheet output includes the following employee primary assignment details:
-
Job Name
-
Employee Number
-
Ethnic Origin
-
Hire Date
-
Age at Hire Date
-
Hired Annual Salary
-
Current Annual Salary
The list of employees is for a given establishment hierarchy.
Business Questions
What are the ethnic origin, gender, and hiredate of my new hires within a given establishment hierarchy?
Parameters
You must specify values for the following parameters:
-
Establishment Hierarchy
-
Top Establishment
-
Start Date
-
End Date
The report includes employees who have a primary assignment within the selected establishment hierarchy during the period from the selected Start Date to the selected End Date.
Headings and Calculations
This worksheet uses the following calculations:
-
Age at Hire Date
Calculates a persons age at their hire date.
-
Current Annual Salary
Calculates the annual salary as of the current date for an assignment.
-
Hired Annual Salary
Calculates the annual salary as at the hire date of an assignment.
By Organization Hierarchy Worksheet
This worksheet enables you to list employee new hires within a given period. The worksheet output includes the following employee primary assignment details:
-
Job Name
-
Employee Number
-
Ethnic Origin
-
Hire Date
-
Age at Hire Date
-
Hired Annual Salary
-
Current Annual Salary
The list of employees is for a given organization hierarchy.
Business Questions
What are the ethnic origin, gender, and hiredate of my new hires within a given organization hierarchy?
Parameters
You must specify values for the following parameters:
-
Organization Hierarchy
-
Top Organization
-
Start Date
-
End Date
The report includes employees who have a primary assignment within the selected organization hierarchy during the period from the selected Start Date to the selected End Date.
Headings and Calculations
This worksheet uses the following calculations:
-
Age at Hire Date
Calculates a persons age at their hire date.
-
Current Annual Salary
Calculates the annual salary as of the current date for an assignment.
-
Hired Annual Salary
Calculates the annual salary as at the hire date of an assignment.
Employee Equal Opportunity for Separations (United States Specific) Detail Workbook
This workbook enables you to report on employee separations within a given period. The workbook output includes the employees' job name, employee number, gender, hire date, separation date, and separation reason.
Worksheets
This workbook has the following worksheets:
-
By Establishment Hierarchy
-
By Organization Hierarchy
By Establishment Hierarchy Worksheet
This worksheet enables you to report on employee separations within a given period. The worksheet output includes the following employee primary assignment details:
-
Job Name
-
Employee Number
-
Gender
-
Hire Date
-
Actual Separation Date
-
Separation Reason
The list of employees is for a given establishment hierarchy.
Business Questions
What are the ethnic origin, gender, and separation reason of my employees separating from a given establishment hierarchy?
Parameters
You must specify values for the following parameters:
-
Establishment Hierarchy
-
Top Establishment
-
Start Date
-
End Date
The report includes employees who have a primary assignment within the selected establishment hierarchy during the period from the selected Start Date to the selected End Date.
By Organization Hierarchy Worksheet
This worksheet enables you to report on employee separations within a given period. The worksheet output includes the following employee primary assignment details:
-
Job Name
-
Employee Number
-
Gender
-
Hire Date
-
Actual Separation Date
-
Separation Reason
The list of employees is for a given organization hierarchy.
Business Questions
What are the ethnic origin, gender, and separation reason of my employees separating from a given organization hierarchy?
Parameters
You must specify values for the following parameters:
-
Organization Hierarchy
-
Top Organization
-
Start Date
-
End Date
The report includes employees who have a primary assignment within the selected organization hierarchy during the period from the selected Start Date to the selected End Date.
Employee Equal Opportunity with Salary (United States Specific) Detail Workbook
This workbook enables you to list employee primary assignment details including job name, employee number, gender, ethnic origin, hire date, and salary.
Worksheets
This workbook has the following worksheets:
-
By Establishment Hierarchy
-
By Organization Hierarchy
By Establishment Hierarchy Worksheet
This worksheet enables your organization to list employee primary assignment details including, Job Name, Employee Number, Gender, Ethnic Origin, Hire date and Salary. The list of employees is for a given Establishment Hierarchy.
Business Questions
What are the ethnic origin, gender, and salary of my employees in a given establishment hierarchy?
Parameters
You must specify values for the following parameters:
-
Establishment Hierarchy
-
Top Establishment
-
Effective Date
The report includes employees who have a primary assignment within the selected establishment hierarchy on the selected Effective Date.
Headings and Calculations
This worksheet uses the following calculations:
-
Annual Salary
Calculates a person’s annual salary as of the current date.
By Organization Hierarchy Worksheet
This worksheet enables your organization to list employee primary assignment details including, job name, employee number, gender, ethnic origin, hire date, and salary.
The list of employees is for a given organization hierarchy.
Business Questions
What are the ethnic origin, gender, and salary of my employees in a given organization hierarchy?
Parameters
You must specify values for the following parameters:
-
Organization Hierarchy
-
Top Organization
-
Effective Date
The report includes employees who have a primary assignment within the selected organization hierarchy during the period on the selected Effective Date.
Headings and Calculations
This worksheet uses the following calculations:
-
Annual Salary
Calculates a person’s annual salary as of the current date.
Workforce Intelligence (HRMSi) for Employment Agreements and Legal Compliance
Employee Equal Opportunity by Job (United States Specific) Comparison Workbook
This workbook enables you to report on employee primary assignments (male, female, total) for your reporting establishments by ethnic origin, location, organization, and job name.
Additional Information: See also My Oracle Support Knowledge Document 2277369.1, Oracle E-Business Suite Support Implications for Discoverer 11gR1.
Worksheets
This workbook has the following worksheets:
-
By Establishment Hierarchy
-
By Organization Hierarchy
By Establishment Hierarchy Worksheet
The Establishment Hierarchy worksheet enables you to report on the number of employee primary assignments (male, female, total) for your reporting establishments by ethnic origin, location, and job name.
Business Questions
Show me the distribution of my employees within each establishment by ethnic origin, gender, work location, and job.
Parameters
You must specify values for the following parameters:
-
Establishment Hierarchy
-
Top Establishment
-
Effective Date
The report includes employees who have a primary assignment within the selected establishment hierarchy on the selected Effective Date.
Headings and Calculations
This worksheet uses the following calculations:
-
Male
This calculation returns 1 if an assignment is for a male and 0 if an assignment is for a female.
-
Female
This calculation returns 1 if an assignment is for a female and 0 if an assignment is for a male.
By Organization Hierarchy Worksheet
The Organization Hierarchy worksheet enables you to report on the number of employee primary assignments (male, female, total) for your reporting establishments by ethnic origin, organization and job name
Business Questions
Show me the distribution of my employees within each organization by ethnic origin, gender, work location, and job.
Parameters
You must specify values for the following parameters:
-
Organization Hierarchy
-
Top Organization
-
Effective Date
The report includes employees who have a primary assignment within the selected organization hierarchy during the period on the selected Effective Date.
Headings and Calculations
This worksheet uses the following calculations:
-
Male
This calculation returns 1 if an assignment is for a male and 0 if an assignment is for a female.
-
Female
This calculation returns 1 if an assignment is for a female and 0 if an assignment is for a male.