Maintaining Your System
This chapter contains general procedures for proper maintenance of the Oracle E-Business Suite files and database.
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Managing Files
- Maintaining the Database
- Performing Maintenance Tasks Non-Interactively
- Distributing Processing Tasks
- Managing Server Processes
Managing Files
This section contains information about maintenance tasks associated with Oracle E-Business Suite files.
Generating Product Files
Requirement
I want to generate missing product files.
Discussion
Every Oracle E-Business Suite product contains generated files, such as form, report, message, and JAR (Java archive) files. Run AD Administration when you suspect generated files are missing. For example, if users are not able to use a certain General Ledger form, regenerating the form file may resolve the issue. You may also need to generate files after you license additional products.
Note: You do not have to shut down your system to generate files. However, users that are accessing the files being generated (for example, for Human Resources forms) must log off.
Actions
Perform the following steps:
-
Determine the file types that require generation.
-
Start AD Administration by setting the environment and then entering adadmin on the command line.
Note: For more information, see Setting the Environment in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
-
From the AD Administration Main menu, go to the Generate Applications Files menu and select the task for the type of files you want to generate, based on the following criteria:
-
When you choose one of the options for generating form or report files, you can select an individual file, a set of files, or all files of the selected type.
-
The "Generate product JAR files" option allows you to generate all JAR files for all products, or only JAR files that are out-of-date.
-
The "Generate message files" option generates all message files for all products.
Note: For more information, see Generating Applications Files Tasks in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
-
-
Repeat the generation task on each APPL_TOP that contains the files (if the system contains multiple APPL_TOPs).
-
Review the AD Administration log file for warnings or errors.
Adding New Off-Cycle Products
Requirement
I want to add a product that was released after the last release update pack.
Discussion
Products that are released in between maintenance releases are sometimes referred to as off-cycle products. Since these new products do not appear in the OAM License Manager, you must add them to your product list by using AD Splicer. This utility splices the product into the list of existing products that are known to your system. This process makes the product available, so that you can register it as active, and thus, make it available to the AD maintenance utilities, such as AutoPatch.
Once you splice the product, you use AutoPatch to install all product-related files.
Note: For more information, see AD Splicer in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
Actions
Perform the following steps:
-
Download the initial product patch from My Oracle Support.
This patch contains information about the new product, AD Splicer control files required to add the product, and the associated product files.
-
Review the readme file.
Unzip the patch in the patch top directory. The patch readme file contains information on how to install the product. It may include manual steps to perform as part of this process.
Important: Do not apply the patch using AutoPatch.
-
Apply prerequisite patches (if any).
Follow the instructions about prerequisite patches in the patch readme file.
-
Create tablespaces (conditional).
If you initially installed your system with Rapid Install 11.5.10 or later, omit this step.
If your system was upgraded to Release 11.5.10 from a previous version of Release 11i, you may have chosen to continue using the OFA tablespace model. If so, create two tablespaces for each product, one for the product tables and another for the product indexes.
Note: For more information, see Tablespace Management in Oracle E-Business Suite Concepts.
-
Copy AD Splicer control files and product configuration file.
Copy <prod>prod.txt, <prod>terr.txt, and newprods.txt to APPL_TOP/admin.
Caution: If a newprods.txt already exists from a previous AD Splicer session, rename the existing file before copying the new newprods.txt file. If you need to edit this file, see AD Splicer in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
-
Add the off-cycle product to the list of products.
Log on as applmgr, set the environment, and run AD Splicer. It modifies the APPL_ TOP and database, then performs the same registration function as OAM License Manager.
UNIX:
$ cd $APPL_TOP/admin $ adsplice
Windows:
C:\>cd %APPL_TOP%\admin C:\>adsplice
Run AD Splicer for each APPL_TOP and database combination so that the Applications utilities recognize the off-cycle products as active and valid.
-
Run the AD Configuration report (adutconf.sql). Review the list of registered products to verify that the product was spliced properly into the database.
Note: For more information, see AD Configuration Report in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
-
Log out and log in again so that the new environment file (UNIX) or environment subkey in the registry (Windows) is used to set up the environment.
Note: For more information, see Setting the Environment in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
-
Verify that <PROD>_TOP registry and environment variables are set correctly for the newly spliced off-cycle products.
-
Download and apply the patch that introduces the product functionality.
The documentation that instructed you to apply this patch using AD Splicer contains information about which patch you need to apply next.
Adding and Maintaining NLS Languages
Requirement
I want to add an additional language to my existing system.
Discussion
You can add a new language to your Release 12 system at any time after your installation or upgrade.
Note: For more information, see My Oracle Support Knowledge Document 252422.1, Requesting Translation Synchronization Patches.
Actions
Perform the following steps:
-
From Oracle Applications Manager, go to License Manager and activate or change your base language to a new one.
-
From AD Administration, run Maintain Multi-lingual Tables (AD Administration Main Menu > Maintain Applications Database Entities Menu).
-
For the language (or languages) you are adding, refer to the Oracle E-Business Suite NLS Release Notes for your current release level to determine if you need to apply any specific NLS patches. If no patches are applicable, skip this step. If you are adding more than one language, and a patch is required for each, you should use AD Merge Patch to create a merged patch.
Note: For more information, see Oracle E-Business Suite Patching Procedures for information about merging NLS patches.
-
Run the Translation Synchronization Patch utility (adgennls.pl). .
If you have already run the Translation Synchronization Patch utility by following the Oracle E-Business Suite NLS Release Notes as mentioned in Step 3, you can omit this step and step 5.
-
When you are notified that it is available, apply your Translation Synchronization Patch (TSP) for all languages you requested.
-
Install the Release 12 NLS Help, if available (optional).
Note: For more information, see Oracle E-Business Suite NLS Release Notes.
Requirement
I want to confirm that my NLS language software is current with the latest US patch levels.
Discussion
If your Oracle E-Business Suite system has active languages other than American English, you can bring them up to the current US Applications patch level by using the Translation Synchronization Patch utility. Alternatively, you can individually download and apply the NLS version of all US patches you have applied to your system. Use AD Merge Patch to create a single patch, and then apply it using AutoPatch.
Note: For more information, see Oracle E-Business Suite Patching Procedures for more information about AD Merge Patch.
Actions
Perform the following steps:
-
For details of how to use the Translation Synchronization Utility, follow the instructions in My Oracle Support Knowledge Document 252422.1, Requesting Translation Synchronization Patches.
Requirement
I want to check if there are translation updates other than those associated with US patches.
Discussion
There may be updates that enhance your translated software that are not associated with US patches, and therefore, are not included in the updates you received when you requested a Translation Synchronization patch. You can request these updates using the Translation Synchronization Patch utility by selecting the Get Latest Translations check box on the file manifest submission form.
Note: For more information, see My Oracle Support Knowledge Document 252422.1, Requesting Translation Synchronization Patches.
Actions
Perform the following steps:
-
Run the Translation Synchronization Patch utility (adgennls.pl).
-
Create a manifest using the form provided in My Oracle Support. When you submit the manifest, click the Get Latest Translations check box option to get translation updates that were made available since the initial Release 12 NLS, in addition to any NLS patches needed to synchronize your NLS patch level with the US patch level.
-
When you are notified that it is available, apply the Translation Synchronization Patch (TSP) for all languages you requested.
Requirement
I want to deactivate a language.
Discussion
Deactivating a language is not supported. Once they have been activated, you must maintain all languages in an NLS system.
Actions
None.
Maintaining Snapshot Information
Requirement
What is a snapshot, and how do I use it?
Discussion
Snapshots are current views of your system: they are created once, and then updated when appropriate to maintain a consistent view. There are two types of snapshot: APPL_TOP snapshots and global snapshots. An APPL_TOP snapshot lists patches and versions of files in the APPL_TOP. A global snapshot lists patches and latest versions of files in the entire Applications system (that is, across all APPL_ TOPs).
Patch Wizard uses a global snapshot to determine which patches have already been applied. AutoPatch uses an APPL_TOP snapshot to determine if prerequisite patches have been applied to a particular APPL_TOP.
Note: For more information, see Maintain Snapshot Information in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
Actions
If you need to perform any of the Maintain Snapshot tasks, select an option from the Maintain Snapshot Information submenu.
-
Access the Maintain Snapshot Information menu.
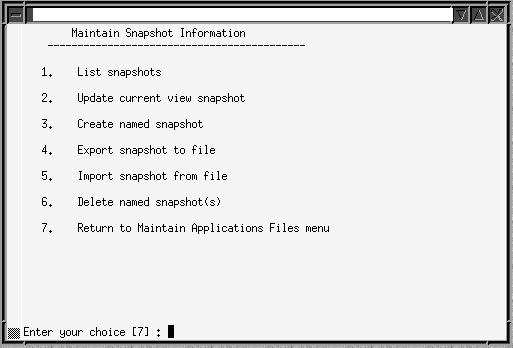
From the AD Administration Main Menu, choose Maintain Applications Files. Then choose Maintain Snapshot Information.
Maintain Snapshot Information Menu
-
Choose an option.
From this menu, you can:
-
List snapshots (stored in the system)
-
Update current view snapshot (full or partial APPL_TOP and global)
-
Create named snapshot (select a current view snapshot to copy and name)
-
Export snapshot to file (select one to export to a text file)
-
Export snapshot to file (select one to export to a text file)
-
Delete named snapshot (select a snapshot for deletion)
In addition to the existing snapshots tasks, you can choose to synchronize selected files - a partial snapshot - instead of synchronizing all files for the entire APPL_TOP. You would use this option when you have copied only a few files to the APPL_TOP.
-
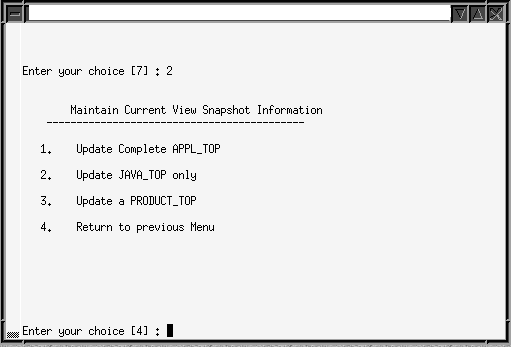
Select the Update Current View Snapshot option.
-
From the snapshot submenu, select one of the following options:
Maintain Current View Snapshot Information Menu
-
Update Complete APPL_TOP.
This is the original functionality of the Update Current View Snapshot option. It synchronizes all the files in your APPL_TOP.
-
Update JAVA_TOP only.
Synchronizes only the files in the JAVA_TOP. At the prompt, enter the path to the JAVA_TOP subdirectory where the files were copied. If the files were copied to more than one directory, press Enter. AD Administration scans the entire JAVA_TOP and updates the information in both the current view and the global view snapshots.
-
Update a <PRODUCT>_TOP.
Synchronizes only the files in a specific <PRODUCT>_TOP. Enter the product abbreviation, then provide the subdirectory information at the prompt.
Enter the path to a single subdirectory in the <PRODUCT>_TOP. If the files were copied to more than one directory in the <PRODUCT>_TOP, press Enter. AD Administration scans the entire <PRODUCT>_TOP and updates the information in both the current and the global view snapshots.
During a new installation, Rapid Install automatically creates a current snapshot as a baseline. Then, each time you run AutoPatch, it automatically creates a new (updated) snapshot so that the information is current as of the application of the patch.
Tip: You can update snapshot information using the AD Administration task any time you think it necessary. However, the process can be time-consuming.
-
Relinking Product Executables
Requirement
How do I relink product executables?
Discussion
Relinking executable programs with the Oracle server product libraries keeps them functioning properly. When you need to relink programs, run the AD Administration "Relink Applications Programs" task.
Note: For more information, see Relinking Applications Programs in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
Actions
Perform the following steps:
-
Start AD Administration.
Set the environment and enter adadmin on the command line.
Note: For more information, see Setting the Environment in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
-
Shut down services.
When relinking files on a concurrent processing server, shut down the concurrent managers. When relinking files on a Forms node, shut down the Forms services.
Note: For more information, see Stopping and Starting Application Tier Services in this chapter.
-
Relink programs.
From the AD Administration Main menu, go to the Maintain Applications Files menu. Then choose the "Relink Applications programs" task. For each product, choose whether to link all executables or only specific ones.
Relinking AD Executables
Requirement
How do I relink AD executables?
Discussion
You cannot use AD Administration to relink AD executables. Instead, you run AD Relink. With this command line utility, you can relink several AD utilities with a single command.
AD Relink requires the force= parameter. There is no default for this parameter. You must specify either "n" to relink the executable program only if the dependent libraries or object files are more recent than the current executable program, or "y" to relink regardless of the status of the libraries or object files.
An optional command line argument is backup_mode. Use it to indicate whether you want to back up executables. There are three possible values for backup_mode:
| Value | Effect |
|---|---|
| backup_mode=none | Do not back up any executables. |
| backup_mode=all | Back up all executables. |
| backup_mode=file | Back up files according to instructions in adlinkbk.txt (the default). |
Note: For more information, see AD Relink in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
Actions
Perform the following steps:
-
Log on as applmgr and set the environment.
Note: For more information, see Setting the Environment in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
Windows users must run %<APPL_TOP>%\relinkenv.cmd, executed from a command window. Change directory to %APPL_TOP% and run apps.sh to set up all required environment variables. (Note there is a space between the dots in this command.)
C:\> . ./apps.sh
-
Relink files.
Run AD Relink using the appropriate command for your operating system.
UNIX:
$ adrelink.sh force={y | n} [<optional arguments>] <ad program name>Windows:
Change directory to %APPL_TOP%\bin and relink the desired file using the following syntax:
C:\> sh adrelink.sh force={y | n} [<optional arguments> <ad program name>If you want to relink several AD utilities, list the programs on the command line, separating each with a space and enclosing it in quotations. For example, to relink both AD Controller (adctrl) and AD Administration (adadmin), enter:
UNIX:
$ adrelink.sh force=y "ad adctrl" "ad adadmin"
Windows:
C:\> sh adrelink.sh force=y "ad adctrl.exe" "ad adadmin.exe"
To create a backup file (for all executables), use the following syntax:
UNIX:
$ adrelink.sh force=y backup_mode=all
Compressing, Archiving, and Deleting Files
Requirement
Which Oracle E-Business Suite files can be safely compressed, archived, or deleted?
Discussion
There are several types of files that can be compressed, archived, or deleted: log and output files, upgrade files, and AutoPatch backup files. However, Oracle recommends this action only if there is no other way to increase available disk space.
Caution: We strongly recommend creating a backup before you delete any files and keeping the backup readily available in case you need to restore files.
Actions
Perform the following tasks, using the commands specific to your operating system.
-
Compress, archive, or delete the following files, according to your operational requirements. The three categories can be treated independently for cleanup purposes.
-
Log and output files.
You can compress, archive, or delete log and output files created by AD utilities. They are located in the following directories, where <SID> is the name of the database instance for the current Applications system: $APPL_ TOP/admin/<SID>/log and $APPL_TOP/admin/<SID>/out (UNIX) or %APPL_TOP%\ admin\<SID>\log and %APPL_TOP%\admin\<SID>\out (Windows).
Caution: Log files may contain passwords. Back up these files to a secure location. Do not delete the directories.
-
Upgrade files.
After you complete and verify an upgrade, you can compress, archive, or delete the upgrade files located in $APPL_TOP/admin/preupg (UNIX) or in %APPL_ TOP%\admin\preupg (Windows).
Caution: Do not remove any files under <PROD>_TOP/admin. They are used by AD utilities such as AutoPatch and AD Administration.
-
AutoPatch backup files.
After you run AutoPatch, you can compress, archive, or delete old files that have been backed up in the patch top subdirectory.
Caution: Verify that the patch was applied successfully and the patched functionalities are fully tested before you delete backup files.
-
Maintaining the Database
This section contains information you can use to maintain your database and effectively manage system resources.
Using System Resources Efficiently
Requirement
How do I keep optimization statistics up to date?
Discussion
Optimization is the process of choosing the most efficient way to execute a SQL statement. Oracle E-Business Suite Release 12 uses cost-based optimization. By analyzing the "cost" of using each resource, you can keep your system tuned for optimum performance. The optimizer uses actual table statistics to determine the most efficient access paths and join methods for executing SQL statements.
These statistics are gathered when you run the Gather Schema Statistics concurrent program. It is important to run this program after an upgrade and, subsequently, on a regular basis to avoid performance degradation (we recommend once a month). The length of time the statistics in an instance are of any value depends on the amount DML that is done during a period of time. For completely static tables, once may be enough for the life of the table. For tables that are completely reloaded all the time, you must run Gather Schema Statistics more often. Tables loaded during a Data Pull in Demand Planning or Advanced Planning and Scheduling are good examples. OE/OM tables are also constantly updated.
Tip: Based on usage, identify the frequency for gathering all statistics, and the frequency that works best for gathering statistics only for specific products.
Actions
Perform the following steps.
-
Log in to Oracle E-Business Suite with the System Administrator responsibility.
-
Navigate to the Submit Request window (Request > Run).
-
Submit the Gather Schema Statistics program.
Set the schema name to ALL to gather statistics for all Oracle E-Business Suite schemas (having an entry in the FND_PRODUCT_INSTALLATIONS table). In addition to gathering index and table-level statistics, the procedure also gathers column-level histogram statistics for all columns listed in the FND_HISTOGRAM_ COLS table.
Note: For more information, see Cost-Based Optimization in Oracle E-Business Suite in the Oracle E-Business Suite System Administrator’s Guide - Configuration.
Validating the APPS Schema
Requirement
How do I verify the integrity of my APPS schema?
Discussion
AD Administration can run a SQL script (advrfapp.sql) against the APPS schema that checks for certain conditions that are undesirable, but will not produce fatal problems. The Validate APPS Schema task executes this script.
You can run this task at any time, but it is most effective if run:
-
Immediately after an upgrade
-
Before converting to Multi-Org
-
After performing an export/import (migration)
-
As a part of custom development in the APPS schema
Actions
Perform the following tasks, using the commands specific to your operating system.
-
Start AD Administration.
Set the environment and enter adadmin on the command line.
Note: For more information, see Setting the Environment in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
-
Select the "Validate APPS schema" task from the Maintain Applications Database Entities menu. Review the output file (<APPS schema name>.lst) for invalid database objects. It is located in $APPL_TOP/admin/<SID>/out (UNIX) or in %APPL_TOP%\admin\<SID>\out (Windows)
Note: For more information, see Validate APPS Schema in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
You can also run this task from SQL*Plus:
UNIX:
$ cd $APPL_TOP/admin<SID>/out $ sqlplus <SYSTEM username>/<SYSTEM password> \ @$AD_TOP/admin/sql/advrfapp.sql \ <APPS schema name> <AOL schema name>
Windows:
Change directory to %APPL_TOP%\bin and relink the desired file using the following syntax:
C:\> cd %APPL_TOP%\admin\<SID>out C:\> sqlplus <SYSTEM username>/<SYSTEM password> @%AD_TOP%\admin\sql\advrfapp.sql <APPS schema name> <AOL schema name>
-
Resolve any issues.
The <APPS schema name>.lst file is divided into three sections:
-
Issues you must fix (not specific to the APPS schema)
-
Issues you must fix (specific to the APPS schema)
-
Issues you may want to address (specific to the APPS schema)
Each section of the file contains instructions for resolving the issues that are listed.
-
Recreating Grants and Synonyms
Requirement
How do I recreate grants and synonyms in the APPS schema?
Discussion
In order to maintain database objects, you should check the APPS schema for missing grants and synonyms. Using the AD Administration menu, you can run tasks to validate the APPS schema and then recreate any missing grants and synonyms.
Note: For more information, see Recreate Grants and Synonyms for APPS Schema in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
Actions
Perform the following steps:
-
Start AD Administration.
Set the environment and enter adadmin on the command line.
Note: For more information, see Setting the Environment in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
-
From the Main AD Administration menu, go to the Maintain Applications Database Entities menu. Select the "Recreate grants and synonyms for APPS schema" task.
Compiling Invalid Objects
Requirement
When should I compile invalid objects?
Discussion
The Oracle database automatically compiles invalid database objects the first time an object is used and during patch application. This action can take some time, so you may want to compile objects before the first use, at a time when you know the system usage is low.
You compile invalid objects with AD Administration. This task is most effective under the following circumstances:
-
After custom packages are moved to the APPS schema and need to be compiled
-
After applying patches that alter packages in the APPS schema
-
After validating the APPS schema and identifying invalid objects
Actions
Perform the following tasks, using the commands specific to your operating system.
-
Start AD Administration.
Set the environment and enter adadmin on the command line.
Note: For more information, see Setting the Environment in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
-
Compile Applications schema.
From the Main AD Administration menu, go to the Compile/Reload Database Entities menu. Choose the "Compile APPS schema" task.
Pre-Allocating Space for Packages and Functions
Requirement
How do I ensure that there is enough space in the System Global Area (SGA) for packages and functions?
Discussion
If SGA space is fragmented, there may not be enough for certain packages or functions. You can pre-allocate space in the SGA shared pool by pinning packages, functions, and sequences. The scripts described in this procedure work well as templates and can be used to create your own custom pinning scripts.
Important: Run these scripts when packages or sequences are patched (and the patch readme file tells you to do so), or any time after objects are invalidated, either because of patching or customizations.
The ADXGNPIN.sql script pins packages and functions in the APPS schema, while ADXGNPNS.sql pins sequences in the base product schemas. Both scripts take the name of a schema as an argument, or % for all schemas. ADXGNPIN.sql generates and invokes another SQL file, ADXSPPIN.sql. ADXGNPNS.sql generates and runs ADXSPPNS.sql.
Actions
Perform the following tasks, using the commands specific to your operating system.
-
Create the appsutil/admin directory in the ORACLE_HOME of the database server, if it does not already exist.
-
Copy ADXGNPIN.sql and ADXGNPNS.sql from the AD_TOP/sql directory of the administration server to this directory.
-
Set the environment to point to the ORACLE_HOME for the database server.
-
On the database server, go to the directory created in Step 1 and run ADXGNPIN.sql and ADXGNPNS.sql from SQL*Plus:
$ sqlplus <SYS username>/<SYS password>@ADXGNPIN.sql \ <APPS schema name> $ sqlplus <SYS username>/<SYS password>@ADXGNPNS.sql \ <Base product schema name>
Listing Objects in the Shared Pool
Requirement
How can I see a list of objects stored in the shared pool?
Discussion
You can run the ADXCKPIN.sql script to query for objects stored in the SGA shared pool. It shows the objects known to the SGA and the size that they consume. The output file is ADXCKPIN.lst.
Actions
-
Run the following commands:
$ cd $APPL_TOP/admin<SID>/out $ sqlplus <SYSTEM username>/<SYSTEM password> \ @%AD_TOP%\sql\ADXCKPIN.sql
Performing Maintenance Tasks Non-Interactively
Unless otherwise noted, maintenance tasks described in this book are performed interactively: they require user intervention, primarily in the form of responding to prompts. However, you can schedule certain AD Administration and AD Controller tasks to run with little or no user intervention by running these utilities non-interactively: instead of responding to prompts each time you run the task, you specify a file that contains the information necessary to complete the task without user intervention. In such a case, there is no need to monitor the process in order to respond to prompts. The file used is referred to as a defaults file.
Scheduling Non-Interactive Maintenance
Requirement
How do I schedule and run maintenance tasks non-interactively?
Discussion
To set up a non-interactive task, you first create and save a defaults file by running the selected task interactively from the AD Administration menu and adding the defaultsfile=<defaults file name> argument. This causes the information you provide at the prompts, and other information pertinent to that task, to be captured in a file and stored in $APPL_TOP/admin/<SID>/<path>.
Tip: AutoConfig automatically creates a defaults file (adalldefaults.txt) each time it runs. This file can be used as a template to create a customized defaults file. However, we recommend that you create the defaults file as described in this procedure.
Once the defaults file is created, you start the utility from the command line, and specify the name of the defaults file, a log file name, and the number of parallel workers.
The same defaults file can be used to run different AD Administration commands: a single such file can contain all your choices for the different menu options. In order to choose which task the defaults file will run, you also add menu_option=<menu choice> to the utility start command. This overrides any menu-specific key stroke information stored in the defaults file initially, and allows you to use the defaults file for any of the AD Administration menu items. It also ensures that the menu option you intended for the defaults file is always valid, even if the menu items are renumbered or relocated in subsequent releases.
Note: For more information, see Preparing for Non-Interactive Processing in Chapter 4 and Monitoring and Controlling Parallel Processes in Chapter 1 of Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities for a list of the menu_option= values.
Actions
Perform the following steps.
-
Create the defaults file.
Start AD Administration, using the defaultsfile= argument, and specifying the file name and the path to the defaults file. This creates a defaults file for the current environment.
UNIX:
The file must be under the $APPL_TOP/admin/<SID>directory, where <SID> is the database name (ORACLE_SID/TWO_TASK). For example:
$ adadmin defaultsfile=$APPL_TOP/admin/testdb1/adadmindef.txt
Windows:
The file must be under the %APPL_TOP%\admin\<SID>directory, where <SID> is the database name (LOCAL). For example:
C:\> adadmin defaultsfile=%APPL_TOP%\admin\testdb1\adadmindef.txt
-
Interactively run the maintenance task to populate the defaults file.
From the AD Administration Main menu, go the appropriate menu and select a maintenance task. As the task runs, respond to all the prompts. You must create a separate defaults file for each task you want to run non-interactively.
Warning: If you omit any information, AD Administration may not be able to complete the session when you run it non-interactively.
-
Verify that the defaults file exists.
-
Run the AD Administration task non-interactively.
On the command line, start the utility and specify non-interactive processing and the defaults file name. In addition, supply the name of the log file, the number of parallel workers, and the name of the menu choice.
For example, to run the "Check DUAL table" task non-interactively, using a defaults file named adadmindef.txt, a log file named adadmin_noninteractive.log, and with 5 workers, you would enter:
UNIX:
$ adadmin interactive=n \ defaultsfile=$APPL_TOP/admin/testdb1/adadmindef.txt \ logfile=adadmin_noninteractive.log workers=5 \ menu_option=CHECK_DUAL
Windows:
C:\> adadmin defaultsfile=%APPL_TOP%\admin\testdb1\adadmindef.txt logfile=adadmin_noninteractive.log workers=5 interactive=n menu_option=CHECK_DUAL
Note: For more information, see the list of options in Preparing for Non-Interactive Processing in Oracle E-Business Suite Maintenance Utilities.
Restarting a Failed Session
Requirement
My non-interactive AD Administration session failed. How do I restart it?
Discussion
To restart a failed non-interactive session, you run AD Administration using the restart=yes parameter.
Actions
Perform the following tasks, using the commands specific to your operating system.
-
Determine the reason the session failed and fix the issue.
-
Run AD Administration from the command line.
Use the same parameters that you used to start the original non-interactive session, plus the restart=yes parameter. For example:
UNIX:
$ adadmin defaultsfile=$APPL_TOP/admin/testdb1/adadmindef.txt \ logfile=adadmin_noninteractive.log workers=5 interactive=n \ restart=y menu_option=CHECK_DUAL
Windows:
C:\> adadmin defaultsfile=%APPL_TOP%\admin\testdb1\adadmindef.txt logfile=adadmin_noninteractive.log workers=5 interactive=n restart=y menu_option=CHECK_DUAL
-
AD Administration runs the task. It does not prompt you to continue the previous (failed) session.
Distributing Processing Tasks
Requirement
How can I run processes concurrently on my multi-node system?
Discussion
Distributed AD is a parallel processing feature that can further reduce task time by utilizing all available resources in systems that have a shared application tier file system. With Distributed AD, AD Administration and AutoPatch run on one node and direct workers running both on that node and on other nodes in the system.
Note: You must have a shared application tier file system to use Distributed AD.
Actions
To take advantage of this processing operation, run AD Administration or AutoPatch on the primary node with the command line options.
workers=<total number of workers> localworkers=<number of workers on primary node>
This is illustrated in the following two examples.
Example 1
-
To run an AutoPatch session with a total of eight workers and three workers on the primary node, enter the command:
$ adpatch workers=8 localworkers=3
-
Now start an AD Controller session on each of the other nodes with the following command:
$ adctrl distributed=y
-
To start workers 4 through to 8 on a secondary node, enter "4-8" in response to the prompt from AD Controller:
Enter the worker range: 4-8
Note: Workers must be specified in contiguous numbered blocks. For example, you cannot start workers 4, 6, 8 on one node, and 5, 7, 9 on another.
Example 2
-
To run a total of twelve workers on a three-node system, enter the command:
$ adpatch workers=12 localworkers=4
-
Now start an AD Controller session on the second node, specifying that workers 5-8 should run there:
$ adctrl distributed=y Enter the worker range: 5-8
Note: Workers must be specified in contiguous numbered blocks. For example, you cannot start workers 4, 6, 8 on one node, and 5, 7, 9 on another.
-
Finally, start AD Controller on the third node, specifying that the last four workers (9-12) should run there:
$ adctrl distributed=y Enter the worker range: 9-12
Managing Server Processes
When running certain scripts or utilities, you may be directed to stop server processes manually. This section contains information about stopping and starting these processes.
Note: Scripts in this section may contain system-specific information. If you change the Rapid Install defaults, you may need to edit the scripts before rerunning them.
Starting and Stopping Application Tier Services
Requirement
How do I start and stop application tier services?
Discussion
When Rapid Install sets up and configures the server processes, it stores a control script for each process in the $INST_TOP/admin/scripts directory.
Certain maintenance procedures require that you stop one or more services or servers manually, and restart them after you complete the procedure. By running the appropriate script on the command line, along with a stop or start argument, you can stop (or start) a single server process, several processes, or all processes. The following table lists the scripts. The application tier logon is applmgr.
Actions
Choose the procedure that meets your needs.
To start or stop a single application tier server process (UNIX)
Use a command of the following format:
<process script name> [stop | start]
Tip: Many of the relevant scripts also have a 'status' option, which is often useful.
-
Open a terminal window.
-
To stop the Concurrent Processing server (for example), run the adcmctl.sh script with the 'stop' option:
% adcmctl.sh stop
To start or stop a single application tier server process (Windows)
On Windows , services can be started or stopped using the appropriate process control script (command file), or from the Services Control Panel.
Using Process Script
-
Open a command window.
-
To stop the Concurrent Processing server (for example), run the adcmctl.cmd script with the 'stop' option:
C:\> adcmctl.cmd stop
Using Services Control Panel
-
Go to Start > Administrative Tools and click Services.
-
Select the relevant service in the Services window.
-
Click Start or Stop, as required.
To start all application tier server processes (UNIX)
Use a command of the following format:
<process script name> [stop | start]
To start all application tier server processes (Windows)
Use a command of the following format:
<process script name> [stop | start]
To stop all application tier server process (UNIX)
Use a command of the following format:
<process script name> [stop | start]
To stop all application tier server process (Windows)
Use a command of the following format:
<process script name> [stop | start]
Starting and Stopping Database Tier Services
Requirement
How do I start or stop the Oracle Net Services listener manually?
Discussion
When Rapid Install sets up and configures the server processes during installation, it stores a script for the Net Services listener process in the Oracle 11g database server $ORACLE_ HOME/appsutil/scripts/<CONTEXT_NAME> directory. You use this script to start or stop the Net Services listener process for the database.
Actions
To start or stop the Net Services listener (UNIX)
-
Open a terminal window.
-
Log in as the oracle user on the database server and navigate to the $ORACLE_ HOME/appsutil/scripts/<CONTEXT_NAME> directory.
-
Enter a command of the form:
$ addlnctl.sh [start|stop] <listener_name>
Tip: Many of the relevant scripts also have a 'status' option, which is often useful.
For example, to start the PROD listener, enter:
$ addlnctl.sh start PROD
Note: For more information, see the Oracle Net Services Administrator’s Guide.
To start or stop the Net Services listener (Windows)
-
As the oracle user, open a command window and navigate to the %ORACLE_ HOME%\appsutil\scripts\<CONTEXT_NAME> directory.
-
Enter a command of the form:
C:\> addlnctl.cmd [start|stop] <listener_name>
For example, to start the PROD listener, enter:
C:\> addlnctl.cmd start PROD
Note: For more information, see the Oracle Net Services Administrator’s Guide.
Requirement
How do I start or stop the Oracle database manually?
Discussion
When Rapid Install sets up and configures the server processes during installation, it creates a script for the database process in the Oracle 11g database server $ORACLE_ HOME/appsutil/scripts/<CONTEXT_NAME> directory. You use this script to start or stop the database on your database tier.
Actions
To start or stop the Oracle database (UNIX)
-
Log in as the oracle user on the database server.
-
Open a terminal window and navigate to the $ORACLE_ HOME/appsutil/scripts/<CONTEXT_NAME> directory.
-
Enter a command of the form:
$ addbctl.sh [start|stop] {immediate|abort|normal}Tip: Many of the relevant scripts also have a 'status' option, which is often useful.
For example, to stop the database using the normal option, you would enter:
$ addbctl.sh stop normal
To start or stop the Oracle database (Windows)
-
Log in as the oracle user on the database server.
-
Open a command window and navigate to the %ORACLE_ HOME%\appsutil\scripts\<CONTEXT_NAME> directory.
-
Enter a command of the form:
C:\> addlnctl.cmd [start|stop] <listener_name>
For example, to start the PROD listener, enter:
For example, to stop the database using the normal option, you would enter:
C:\> addbctl.cmd stop normal