User Authentication
SunScreen EFS 3.0 allows you to configure user entities to authenticate individual administrators and to allow access through the firewall when using proxied services.
Authentication allows you to verify the identity of both internal and external users based on user name and a simple text password, or on a user name and SecurID\256 token passcode, or both.
Proxies provide a means to validate, regulate, and extend the abilities of certain services beyond those afforded by kernel-based stateful packet filtering. (See Chapter 5, "Proxies," for more information regarding user authentication.)
SunScreen EFS 3.0 provides two distinct levels of user identification: Authorized User, through the authuser database, and Proxy User, through the proxyuser database.
Authorized Users
Authorized User is a named common object that describes an individual administrative user who is distinct from all others. The attributes provide a repository for demographic and authentication data about that individual.
Access to and use of the administrative GUI functions require that you establish the Authorized User identity before administration is allowed. Both the administration GUI Login screen and the login sub-command of the ssadm command line facility reference an Authorized User object.
Note -
Authorized User authenticity establishes only the identity of an individual administrator, not the various roles they may play while using SunScreen EFS 3.0. Role establishment is afforded in one of two ways: (1) reference within the User field in the administrative access rules of a policy, (2) reference from a packet filtering rule that utilizes user authentication (proxies).
Proxy Users
Proxy User is a named common object distinct from the Authorized User. Proxy Users are either SIMPLE or GROUP objects. SIMPLE objects are used to provide for and establish an association between an individual administrator and the role they play in usage of the facilities controlled by SunScreen EFS 3.0. GROUP objects are used to allow creation of groups of SIMPLE Proxy Users that share common access to facilities. Thus, GROUPs streamline the task of allowing or removing access to established facilities.
Some special Proxy User objects also provide the means to map external collections of users into the SunScreen EFS 3.0 access control facilities. SunScreen EFS 3.0 provides external access to SecurID and RADIUS users. (Access to other external user databases is afforded using RADIUS as an intermediary agent. For example, access to LDAP user databases stored through Sun Directory Services (SDS) are accessible through RADIUS.)
The following diagram summarizes the relationship between Rules, Authorized Users, Proxy Users, and external user databases:
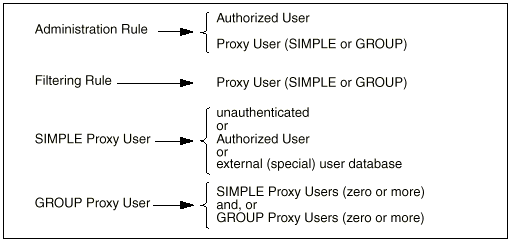
Authorized Users and Proxy Users names are distinct, and you can have objects with identical names in each. Choose a naming strategy for each set that best reflects the naming systems already employed. For example, you can choose to name Authorized Users by employee identities, like distinguished names or employee numbers, and Proxy Users by names that reflect their normal user login names deployed on server systems (for example: Unix login name).
Note -
Names cannot contain any of the following characters: "!", "#", "$", "%", "^", "&", "*", "{", "}", "[", "]", "<", ">", """, "', "?", "`", "/", "@", or NUL characters.
Space, tab, and other whitespace characters are allowed in names, but in doing so you should be prepared to supply quotation marks in some situations in order to protect such whitespace within names.
Names of Authorized Users, Proxy Users, and other user naming items are often deliberately chosen to be different for purposes of clarity.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
