Log Page
To View the Log Page
-
Click the Information button in the SunScreen banner.
The Information page displays.
-
Click the Log tab.
The Log page displays.
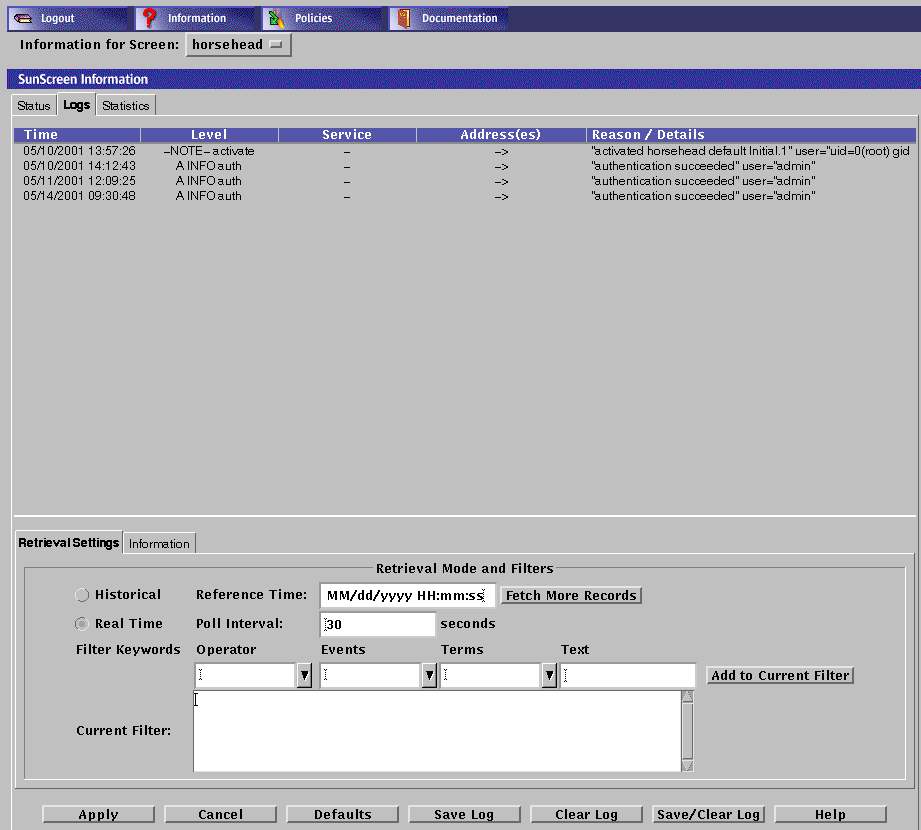
The following table describes the column headings for the log panel of the SunScreen Information page.
Table 9-2 Column Headings on the Log Panel of the SunScreen Information Page|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Time |
Indicates the time that the packet or event represented by this record was logged by the Screen. Use this time field to retrieve records in Historical mode as set in the Log Browser Tab Retrieval Setting. |
|
Level |
Indicates the type and severity level of the logged event. |
|
Service |
Indicates the network service or protocol, such as TCP, IP, NFS, Telnet, or HTTP, over which this packet was sent or to which the event is related. |
|
Address(es) |
Shows the address from which and to which a packet was sent. Arrows indicate direction. Some events that, by themselves, are not related to IP traffic will not have an address or addresses, as shown in the example. |
|
Reason/Detail |
Shows the reason a packet or event was logged or the detail regarding the logging. This information depends on the requirements of the rules within a policy. |
The logs tab also displays the Retrieval Setting tab and Information tab for the logs.
Logged packets are configured in the packet filtering rules so that a packet or an event is displayed which meets the requirements of a rule in a policy. The log has two retrieval modes: Historical and Real Time.
-
The Historical mode allows you to examine a particular segment for a particular time.
-
The Real Time mode displays information as the packets pass through the Screen while you are looking at the log.
Retrieval Setting Tab
The following table describes the controls on the Retrieval Setting tab.
Table 9-3 Controls on the Retrieval Setting Tab|
Control |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Retrieval Mode radio buttons |
Specifies the time frame for which you want log messages:
|
|
Fetch More Records button |
Retrieves more log records in the historical mode only. If you check Historical Reference Time and click the Apply button after specifying a date and time for retrieving records, the display will retrieve log records using the date and time that the log file was last cleared. Using this button, you can display the next screen of later records. |
|
Filter Keywords field |
Provide the ability to create many simple filtering expressions from the choice lists available. These controls reduce typing effort as well as serving as reminders of filtering options. For more detail, see the following section, "Setting a Log Viewing Filter". |
|
Add to Current Filter button |
Causes these items chosen in the Filter Keywords fields to be added to the Filter Keywords text entry box at its current insertion pointer. For more detail, see the following section, "Setting a Log Viewing Filter". It adds all text that is currently selected in the four combo boxes. |
|
Current Filter text box |
Allows you to enter an expression of the log-browser filtering language. An arbitrary logdump expression can be entered there and activated using the Apply button. For more detail, see "Setting a Log Viewing Filter" below. |
Setting a Log Viewing Filter
The Log Browser filters log events to be displayed. The language that it uses is identical to the filtering options of the logdump command in the command-line program; it is a superset of the language used by the Solaris snoop packet monitor tool.
You have full access to this language typing an arbitrary logdump expression in the Current Filter text entry box in its Retrieval Settings tab and clicking the Apply button to activate it.
In addition, the Filter Keywords controls provide the ability to create many simple filtering expressions. These controls reduce typing effort as well as serving as reminders of filtering options.
The Filter Keywords controls are used by selecting one or more operations from their choice lists or entering a target (operand) in the Text box. After choosing or typing your entry, click the Add to Current Filter button to add these items to the Filter Keywords text entry box at its current insertion pointer.
The leftmost editable combo box contains the Boolean operators and, or, and not.
The Events box provides filtering terms that are complete and restrict the type of log event displayed. The following table describes the terms in the Events box.
Table 9-4 Filter Terms of the Events Box|
Term |
Description |
|---|---|
|
loglvl pkt |
Allows displaying network packet-type events |
|
loglvl sess |
Allows displaying network session-type events |
|
loglvl auth |
Allows displaying events related to authentication operations |
|
loglvl app |
Allows displaying events related to screen application (usually proxy) operations |
|
logapp activate |
Allows displaying events related to policy activation. |
|
logapp auth |
Allows displaying events from the authentication subsystem |
|
logapp compiler |
Allows displaying events related to policy compilation |
|
logapp edit |
Allows displaying events related to registry or policy editing |
|
logapp ftpp |
Allows displaying events from the FTP proxy |
|
logapp ha |
Allows displaying events related to HA operation |
|
logapp httpp |
Allows displaying events from the HTTP proxy |
|
logapp iked |
Allows displaying events related to the IKE daemon |
|
logapp log |
Allows displaying events related to the logging facilities themselves |
|
logapp restore |
Allows displaying events related to policy restoration |
|
logapp scan |
Allows displaying events related to proxy content scanning and redirection |
|
logapp smtpp |
Allows displaying events from the SMTP proxy |
|
logapp telnetp |
Allows displaying events from the Telnet proxy |
|
logsev emerg |
Allows displaying events of an emergency severity |
|
logsev alert |
Allows displaying events of an alert severity or above |
|
logsev crit |
Allows displaying events of a critical severity or above |
|
logsev err |
Allows displaying events of an erroneous severity or above |
|
logsev warn |
Allows displaying events of a warning severity or above |
|
logsev note |
Allows displaying events of a notice severity or above |
|
logsev info |
Allows displaying events of an informative severity or above (all events that are not of debug severity) |
|
logsev debug |
Allows displaying events of a debug severity or above (all events) |
TheTerms box provides filtering terms most of which are incomplete and require an operand value, You type these in the Text box. They are added to the choice list of the Text box for reference so that you need not retype the value if you want to use it again. The following table describes the filter terms in the Terms box.
Table 9-5 Filter Terms in the Terms Box|
Term |
Description |
|---|---|
|
logwhy reason# |
Restricts display to packets that have the given logging reason why code |
|
logiface iface |
Restricts display to packets that arrived on the interface named iface |
|
host hostname |
Restricts display to events either from or to hostname |
|
dst hostname |
Restricts display to events destined for hostname |
|
src hostname |
Restricts display to events origination from hostname |
|
port hostname |
Restricts display to events related to the service svcname |
|
dstport hostname |
Restricts display to events targeted to the service svcname |
|
srcport svcname |
Restricts display to events originating from the service svcname |
|
net netaddr |
Restricts display to events either from or to the network whose number is netaddr |
|
udp |
Restricts display to events related to the UDP transport protocol |
|
tcp |
Restricts display to events related to the TCP transport protocol |
|
icmp |
Restricts display to packets of the ICMP control protocol |
|
rpc |
Restricts display to packets of the RPC protocol |
The terms in italics are variables for which you must supply a value or values in the when you choose this term from the choice list. The values for the variable are as follow:
-
reason # The reason number is shown in "Error Messages" in SunScreen 3.2 Administrator's Overview.
-
hostname can be:
-
svcname can be:
-
A numeric TCP or UDP port number (for example, 23 for Telnet)
-
A numeric TCP or UDP port number range (for example, 6000. .6023 for X windows)
-
A service name known to the screen's naming service (for example, domain found in /etc/services)
-
-
iface can be:
-
The name of an interface (for example hme0)
-
-
netaddr can be:
-
The IP network number (for example 199.12.200)
-
The Information Tab
The log-browser Information tab on the Screen Information page and shown in below provides the statistics for the current log.
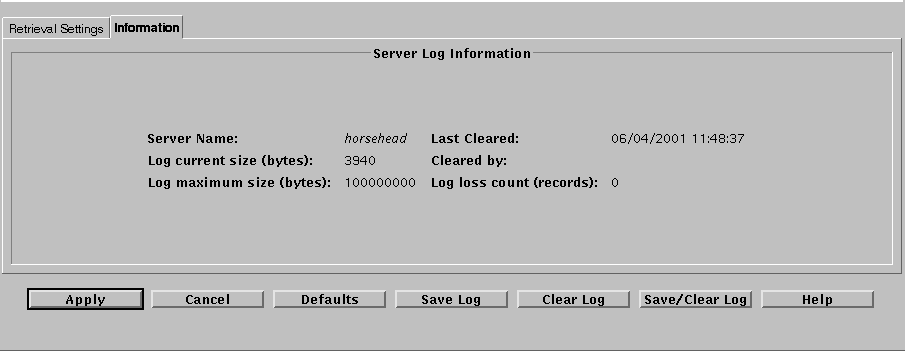
The following table describes the fields on the Information tab. You cannot edit the fields on this page.
Table 9-6 Fields on the Information Tab|
Control |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Server Name field |
Indicates the name of the Screen to which the Log Browser is connected. |
|
Log current size field (bytes) |
Indicates the current size of the log file in bytes on the server. |
|
Log maximum size field (bytes) |
Indicates the maximum size of the log file in bytes on the server. |
|
Last Cleared field |
Indicates the date and time the log file was last cleared. |
|
Cleared By field |
Identifies the login name of the administrator who last cleared the log file. |
|
Log loss count (records) field |
Indicates the number of log records that have been thrown away since the last "clear" operation. Log records are lost if the log grows beyond its maximum size or if the file system on which the log is written fills before that maximum is reached. Packets that cannot be logged because the traffic load exceeds the logger's ability to store entries are not counted. |
Action Buttons
The following table describes the action buttons on the SunScreen Information Page.
Table 9-7 Action Buttons on the SunScreen Information Page
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
