Chapter 1 Introduction
SunScreen 3.2 is dynamic, stateful, IP-packet filtering firewall software used to protect a host or a network of hosts by controlling packet flow to or through the machine on which it is installed. SunScreen uses ordered rules that restrict access based on IP addresses and network service ports. Using both SunScreen SKIP and IPSec IKE, you can configure SunScreen to encrypt IP packets between hosts or a network of hosts to prevent data compromise. SunScreen generally provides authentication of hosts using certificates but you can also use IKE manual or pre-shared keys for encryption with Packet Filtering rules.
SunScreen supports Network Address Translation (NAT) , High Availability (HA), and Centralized Management Groups (CMG). Also, SunScreen includes user-level proxies for application-level packet examination or user authentication through internal or external means.
The administration graphical user interface (GUI) works on any browser supporting JDK 1.1 (or compatible versions) and has end-system SKIP or IPSec IKE installed . The installer program adds the required SunScreen SKIP and IKE packages automatically by or you can install these packages using command line installation.
For detailed information on how SunScreen SKIP encryption works, refer to the SunScreen SKIP 1.5.1 User's Guide. You can find a description of SunScreen's IKE implementation in the SunScreen Administrators Overview.
What Is the Configuration Examples Manual?
This document is a collection of hypothetical network configurations using the SunScreen firewall. The examples are real-life examples that use the following features of this product.
-
Remote administration of a Screen using an Administration Station. The administration GUI runs on the Administration Station but the configuration files it uses are stored on the Screen. One Administration Station can manage any number of Screens that have the access rules defined to grant administrative access.
-
SunScreen supports Network Address Translation (NAT) and this manual contains an example of how you use both the STATIC and DYNAMIC NAT features with the firewall.
-
Sunscreen has both Routing mode allowing normal routing of traffic and Stealth mode which makes the firewall invisible to the outside world. You can also configure SunScreen in a mixed mode where one interface of the firewall is stealth and other interfaces are routing. Examples using all three of these modes are included in this manual.
-
SunScreen allows you to set up Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). This manual provides three examples that use encryption with Packet Filtering and VPN rules. The examples use both SKIP and IKE
-
The High Availability (HA) feature lets you use a redundant machine to mirror all network traffic and firewall configurations. Should the active machine in the HA configuration fail for any reason, the passive partner takes over providing uninterrupted operation.
-
The Centralized Management Group feature enables you to connect to one Screen that is designated as the primary Screen. You can manipulate policy there , and then push that changed policy to secondary Screens.
-
Proxies allow for authentication of users before they access supported services. This manual includes a proxy example of a Screen supporting FTP, telnet, and http proxies.
-
SunScreen 3.2 systems and Windows 2000 systems can interoperate using the IPSec IKE protocol. This manual provides you with the information you need to know to make this feature work properly.
While this manual contains detailed examples of how you might use SunScreen's features. It is beyond the scope of this manual to suggest any particular security policies.
To determine the policy you want to implement, you should first:
-
Identify your own security requirements for protecting the integrity and accessibility of your corporate data and computer resources.
-
Determine the services you want to support at your site for employees and customers.
-
Define the layout for your network and then configure SunScreen to implement this policy.
How SunScreen Works
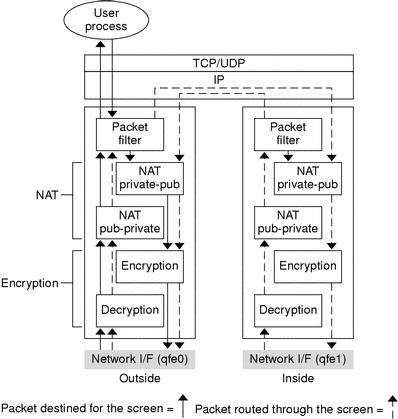
Figure 1-1 shows where the SunScreen software resides in relation to the network protocol stack. Packets can flow from the network to an application; they can flow through the screen (between segments); or flow out to the network from an application running on the screen. For a detailed description of how SunScreen does Packet Filtering, see the SunScreen 3.2 Administrators Overview
Figure 1-1 SunScreen Functions
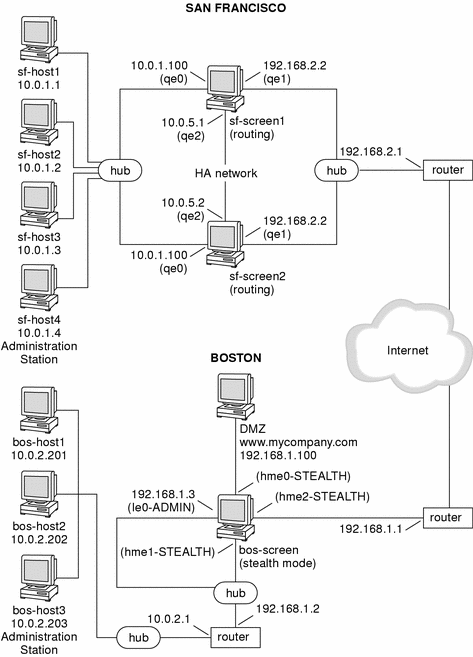
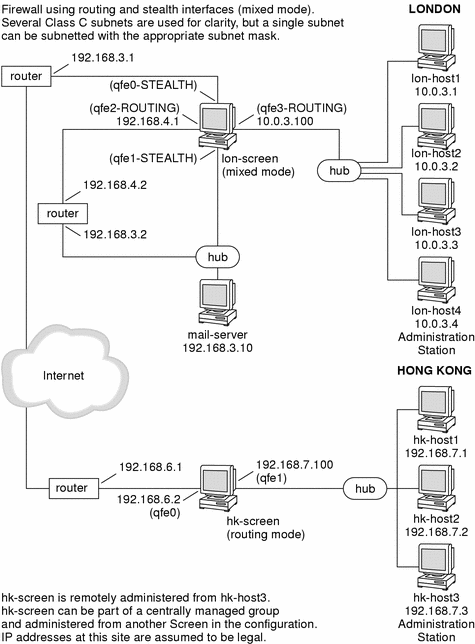
Network Map
Segments of the sample company network shown in the following figures are used in the configuration examples described in this document.
The machines used in the examples are assumed to include any required patches or plug-in software. In your own configurations, you should be familiar with the following topics and which prerequisite you need to satisfy. See the SunScreen manuals for specific information on:
-
Using the Netscape NavigatorTM browser for administration
-
Preparing for installation
-
Choosing a certificate
-
Dedicating interfaces.
For the purpose of these configuration examples, addresses starting with 192.168 are considered legal, routable, IP addresses, while addresses starting with 10.0 are considered illegal IP addresses. All networks shown assume a class C (255.255.255.0) subnet mask. In a real-life configuration, you would replace these IP addresses with your own addresses.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
