Configuring PPP
This section explains how to configure Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) with the ChorusOS product standard interface and drivers. It assumes the serial line or modem is already physically connected. On some platforms, a unique serial line is used both for the console (accessed through tip), and for PPP. At boot time, the serial line connector must be connected to the host tip line.
Note -
Systems often have two IP addresses: one for Ethernet, one for PPP.
This document differentiates between Ethernet Internet addresses and PPP addresses. As you read, be aware that hostname refers to the Ethernet hostname corresponding to the Ethernet IP address, and that host_PPP refers to the hostname corresponding to the PPP address.
PPP as implemented in this version of the ChorusOS operating system handles IP traffic in a different way to previous releases of the ChorusOS operating system. The entire process is described in this chpater in detail but can be summarized as follows:
-
First, run pppstart, a daemon that listens for requests for connection.
-
Next, use the pppd command to enable rsh connection to a specific serial line.
-
When finished with a PPP connection, you may close it using the pppclose command.
-
Finally, disable PPP services altogether using the pppstop command.
Figure 11-1 IP Traffic--PPP Only
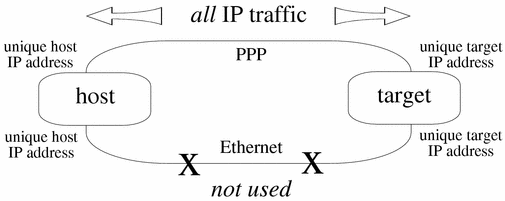
In order to make sure the Ethernet interface can still be used for IP traffic, use different IP addresses for Ethernet and IP.
Figure 11-2 IP Traffic--Both Ethernet and PPP
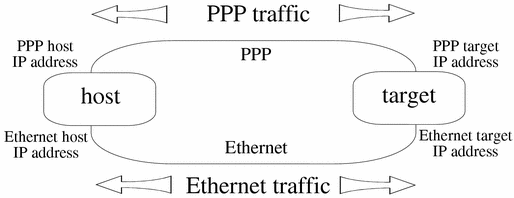
It is strongly recommended for this release that you use different IP addresses for PPP and Ethernet.
As shown above, if each system has only one IP address, when an ifnet interface is set up between target_PPP and host_PPP, all traffic to host_PPP is routed through target_PPP. In other words, all IP traffic passes through the serial line.
Enabling PPP Services
Enabling PPP services involves using the pppstart process. You can choose to enable PPP services either automatically at boot time, or manually, via the command line.
Enabling PPP at Boot Time by Including pppstart in the System Image
-
Change to the directory where you build system images:
host% cd build_dir
-
Use the hints in the table below to set system image features and tunables:
Set...
Comments
VTTY=true
PPP requires virtual ttys.
PPP=true
iom.nfs.rsize=1024
Optimizing NFS read and write buffer sizes for use with PPP by setting them to a maximum of 1024
iom.nfs.wsize=1024
host% configurator -set VTTY=true
host% configurator -set PPP=true
-
Ensure that both serial lines and network interfaces are available for PPP by including the necessary commands in the conf/sysadm.ini file that you build into the system image. For example:
# set umask to 0 during system configuration umask 0 # Build the various interfaces you need using the mkdev command. # All interfaces require a unit number. For bpf and tty, this number also # to the device minor. Thus: # mkdev tty 0 /pci/pci-isa/ns16550-2 # corresponds to # mknod /dev/tty01 major 0 # Create the tty interface using the second serial port # because the first is reserved for the tip line mkdev tty 0 /pci/pci-isa/ns16550-2 # rarp needs bpf, again the unit number corresponds to the device minor. mkdev bpf 0 mkdev bpf 1 # Create a PPP interface that is not bound to the tty yet. mkdev ppp 0 # Ethernet # mkdev ifeth 0 /pci/epic100 mkdev ifeth 0 # loopback interface mkdev lo 0 # Create a tty special file mknod /dev/tty01 c 0 0 # Pseudo tty devices, needed for dialup on demand. # mknod /dev/ttyp0 c 5 0 # mknod /dev/ptyp0 c 6 0 # Enable PPP # Requires pppstart in system image # /image/sys_bank/pppstart & pppd /dev/tty01 # Open a PPP line. # Wait for the interface to be up. # ifwait ppp0
See the appropriate document in the ChorusOS 5.0 Target Platform Collection for serial device IDs for other serial line hardware.
-
Start the Ews configuration utility:
host% ews conf/ChorusOS.xml &
-
Include the pppstart process in the system image (see "Embedding the
pppstartprocess into the ChorusOS system image" for information about how to do this). -
(Optional) If you need chat, include the chat process in the system image (see "Embedding the
chatprocess into the ChorusOS system image" for information about how to do this). -
Rebuild the system image.
host% make chorus
-
Copy the system image to the boot server:
host% rcp system_image_name boot_server:/tftpboot
-
Reboot the target system:
host% rsh target reboot
Enabling PPP Manually
-
Make the serial lines and network interfaces available for PPP:
-
Create a tty interface:
host% mkdev tty 0
-
Create a PPP interface:
host% mkdev ppp 0
-
Create a special tty file:
host% mknod /dev/tty01 c 0 0
-
-
Embed the pppstart process into the ChorusOS system image (see "Embedding the
pppstartprocess into the ChorusOS system image"). -
Run the pppstart process:
host% rsh target pppstart &
Opening PPP Lines
Opening an available PPP line involves the built-in C_INIT command, pppd.
Opening a PPP Line Manually
-
Run the built-in
C_INITcommand, pppd, on the target system:
host% rsh target pppd device pppd device:info: Using interface ppp0 pppd device:notice: Connect: ppp0 <--> device pppd device:notice: local IP address local_addr pppd device:notice: remote IP address remote_addr
where device is either /dev/tty01 or /dev/tty02.
See pppd(1M) for details.
Closing PPP Lines
Closing an open PPP line involves using the pppclose command.
Closing a PPP Line Manually
-
Run the built-in
C_INITcommand, pppclose, on the target system:
host% rsh target pppclose device pppd device:info: Terminating on signal 15. pppd device:notice: Connection terminated, connected for 2 minutes pppd device:info: Exit.
where device is either /dev/tty01 or /dev/tty02.
Disabling PPP Services
Disabling PPP services involves using the pppstop command. This kills the pppstop process daemon.
Disabling PPP Services Manually
Run the built-in C_INIT command, pppstop, on the target system:
host% rsh target pppstop |
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
