This chapter tells how to monitor logical domains
by querying the LDoms MIB using tables and scalar MIB variables,
and provides descriptions of the various types of output.
Note - Be sure that you have added the ldom prefix to
table names, objects in the table, and scalar object names when
using the SNMP commands to retrieve data from the LDoms MIB. |
This chapter contains the following sections:
Retrieving LDoms MIB Information
This section shows the information you can retrieve from the
Logical Domains MIB. The information can come in the form of tables
or scalar objects. Both are shown and identified in this section.
Logical Domains Table (ldomTable)
The following table summarizes each logical domain in the
system, including the resource constraints for virtual CPUs, memory,
cryptographic units, and I/O buses.
TABLE 4-1 Logical Domains (ldomTable) Table
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| ldomIndex |
Integer |
Not accessible |
Integer used as an index of the table |
| ldomName |
Display string |
Read-only |
Name of the logical domain |
| ldomAdminState |
Integer |
Read/Write |
Write -
1 (Active) starts the domain
2 (Stopping) stops the domain |
| ldomOperState |
Integer |
Read-only |
Current actual state of the logical domain:
1=Active
2=Stopping
3=Inactive
4=Binding
5=Unbinding
6=Bound
7=Starting |
| ldomNumVCPU |
Integer |
Read-only |
Number of virtual CPUs used. If the logical
domain is in a inactive state, then this is the requested number
of virtual CPUs. |
| ldomMemSize |
Integer |
Read-only |
Amount of virtual memory used. If the
logical domain is in a inactive state, then this is the requested
memory size. |
| ldomMemUnit |
Integer |
Read-only |
Memory unit:
1=KB (kilobytes)
2=MB (megabytes)
3=GB (gigabytes)
4=(bytes)
Default is bytes if the memory unit is missing. |
| ldomNumCrypto |
Integer |
Read-only |
Number of cryptographic (crypto) units
used. If the logical domain is in a inactive state, then this is
the requested number of crypto units. |
| ldomNumIOBus |
Integer |
Read-only |
Number of physical I/O devices used |
LDoms Resource Pool and Scalar
Variables
The following resources can be assigned to logical domains:
Virtual CPU (vcpu)
Memory (mem)
Cryptographic unit (mau)
Virtual switch (vsw)
Virtual network (vnet)
Virtual disk server (vds)
Virtual disk server device (vdsdev)
Virtual disk (vdisk)
Virtual console concentrator (vcc)
Virtual console (vcons)
Physical I/O device (io)
Following are the scalar MIB variables that are used to represent
these resource pools and their properties.
TABLE 4-2 Scalar Variables for CPU Resource Pool
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| CpuRpCapacity |
Integer |
Read-only |
Maximum reservation allowed by the pool,
in CpuRpCapacityUnit |
| CpuRpReserved |
Integer |
Read-only |
Quantity of resources from pool in CpuRpReservedUnit, which
are currently reserved |
| CpuRpCapacityUnit and
CpuRpReservedUnit |
Integer |
Read-only |
Various CPU allocation units:
1=MHz (megahertz)
2=GHz (gigahertz)
Set to 1(MHz) |
TABLE 4-3 Scalar Variables for Memory Resource Pool
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| MemRpCapacity |
Integer |
Read-only |
Maximum reservation allowed by the pool,
in MemRpCapacityUnit |
| MemRpReserved |
Integer |
Read-only |
Quantity of resources from pool in MemRpReservedUnit,
which are currently reserved |
| MemRpCapacityUnit and
MemRpReservedUnit |
Integer |
Read-only |
Various memory allocation units:
1=KB (kilobytes)
2=MB (megabytes)
3=GB (gigabytes)
4= (bytes)
Default set to 4 (bytes) |
TABLE 4-4 Scalar Variables for Crypto Resource Pool
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| CryptoRpCapacity |
Integer |
Read-only |
Maximum reservation allowed by the pool |
| CryptoRpReserved |
Integer |
Read-only |
Quantity of resources from the pool,
which are currently reserved |
TABLE 4-5 Scalar Variables for I/O Bus Resource Pool
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| IOBusRpCapacity |
Integer |
Read-only |
Maximum reservation allowed by the pool |
| IOBusRpReserved |
Integer |
Read-only |
Quantity of resources from the pool that
are currently reserved |
Virtual CPU Table (VcpuTable)
This table describes virtual CPUs belonging to all logical
domains.
TABLE 4-6 Virtual CPU (VcpuTable) Table
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| VcpuLdomIndex |
Integer |
Read-only |
An integer used to index to the ldomTable representing
the logical domain containing the virtual CPU (vcpu) |
| VcpuIndex |
Integer |
Not accessible |
An integer used to index the vcpu in
this table |
| VcpuDeviceID |
Display string |
Read-only |
Identifier of the virtual CPU |
| VcpuOperationalStatus |
Integer |
Read-only |
Various CPU statuses:
1=Unknown
2=Other
3=OK
4=Degraded
5=Stressed
6=Predictive Failure
7=Error
8=Nonrecoverable error
9=Starting
10=Stopping
11=Stopped
12=In service
13=No contact
14=Lost communication
15=Aborted
16=Dormant
17=Supporting entity in error
18=Completed
19=Power mode
Set to 1 (Unknown), because the Logical Domains Manager does
not provide the CPU state. |
| VcpuPhysBind |
Display string |
Read-only |
Physical binding. Contains identifier
of strand (hardware thread) that is assigned to this virtual CPU.
This ID also uniquely identifies the core and chip. |
| VcpuPhysBindUsage |
Integer |
Read-only |
Indicates how many megahertz of the total capacity
of the strand is used for this virtual CPU. For example, if a thread
can run at a maximum of one gigahertz, and only half of that is
allocated to this virtual CPU (that is, 50% of the strand), this
field would have the value of 500. |
Virtual Memory Tables
Memory space seen in a logical domain is referred to as real memory;
that is, virtual memory. Host platform memory space seen by the
hypervisor is referred to as physical memory.
The hypervisor maps blocks of physical memory to form a block of real
memory which is used by a logical domain. For example, a logical
domain that asks for 521 megabytes of real memory can be assigned
by two blocks of 256 megabytes in the host system as physical memory
in the format {physical-address, real-address, size}:
{0x1000000, 0x1000000, 256}, {0x2000000, 0x2000000,256}
Because a logical domain can have up to 64 physical memory
segments assigned to a guest, an auxiliary table is used to hold
each memory segment instead of using the display string which has
a 255-character limit.
Virtual Memory Table (VmemTable)
This table describes properties of virtual memory belonging
to logical domains.
TABLE 4-7 Virtual Memory (VmemTable) Table
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| VmemLdomIndex |
Integer |
Read-only |
An integer used to index to the ldomTable representing the
logical domain containing the virtual memory |
| VmemIndex |
Integer |
Not accessible |
An integer used to index virtual memory
in this table |
| VmemNumberofBlocks |
Integer |
Read-only |
Number of blocks of virtual memory |
Virtual Memory Physical Binding Table (VmemPhysBind)
This is an auxiliary table containing physical memory segments
for all logical domains.
TABLE 4-8 Virtual Memory Physical Binding (VmemPhysBind)
Table
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| VmemPhysBindLdomIndex |
Integer |
Read-only |
An integer used to index to the ldomTable representing
the logical domain containing physical memory segments |
| VmemPhysBind |
Display string |
Read-only |
List of physical memory in the format
{physical-address, real-address, size} that is mapped to this virtual
memory block |
Virtual Disk Tables
A virtual disk service (vds) and the physical
device to which it maps (vdsdev) provides the
virtual disk capability to the Logical Domains 1.0.1 technology.
A virtual disk service exports a number of local volumes (physical
disk or file system). When a virtual disk service is specified,
included are the complete /dev path of the backing
device (vdsdev) and a unique name (volume name)
for the device being added to the service.
One or more disks (or disk slices) or file systems can be
bound to a single disk service. Each disk has a unique name and
volume name. This volume name is used when the disk is bound to
the service. The Logical Domains Manager creates virtual disk clients
(vdisk) from the virtual disk service and its
logical volumes.
Virtual Disk Service (Vds) Table
This table describes virtual disk services for all logical
domains.
TABLE 4-9 Virtual Disk Service (Vds) Table
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| VdsLdomIndex |
Integer |
Read-only |
An integer used to index to the ldomTable representing
the logical domain containing the virtual disk service |
| VdsIndex |
Integer |
Not accessible |
An integer used to index vds in
this table |
| VdsServiceName |
Display string |
Read-only |
Service name for the virtual disk service.
This is the service_name of the ldm add-vds command. |
| VdsNumofAvailVolume |
Integer |
Read-only |
Number of logical volumes exported by
this virtual disk service |
| VdsNumofUsedVolume |
Integer |
Read-only |
Number of logical volumes used (bound)
to this virtual disk service |
Virtual Disk Service Device (VdsDev)
Table
This table describes virtual disk service devices belonging
to all virtual disk services.
TABLE 4-10 Virtual Disk Service Device (VdsDev) Table
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| VdsdevVdsIndex |
Integer |
Read-only |
An integer used to index to the Virtual
Disk Service Table representing the virtual disk service containing the
virtual disk device |
| VdsdevIndex |
Integer |
Not accessible |
An integer used to index the virtual
disk service device in this table |
| VdsdevVolumeName |
Display string |
Read-only |
Volume name for the virtual disk service
device. This is a unique name for the device being added to the virtual
disk service. This name is exported by this virtual disk service
to the clients for adding. This is the volume_name property in the ldm add-vdsdev command. |
| VdsdevDevPath |
Display string |
Read-only |
Path name of the disk device. This is
the device property in the ldm add-vdsdev command. |
Virtual Disk (Vdisk) Table
This table describes virtual disks for all logical domains.
TABLE 4-11 Virtual Disk (Vdisk) Table
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| VdiskLdomIndex |
Integer |
Read-only |
An integer used to index to the ldomTable |
| VdiskVdsDevIndex |
Integer |
Read-only |
An integer used to index to the Virtual
Disk Service Device Table representing the virtual disk service device |
| VdiskIndex |
Integer |
Not accessible |
An integer used to index the virtual
disk in this table |
| VdiskName |
Display string |
Read-only |
Name of the virtual disk. This is the disk-name property in
the ldm add-vdisk command. |
The following diagram shows an example of the relationships
among the virtual disk tables and the Logical Domains Table.
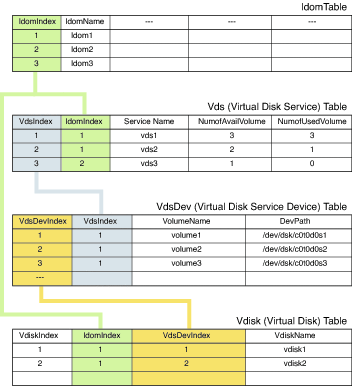
Virtual Network Tables
The virtual network support in Logical Domains software enables
guest domains to communicate with each other and with external hosts
through a physical Ethernet device. The virtual network contains two
main components:
After you create a virtual switch on a service logical domain,
you can bind a physical network device to the virtual switch. After
that, you can create a virtual network device for a logical domain that
uses the virtual switch service to communicate with other logical
domains (connecting to the same virtual switch) and to the outside
world (if a physical device is bound to the virtual switch).
Virtual Switch Service (Vsw) Table
This table describes virtual switch services for all logical
domains.
TABLE 4-12 Virtual Switch Service (Vsw) Table
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| VswLdomIndex |
Integer |
Read-only |
An integer used to index to the ldomTable representing the
logical domain containing the virtual switch service |
| VswIndex |
Integer |
Not accessible |
An integer used to index vsw in
this table |
| VswServiceName |
Display string |
Read-only |
Virtual switch service name |
| VswMacAddress |
Display string |
Read-only |
MAC address used by the virtual switch |
| VswPhysDevPath |
Display string |
Read-only |
Physical device path for the virtual
network switch. This is null when no physical device is bound to
the virtual switch. |
| VswMode |
Integer |
Read-only |
Mode of how the switch operates:
1=Switched (same as Programmed)
2=Promiscuous
3=SwitchedAndPromiscuous (same as Programmed/Promiscuous)
4=Routed |
Virtual Network Device (Vnet) Table
This table describes the virtual network devices for all logical
domains.
TABLE 4-13 Virtual Network Device (Vnet) Table
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| VnetLdomIndex |
Integer |
Read-only |
An integer used to index to the ldomTable representing
the logical domain containing the virtual network |
| VnetVswIndex |
Integer |
Read-only |
An integer used to index to the virtual
switch service table |
| VnetIndex |
Integer |
Not accessible |
An integer used to index vnet in
this table |
| VnetDevName |
Display string |
Read-only |
Virtual network device name. This is
the net-dev property in the ldm add-vnet command. |
| VnetDevMacAddress |
Display string |
Read-only |
MAC address for this network device.
This is the mac-addr property in the ldm add-vnet command. |
Virtual Console Tables
The Logical Domains service domain provides a virtual network
terminal service (vNTS). The virtual network
terminal service provides a virtual console service, called a virtual
console concentrator (vcc), with a range of port
numbers. Each virtual console concentrator has multiple console
groups (vcons), and each group is assigned a
port number. Each group can contain multiple logical domains.
Virtual Console Concentrator (Vcc)
Table
This table describes virtual console concentrators for all
logical domains.
TABLE 4-14 Virtual Console Concentrator (Vcc) Table
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| VccLdomIndex |
Index |
Read-only |
An integer used to index to the ldomTable representing
the logical domain containing the virtual console service |
| VccIndex |
Integer |
Not accessible |
An integer used to index vcc in
this table |
| VccName |
Display string |
Read-only |
Virtual console concentrator name. This
is the vcc_name property in the ldm add-vcc command. |
| VccPortRangeLow |
Integer |
Read-only |
Low number for the range of TCP ports
to be used by the virtual console concentrator. This is the port-range
x property in the ldm add-vcc command. |
| VccPortRangeHigh |
Integer |
Read-only |
High number for the range of TCP ports
to be used by the virtual console concentrator. This is the port-range
y property in the ldm add-vcc command. |
Virtual Console Group (Vcons) Table
This table describes virtual console groups for all virtual
console services.
TABLE 4-15 Virtual Console Group (Vcons) Table
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| VconsIndex |
Integer |
Not accessible |
An integer used to index a virtual group
in this table |
| VconsGroupName |
Display string |
Read-only |
Group name to which to attach the virtual
console. This is the group property in
the ldm set-vcons command. |
| VconsPortNumber |
Integer |
Read-only |
Port number assigned to this group. This
is the port property in the ldm set-vcons command. |
Virtual Console Relationship (VconsVccRel)
Table
This table contains index values to show the intertable relationships
between a logical domain, a virtual console concentrator, and console
groups.
TABLE 4-16 Virtual Console Relationship (VconsVccRel)
Table
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| VconsVccRelVconsIndex |
Integer |
Read-only |
Value of the ldomVconsIndex in
the ldomVconsTable |
| VconsVccRelLdomIndex |
Integer |
Read-only |
Value of the ldomIndex in
the ldomTable |
| VconsVccRelVccIndex |
Integer |
Read-only |
Value of the ldomVccIndex in
the ldomVccTable |
FIGURE 4-2 shows an example of
the relationships among the virtual console tables and the Logical
Domains Table.
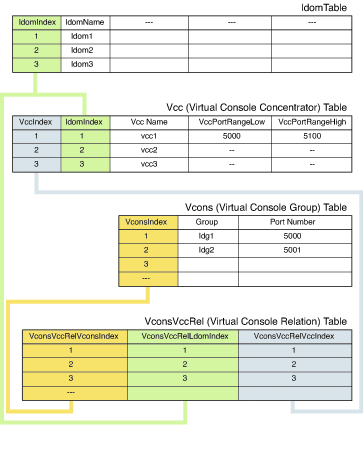
Other Scalar Variables and Tables
This section describes the following other scalar variables
and tables provided by the LDoms MIB:
Scalar Variables for
Logical Domain Version Information
Environment Variables Table
Cryptographic Units Table
I/O Bus Table
Scalar Variables for Logical Domain Version Information
The Logical Domains Manager protocol supports logical domains
versions. The version consists of both a major and minor number.
The Logical Domain MIB has scalar variables to describe the logical
domain version information.
TABLE 4-17 Scalar Variables for Logical Domain Version Information
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| VersionMajor |
Integer |
Read-only |
Major version number |
| VersionMinor |
Integer |
Read-only |
Minor version number |
Environment Variables (EnvVars)
Table
This table contains the OpenBoot PROM
environment variables of all logical domains.
PROM
environment variables of all logical domains.
TABLE 4-18 Environmental Variables (EnvVars) Table
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| EnvVarsLdomIndex |
Integer |
Read-only |
An integer used to index to the ldomTable representing
the logical domain containing the environmental variables |
| EnvVarsIndex |
Integer |
Not accessible |
Integer for an index of the table |
| EnvVarsName |
Display string |
Read-only |
Name of the OpenBoot PROM variable |
| EnvVarsValue |
Display string |
Read-only |
Value of the OpenBoot PROM variable |
Cryptographic Units Table (CryptoTable)
This table describes the cryptographic (crypto) units belonging
to all logical domains:
TABLE 4-19 Cryptographic Units (CryptoTable) Table
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| CryptoLdomIndex |
Integer |
Read-only |
An integer used to index to the ldomTable representing the
logical domain containing the cryptographic unit |
| CryptoIndex |
Integer |
Not accessible |
An integer used to index the cryptographic
unit in this table |
| CryptoCpuSet |
Display string |
Read-only |
List of CPUs that is mapped to MAU-unit cpuset.
For example, {0, 1, 2, 3} |
Input/Output Bus Table (IOBusTable)
This table describes physical I/O devices, PCI buses, belonging
to all logical domains.
TABLE 4-20 Input/Output Bus (IOBusTable) Table
| Name |
Data Type |
Access |
Description |
| IOBusLdomIndex |
Integer |
Read-only |
An integer used to index to the ldomTable representing the
logical domain containing the I/O bus |
| IOBusIndex |
Integer |
Not accessible |
An integer used to index the I/O bus
in this table |
| IOBusDevName |
Display string |
Read-only |
Physical I/O device name |
| IOBusDevPath |
Display string |
Read-only |
Physical I/O device path |
 Retrieve a single MIB object
using the snmpget(1M) command:
Retrieve a single MIB object
using the snmpget(1M) command:

 PROM
environment variables of all logical domains.
PROM
environment variables of all logical domains.