Address Space Display Layout
The Address Space display (see Figure 2-8) is laid out in rows and columns that are made up of individual squares (pages) or rectangles (segments). The rows and columns are numbered to describe their address in memory. Gaps (shown as white space) represent a region of the address space that was not used by the application.
Figure 2-8 Address Space Display
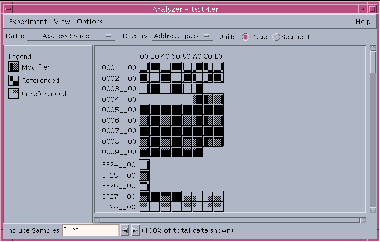
Sun systems use either 4-Kbyte or 8-Kbyte pages. The address of a page is a multiple of 0x1000 (4 Kbytes in hexadecimal) or 0x2000 (8 Kbytes in hexadecimal).
To verify the page size of your system, go to a prompt and type:
% pagesize
The pagesize command returns the page size in bytes:
-
4096 (4-Kbyte pages)
-
8192 (8-Kbyte pages)
If the page size is 4 Kbytes, the number of pages per row is 16. If the page size is 8 Kbytes, the number of pages per row is 8.
You can determine the address of a page by combining the hexadecimal values of the row and column that contains the page. For example, if the page you are examining is in the fourth row (0004_ _00) and the third column (20), then the address of that page is 00042000.
To view memory units at various levels of granularity in the Address Space display, select Page or Segment in the Unit type area.
Selected pages and segments are shadowed and raised to the left. If you keep the right mouse button pressed down over a selected page, the segment containing that page is also displayed and shadowed; likewise, if you keep the right mouse button pressed down over a selected segment, the pages contained within that segment are also displayed and selected.
To view information about the properties of a selected page or segment, choose View Show Details to open either the Page Properties or Segment Properties dialog, which displays the following information:
-
Address
-
Size of the page or size range of the segment in bytes
-
Functions contained in the page or segment
-
Name of the segment
To select which samples to include in the Address Space display, you can:
-
Type sample numbers directly into the Includes Samples text field: separate numbers with commas (1,3,6), and define ranges using a hyphen (1-6).
-
Select the columns containing those samples while still in the Overview display.
-
Choose either View Select or View Select None while still in the Overview display to include or exclude all samples in the experiment.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
