Editing a Configuration Template
Copy the applicable template to /opt/SUNWsma/sci_config.hpc. For example, to create a configuration file for the two-node striped topology,
# cd /opt/SUNWsma # cp /opt/SUNWhpc/bin/Install_Utilities/config_dir/sma2-2stripes.hpc sci_config.hpc |
Use the sma4-2stripes.hpc template for creating a three-node, striped configuration.
Next, edit sci_config.hpc. Every template type is organized into eight sections. Instructions for editing each section are provided below.
Section 1 - Cluster Configuration Type
Section 1 asks you to specify the type of cluster you have; you are given the options: SC (Sun Cluster) or HPC. Enter HPC, as follows:
Cluster is configured as = HPC
SC is not a valid entry for clusters running Sun HPC ClusterTools software.
Section 2 - Host Names
List all of the nodes in the cluster by replacing <host_namen> placeholders with the host names of the cluster's nodes. For example, if your cluster contains the nodes: node3, node4, node5, and node6, Section 2 should look like this:
HOST 0 = node3 HOST 1 = node4 HOST 2 = node5 HOST 3 = node6
The nodes can be listed in any order.
Section 3 - Number of Switches
Specify the number of SCI switches in the cluster. This will be determined by which network topology you implement, as follows:
-
Two-node cluster - either nonstriped or striped, set
Number of Switches in cluster = 0
-
Three- or four-node cluster - nonstriped, set
Number of Switches in cluster = 1
-
Three- or four-node cluster - striped, set
Number of Switches in cluster = 2
Section 4 - Number of Direct Links
Specify the number of unswitched node-to-node connections your cluster has. Again, this will depend on which topology you implement, as follows:
-
Two-node cluster - nonstriped, set
Number of Direct Links in cluster = 1
-
Two-node cluster - striped, set
Number of Direct Links in cluster = 2
-
Three- or four-node cluster - either nonstriped or striped, set
Number of Direct Links in cluster = 0
Section 5 - Number of Ring Connections
Ring connections are not supported by Sun HPC ClusterTools 3.0 software. Therefore, always specify
Number of Rings in cluster = 0
Section 6- Adapter Information
List all SCI adapters in the cluster and describe the connection details for each.
Use a separate line for each adapter description. The format for describing unswitched connections is
host n :: adp n is connected to = link n :: endpt n
When no switch is used, an adapter (adp) is connected to a particular endpoint (endpt n) on a particular channel (link n). See Figure 3-2 and Figure 3-3.
Each adapter has its own endpoint. That is why two different endpoints are shown on one link.
Figure 3-2 Two-Node Nonstriped Configuration
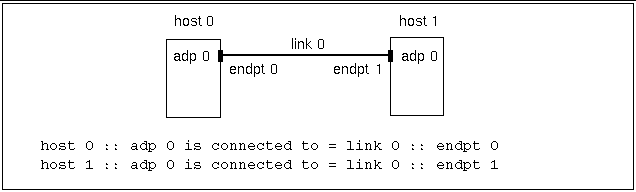
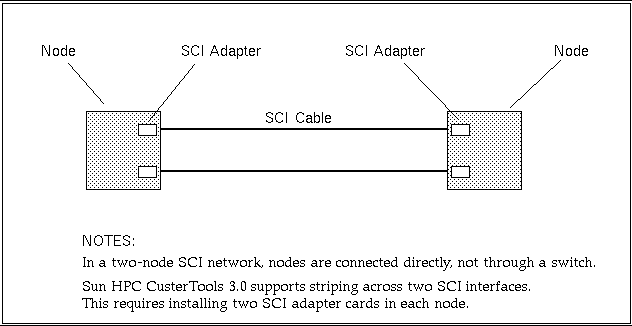
Figure 3-3 Two-Node, Striped Configuration
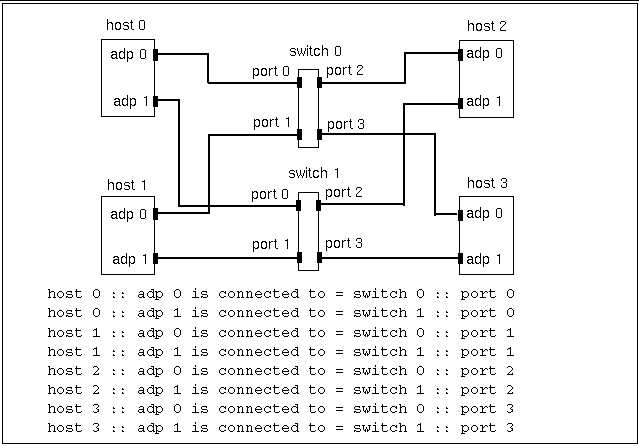
The format for describing switched connections is slightly different.
host n :: adp n is connected to = switch n :: port n
Here, an adapter is connected to port n of switch n. Figure 3-4 through Figure 3-7 show examples of this format.
Figure 3-4 Three-Node, Nonstriped Configuration
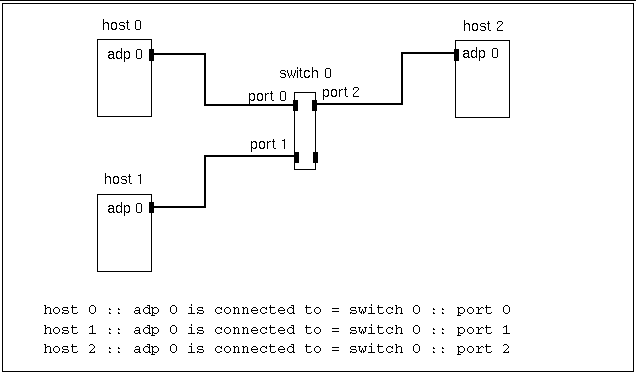
Figure 3-5 Three-Node, Striped Configuration
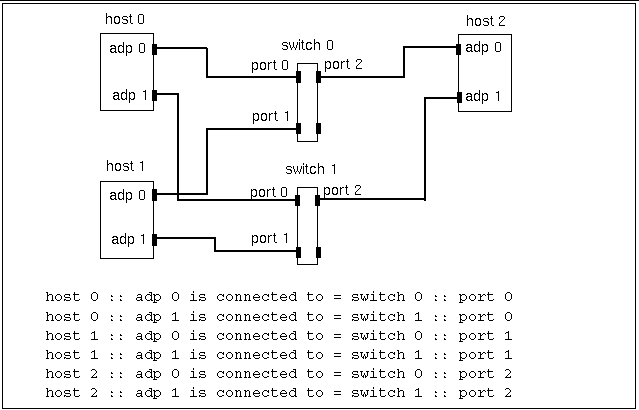
Figure 3-6 Four-Node, Nonstriped Configuration
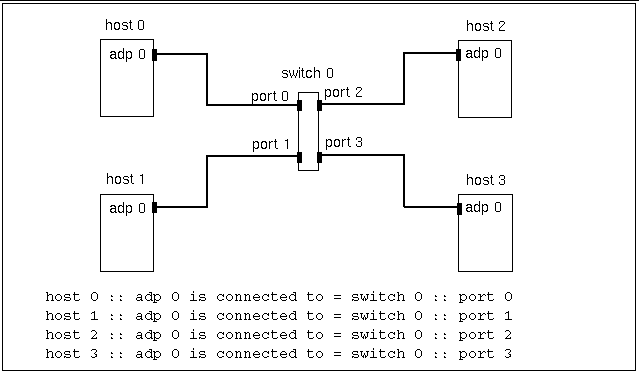
Figure 3-7 Four-Node, Striped Configuration
Adapter ID values are assigned automatically by the device driver. Initially, the device driver assigns ID 0 to the adapter installed in the lowest-numbered SBus slot, ID 1 to the adapter in the next higher-numbered slot, and so forth. ID value assignments are always consecutive, even if the adapters are not installed in adjacent slots. Consequently, if adapter cards are not installed in adjacent slots, adapter ID values do not necessarily correspond to SBus slot numbers.
Once an ID value is assigned, it will not be reassigned, even if the adapter to which it was originally assigned is removed.
Because a ID values do not necessarily correspond to SBus slot numbers, the adp n values that you assign in the sci_config.hpc file may not match the actual ID assignments made by the device driver. For this reason, you may need to revise this adapter connection description (that is, the contents of Section 7) to match the actual adapter connections.
This is why you were advised to make the temporary map of the physical network layout. Instructions for ensuring that the sci_config.hpc file matches the actual adapter ID values are provided in "Compare sm_config Output With Contents of sci_config.hpc"
Section 7 - Network IP Addresses
Specify the first three octets of the IP address of each link or switch. For example, for a two-node, striped configuration,
Network IP address for Link 0 = 204.71.29 Network IP address for Link 1 = 204.71.15
An example of a four-node, nonstriped configuration might be
Network IP address for Switch 0 = 204.101.30
Section 8 - Netmask Value
Specify the netmask to be used for the private SCI subnet. For example,
Netmask = e0
This netmask value will support up to eight subnets with up to 30 hosts per subnet.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
