The get_ci_status Command
You can use the results of the get_ci_status command to troubleshoot clusters that have SCI switches. For example, for the configuration in Figure 6-2, if the get_ci_status command is used on interconn1, a typical output would be:
# /opt/SUNWsma/bin/get_ci_status sma: sci #0: sbus_slot# 1; adapter_id 8 (0x08); ip_address 1; switch_id# 0; port_id# 0; Adapter Status - UP; Link Status - UP sma: Switch_id# 0 sma: port_id# 1: host_name = interconn2; adapter_id = 72; active | operational sma: port_id# 2: host_name = interconn3; adapter_id = 136; active | operational sma: port_id# 3: host_name = interconn4; adapter_id = 200;inactive|inoperational # |
In this example, the line
sma: port_id# 3: host_name = interconn4; adapter_id = 200;inactive|inoperational |
indicates that the path between SCI switch 0, port 3 and interconn4 is inactive and not operational.
Figure 6-2 Typical Four-Node Configuration with an SCI Switch
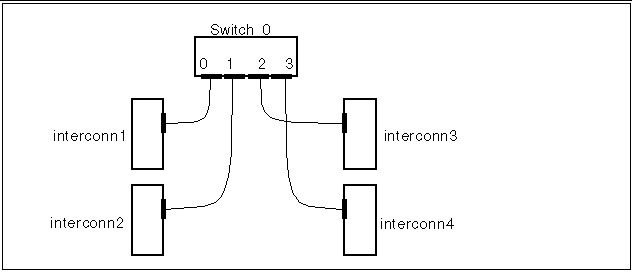
In this instance, if the get_ci_status command were run on all four nodes, and if the same path was inactive and inoperative between SCI switch 0, port 3 and interconn4, it is more than likely that either the SCI switch 0, port 3, the cable, or the interconn4 host adapter is faulty.
However, if the get_ci_status command indicates that the same path is inactive and inoperative for one node only, such as in the instance of interconn1, then it is more than likely that either the interconn 1 host adapter, the cable, or SCI switch 0, port 0 is faulty.
Note that some aspects of the get_ci_status command output, such as host names, will vary according to your configuration.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
