Disk Pathgroup
A disk pathgroup, as illustrated in Figure 1-7, consists of two physical paths leading to the same disk array. When a physical path is part of a pathgroup, it is called an alternate path. An alternate path to a disk can be uniquely identified by the pln port or sf port that the alternate path uses. Only one alternate path at a time handles disk I/O. The alternate path that is currently handling I/O is called the active alternate.
Note that whereas a metadisk provides a means for you to access a disk (in your scripts and programs), a disk pathgroup provides a means for you to manipulate the path to that disk (when you run AP commands). For example, to perform a switch operation (that is, change the active alternate from one alternate path to another), you reference a disk pathgroup within an apconfig(1M) command.
One of the alternate paths is designated as the primary path. The primary path is initially the active alternate. Although the active alternate changes when you perform a switch operation, the primary path remains constant. You reference a disk pathgroup by specifying the pln port (for example, pln1) or sf port (for example, sf1) that corresponds to the primary path. (For information about determining the pln or sf port name, see "Device Nodes for Metadisks".)
For example, Figure 1-7 shows the results of using the apconfig command to switch the active alternate of a disk pathgroup.
Figure 1-7 Disk Pathgroup
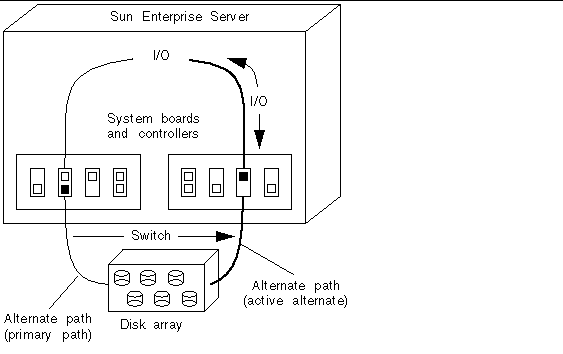
You reference a disk pathgroup (for example, to switch from one path to another) by specifying the primary path, for example, apconfig-P pln2-apln9.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
