The Purpose of Alternate Pathing
Alternate Pathing (AP) supports high availability of I/O controllers--the hardware components that reside on system boards and enable the Sun Enterprise server to communicate with I/O devices such as disks and networks. With AP, each I/O device connects to two I/O controllers.
Figure 1-1 Alternately Pathed I/O Device
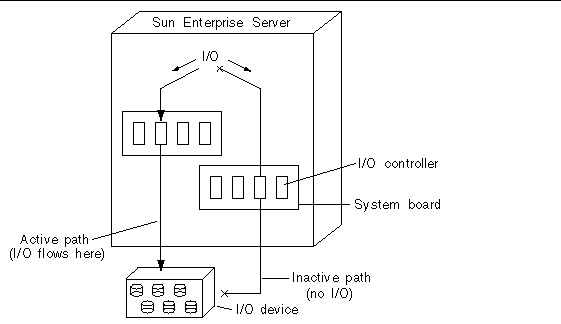
The I/O controllers are part of two separate electrical pathways to the I/O device, known as alternate paths. AP enables you to set up and use alternate paths on the Sun Enterprise servers.
There are two purposes for AP. Perhaps the most obvious purpose is to help protect against I/O controller failures. With AP, if one I/O controller fails, you can switch to the alternate controller.
Figure 1-2 Switching Paths After an I/O Controller Failure
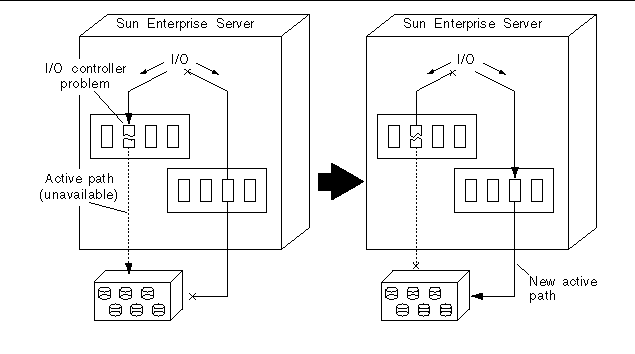
For disk controllers, this switch occurs automatically whenever a path failure is detected during normal operation. For network controllers, you must manually switch paths (using a single AP command).
The second purpose of AP is to support Dynamic Reconfiguration (DR). DR is used to logically attach and detach system boards from the operating system without having to halt and reboot. For example, with DR you can detach a board from the operating system, physically remove and service the board, and then re-insert the board and attach it to the operating system again. You can do all of this without halting the operating system or terminating any user applications.
If you want to detach a board that is connected to an I/O device, and if that I/O device is alternately pathed, you can first use AP to redirect the I/O flow to a controller on a different board. You can then use DR to detach the system board without interrupting the I/O flow. On the Sun Enterprise 10000 server, the switch occurs automatically during the DR operation (for both disk and network devices), assuming a viable alternate controller exists on another board. Figure 1-3 shows the relationship between AP and DR.
Figure 1-3 Switching Paths for a DR Detach Operation
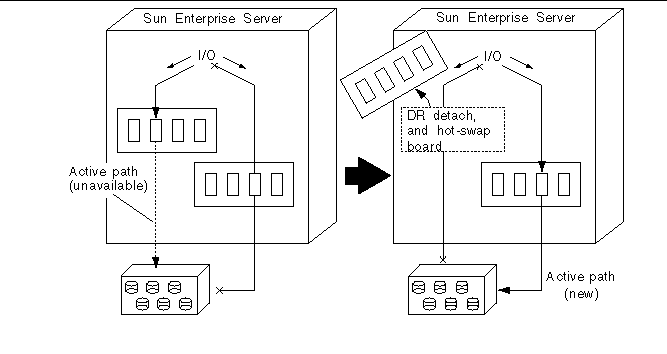
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
