| C H A P T E R 12 |
|
Sun Mainframe Administration Tool (Sun MAT) |
This chapter describes the Sun MAT software. It includes the following topics:
The Sun MAT software is designed to provide remote administrative access to one or more Sun MTP regions running on one or more systems distributed throughout a network. The tool is comprised of three components:
Each system hosting one or more Sun MTP regions must also host a running instance of Sun MAA to provide access to those regions. Sun MAT can run anywhere in the network.
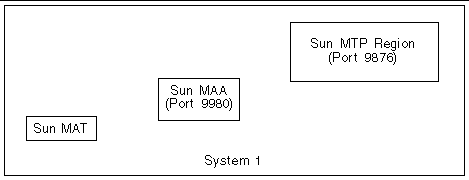
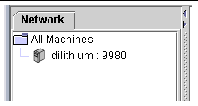
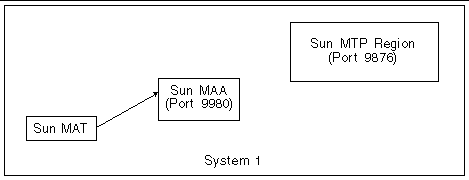
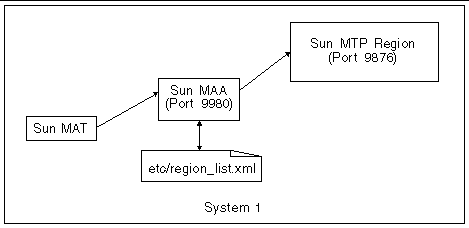
In a simple environment where one system has one region to be administered, the three components (Sun MAT, Sun MAA, and Sun MTP) are all co-located, as shown in the following figure:
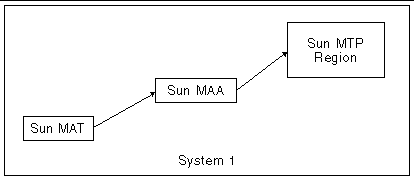
The following figure illustrates a more complex environment that has multiple regions running on multiple systems, all monitored from a single point.
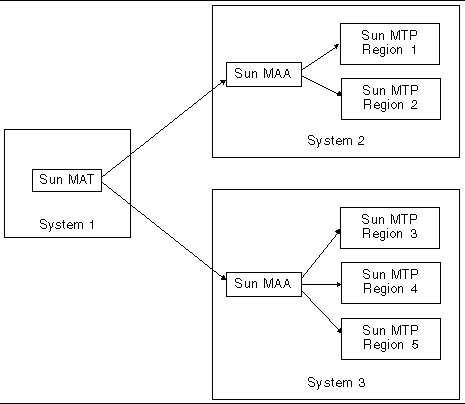
It is also possible for more than one administrator to run Sun MAT concurrently and access the same regions. This is illustrated in FIGURE 12-3.
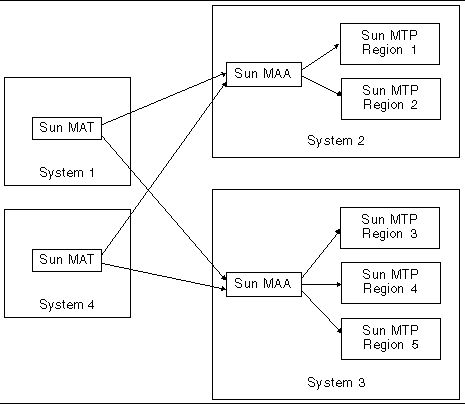
Any Sun MTP regions that are to be remotely administered through Sun MAA must be at Release 8.0.0 or later.
Sun MAA is a Java application that requires Java 2 Standard Edition (J2SE) version 1.4. Before attempting to start Sun MAA, J2SE 1.4 must be installed on the system where you plan to run Sun MAA.
J2SE version1.4 must also be defined on the $PATH of the user that will start Sun MAA. To test whether J2SE 1.4 is properly defined, type the following commands. The output should be as shown:
$ which java /usr/java1.4.0/bin/java $ java -version java version "1.4.0" Java(TM) 2 Runtime Environment, Standard Edition (build 1.4.0-b92) Java HotSpot(TM) Client VM (build 1.4.0-b92, mixed mode) |
The location of J2SE might be different on your system. Contact your system administrator to determine if and where J2SE 1.4 is installed. If J2SE 1.4 is not installed on your system, it can be downloaded from:
Sun MAT is also a Java application, and can run anywhere that a J2SE 1.4 runtime is available.
This section describes how to install the Sun MAA and Sun MAT on the various platforms on which they run.
Sun MAA is distributed as a tar file named MAA1.0.0.zip. It should be installed on each system on which there are Sun MTP regions that you want to administer.
Follow these guidelines when installing Sun MAA:
|
1. Create the top-level installation directory:
2. Change to the installation directory:
3. Extract the tar archive. For example:
Refer to the unzip(1) man page for information on command options..
This will create the following directory structure:
/pkgs/maa/MAA1.0.0 /pkgs/maa/MAA1.0.0/bin /pkgs/maa/MAA1.0.0/etc /pkgs/maa/MAA1.0.0/lib /pkgs/maa/MAA1.0.0/lib/dependencies |
MAA1.0.0 indicates the version of Sun MAA that you have installed.
Sun MAT provides an administrator with a graphical user interface (GUI) to remotely administer Sun MTP regions. It is provided in three distribution formats appropriate for different platforms. The distribution files are named as follows:
Choose the installation file most appropriate for your platform.
Follow these guidelines when installing Sun MAT:
1. Create the top-level installation directory:
2. Change to the installation directory:
where tar-file-location specifies the location of the MAT1.0.0.tar file.
This will create the following directory structure:
/pkgs/mat/MAT1.0.0 /pkgs/mat/MAT1.0.0/bin /pkgs/mat/MAT1.0.0/doc /pkgs/mat/MAT1.0.0/doc/images /pkgs/mat/MAT1.0.0/lib /pkgs/mat/MAT1.0.0/lib/dependencies |
MAT1.0.0 indicates the version of Sun MAT that you have installed.
For 32-bit Microsoft Windows platforms, Sun MAT is supplied as a self-installing InstallShield executable. This executable contains an integrated J2SE 1.4.0 runtime.
 Execute the MAT1.0.0.exe file and follow the on-screen instructions.
Execute the MAT1.0.0.exe file and follow the on-screen instructions.
Sun MAT can also be installed and run on other platforms supporting J2SE 1.4.
1. Create a directory or folder for the Sun MAT product.
2. Unpack the zip archive MAT1.0.0.zip to the directory you just created.
This will create the following directory structure:
|
Note - There is no bin directory for this type of installation. |
MAT1.0.0 indicates the version of Sun MAT that you have installed.
Before starting Sun MAA, you must decide on a port number on which the agent will listen, and you must choose the userid that will start the agent.
When Sun MAA starts, it listens for Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI) calls from instances of the Sun MAT, by listening on a TCP/IP port. This port is 9980 by default. If you want to use a different port number, you can edit the sunmaa startup script, which is located in the bin directory of the Sun MAA installation. Instructions on editing the script are provided in the script itself.
Sun MAA should be started as the same UNIX user that was used to install it. This is usually the same UNIX user that is used to run each of the Sun MTP regions on the system.
In more complex environments, however, several regions can exist, each running as a different UNIX user. In this case, use the following guidelines to decide what UNIX user should run the agent:
/pkgs/maa/MAA1.0.0/etc/region_list.xml
|
 Execute the sunmaa shell script, which is located in the Sun MAA bin directory:
Execute the sunmaa shell script, which is located in the Sun MAA bin directory:
Output similar to the following will be displayed on the screen:
MAA: Starting MAAMaster: control file name is <etc/region_list.xml> MAA: started RMI connector on port 9980 |
The etc/region_list.xml control file is the file in which Sun MAA stores information about each region for which it is responsible. Each region that you want to administer must be registered with the agent running on that system. See Registering a Region With Sun MAA.
This section describes how to start Sun MAT on the different platforms on which it is supported.
|
1. Verify that the J2SE 1.4.0 runtime is installed on the system and its location is defined in your PATH environment variable.
See Prerequisites.
2. Execute the sunmat shell script, which is located in the Sun MAT bin directory:
The Sun MAT GUI starts. See FIGURE 12-4.

|
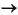 Programs
Programs  Sun MAT 1.0.0
Sun MAT 1.0.0  Administration Tool
Administration Tool
The Sun MAT GUI starts. See FIGURE 12-4.
|
1. Verify that the J2SE 1.4.0 runtime is installed and available on your system.
2. Run the executable JAR file supplied in the lib directory of the Sun MAT installation. Depending on your system, use one of the following methods:
The Sun MAT GUI starts. See FIGURE 12-4.
This section describes the procedures you must perform to access each of the regions you want to administer.
|
See Configuring and Starting Sun MAA.
See Starting Sun MAT.
3. Configure Sun MAT to access each system on which an agent (Sun MAA) is running.
See Configuring Sun MAT to Access an Agent System.
4. Register each region running on a system with the agent (Sun MAA) running on that system.
See Registering a Region With Sun MAA.
The example in this section uses a simple configuration like the one shown in the following figure. The procedure also applies to complex configurations.
In this example Sun MAT is running on the same system as Sun MAA, although it need not be. Sun MAA has been started listening on the default port of 9980.
 [ D ]
[ D ]
|
1. Make sure Sun MAA is started.
See Configuring and Starting Sun MAA
2. Make sure Sun MAT is started and the GUI is displayed.
See Starting Sun MAT.
3. On the GUI menu, select File 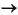 Add Machine.
Add Machine.
This option will make an agent known to Sun MAT. See FIGURE 12-6.
a. Type the name of the system on which the agent is running.
b. Verify the port number on which the agent is listening.
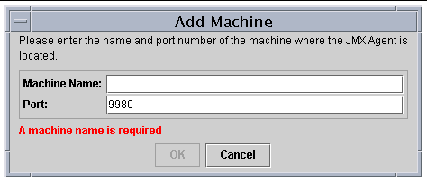
Sun MAT will contact the agent, and a machine entry will be displayed in the tree panel on the left side of the Sun MAT display.
Communication is now established between Sun MAT and Sun MAA, as shown in FIGURE 12-8.
Before a region can be registered with an agent, the region must be started with the unikixadmin process enabled. The unikixadmin server is a daemon process that allows a region to be monitored by Sun MAT.
1. Make sure the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable points to the location of the Java virtual machine (JVM).
2. Start the region using the -X option to unikixmain.
The -X option requires that you specify the port number to be used by unikixadmin. It must be a unique port number. For example:
When the unikixadmin server starts as part of region initialization, a message similar to the following is written to the unikixmain.log file:
The server advertises its startup with a message similar to the following:
2. In the left tree pane, highlight the machine where the region you want to register is located.
3. On the menu, select File 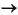 Register Region.
Register Region.
a. Type the name of the region as you want it to display on the screen.
b. Type the fully qualified directory name of the region's $KIXSYS directory.
|
Note - The agent will determine the port number the unikixadmin daemon is listening on by accessing $KIXSYS. |
An entry representing the region will appear beneath the machine name in the left pane of the Sun MAT GUI. You can now use Sun MAT to perform administrative functions on the region.
|
Note - Since the region is directly registered only with its agent, it will immediately become visible to the user of any other instance of SunMAT that has been configured to access the same agent. |
The details about the region are stored by the agent to a local disk file (etc/region_list.xml under the Sun MAA installation directory), so that they will be available even after the agent is stopped and restarted.
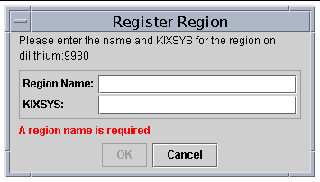
FIGURE 12-11 shows a region that is accessible to Sun MAT.
|
 Double-click the region entry in the left pane.
Double-click the region entry in the left pane.
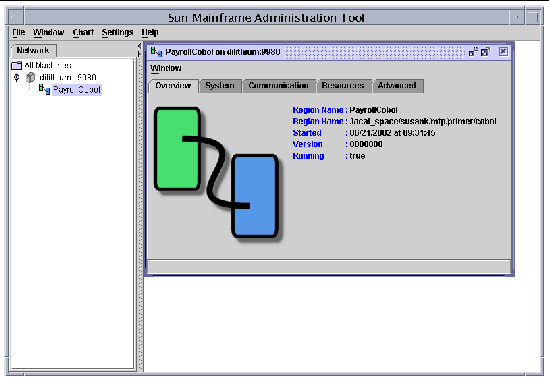
FIGURE 12-12 shows the region's Overview tab.
Refer to the Sun Mainframe Administration Tool User's Guide for information about using the tool.
Copyright © 2004, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.