| Sun Fire T2000 Server Installation Guide
|
|
This chapter includes instructions for booting the Sun Fire T2000 system and for enabling the system controller network management port.
The following topics are discussed:
Powering On the System for the First Time
|
Tip - The serial terminal or a terminal emulator should be connected before you connect the power cables, or you will not see the system messages. The server goes into standby mode and the ALOM-CMT system controller initializes as soon as the AC power cables are connected to the power source.
|

|
Note - If you are not logged in, ALOM-CMT times out after 60 seconds and reverts to the system console. For more information, refer to the Sun Fire T2000 Server Advanced Lights Out Management (ALOM) Guide.
|
The system controller runs on the 3.3v standby voltage. As soon as AC power is connected to the system, the system controller powers on, runs diagnostics, and initializes the ALOM-CMT firmware.
1. If you have not already done so, connect a terminal or a terminal emulator (PC or workstation) to the SC serial management port. Configure the terminal or terminal emulator with these settings:
- 9600 baud
- 8 bits
- No parity
- 1 Stop bit
- No handshaking
|
Note - When you power on the server for the first time and you do not have a terminal or terminal emulator (PC or workstation) connected to the SC serial management port, you will not see system messages. The display times out and disappears after about 60 seconds.
|
2. Turn on the terminal or terminal emulator.
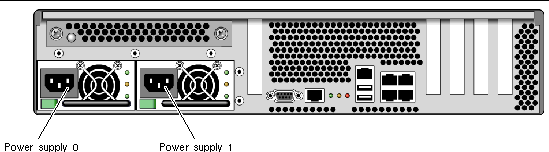
3. Connect the AC power cables to Power Supply 0 and Power Supply 1, and watch the terminal for system messages.
FIGURE 3-1 Rear Panel Power Connectors
After the system controller boots, the system controller login prompt is displayed on the serial console. The following example shows a partial output from the system controller boot sequence leading to the login prompt.
CODE EXAMPLE 3-1 Sample System Controller Output
ALOM POST 1.0
Dual Port Memory Test, PASSED.
TTY External - Internal Loopback Test
TTY External - Internal Loopback Test, PASSED.
TTYC - Internal Loopback Test
TTYC - Internal Loopback Test, PASSED.
TTYD - Internal Loopback Test
TTYD - Internal Loopback Test, PASSED.
....................
Full VxDiag Tests - PASSED
Status summary - Status = 7FFF
VxDiag - - PASSED
POST - - PASSED
LOOPBACK - - PASSED
I2C - - PASSED
EPROM - - PASSED
FRU PROM - - PASSED
ETHERNET - - PASSED
MAIN CRC - - PASSED
BOOT CRC - - PASSED
TTYD - - PASSED
TTYC - - PASSED
MEMORY - - PASSED
MPC885 - - PASSED
Please login:
|
Enabling the System Controller Network Management Port
The system controller network management port is not operational until you configure network settings for the system controller. Configure the system controller in this order:
1. After the system controller boots, access the ALOM-CMT command line interface through the serial management port. See To Log Into the System Controller Using the Serial Management Port.
2. Configure the system controller. See To Configure the System Controller Network Management Port.
3. Enable the new values by resetting the system controller. See To Reset the System Controller.
You can now use the SP network management port at any time to access the system controller. See To Log Into the System Controller Using the Network Management Port.
Logging Into the System Controller
If you are powering on the system for the first time after installation, use the system controller serial port to power on the system and run POST. See To Log Into the System Controller Using the Serial Management Port.
If the network management port has already been configured, you can use it instead of the serial management port. See To Log Into the System Controller Using the Network Management Port.
 To Log Into the System Controller Using the Serial Management Port To Log Into the System Controller Using the Serial Management Port
|
After the system controller boots you can access the ALOM-CMT command line interface to configure and manage the system.
The sc prompt is displayed at the first time the system controller is booted. The default configuration provides an ALOM-CMT user account called admin. There is no default password, so you must create a password using the system controller (sc) password command.
1. If this is the first time the system has been powered on, use the password command to set the admin password.
.........................
TTYD - - PASSED
TTYC - - PASSED
MEMORY - - PASSED
MPC885 - - PASSED
sc> password
password: Changing password for admin
Setting password for admin.
New password: new_password
Re-enter new password: new-password
sc>
|
After the admin password has been set, on subsequent reboots, the sc login prompt is displayed.
2. Enter admin for the login name followed by your password.
TTYD - - PASSED
TTYC - - PASSED
MEMORY - - PASSED
MPC885 - - PASSED
Please login: admin
Please Enter password: password
(Press Return twice)
sc>
|
 To Configure the System Controller Network Management Port To Configure the System Controller Network Management Port
|
To access the system controller using the network for the first time, you must first configure the SC network management port through the SC serial management port.
Set these network parameters according to the specific details of your network configuration:
- netsc_ipnetmask - Netmask for the system controller subnet
- netsc_ipaddr - IP Address of the system controller
- netsc_ipgateway - IP address of the gateway for the subnet
- if_network - Specified whether the SC is on the network or not
To configure these parameters you must use the setsc command. The usage is:
setsc parameter
1. Set the netmask for the system controller.
sc> setsc netsc_ipnetmask 255.255.255.0
|
This example uses 255.255.255.0 to set the netmask. Your network environment subnet might require a different netmask. Use a netmask number most appropriate to your environment.
2. Set the IP address for the system controller.
sc> setsc netsc_ipaddr service-processor-IPaddr
|
3. Set the IP address for the system controller gateway.
sc> setsc netsc_ipgateway gateway-IPaddr
|
4. Set the if_network parameter to true.
sc> setsc if_network true
|
5. Use the showsc command to verify that the parameters were set correctly.
The showsc command displays all the configuration parameters and their values, as listed in TABLE 3-1.
|
Note - The highlighted parameters must be set according to the specific details of your network configuration for the network management port to function properly.
|
TABLE 3-1 Sample Configuration Parameter Settings
|
parameter
|
value
|
|
if_network
|
true
|
|
if_modem
|
false
|
|
if_emailalerts
|
false
|
|
netsc_dhcp
|
false
|
|
netsc_ipaddr
|
xxx.xxx.xx.xx
|
|
netsc_ipnetmask
|
255.255.255.0
|
|
netsc_ipgateway
|
xxx.xxx.xx.xxx
|
|
mgt_mailhost
|
|
|
mgt_mailalert
|
|
|
sc_customerinfo
|
|
|
sc_escapechars
|
#.
|
|
sc_powerondelay
|
false
|
|
sc_powerstatememory
|
false
|
|
sc_clipasswdecho
|
true
|
|
sc_cliprompt
|
sc
|
|
sc_clitimeout
|
0
|
|
sc_clieventlevel
|
2
|
|
sc_backupuserdata
|
true
|
|
diag_trigger
|
power-on-reset
|
|
diag_verbosity
|
max
|
|
diag_level
|
max
|
|
diag_mode
|
normal
|
|
sys_autorunonerror
|
false
|
|
ser_baudrate
|
9600
|
|
ser_parity
|
none
|
|
ser_stopbits
|
1
|
|
ser_data
|
8
|
|
netsc_enetaddr
|
xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
|
|
sys_enetaddr
|
xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
|
 To Reset the System Controller To Reset the System Controller
|
After all of the configuration parameters are set, you must reset the system controller for the new values to take affect.
 Issue the resetsc command.
Issue the resetsc command.
You are prompted to confirm that you want to reset the system controller. Reply y when prompted.
sc> resetsc
Are you sure you want to reset the SC [y/n]? y
User Requested SC Shutdown
|
|
Note - You can specify the -y flag to the resetsc command and bypass the confirmation message.
|
The system controller resets, runs diagnostics, and returns to the login prompt.
ALOM POST 1.0
Dual Port Memory Test, PASSED.
TTY External - Internal Loopback Test
TTY External - Internal Loopback Test, PASSED.
TTYC - Internal Loopback Test
TTYC - Internal Loopback Test, PASSED.
TTYD - Internal Loopback Test
TTYD - Internal Loopback Test, PASSED.
....................
Full VxDiag Tests - PASSED
Status summary - Status = 7FFF
VxDiag - - PASSED
POST - - PASSED
LOOPBACK - - PASSED
I2C - - PASSED
EPROM - - PASSED
FRU PROM - - PASSED
ETHERNET - - PASSED
MAIN CRC - - PASSED
BOOT CRC - - PASSED
TTYD - - PASSED
TTYC - - PASSED
MEMORY - - PASSED
MPC885 - - PASSED
Please login:
|
 To Log Into the System Controller Using the Network Management Port To Log Into the System Controller Using the Network Management Port
|
1. Open a telnet session and connect to the system controller by specifying its network address.
% telnet 129.148.40.30
Trying 129.148.40.30...
Connected to 129.148.40.30.
Escape character is '^]'.
Copyright 2003 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Use is subject to license terms.
Sun(tm) Advanced Lights Out Manager 1.0.11 ()
Please login:
|
2. Login as admin using the password you previously set.
Please login: admin
Please Enter password: password
sc>
|
Using the System Controller for Common Operations
 To Power On the System To Power On the System
|
Powering on the system requires you to use the poweron command at the SC console.
 To initiate the power-on sequence, issue the poweron command.
To initiate the power-on sequence, issue the poweron command.
You will see an sc> alert message on the system console. This indicates that the system has reset.
sc> poweron
SC Alert: Host System has Reset
sc>
|
 To Connect to the System Console To Connect to the System Console
|
Output from POST, OpenBoot, and the Solaris OS is displayed in the system console using the network console on the system controller.
 Execute the console command, and use the -f option to force the console to be attached to your session.
Execute the console command, and use the -f option to force the console to be attached to your session.
Multiple users can be connected to the console, but only one can be attached.
sc> console -f
Enter #. to return to ALOM.
|
 To Perform a Normal System Initialization To Perform a Normal System Initialization
|
After you issue the poweron command, the CPU and memory controllers initialize, and eventually OpenBoot initializes. After a number of system messages, you will see the ok prompt.
The example output below is a small section of the complete output.
Find dropin, Copying Done, Size 0000.0000.0000.1110
Find dropin, (copied), Decompressing Done, Size 0000.0000.0006.06e0 ^Qcpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu cpu vpci mem32base, mem64base, cfgbase: e800000000 e000000000 e900000000
pci /pci@780: Device 0 pci pci
/pci@780/pci@0: Device 0 Nothing there
/pci@780/pci@0: Device 1 pci pci
....................
/pci@7c0/pci@0: Device a Nothing there
/pci@7c0/pci@0: Device b Nothing there
/pci@7c0/pci@0: Device c Nothing there
/pci@7c0/pci@0: Device d Nothing there
/pci@7c0/pci@0: Device e Nothing there
/pci@7c0/pci@0: Device f Nothing there
Probing I/O buses
Sun Fire T200, No Keyboard
Copyright 1998-2004 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.
OpenBoot Ontario FW build_11***PROTOTYPE_BUILD***, 16376 MB memory installed, Serial #51454515.
[firmware obp4.x #0]
Ethernet address 0:3:ba:ce:a1:3d, Host ID: 83112233.
{0} ok
|
To understand the various devices and their path names as represented in the OpenBoot PROM device tree, refer to TABLE 3-2. The table identifies each of the devices, their full path name and their location or NAC name used to identify their physical location.
TABLE 3-2 Map of Devices, OpenBoot Path Names, and Locations
|
OpenBoot Device Path Name
|
Device
|
Location Name
|
|
/pci@780
|
Fire IO Bridge Bus A
|
IOBD/PCIEa
|
|
/pci@780/pci@0
|
PLX 8532 PCI-E Switch A (U0901)
|
IOBD/PCI-SWITCH0
|
|
/pci@780/pci@0/pci@1
|
Intel Ophir GBE Chip (U2401)
|
IOBD/GBE0
|
|
/pci@780/pci@0/pci@8
|
PCI-E Slot 0 (J2100)
|
PCIE0
|
|
/pci@780/pci@0/pci@9
|
LSI 1064-E SAS Controller (U3401)
|
IOBD/SASHBA
|
|
/pci@7c0
|
Fire IO Bridge Bus B
|
IOBD/PCIEb
|
|
/pci@7c0/pci@0
|
PLX 8532 PCI-E Switch B (U1501)
|
IOBD/PCI-SWITCH1
|
|
/pci@7c0/pci@0/pci@1
|
Intel Ophir GBE Chip (U2601)
|
IOBD/GBE1
|
|
/pci@7c0/pci@0/pci@2
|
Intel 41210 Bridge Chip (U2901)
|
IOBD/PCI-BRIDGE
|
|
/pci@7c0/pci@0/pci@2/pci@0
|
PCI-X Slot 0 (J3201)
|
PCIX0
|
|
/pci@7c0/pci@0/pci@2/pci@0
|
PCI-X Slot 1 (J3301)
|
PCIX1
|
|
/pci@7c0/pci@0/pci@2/pci@0,2
|
ULI Southbridge Chip (U3702)
|
IOBD/PCIX-IO
|
|
/pci@7c0/pci@0/pci@8
|
PCI-E Slot 2 (J2202)
|
PCIE2
|
|
/pci@7c0/pci@0/pci@9
|
PCI-E Slot 1 (J2201)
|
PCIE1
|
Booting the Solaris Operating System
The Solaris OS is preinstalled on Sun Fire T2000 servers on the disk in slot 0. The Solaris OS is not configured (that is, the sys-unconfig command was run in the factory). If you boot the system from this disk, you will be prompted to configure the Solaris OS for your environment.
 To Boot the Solaris Operating System To Boot the Solaris Operating System
|
1. At the ok prompt, boot from the disk that contains the Solaris OS.
If you know which disk to boot from, skip Step a and perform Step 2.
a. If you need to determine which disk to boot from, issue the show-disks command at the ok prompt to see the path to the configured disks.
ok show-disks
a) /pci@7c0/pci@0/pci@2/pci@0,2/LSILogic,sas@4/disk
q) NO SELECTION
Enter Selection, q to quit: q
ok
|
2. Type the boot command at the ok prompt.
Use the value from Step 1 to construct the boot command. You will need to append the target to the disk path. In the following example, the system is being booted from disk 0 (zero), so @0,0 is appended to the disk path.
ok boot /pci@7c0/pci@0/pci@2/pci@0,2/LSILogic,sas@4/disk@0,0
Boot device: / pci@7c0/pci@0/pci@2/pci@0,2/LSILogic,sas@4/
disk@0,0
File and args:
Notice: Unimplemented procedure 'encode-unit' in /pci@7c0/pci@0/pci@2/pci@0/LSILogic,sas@4
Loading ufs-file-system package 1.4 04 Aug 1995 13:02:54.
FCode UFS Reader 1.12 00/07/17 15:48:16.
Loading: /platform/SUNW,Ontario/ufsboot
Loading: /platform/sun4v/ufsboot
SunOS Release 5.10 Version /net/spa/export/spa2/ws/pothier/grlks10-ontario:12/01/2004 64-bit
Copyright 1983-2004 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Use is subject to license terms.
DEBUG enabled
misc/forthdebug (159760 bytes) loaded
/platform/sun4v/kernel/drv/sparcv9/px symbol intr_devino_to_sysino multiply defined
...
os-tba FPU not in use
configuring IPv4 interfaces: ipge0.
Hostname: wgs94-181
The system is coming up. Please wait.
NIS domain name is Ecd.East.Sun.COM
starting rpc services: rpcbind keyserv ypbind done.
Setting netmask of lo0 to 255.0.0.0
Setting netmask of bge0 to 255.255.255.0
Setting default IPv4 interface for multicast: add net 224.0/4: gateway wgs94-181
syslog service starting.
volume management starting.
Creating new rsa public/private host key pair
Creating new dsa public/private host key pair
The system is ready.
wgs94-181 console login:
|
 To Reset the System To Reset the System
|
 If it is necessary to reset the system, use the uadmin command.
If it is necessary to reset the system, use the uadmin command.
To simply reset the system, it is not necessary to power the system off and on.
 To Power Cycle the System To Power Cycle the System
|
If a simple reset does not clear a system problem, you can power the system off and on with this procedure.
1. Shut down the Solaris OS.
At the Solaris OS prompt, issue the uadmin command to halt the Solaris OS and to return to the ok prompt.
# uadmin 2 0
WARNING: proc_exit: init exited
syncing file systems... done
Program terminated
ok
|
2. Switch from the system console prompt to the SC console prompt by issuing the #. escape sequence.
3. Using the SC console, issue the poweroff command.
sc> poweroff -fy
SC Alert: SC Request to Power Off Host Immediately.
|
4. Issue the poweron command.
sc> poweron
sc> SC Alert: Host System has Reset
|
5. Reconnect to the system console using the console command.
sc> console -f
Enter #. to return to ALOM.
|
The systems displays various messages, followed by the ok prompt.
| Sun Fire T2000 Server Installation Guide
|
819-2546-11
|
   
|
Copyright © 2006, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.


 To initiate the power-on sequence, issue the poweron command.
To initiate the power-on sequence, issue the poweron command.
 Execute the console command, and use the -f option to force the console to be attached to your session.
Execute the console command, and use the -f option to force the console to be attached to your session.
 If it is necessary to reset the system, use the uadmin command.
If it is necessary to reset the system, use the uadmin command.