Chapter 23 Managing Devices for Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
This chapter describes how to administer and use devices on a system that is configured with Solaris Trusted Extensions.
Handling Devices in Trusted Extensions (Task Map)
The following task map points to task maps for administrators and users for handling peripheral devices.
|
Task |
Description |
For Instructions |
|---|---|---|
|
Use devices. |
Uses a device as a role or as a regular user. | |
|
Administer devices. |
Configures devices for ordinary users. | |
|
Customize device authorizations. |
The Security Administrator role creates new authorizations, adds them to the device, places them in a rights profile and assigns this profile to the user. |
Customizing Device Authorizations in Trusted Extensions (Task Map) |
Using Devices in Trusted Extensions (Task Map)
In Trusted Extensions, all roles are authorized to allocate a device. Like users, roles must use the Device Manager. The Solaris allocate command does not work in Trusted Extensions. The following task map points to user procedures that include using devices to perform administrative tasks.
|
Task |
For Instructions |
|---|---|
|
Allocate and deallocate a device. |
How to Allocate a Device in Trusted Extensions in Solaris Trusted Extensions User’s Guide |
|
Use portable media to transfer files. |
Managing Devices in Trusted Extensions (Task Map)
The following task map describes procedures to protect devices at your site.
|
Task |
Description |
For Instructions |
|---|---|---|
|
Set or modify device policy. |
Changes the privileges that are required to access a device. |
Configuring Device Policy (Task Map) in System Administration Guide: Security Services |
|
Authorize users to allocate a device. |
The Security Administrator role assigns a profile with the Allocate Device authorization to the user. |
How to Authorize Users to Allocate a Device in System Administration Guide: Security Services |
|
The Security Administrator role assigns a profile with the site-specific authorizations to the user. |
Customizing Device Authorizations in Trusted Extensions (Task Map) |
|
|
Configure a device. |
Chooses security features to protect the device. | |
|
Revoke or reclaim a device. |
Uses the Device Manager to make a device available for use. | |
|
Uses Solaris commands to make a device available or unavailable for use. |
Forcibly Allocating a Device in System Administration Guide: Security Services Forcibly Deallocating a Device in System Administration Guide: Security Services |
|
|
Prevent access to an allocatable device. |
Provides fine–grained access control to a device. | |
|
Denies everyone access to an allocatable device. | ||
|
Protect printers and frame buffers. |
Ensures that nonallocatable devices are not allocatable. | |
|
Configure serial login devices. |
Enables logins by serial port. | |
|
Use a new device-clean script. |
Places a new script in the appropriate places. |
 How to Configure a Device in Trusted Extensions
How to Configure a Device in Trusted Extensions
By default, an allocatable device has a label range from ADMIN_LOW to ADMIN_HIGH and must be allocated for use. Also, users must be authorized to allocate the device. These defaults can be changed.
Before You Begin
You must be in the Security Administrator role in the global zone.
-
From the Trusted Path menu, select Allocate Device.
The Device Manager appears.
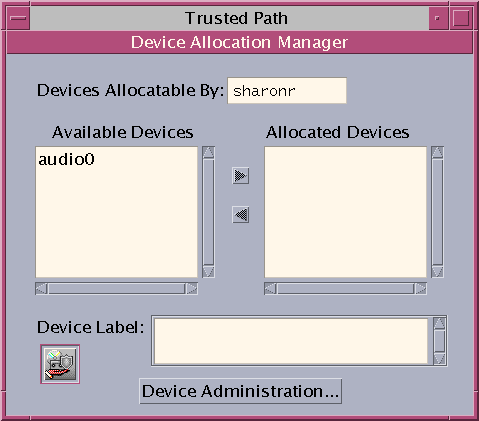
-
View the default security settings.
Click Device Administration, then highlight the device. The following figure shows a CD-ROM drive with default security settings.
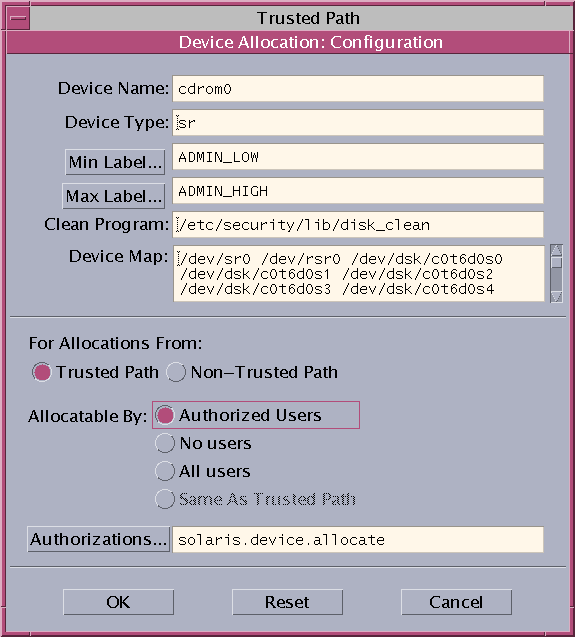
-
(Optional) Restrict the label range on the device.
-
Set the minimum label.
Click the Min Label... button. Choose a minimum label from the label builder. For information about the label builder, see Label Builder in Trusted Extensions.
-
Set the maximum label.
Click the Max Label... button. Choose a maximum label from the label builder.
-
-
Specify if the device can be allocated locally.
In the Device Configuration dialog box, under For Allocations From Trusted Path, select an option from the Allocatable By list. By default, the Authorized Users option is checked. Therefore, the device is allocatable and users must be authorized.
-
Specify if the device can be allocated remotely.
In the For Allocations From Non-Trusted Path section, select an option from the Allocatable By list. By default, the Same As Trusted Path option is checked.
-
If the device is allocatable, and your site has created new device authorizations, select the appropriate authorization.
The following dialog box shows the solaris.device.allocate authorization is required to allocate the cdrom0 device.
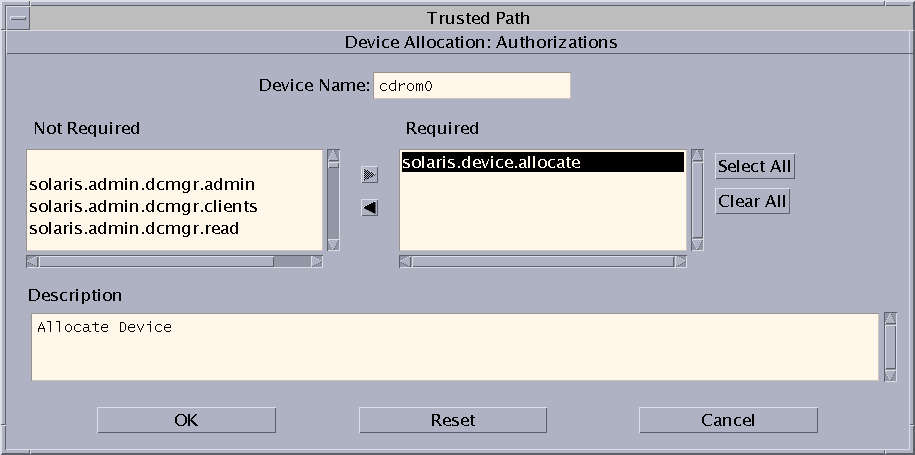
To create and use site-specific device authorizations, see Customizing Device Authorizations in Trusted Extensions (Task Map).
-
To save your changes, click OK.
 How to Revoke or Reclaim a Device
in Trusted Extensions
How to Revoke or Reclaim a Device
in Trusted Extensions
If a device is not listed in the Device Manager, it might already be allocated or it might be in an allocate error state. The system administrator can recover the device for use.
Before You Begin
You must be in the System Administrator role in the global zone. This role includes the solaris.device.revoke authorization.
-
From the Trusted Path menu, select Allocate Device.
In the following figure, the audio device is already allocated to a user.
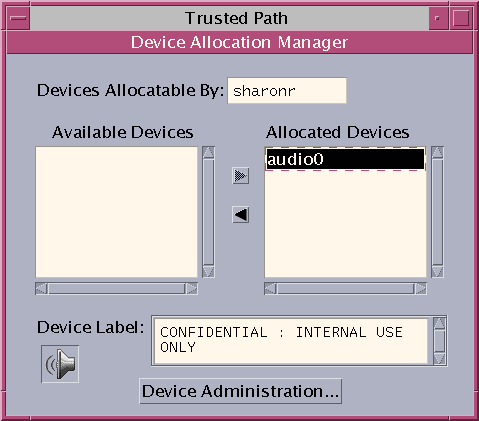
-
Click the Device Administration button.
-
Check the status of a device.
Select the device name and check the State field.
-
Close the Device Manager.
 How to Protect Nonallocatable Devices
in Trusted Extensions
How to Protect Nonallocatable Devices
in Trusted Extensions
The No Users option in the Allocatable By section of the Device Configuration dialog box is used most often for the frame buffer and printer, which do not have to be allocated to be used.
Before You Begin
You must be in the Security Administrator role in the global zone.
-
From the Trusted Path menu, select Allocate Device.
-
In the Device Manager, click the Device Administration button.
-
Select the new printer or frame buffer.
-
To make the device nonallocatable, click No Users.
-
(Optional) Restrict the label range on the device.
-
Set the minimum label.
Click the Min Label... button. Choose a minimum label from the label builder. For information about the label builder, see Label Builder in Trusted Extensions.
-
Set the maximum label.
Click the Max Label... button. Choose a maximum label from the label builder.
-
-
Example 23–1 Preventing Remote Allocation of the Audio Device
The No Users option in the Allocatable By section prevents remote users from hearing conversations around a remote system.
The security administrator configures the audio device in the Device Manager as follows:
Device Name: audio For Allocations From: Trusted Path Allocatable By: Authorized Users Authorizations: solaris.device.allocate |
Device Name: audio For Allocations From: Non-Trusted Pathh Allocatable By: No Users |
 How to Configure a Serial Line for
Logins
How to Configure a Serial Line for
Logins
Before You Begin
You must be in the Security Administrator role in the global zone.
-
Open the Solaris Management Console in the Files scope.
Figure 23–1 Serial Ports Tool in the Solaris Management Console
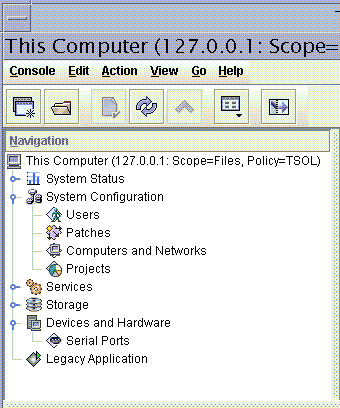
-
Under Devices and Hardware, navigate to Serial Ports.
Provide a password when prompted. Follow the online help to configure the serial port.
-
To change the default label range, open the Device Manager.
The default label range is ADMIN_LOW to ADMIN_HIGH.
Example 23–2 Restricting the Label Range of a Serial Port
After creating a serial login device, the security administrator restricts the label range of the serial port to a single label, Public. The administrator sets the following values in the Device Administration dialog boxes.
Device Name: /dev/term/[a|b] Device Type: tty Clean Program: /bin/true Device Map: /dev/term/[a|b] Minimum Label: Public Maximum Label: Public Allocatable By: No Users |
 How to Add a Device_Clean Script
in Trusted Extensions
How to Add a Device_Clean Script
in Trusted Extensions
If no device_clean script is specified at the time a device is created, the default script, /bin/true, is used.
Before You Begin
Have ready a script that purges all usable data from the physical device and that returns 0 for success. For devices with removable media, the script attempts to eject the media if the user does not do so. The script puts the device into the allocate error state if the medium is not ejected. For details about the requirements, see the device_clean(5) man page.
You must be in the System Administrator role in the global zone.
-
Copy the script into the /etc/security/lib directory.
-
In the Device Administration dialog box, specify the full path to the script.
-
Save your changes.
Customizing Device Authorizations in Trusted Extensions (Task Map)
The following task map describes procedures to change device authorizations at your site.
|
Task |
Description |
For Instructions |
|---|---|---|
|
Create new device authorizations. |
Creates site-specific authorizations. | |
|
Add authorizations to a device. |
Adds site-specific authorizations to selected devices. |
How to Add Site-Specific Authorizations to a Device in Trusted Extensions |
|
Assign device authorizations to users and roles. |
Enables users and roles to use the new authorizations. |
 How to Create New Device Authorizations
How to Create New Device Authorizations
If no authorization is specified at the time a device is created, by default, all users can use the device. If an authorization is specified, then, by default, only authorized users can use the device.
To prevent all access to an allocatable device without using authorizations, see Example 23–1.
Before You Begin
You must be in the Security Administrator role in the global zone.
-
Edit the auth_attr file.
Use the trusted editor. For details, see How to Edit Administrative Files in Trusted Extensions.
-
Create a heading for the new authorizations.
Use the reverse-order Internet domain name of your organization followed by optional additional arbitrary components, such as the name of your company. Separate components by dots. End heading names with a dot.
domain-suffix.domain-prefix.optional.:::Company Header::help=Company.html
-
Add new authorization entries.
Add the authorizations, one authorization per line. The lines are split for display purposes. The authorizations include grant authorizations that enable administrators to assign the new authorizations.
domain-suffix.domain-prefix.grant:::Grant All Company Authorizations:: help=CompanyGrant.html domain-suffix.domain-prefix.grant.device:::Grant Company Device Authorizations:: help=CompanyGrantDevice.html domain-suffix.domain-prefix.device.allocate.tape:::Allocate Tape Device:: help=CompanyTapeAllocate.html domain-suffix.domain-prefix.device.allocate.floppy:::Allocate Floppy Device:: help=CompanyFloppyAllocate.html
-
Save the file and close the editor.
-
If you are using LDAP as your naming service, update the auth_attr entries on the Sun Java System Directory Server (LDAP server).
For information, see the ldapaddent(1M) man page.
-
Add the new authorizations to the appropriate rights profiles. Then assign the profiles to users and roles.
Use the Solaris Management Console. Assume the Security Administrator role, then follow the Solaris procedure How to Create or Change a Rights Profile in System Administration Guide: Security Services.
-
Use the authorization to restrict access to tape and diskette drives.
Add the new authorizations to the list of required authorizations in the Device Manager. For the procedure, see How to Add Site-Specific Authorizations to a Device in Trusted Extensions.
Example 23–3 Creating Fine-Grained Device Authorizations
A security administrator for NewCo needs to construct fine-grained device authorizations for the company.
First, the administrator writes the following help files, and places the files in the /usr/lib/help/auths/locale/C directory:
Newco.html NewcoGrant.html NewcoGrantDevice.html NewcoTapeAllocate.html NewcoFloppyAllocate.html |
Next, the administrator adds a header for all of the authorizations for newco.com in the auth_attr file.
# auth_attr file com.newco.:::NewCo Header::help=Newco.html |
Next, the administrator adds authorization entries to the file:
com.newco.grant:::Grant All NewCo Authorizations:: help=NewcoGrant.html com.newco.grant.device:::Grant NewCo Device Authorizations:: help=NewcoGrantDevice.html com.newco.device.allocate.tape:::Allocate Tape Device:: help=NewcoTapeAllocate.html com.newco.device.allocate.floppy:::Allocate Floppy Device:: help=NewcoFloppyAllocate.html |
The lines are split for display purposes.
The auth_attr entries create the following authorizations:
-
An authorization to grant all NewCo's authorizations
-
An authorization to grant NewCo's device authorizations
-
An authorization to allocate a tape drive
-
An authorization to allocate a diskette drive
Example 23–4 Creating Trusted Path and Non-Trusted Path Authorizations
By default, the Allocate Devices authorization enables allocation from the trusted path and from outside the trusted path.
In the following example, site security policy requires restricting remote CD-ROM allocation. The security administrator creates the com.someco.device.cdrom.local authorization. This authorization is for CD-ROM drives that are allocated with the trusted path. The com.someco.device.cdrom.remote authorization is for those few users who are allowed to allocate a CD-ROM drive outside the trusted path.
The security administrator creates the help files, adds the authorizations to the auth_attr database, adds the authorizations to the devices, and then places the authorizations in rights profiles. The profiles are assigned to users who are allowed to allocate devices.
-
The following are the auth_attr database entries:
com.someco.:::SomeCo Header::help=Someco.html com.someco.grant:::Grant All SomeCo Authorizations:: help=SomecoGrant.html com.someco.grant.device:::Grant SomeCo Device Authorizations:: help=SomecoGrantDevice.html com.someco.device.cdrom.local:::Allocate Local CD-ROM Device:: help=SomecoCDAllocateLocal.html com.someco.device.cdrom.remote:::Allocate Remote CD-ROM Device:: help=SomecoCDAllocateRemote.html
-
The following is the Device Manager assignment:
The Trusted Path enables authorized users to use the Device Manager when allocating the local CD-ROM drive.
Device Name: cdrom_0 For Allocations From: Trusted Path Allocatable By: Authorized Users Authorizations: com.someco.device.cdrom.local
The Non-Trusted Path enables users to allocate a device remotely by using the allocate command.
Device Name: cdrom_0 For Allocations From: Non-Trusted Path Allocatable By: Authorized Users Authorizations: com.someco.device.cdrom.remote
-
The following are the rights profile entries:
# Local Allocator profile com.someco.device.cdrom.local # Remote Allocator profile com.someco.device.cdrom.remote
-
The following are the rights profiles for authorized users:
# List of profiles for regular authorized user Local Allocator Profile ... # List of profiles for role or authorized user Remote Allocator Profile ...
 How to Add Site-Specific Authorizations
to a Device in Trusted Extensions
How to Add Site-Specific Authorizations
to a Device in Trusted Extensions
Before You Begin
You must be in the Security Administrator role, or in a role that includes the Configure Device Attributes authorization. You must have already created site-specific authorizations, as described in How to Create New Device Authorizations.
-
Follow the How to Configure a Device in Trusted Extensions procedure.
-
Select a device that needs to be protected with your new authorizations.
-
Open the Device Administration dialog box.
-
In the Device Configuration dialog box, click the Authorizations button.
The new authorizations are displayed in the Not Required list.
-
Add the new authorizations to the Required list of authorizations.
-
-
To save your changes, click OK.
 How to Assign Device Authorizations
How to Assign Device Authorizations
The Allocate Device authorization enables users to allocate a device. The Allocate Device authorization, and the Revoke or Reclaim Device authorization, are appropriate for administrative roles.
Before You Begin
You must be in the Security Administrator role in the global zone.
If the existing profiles are not appropriate, the security administrator can create a new profile. For an example, see How to Create a Rights Profile for Convenient Authorizations.
-
Assign to the user a rights profile that contains the Allocate Device authorization.
For assistance, see the online help. For the step-by-step procedure, see How to Change the RBAC Properties of a User in System Administration Guide: Security Services.
The following profiles enable a role to allocate devices:
-
All Authorizations
-
Device Management
-
Media Backup
-
Media Restore
-
Object Label Management
-
Software Installation
The following profiles enable a role to revoke or reclaim devices:
-
All Authorizations
-
Device Management
The following profiles enable a role to create or configure devices:
-
All Authorizations
-
Device Security
-
Example 23–5 Assigning New Device Authorizations
-
Creates new device authorizations, as in How to Create New Device Authorizations
-
In the Device Manager, adds the new device authorizations to the tape and diskette drives
-
Places the new authorizations in the rights profile, NewCo Allocation
-
Adds the NewCo Allocation rights profile to the profiles of users and roles who are authorized to allocate tape and diskette drives
In this example, the security administrator configures the new device authorizations for the system and assigns the rights profile with the new authorizations to trustworthy users. The security administrator does the following:
Authorized users and roles can now use the tape drives and diskette drives on this system.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
