Discovering Servers
This section describes how to use the discovery process to add servers to the N1 System Manager.
Note –
Before you can perform any of the management activities in this section, physical servers must be cabled and prepared according to the instructions in Chapter 2, Sun N1 System Manager System and Network Preparation, in Sun N1 System Manager 1.1 Site Preparation Guide.
Servers must also comply with the following revisions of firmware to be discovered. See Downloading V20z and V40z Server Firmware Updates for instructions or refer to Sun System Handbook documentation for your provisionable server.
|
Minimum Requirement |
Best Practice |
|
|
Sun Fire V20z and V40z Service Processor (SP) |
2.1.0.5 |
2.3.0.11 |
|
Sun Fire V20z Server Platform BIOS |
N/A |
1.33.5.2 |
|
Sun Fire V40z Server Platform BIOS |
N/A |
2.33.5.2 |
|
Sun Fire X4100 and X4200 with Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM) |
1.0 |
1.0 |
|
Sun SPARC servers with Advanced Lights Out Manager (ALOM) |
1.4 |
1.5.3 |
The Discovery job uses a Service Access Point (SAP) to access server capabilities. A SAP is generically defined as an IP address, protocol, and security credentials.
If you do not specify the Secure Shell (SSH) and Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) accounts and passwords, the discovery process assumes that the following credentials are configured on the provisionable servers:
-
Sun Fire X4100 and X4200 servers
-
SSH user = root
-
SSH password = changeme
-
IMPI user = root
-
IMPI password = changeme
-
-
Sun Fire V20z and V40z servers
-
SSH user = admin
-
SSH password = admin
-
IMPI user = Null
-
IMPI password= admin
-
SNMP read community string = public
-
-
Sun Fire V210, V240, V440 servers
-
Telnet login = admin
-
Telnet password = admin
-
Note –
Automatic configuration of credentials is supported for Sun Fire V20z and V40z servers if they are in the factory default state. See Setting Up Provisionable Servers in Sun N1 System Manager 1.1 Site Preparation Guide.
If you do specify the login accounts and passwords, the discovery process configures the user-specified credentials. If only one credential is specified, the missing credential is configured with one of the defaults specified.
If you want to disable autoconfiguration, add the following line to the /etc/opt/sun/n1gc/domain.properties file before you run discovery:
com.sun.hss.domain.internal.discovery.initializeDevice=false
The N1 System Manager must be restarted for the disabling of autoconfiguration to take effect. Note that after autoconfiguration is disabled, any servers in the factory default state cannot be discovered until their SSH and IPMI accounts are configured. For further information, see Sun N1 System Manager 1.1 Site Preparation Guide.
Do not use the N1 System Manager to discover servers that have system management software installed on them such as Sun Management Center, Sun Control Station, and any other system management applications including the N1 System Manager.
 To Discover
New Servers
To Discover
New Servers
You must discover servers to manage them with the N1 System Manager. This procedure describes how to use the browser interface to initiate and track discovery. Example 2–1 at the end of this procedure provides the command-line equivalent.
Note –
Discovered servers are automatically monitored for hardware health.
Before You Begin
-
Before you discover a new hardware component, read Chapter 2, Sun N1 System Manager System and Network Preparation, in Sun N1 System Manager 1.1 Site Preparation Guide.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
See To Access the N1 System Manager Browser Interface for details.
The All Servers page appears.
-
Click the Discover button in the Servers table.
The Discover Servers wizard appears.
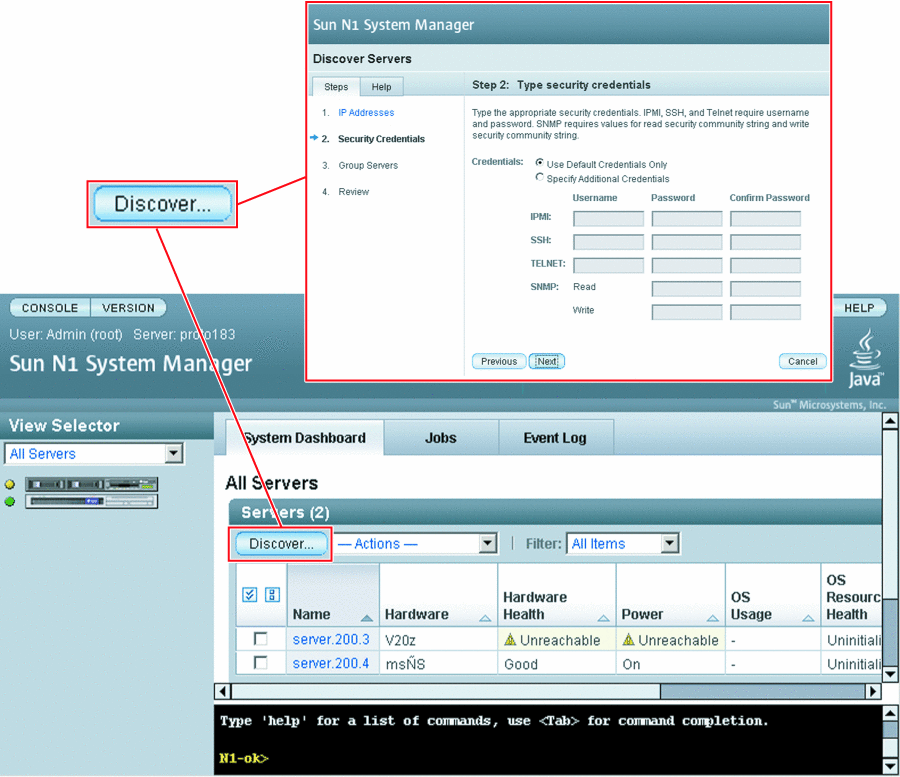
-
Use the wizard steps to guide you through the screens.
-
Click the Finish button to begin the discovery operation.
The wizard window closes and a job ID appears in the Command Line pane.
-
To view the Discovery job, click the Jobs tab.
The Discovery job appears in the Jobs table.
-
When the job completes successfully, do one of the following:
-
Choose All Servers from the View Selector menu.
The discovered server appears in the list.
-
If you selected a group for the discovered servers, view the list of server groups as follows:
The server or servers are available for OS provisioning.
-
-
If you installed an OS on a server before it was discovered, add the OS monitoring feature.
Note –The SSH user account that is used in the following command must have root privileges on the remote machine.
N1-ok> add server server feature osmonitor agentip agentip agentssh username/password
See add server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.1 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
Example 2–1 Discovering Servers Through the Command Line
IP addresses, IP address ranges, and IP subnets can be input as a comma-separated list. Overlapping IP address ranges are allowed. Security credentials for IPMI, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), SSH, and Telnet are optional. However, for Sun Fire X4000 series servers, username is required by IPMI. If credentials are not specified, the manufacturer defaults are used. See Sun N1 System Manager 1.1 Site Preparation Guide for information about the default accounts.
N1-ok> discover IP,IP-IP,subnet/mask [group group] [ipmi username/password] [snmp credential/credential] [ssh username/password] [telnet username/password] |
The following example of the discover command shows how to discover servers that have the following management network IP addresses: 192.168.1.1–192.168.1.3 , 192.168.1.5-192.168.1.95, and 192.168.1.107.
N1-ok> discover 192.168.1.1-192.168.1.3,192.168.1.5-192.168.1.95,192.168.1.107 group dev ssh root/admin Job 3 started. |
The group subcommand adds the successfully discovered servers into a server group called dev. The ssh option specifies the user name and password configured for access on the management port. In this example, the SSH user name root and password admin are used to authenticate the hardware discovery.
The following example command shows how to view the Discovery job and the job status.
N1-ok> show job all Job ID Date Type Status Owner 3 2005-06-28T06:53:53-0700 Discovery Completed root 2 2005-06-28T06:01:20-0700 Create OS Distribution Completed root 1 2005-06-28T05:57:14-0700 Create OS Distribution Completed root |
The following example command shows how to verify that the discovered servers were added to the server group.
N1-ok> show group all Name Status Jobs Servers Spare dev 7 |
The following example command shows how to view the list of servers in the group and the power and hardware health status.
N1-ok> show group dev Name Hardware Hardware Health Power OS Usage OS Resource Health 192.168.1.1 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.2 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.5 V40z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.15 NETRA-240 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.25 X4100 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.95 X4200 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.107 SF-V240 Good On -- Uninitialized |
The following example of the discover command shows how to discover any servers that have management network IP addresses assigned in the 192.168.1.0/8 netmask.
N1-ok> discover 192.168.1.0/8 ssh root/admin Job 18 started. |
The following example shows how to view the discovered servers.
N1-ok> show server all Name Hardware Hardware Health Power OS Usage OS Resource Health 192.168.1.1 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.2 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.5 V40z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.15 NETRA-240 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.25 X4100 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.95 X4200 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.107 SF-V240 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.200 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.245 V40z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.255 NETRA-240 Good On -- Uninitialized |
Example 2–2 Adding the OS Management Feature
The following example of the add command shows how to add the OS monitoring feature to a server that had an OS installed prior to being discovered.
N1-ok> add server 192.168.1.1 feature osmonitor agentip 192.168.10.10 agentssh admin/admin |
The agentip parameter sets the IP address of the provisionable server's data network interface to be monitored by the management server. The ssh user name admin and password admin are used for root access authentication.
The following example of the show command shows how to verify that the OS monitoring feature was added successfully to a server that had an OS installed prior to being discovered.
N1-ok> show server 192.168.1.1 Name Hardware Hardware Health Power OS Usage OS Resource Health 192.168.1.1 V20z Good On Solaris Good |
Troubleshooting
The discover command credential attributes are used for security. SSH, IPMI, and Telnet require a username and a password. SNMP requires that you input a valid value for the read security community string. If credentials are not specified, the discovery process uses the default credentials that were defined during installation. See Discovering Servers for default credentials.
Discovery might fail due to stale SSH entries on the management server. If the discover command fails with an error message indicating that there are invalid credentials and no true security breach has occurred, remove the /root/.ssh/known_hosts file or the specific entry in the file that corresponds to the provisionable server. Then, retry the discover command.
The OS does not belong to the server in question if the add command fails with the following error:
Internal error: No mac address match found
See Also
Sun N1 System Manager 1.1 Site Preparation Guide
Next Steps
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
