Sun N1 System Manager Connection Information
This section provides the connectivity requirements for the Sun N1 System Manager servers.
The following topics are discussed:
Management Server Connections
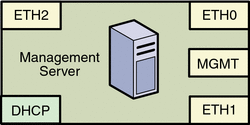
This section provides the logical port diagram and connectivity requirements for the Sun N1 System Manager management server.
A SPARC or x86 based server can be used as the management server as described by Table 2–1. Each server provides at least one 10/100/1000 (1 Gbit) network interface port, but adding additional Gbit network interface cards to the management server increases ease of management and physical separation of the corporate and provisioning networks. If you do not additional NICs, you can configure your network to route the corporate and provisioning networks through a single 1 Gbit port. This document assumes that your management server has three Gbit NICs.
Each server also provides one or two system management ports depending on server architecture, labeled Net Mgmt (Network Management), ALOM (Advanced Lights Out Manager port), or ILOM (Integrated Lights Out Manager port) on single management port servers, and labeled SP0 and SP1 (Service Processor 1 and 2) on dual management port servers. The management server requires only a single management port to provide connectivity with the corporate network. In this document, the management port is always shown as MGMT.
Note –
Depending on the system architecture and the operating system installed, the operating system refers to the Ethernet ports by different names. For example, the first Ethernet port on a machine is referred to as ETH0, HME0, or BGE0 depending on the operating system. This document refers to the lowest order Ethernet port on a machine as ETH0, the next port as ETH1 and so on regardless of architecture and operating system.
The following illustration provides the logical diagram of the management server ports, and is used in subsequent sections to illustrate reference architecture and production VLAN diagrams.
|
The management server should provide connectivity to three separate networks using the ports as follows:
-
The management port connects the management server to the corporate network. The management port connection provides external power up and power down access to the management server, enables firmware updates from the corporate network, and enables you to check the status of the management server from the corporate network. The management port is a 100–Mbit NIC interface.
-
ETH0 connects the management server to the corporate network to provide external access to the management server. The management server ETH0 IP address, netmask, and gateway should be configured to meet your corporate environment connectivity requirements. DNS configuration is performed during the N1 System Manager configuration process. ETH0 should be a 1 Gbit NIC interface.
-
ETH1 connects the management server to the provisioning network and should be on the same switch and network as the ETH0 connections of the provisionable servers. The management server ETH1 IP address, netmask, and gateway can be configured to support hundreds of provisionable servers. No devices other than the management server and the provisionable servers should reside on the provisioning network. ETH1 should be a 1 Gbit NIC interface.
-
ETH2 connects the management server to the management network and should be on the same switch and network as the management port connections of the provisionable servers. The management server connection is not required to be on the same switch as the management port connections of the provisionable servers as long as connectivity to the provisionable servers management port is provided. The management server ETH2 IP address, netmask, and gateway should be configured to enable connectivity to the provisionable servers management port IP addresses. ETH2 should be a 1 Gbit NIC interface.
-
The management server DCHP service allocates IP addresses to the provisionable servers for loading operating systems and updates over the provisioning network, and for runtime monitoring of the provisionable server operating environment.
Note –The management server DCHP service does not provide DHCP services for the data network. If you plan to dynamically configure IP services on the data network, you must provide an external DHCP server for the data network. You must not have another DHCP server on the same provisioning network.
Provisionable Server Connections
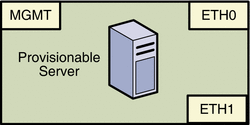
This section provides the logical port diagrams and connectivity requirements for the Sun N1 System Manager provisionable server.
A SPARC or x86–based server can be used as a provisionable server as described by Management Server Requirements. Each server provides two 10/100/1000 network interface ports. Each server also provides one or two system management ports depending on server architecture, labeled ALOM or ILOM on single management port servers, and labeled SP0 and SP1 on dual management port servers. In this document, the management port is always shown as MGMT.
The following illustrations provide the logical diagrams for the provisionable server ports based on the server architecture, and are used in subsequent sections to illustrate reference diagrams.
|
Each provisionable server should provide connectivity to three separate networks as follows:
-
The management port connects the provisionable server to the management network and should be on the same switch and network as the ETH2 connection of the management server. The provisionable server management port connection is not required to be on the same switch as the ETH2 connection of the management server as long as connectivity to the management server ETH2 port is provided.
The management port should be a 100 megabit connection.
-
ETH0 connects the provisionable server to the provisioning network and must be on the same switch and network as the ETH1 connection of the management server.
ETH0 should be a 1 Gbyte connection.
-
ETH1 connects the provisionable server to the data network through the switch to provide external corporate network access to the provisionable server.
ETH1 should be a 1 Gbyte connection.
The next section provides reference system connection and VLAN configurations for the N1 System Manager.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
