Connecting to the Serial Console for a Server
This section describes how to open the serial console for a server.
To remotely access the serial console for a server, use the connect command with the server keyword.
Note –
The Command Line pane in the browser interface does not support this operation. You must use the n1sh shell to access the connect command.
You can also perform this operation from the browser interface's Server Details page.
 To Open a Server's Serial Console
To Open a Server's Serial Console
This procedure describes how to remotely access the serial console of provisionable servers. This feature is particularly useful for performing diagnosis before and during the OS installation and during the server power cycle.
The terminal emulator applet that is used by the browser interface for the serial console feature does not provide a certificate-based authentication of the applet. The applet also requires that you enable SSHv1 for the management server. For certificate-based authentication or to avoid enabling SSHv1, use the serial console feature by running the connect command from the n1sh shell.
For most hardware platforms, the first user to log in is given read-and-write privileges on the serial console. Subsequent user sessions are in read-only mode. Sun Fire X4100 and X4200 servers do not support read-only mode, so subsequent user session requests fail.
Note –
Use of the serial console is not supported for Sun Fire X2100 servers.
When the escape sequence is issued, the connection closes and a disconnect from server-name message appears in the output. If another user has the console and you are in read-only mode, you are logged in to the console when the other user disconnects. When you click the Close button on the Serial Console window, the connection is closed.
The following list shows the supported serial console escape sequences:
-
ALOM – #.
-
Sun Enterprise X4100, X4200 – ESC (
-
Sun Fire V20z and V40z – ^Ec.
For HTTP connections, standard 128–bit SSL encryption is used for transport, authentication is password based, and a security session is used for each subsequent operation.
Note –
If another user is logged in to the serial console for the server, you are logged in with read-only privileges. If another user has logged in to the physical serial console on a SPARC server, you are logged in with read-only privileges. The physical serial console is separate from the one that is available from the ALOM port.
Before You Begin
To use the Serial Console feature from the browser interface, the Sun Java Plugin 1.4.2 or later must be installed on the system where you are running the browser.
Steps
-
Choose All Servers from the View Selector menu.
The Servers table appears.
-
Select the server for which you want to open a serial console.
The Server Details page appears.
-
Choose Open Serial Console from the Actions menu.
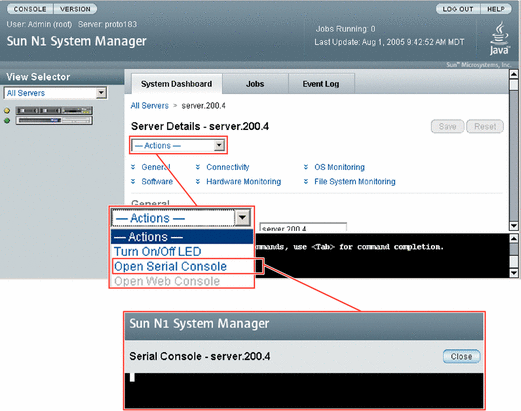
The management server redirects output of the provisionable server's serial console to the terminal emulator applet that is running in the browser interface.
The serial emulator appears and takes you either to the root prompt or a read-only prompt.
Note –If a server is powered off, the console still connects, but no output appears until the server is powered on.
Example 4–26 Connecting to the Serial Console Through the Command Line
When in serial console mode, the n1sh shell sends all user input to the remote serial console. The N1 System Manager neither blocks nor supplements the platform-specific exit-control sequence. Note that the connect command is not implemented in the browser interface's Command Line pane. The connect command may only be run from the n1sh shell.
This example shows how to connect to the serial console as a root user. However, any user role with the ServerConsole privilege may issue the connect command.
% ssh -l root server1.central:6789 password: Copyright (c) 2005 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved Use is subject to license terms. N1-ok> connect server server1 |
Troubleshooting
If the Open Serial Console menu item does not appear, SSHv1 is not enabled. To enable SSHv1, use the n1smconfig utility. See To Configure the N1 System Manager System in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Installation and Configuration Guide.
See Also
After you have opened the serial console, you can view the detailed output during an OS deployment or a power cycle. For instructions, see Deploying OS Profiles and To Reboot a Server or a Server Group.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
