Adding and Upgrading Base Management and OS Monitoring Features
The base management and OS monitoring features provide support for monitoring and patching the installed OS profiles, and for executing remote commands. This section describes how to add the base management and OS monitoring features, modify supported attributes, remove feature support, and upgrade the base management and OS monitoring features to the latest versions.
Adding the OS monitoring features provides support for monitoring and enables monitoring by default. You can subsequently enable and disable monitoring by using the set server command as explained in Enabling and Disabling Monitoring.
This section describes the following tasks:
-
To Modify the Secure Shell Credentials for the Management Features of a Server
-
To Modify the SNMP Credentials for the Management Features of a Server
-
To Modify the SNMPv3 Credentials for the Management Features of a Server
 To Add the Base Management Feature
To Add the Base Management Feature
This procedure describes how to add the base management feature on a server with a newly deployed OS. The base management feature is used to enable remote command execution and package deployment.
Note –
Uninstallation of the base management feature is not supported.
The agent IP used in this procedure is the IP address of the provisionable server's data network interface to be monitored by the management server. The interface can be eth1/bge1 or eth0/bge0, but usually is eth0/bge0. For more information on the server's agent IP address, see To Modify the Agent IP for a Server.
Note –
You can add the base management feature automatically as part of the load server or load group commands. See load server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual or load group in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
Before You Begin
-
Discover servers. See Chapter 2, Discovering, Grouping, and Replacing Servers in the Sun N1 System Manager
-
Load an OS if an OS is not already installed. See To Load an OS Profile on a Server or a Server Group and load server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
See To Access the N1 System Manager Command Line for details.
-
Type the following command:
Note –The SSH user account that is used in the following command must have root privileges on the remote machine:
N1-ok> add server server feature basemanagement agentip agentip agentssh username/password
An Add Base Management Support job is started.
The necessary packages and scripts are added. See add server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
-
After successful completion of the Add Base Management Support job, type the following command:
N1-ok> show server server
The Base Management Supported field should appear with OK as the value.
Next Steps
To Add the OS Monitoring Feature
 To Add the OS Monitoring Feature
To Add the OS Monitoring Feature
This procedure describes how to add the OS monitoring feature on a server. You can add the OS monitoring feature to a server that already has the base management feature added. Alternatively, you can add the OS monitoring feature to a server with a newly loaded OS and the base management feature is added automatically. The OS monitoring feature is used for OS health monitoring and inventory management. See Chapter 5, Monitoring Your Servers for details.
The add server feature osmonitor command creates an Add OS Monitoring Support job. You can submit multiple, overlapping add server feature osmonitor commands and have them run in parallel. However, you should limit the number of overlapping Add OS Monitoring Support jobs to a maximum of 15.
If you submit add server feature commands by using a script, see Example 5–1 for an example.
Note –
You can add the OS monitoring feature automatically as part of the load server or load group commands. See load server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual or load group in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
Before You Begin
-
Discover servers. See Chapter 2, Discovering, Grouping, and Replacing Servers in the Sun N1 System Manager
-
Load an OS if one is not already installed, see To Load an OS Profile on a Server or a Server Group and load server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
See To Access the N1 System Manager Command Line for details.
-
To add the OS monitoring feature, perform one of the following actions:
-
If you have not added the base management feature, type the following command:
Note –The SSH user account that is used in the following command must have root privileges on the remote machine.
N1-ok> add server server feature osmonitor agentip agentip agentssh username/password
-
If you have already added the base management feature, type the following command:
Note –You cannot specify the agent IP or SSH credentials when adding OS monitoring support to a server that has base management support.
N1-ok> add server server feature osmonitor
An Add OS Monitoring Support job starts.
See add server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual for details about command syntax.
-
-
Track the Add OS Monitoring Support job to completion.
After the job completes successfully, the Servers table on the System Dashboard tab appears with values for OS Usage and OS Resource Health.
Verify that the OS monitoring feature is supported by issuing the show server command. Output for the server appears with the OS Monitoring Supported value as OK one of the following sets of commands on the provisionable server.
Note –It can take 5-7 minutes before all OS monitoring data is fully initialized. You may see that CPU idle is at 0.0%, which causes a Failed Critical status with OS usage. This should clear up within 5-7 minutes after adding or upgrading the OS monitoring feature.
If no monitoring data is available for the server, see Resolving Command Failures Related to OS Monitoring.
If the provisionable server's IP address changes, use the set server command again before enabling or disabling monitoring
Example 5–1 Scripting OS Monitoring Support
The following example script issues multiple add server feature commands on servers that do not have the base management feature support:
n1sh add server 10.0.0.10 feature=osmonitor agentip 10.0.0.110 agentssh root/admin & n1sh add server 10.0.0.11 feature=osmonitor agentip 10.0.0.111 agentssh root/admin & n1sh add server 10.0.0.12 feature=osmonitor agentip 10.0.0.112 agentssh root/admin & |
Troubleshooting
Adding the OS monitoring feature might fail due to stale SSH entries on the management server. If the add server feature osmonitor agentip command fails and no true security breach has occurred, remove the known_hosts file or the specific entry in the file that corresponds to the provisionable server. Then, retry the add server feature osmonitor agentip command. If the management server is running Linux, the known_hosts file is at /root/.ssh/known_hosts. If the management server is running the Solaris OS, the known_hosts file is at /.ssh/known_hosts.
Adding the OS monitoring feature will fail if you specify the agent IP or the SSH credentials in the add server feature osmonitor command when running it on servers that already have the base management feature support. To solve this problem, issue the add server feature osmonitor command without specifying values for the agent IP or for the SSH credentials.
 To Remove the OS Monitoring Feature
To Remove the OS Monitoring Feature
There are two levels of removing the OS monitoring feature with this command. If you don't specify the uninstall keyword, the OS monitoring feature remains installed on the provisionable server, but the feature is no longer supported and the server's OS can no longer be monitored with the N1 System Manager. If you specify the uninstall keyword, the OS monitoring feature is completely uninstalled from the provisionable server and consequently the OS monitoring feature is no longer supported.
Once removed in either case, the OS resource health state for the server becomes uninitialized.
After you remove a feature, provided you used the recommended procedure, you can always use the add server command to add it back again. The Base Management Supported and OS Monitoring Supported fields in the show server output provide the current status on a server's features.
Note –
Do not manually remove the OS monitoring feature by attempting to delete the agent. Doing so will make it impossible to reinstall or reutilize the OS monitoring feature. Instead, to remove the OS monitoring feature, use the remove server feature procedure as described.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
See To Access the N1 System Manager Command Line for details.
-
Remove the OS monitoring feature.
N1-ok> remove server server feature osmonitor [uninstall]
The necessary packages and scripts are removed. See remove server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual for details about command syntax.
 To Remove the Base Management Feature
To Remove the Base Management Feature
The OS monitoring feature must be removed before the base management feature can be removed. See To Remove the OS Monitoring Feature for details.
When you remove the base management feature, the feature is uninstalled from the provisionable server and it is no longer supported.
After you remove a feature, provided you used the recommended procedure, you can always use the add server command to add it back again. The Base Management Supported and OS Monitoring Supported fields in the show server output provide the current status on a server's features.
Note –
Do not manually remove the base management feature by attempting to delete the agent. Doing so will make it impossible to reinstall or reutilize the base management feature. Instead, to remove the base management feature, use the remove server feature procedure as described.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
See To Access the N1 System Manager Command Line for details.
-
Remove the OS monitoring feature.
N1-ok> remove server server feature basemanagement
The necessary packages and scripts are removed. See remove server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual for details about command syntax.
 To Modify the Agent IP for a Server
To Modify the Agent IP for a Server
This procedure describes how to modify the agent IP for a server. The agent IP is the IP address of the provisionable server's data network interface to be monitored by the management server. The agent IP is not the same as the server's management network IP address.
The following graphic shows the agent IP address for a server from the results table of a job, displayed in the Jobs tab. The graphic distinguishes the agent IP address for the server from the server's IP address.
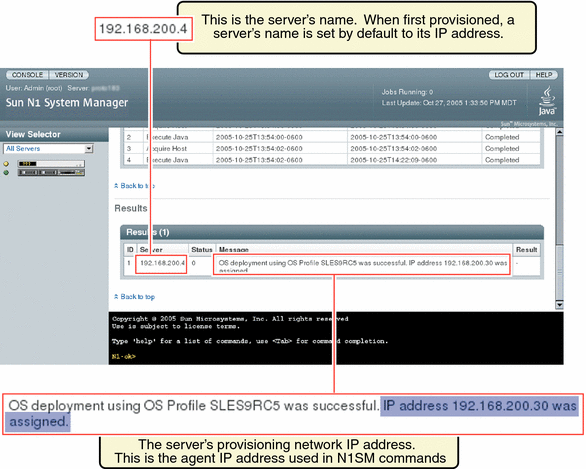
Note –
If you change the provisionable server's IP address and credentials or manually remove some services outside the N1 System Manager, the enabling of the services will not succeed. Arbitrary changes to the OS outside of the N1 System Manager require a rediscovery and subsequent addition of the base and OS management features.
When the load server or load group command is used to install software on the provisionable server, the provisionable server's networktype attribute could be set to dhcp. This setting means that the server uses DHCP to get its provisioning network IP address. If the system reboots and obtains a different IP address than the one that was used for the agentip parameter during the load command or add server commands, then the following features may not work:
-
The OS Monitoring content of the show server command. (No OS monitoring)
-
The load server server update and load group group update commands
-
The start server server command command
-
The set server server threshold command
-
The set server server refresh command
In this case, use the set server server agentip command to correct the server's agent IP address as shown in this procedure.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
See To Access the N1 System Manager Command Line for details.
-
Run the following command:
N1-ok> set server server agentip IP
The agent IP is modified. See set server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual for details about command syntax. This operation touches the provisionable server.
 To Modify the Secure Shell Credentials for the Management
Features of a Server
To Modify the Secure Shell Credentials for the Management
Features of a Server
This procedure describes how to modify the Secure Shell (SSH) credentials for the base management and OS monitoring features for a provisionable server. These management SSH credentials are required by or used in many N1 System Manager commands including add server, set server, load server, start server, load group, and start group. These credentials, specifically for the base management and OS monitoring features for a provisionable server and referred to by the examples in this chapter as agentssh credentials, are not the same as the SSH credentials required for the server's management network IP address.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
See To Access the N1 System Manager Command Line for details. You need to have an SSH login and password for this step. Default SSH login/password pairs are provided in Discovering Servers.
-
Run the following command:
Note –The SSH user account that is used in the following command must have root privileges on the remote machine.
N1-ok> set server server agentip IP agentssh username/password
The agentssh user name and password are modified. See set server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual for details about command syntax.
 To Modify the SNMP Credentials for the Management Features
of a Server
To Modify the SNMP Credentials for the Management Features
of a Server
This procedure describes how to modify the management feature SNMP credentials for a server. The management feature SNMP credentials allow the N1 System Manager to communicate with the Sun Management Center SNMP agent and are specifically for the base management and OS monitoring features for a provisionable server. These credentials, specifically for the base management and OS monitoring features for a provisionable server and referred to by the examples in this chapter as agentsnmp credentials, are not the same as the SNMP credentials required for the server's management network IP address.
See Introduction to Monitoring for more information about the SNMP agents for OS monitoring in the N1 System Manager.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
See To Access the N1 System Manager Command Line for details.
-
Run the following command to specify the SNMP credentials on a server:
N1-ok> set server server agentsnmp agentsnmp
The SNMP credentials are modified. See set server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual for details about command syntax.
This set server operation does not actually touch the provisionable server. It just synchronizes the data on the management server itself.
 To Modify the SNMPv3 Credentials for the Management Features
of a Server
To Modify the SNMPv3 Credentials for the Management Features
of a Server
This procedure describes how to modify the management feature SNMPv3 credentials for a server. The management feature SNMPv3 credentials allow the N1 System Manager to communicate with the Sun Management Center SNMP agent and are specifically for the base management and OS monitoring features for a provisionable server. These credentials, specifically for the base management and OS monitoring features for a provisionable server and referred to by the examples in this chapter as agentsnmpv3 credentials, are not the same as the SNMP credentials required for the server's management network IP address.
See Introduction to Monitoring for more information about the SNMP agents for OS monitoring in the N1 System Manager.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
See To Access the N1 System Manager Command Line for details.
-
Run the following command to specify the SNMP credentials on a server:
N1-ok> set server server agentsnmpv3 agentsnmpv3
The SNMP credentials are modified. See set server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual for details about command syntax.
This set server operation does not actually touch the provisionable server. It just synchronizes the data on the management server itself.
 To Manually Uninstall the Linux OS Monitoring
Feature
To Manually Uninstall the Linux OS Monitoring
Feature
After successful completion of this procedure, the OS monitoring feature is unsupported for the provisionable server:
Steps
-
Log in to the provisionable server as root.
-
Type the following command:
# /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S99es_agent stop
-
Issue the following command and follow the prompts.
# /opt/SUNWsymon/sbin/es-uninst
The agent is uninstalled.
-
Manually remove the feature.
# rpm -e n1sm-linux-agent
The feature is removed.
-
Remove directories related to the feature.
# rm -rf /var/opt/SUNWsymon
The directories are removed.
 To Manually Uninstall the Solaris OS Monitoring
Feature
To Manually Uninstall the Solaris OS Monitoring
Feature
After successful completion of this procedure, the OS monitoring feature will be unsupported for the provisionable server.
Steps
-
Log in to the provisionable server as root.
-
Stop the agent.
# /etc/rc3.d/S81es_agent stop
-
Run the uninstaller.
# /var/tmp/solx86-agent-installer/disk1/x86/sbin/es-uninst -X
-
Remove the packages.
For the Solaris OS running on the SPARC architecture:
# pkgrm SUNWn1smsparcag-1-2
For the Solaris OS running on the x86 architecture:
# pkgrm SUNWn1smx86ag-1-2
-
Remove associated directories.
# /bin/rm -rf /opt/SUNWsymon # /bin/rm -rf /var/opt/SUNWsymon
The directories are removed.
 To Upgrade the Base Management Feature on a Server
To Upgrade the Base Management Feature on a Server
This procedure describes how to upgrade the base management feature on a server. This procedure is necessary after upgrading the N1 System Manager from a previous release, for provisionable servers on which the previous version of the base management feature is still installed. This procedure is for individual servers. You can upgrade the base management feature on multiple servers at once. See Chapter 2, Upgrading the Sun N1 System Manager Software and Provisionable Server Management Agents, in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Installation and Configuration Guide for details.
Note –
If the server was freshly installed using the load server or load group commands from the latest version of the N1 System Manager, and the feature subcommand was used, this procedure is not necessary.
Use the add server feature basemanagement command with the upgrade keyword to upgrade a provisionable server to a new version from the existing base management feature.
If you submit add server feature commands by using a script, see Example 5–1 for an example.
Before You Begin
-
Discover servers. See Chapter 2, Discovering, Grouping, and Replacing Servers in the Sun N1 System Manager.
-
This base management feature upgrade procedure applies to provisionable servers on which the base management feature is already installed by a previous version of the N1 System Manager.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
See To Access the N1 System Manager Command Line for details.
-
To upgrade the base management feature, type the following command:
N1-ok> add server server feature basemanagement upgrade
An Add Base Management Support job starts.
See add server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual for details about command syntax.
-
Track the Add Base Management Support job to completion.
After the job completes successfully, the show server command output for the server appears with the OS Monitoring Supported value as OK. In addition, the Base Management Supported column on the Server Details page is marked as Yes. See Enabling and Disabling Monitoring for a graphic that shows this.
Troubleshooting
Adding the base management feature might fail due to stale SSH entries on the management server. If the add server feature osmonitor agentip command fails and no true security breach has occurred, remove the known_hosts file or the specific entry in the file that corresponds to the provisionable server. Then, retry the add server feature osmonitor agentip command. If the management server is running Linux, the known_hosts file is at /root/.ssh/known_hosts. If the management server is running the Solaris OS, the known_hosts file is at /.ssh/known_hosts.
 To Upgrade the OS Monitoring Feature on
a Server
To Upgrade the OS Monitoring Feature on
a Server
This procedure describes how to upgrade the OS monitoring feature on a server. This procedure is necessary after upgrading the N1 System Manager from a previous release, for provisionable servers on which the previous version of the OS monitoring feature is still installed. This procedure is for individual servers. You can upgrade the OS monitoring feature on multiple servers at once. See Chapter 2, Upgrading the Sun N1 System Manager Software and Provisionable Server Management Agents, in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Installation and Configuration Guide for details.
Note –
If the server was freshly installed using the load server or load group commands from the latest version of the N1 System Manager, and the feature subcommand was used, this procedure is not necessary.
Use the add server feature osmonitor command with the upgrade keyword to upgrade a provisionable server to a new version from the existing base management feature and OS monitoring feature.
If you submit add server feature commands by using a script, see Example 5–1 for an example.
Before You Begin
-
Discover servers. See Chapter 2, Discovering, Grouping, and Replacing Servers in the Sun N1 System Manager
-
This OS monitor feature upgrade procedure applies to provisionable servers on which the OS is already installed by a previous version of the N1 System Manager.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
See To Access the N1 System Manager Command Line for details.
-
To upgrade the OS monitoring feature, type the following command:
N1-ok> add server server feature osmonitor upgrade
An Modify OS Monitoring Support job starts. Note that this command also upgrades the base management feature.
See add server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Command Line Reference Manual for details about command syntax.
-
Track the Add OS Monitoring Support job to completion.
After the job completes successfully, the Servers table on the System Dashboard tab appears with values for OS Usage and OS Resource Health.
Verify that the OS monitoring feature is supported by issuing the show server command. Output for the server appears with the OS Monitoring Supported value as OK one of the following sets of commands on the provisionable server.
Note –It can take 5-7 minutes before all OS monitoring data is fully initialized. You may see that CPU idle is at 0.0%, which causes a Failed Critical status with OS usage. This should clear up within 5-7 minutes after adding or upgrading the OS monitoring feature.
Troubleshooting
Upgrading the OS monitoring feature might fail due to stale SSH entries on the management server. If the add server feature osmonitor agentip command fails and no true security breach has occurred, remove the known_hosts file or the specific entry in the file that corresponds to the provisionable server. Then, retry the add server feature osmonitor agentip command. If the management server is running Linux, the known_hosts file is at /root/.ssh/known_hosts. If the management server is running the Solaris OS, the known_hosts file is at /.ssh/known_hosts.
Upgrading the OS monitoring feature will fail if you specify the agent IP or the SSH credentials in the add server feature osmonitor upgrade command when running it on servers that already have the base management feature support. To solve this problem, issue the add server feature osmonitor command without specifying values for the agent IP or for the SSH credentials.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
