Chapter 3 Common Problems
This chapter provides a list of issues and problems that might occur during installation, configuration, and operation of the N1 System Manager, and provides solutions for each.
The following topics are discussed:
-
Job IDs are Missing After Power Cycling the Management Server
-
N1 System Manager Services do not Start After Reboot or Restart
Base Management Installation for a Managed Server Fails
Installing the base management feature support might fail due to stale SSH entries on the management server. If the add server feature command fails and no true security breach has occurred, note the name and IP address of the management server, and then remove the entry for that server as described in To Update the ssh_known_hosts File.
Cannot Determine the Firmware Version on a Managed Server
If the firmware version cannot be reported by the N1 System Manager, one or all of the following situations might be the cause:
-
The IP address of the manageable server's management processor has not been set, and thus the server cannot be discovered.
Check whether the management processor IP address has been set and, if it has been set, whether it is accessible by the N1 System Manager.
If the management processor IP address is not correct, assign an IP address to the processor as directed by the hardware documentation.
If the IP address is correct, go to the next item in this list.
-
The manageable server's management processor account credentials (login account and password) are not recognized by the N1 System Manager. Check the credentials used by the N1 System Manager, and then try accessing the manageable server's management processor account. For information about the processor accounts, see SPARC Architecture Manageable Server Credentials in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide and x86 Architecture Manageable Server Credentials in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.g
If you cannot access the management processor, reset the manageable server to the factory defaults as directed by the hardware documentation, and reassign an IP address to the manageable server's management processor. When you have completed resetting the manageable server, run discovery on the server as described in SP-Based Discovery in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Discovery and Administration Guide.
If discovery is successful, verify the managed server's firmware version as described in To List the Firmware Updates Installed on a Managed Server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Operating System Provisioning Guide.
If the firmware version still cannot be reported by the N1 System Manager, you need to manually check the managed server's firmware by logging into the service processor on the managed server and running a specific service processor command as directed by the server's hardware documentation. For example, to view all of the firmware for an ALOM-enabled server, log into the service processor and type the following command:
showsc version -v Advanced Lights Out Manager v1.5.3 SC Firmware version: 1.5.3 SC Bootmon version: 1.5.3 SC Bootmon Build Release: 02 SC bootmon checksum: 4F888E28 SC Bootmon built Jan 6 2005, 17:05:24 SC Build Release: 02 SC firmware checksum: 6FFB200D SC firmware built Jan 6 2005, 17:05:12 SC firmware flashupdate MAY 25 2005, 01:33:55 SC System Memory Size: 8 MB SC NVRAM Version = b SC hardware type: 0
Compare the service processor firmware versions to the supported firmware versions. See Manageable Server Firmware Requirements in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide, and update the firmware to a supported version as directed by the hardware documentation.
Cannot Discover a Manageable Server
Failure to discover a manageable server can be caused by many different issues. This section provides guidelines and references to help you resolve each issue.
The following topics are discussed:
Discovery of RSC Servers
Manageable servers based on the Remote System Control (RSC) technology, such as Sun Fire V490 and V890 series servers, must be powered off before they can be discovered by N1 System Manager. RSC servers must remain powered off until discovery is complete and discovery has been confirmed by using the show server command.
Note –
The first time the show server command is used to identify a newly discovered RSC server, the command can take up to 5 minutes to complete.
The console of an RSC server must not be in use when being discovered. These servers must also be bench configured prior to discovery. For details on bench configuration of RSC servers, see Preparing RSC-based Manageable Servers in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
If the RSC manageable server was not powered off before being discovered by N1 System Manager, the server MAC address is not detected. Subsequent attempts to load an OS on the server fail with the following message:
Operation failed
In this case, stop the managed server:
N1-ok> stop server server force true |
Refresh the managed server to retrieve the server's MAC address:
N1-ok> set server server refresh |
This command can take up to 5 minutes to complete. Once complete, an OS can be provisioned on to the RSC server using N1 System Manager.
Incorrect Firmware is Installed on the Managed Server
The managed server firmware might be too old.
Verify the firmware version and, if necessary, update the firmware. For a list of qualified firmware versions, see Manageable Server Firmware Requirements in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
Maximum Number of SNMP Connections has been Exceeded
If discovery fails, the target server has reached its maximum number of SNMP connections if the following is contained in the job output:
Error. The limit on the number of SNMP destinations has been exceeded.
The service processor of the Sun Fire V20z and V40z server has a limit of three SNMP destinations. To see the current SNMP destinations, perform the following steps:
-
Log into the service processor using SSH.
-
Run the following command:
sp get snmp-destinations
The SNMP destinations appear in the output.
If there are three destinations for a V20z or a V40z, discovery will fail. The failure occurs because the N1 System Manager adds another snmp-destination to the service processor during discovery.
The SNMP destinations can be configured in a service processor by N1 System Manager or some other management software. You can delete entries from the SNMP destinations if you know that the SNMP destination entry is no longer needed. This would be the case if you discovered the target server using N1 System Manager on one management server and then decided to not use that management server without deleting the server. You can use the sp delete snmp-destination command on the service processor if you need to delete an entry. Use the delete command with caution because some other management software may need the entry for monitoring. A manageable server's SNMP destination is deleted, however, when the server is deleted from the N1 System Manager using the delete server command. It is best practice always to use the delete server command when removing a manageable server.
Firmware Update for a Sun Fire V20z or Sun Fire V40z fails
- Cause:
-
Auto-negotiate link speed has not been enabled on the management network switch.
- Solution:
-
Enable auto-negotiate link speed on the management network switch for all management network connections.
Job IDs are Missing After Power Cycling the Management Server
If the N1 System Manager management server is rebooted or power cycled while jobs are running, the show jobs command will not list the jobs that were running when the management server was power cycled. Subsequent jobs will start at a higher job number, and the list of jobs produced by the show jobs command will display a gap in the job numbers. This can occur if there is a power loss, or if the management server was manually power cycled.
To avoid this problem, wait until all jobs have completed, then stop the N1 System Manager and wait for all processes to stop before rebooting or powering off the management server.
Management Server IP Address Resolves to 127.0.0.1
- Cause:
-
The /etc/hosts file does not contain an IP address and server name assignment for the management server.
- Solution:
-
Update the /etc/hosts file as described in To Update the /etc/hosts File.
Management Server Reboots During Discovery
- Cause:
-
The IP address range specified for discovery includes the management server IP addresses. The discovery process has discovered the management server and attempted to configure the management server as a managed server, which causes the management server/
- Solution 1:
-
Specify an IP address range for discovery that does not include the management server IP addresses.
- Solution 2:
-
Run n1smconfig, and when prompted whether to specify a range of IP addresses for the DHCP server to use:
-
Type y to configure the IP addresses that are to be used for discovery.
-
Specify a range of IP addresses that does not include the management server IP addresses.
For further information, see To Configure the N1 System Manager in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Installation and Configuration Guide.
-
N1 System Manager Services do not Start After Reboot or Restart
If you reboot the management server, and the N1 System Manager services do not restart, you must regenerate security keys as described in Regenerating Security Keys.
If you stop and then start the N1 System Manager and the services do not restart you must regenerate security keys as described in Regenerating Security Keys.
Management Features Unavailable on Manageable Servers After Rebooting
When the load server or load group command is used to install software on the manageable server, the manageable server's networktype attribute could be set to dhcp. This setting means that the server uses DHCP to get its provisioning network IP address. If the system reboots and obtains a different IP address than the one that was used for the agentip parameter during the load command or add server commands, then the following features may not work:
-
The OS Monitoring content of the show server command. (No OS monitoring)
-
The load server update and load group update commands
-
The start server command command
-
The set server threshold command
-
The set server refresh command
In this case, use the set server agentip command to correct the server's agent IP address. See To Modify the Agent IP for a Server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Discovery and Administration Guide for details.
OS Distributions and Deployment
OS distribution creation and OS deployment failures can be caused by many different issues. This section provides guidelines and references to help you resolve each issue.
The following topics are discussed:
-
Deploying Solaris OS 9 Update 7 or Lower from a Linux Management Server Fails
-
OS Deployment Fails on a V20z or V40z With internal error Message
Possible Causes for Distribution and Deployment Failure
OS deployments might fail or fail to complete if any of the following conditions occur:
-
The target RSC technology server was not powered off before discovery was run. RSC servers must remain powered off until discovery is complete and discovery has been confirmed by using the show server command. See Discovery of RSC Servers.
-
Partitions are not modified to suit a Sun Fire V40z or SPARC V440 server. See To Modify the Default Solaris OS Profile for a Sun Fire V40z or a SPARC V440 Server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Operating System Provisioning Guide.
-
Scripts are not modified to install the driver needed to recognize the Ethernet interface on a Sun Fire V20z server. See To Modify a Solaris 9 OS Profile for a Sun Fire V20z Server With a K2.0 Motherboard in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Operating System Provisioning Guide.
-
DHCP is not correctly configured. See Solaris Deployment Job Times Out or Stops.
-
OS profile installs only the Solaris Core System Support distribution group. See Solaris OS Profile Installation Fails.
-
The target server cannot access DHCP information or mount distribution directories. See Invalid Management Server Netmask.
-
The management server cannot access files during a Load OS operation. See Restarting NFS to Resolve Boot Failed Errors.
-
The Linux deployment stops. See Linux Deployment Stops.
-
The Red Hat deployment fails. See Red Hat Linux OS Profile Creation Fails.
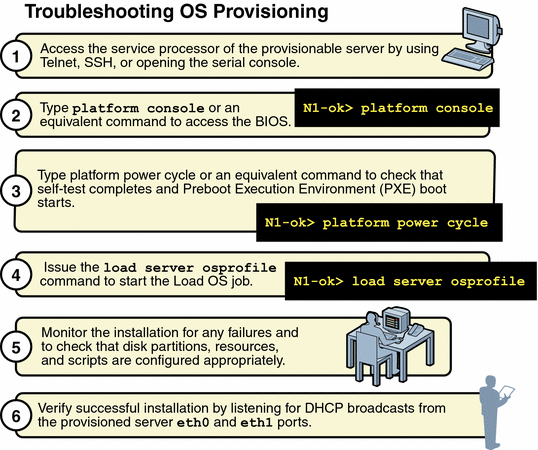
Use the following graphic as a guide to troubleshooting best practices. The graphic describes steps to take when you initiate provisioning operations. Taking these steps will help you troubleshoot deployments with greater efficiency.
Solaris Deployment Job Times Out or Stops
If you attempt to load a Solaris OS profile and the OS Deploy job times out or stops, check the output in the job details to ensure that the target server completed a PXE boot. For example:
PXE-M0F: Exiting Broadcom PXE ROM.
Broadcom UNDI PXE-2.1 v7.5.14
Copyright (C) 2000-2004 Broadcom Corporation
Copyright (C) 1997-2000 Intel Corporation
All rights reserved.
CLIENT MAC ADDR: 00 09 3D 00 A5 FC GUID: 68D3BE2E 6D5D 11D8 BA9A 0060B0B36963
DHCP.
|
If the PXE boot fails, the /etc/dhcpd.conf file on the management server might have not been set up correctly by the N1 System Manager.
Note –
The best diagnostic tool is to open a console window on the target machine and then run the deployment. See Connecting to the Serial Console for a Managed Server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Discovery and Administration Guide.
If you suspect that the /etc/dhcpd.conf file was configured incorrectly, complete the following procedure to modify the configuration.
 To Modify the Network Interface Configuration
To Modify the Network Interface Configuration
Steps
-
Log in to the management server as root.
-
Inspect the dhcpd.conf file for errors.
# vi /etc/dhcpd.conf
-
If errors exist that need to be corrected, run the following command:
# /usr/bin/n1smconfig
The n1smconfig utility appears.
-
Modify the provisioning network interface configuration.
See Configuring the N1 System Manager in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Installation and Configuration Guide for detailed instructions.
-
Load the OS profile on the target server.
Solaris OS Profile Installation Fails
OS profiles that install only the Core System Support distribution group do not load successfully. Specify “Entire Distribution plus OEM Support” as the value for the distributiongroup parameter. Doing so configures a profile that will install the needed version of SSH and other tools that are required for servers to be managed by the N1 System Manager.
Deploying Solaris OS 9 Update 7 or Lower from a Linux Management Server Fails
The inability to deploy Solaris 9 Update 7 or lower OS distributions to servers from a Linux management server is usually due to a problem with NFS mounts. To solve this problem, you need to apply a patch to the mini-root of the Solaris 9 OS distribution. The instructions differ according to the management and patch server configuration scenarios in the following table. The patch is not required if you are deploying Solaris 9 Update 8 or later.
Table 3–1 Task Map for Patching a Solaris 9 Distribution|
Management Server |
Patch Server |
Task |
|---|---|---|
|
Red Hat 3.0 u2 |
Solaris 9 OS on x86 platform |
To Patch a Solaris 9 OS Distribution by Using a Solaris 9 OS on an x86 Patch Server |
|
Red Hat 3.0 u2 |
Solaris 9 OS on SPARC platform |
To Patch a Solaris 9 OS Distribution by Using a Solaris 9 OS on a SPARC Patch Server |
Red Hat Linux OS Profile Creation Fails
Building Red Hat OS profiles on the N1 System Manager might require additional analysis to avoid failures. If you have a problem with a custom OS profile, perform the following steps while the problem deployment is still active.
-
Log into the management server as root.
-
Run the following script:
# cat /var/opt/sun/scs/share/allstart/config/ks*cfg > failed_ks_cfg
The failed_ks_cfg file will contain all of the KickStart parameters, including those that you customized. Verify that the parameters stated in the configuration file are appropriate for the current hardware configuration. Correct any errors and try the deployment again.
Linux Deployment Stops
If you are deploying a Linux OS and the deployment stops, check the console of the target server to see if the installer is in interactive mode. If the installer is in interactive mode, the deployment timed out because of a delay in the transmission of data from the management server to the target server. This delay usually occurs because the switch or switches connecting the two machines has spanning tree enabled. Either turn off spanning tree on the switch or disable spanning tree for the ports that are connected to the management server and the target server.
If spanning tree is already disabled and OS deployment stops, there may be a problem with your network.
Note –
For Red Hat installations to work with some networking configurations, you must enable spanning tree.
Windows Deployment Fails
Provisioning a Windows distribution to a managed server can fail for several reasons:
-
The Windows operating system might not be compatible with the managed server. For a list of qualified servers, see Manageable Server Requirements in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
-
The SSH entries for that managed server on the management server known_hosts file might be stale or obsolete. Determine the management server name and IP address, and then remove the entry for that managed server from the known_hosts as described in To Update the ssh_known_hosts File.
-
The product key is unique to each release of the Windows OS. To ensure that the correct product key applies, either modify the OS profile to include the correct product key or use the productkey attribute on the load server command.
-
If you encounter a TFTP error when loading the OS profile, the GUID is likely incorrect. To find the GUID of a system, use the Pre-Boot eXecution Environment (PXE) to boot the system.
-
If Linux was installed previously on the managed server, Windows will ask about partitions the first time that you try to install Windows on the system. To resolve this issue, delete the partitions on the console, or wipe out the first part of the disk before you install Windows.
Invalid Management Server Netmask
If the target server cannot access DHCP information or mount the distribution directories on the management server during a Solaris 10 deployment, you might have network problems caused by an invalid netmask. The console output might be similar to the following:
Booting kernel/unix... krtld: Unused kernel arguments: `install'. SunOS? Release 5.10 Version Generic 32-bit Copyright 1983-2005 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved. Use is subject to license terms. Unsupported Tavor FW version: expected: 0003.0001.0000, actual: 0002.0000.0000 NOTICE: tavor0: driver attached (for maintenance mode only) Configuring devices. Using DHCP for network configuration information. Beginning system identification... Searching for configuration file(s)... Using sysid configuration file /sysidcfg Search complete. Discovering additional network configuration... Completing system identification... Starting remote procedure call (RPC) services: done. System identification complete. Starting Solaris installation program... Searching for JumpStart directory... /sbin/dhcpinfo: primary interface requested but no primary interface is set not found Warning: Could not find matching rule in rules.ok Press the return key for an interactive Solaris install program... |
To fix the problem, set the management server netmask value to 255.255.255.0. See To Configure the N1 System Manager in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Installation and Configuration Guide.
OS Distribution Creation Fails with a Copying Files Error
If the creation of an OS distribution fails with a copying files error, check the size of the ISO image and ensure that it is not corrupted. You might see output similar to the following in the job details:
bash-3.00# /opt/sun/n1gc/bin/n1sh show job 25 Job ID: 25 Date: 2005-07-20T14:28:43-0600 Type: Create OS Distribution Status: Error (2005-07-20T14:29:08-0600) Command: create os RedHat file /images/rhel-3-U4-i386-es-disc1.iso Owner: root Errors: 1 Warnings: 0 Steps ID Type Start Completion Result 1 Acquire Host 2005-07-20T14:28:43-0600 2005-07-20T14:28:43-0600 Completed 2 Run Command 2005-07-20T14:28:43-0600 2005-07-20T14:28:43-0600 Completed 3 Acquire Host 2005-07-20T14:28:46-0600 2005-07-20T14:28:46-0600 Completed 4 Run Command 2005-07-20T14:28:46-0600 2005-07-20T14:29:06-0600 Error 1 Errors Error 1: Description: INFO : Mounting /images/rhel-3-U4-i386-es-disc1.iso at /mnt/loop23308 INFO : Version is 3ES, disc is 1 INFO : Version is 3ES, disc is 1 INFO : type redhat ver: 3ES cp: /var/opt/SUNWscs/data/allstart/image/3ES-bootdisk.img: Bad address INFO : Could not copy PXE file bootdisk.img INFO : umount_exit: mnt is: /mnt/loop23308 INFO : ERROR: Could not add floppy to the Distro Results Result 1: Server: - Status: -1 Message: Creating OS rh30u4-es failed. |
In the above case, try copying a different set of distribution files to the management server. See To Copy an OS Distribution From CDs or a DVD in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Operating System Provisioning Guide or To Copy an OS Distribution From ISO Files in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Operating System Provisioning Guide.
Mount Point Issues
Distribution copy failures might also occur if there are file systems on the /mnt mount point. Move all file systems off of the /mnt mount point before attempting create os command operations.
OS Deployment Fails on a V20z or V40z With internal error Message
If OS deployment fails on a V20z or a V40z with the internal error occurred message provided in the job results, direct the platform console output to the service processor. If the platform console output cannot simply be directed to the service processor, reboot the service processor. To reboot the service processor, log on to the service processor and run the sp reboot command.
To check the console output, log on to the service processor, and run the platform console command. Examine the output during OS deployment to resolve the problem.
Restarting NFS to Resolve Boot Failed Errors
Error: boot: lookup /js/4/Solaris_10/Tools/Boot failed boot: cannot open kernel/sparcv9/unix
Solution:The message differs depending on the OS that is being deployed. If the management server cannot access files during a Load OS operation, it might be caused by a network problem. To possibly correct this problem, try restarting NFS.
On a Solaris system, type the following:
# svcadm nfs restart |
On a Linux system, type the following:
# /etc/init.d/nfs restart |
Monitoring Problems
This section describes the most common monitoring problems, their causes, and solutions.
Basic Monitoring
If monitoring is enabled as described in Enabling and Disabling Monitoring in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Discovery and Administration Guide, and the status in the output of the show server or show group commands is unknown or unreachable, then the server or server group is not being reached successfully for monitoring. If the status remains unknown or unreachable for less than 30 minutes, it is possible that a transient network problem is occurring. However if the status remains unknown or unreachable for more than 10 minutes, it is possible that monitoring has failed. This could be the result of any of the following issues.
-
The base monitoring agent on the managed server has stopped running.
-
The managed server has been powered off or been unplugged.
-
The managed server IP address or name has been changed independently of N1 System Manager.
If monitoring traps are lost, a particular threshold status may not be refreshed for up to 30 hours, although the overall status should still be refreshed every 10 minutes.
A time stamp is provided in the monitoring data output. The relationship between this time stamp and the current time can also be used to judge if there is an error with the monitoring agent.
OS Monitoring
It can take 5 to 7 minutes before all OS monitoring data is fully initialized. You may see that CPU idle is at 0.0%, which causes a Failed Critical status with OS usage. This should clear up within 5-7 minutes after adding or upgrading the OS monitoring feature to the managed server. At that point, OS monitoring data should be available for the managed server by using the show server server command. For further information, see To Add the OS Monitoring Feature in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Discovery and Administration Guide
Adding the base management feature to a managed server might fail due to stale or obsolete SSH entries for that managed server on the management server known_hosts file. If the add server server-name feature osmonitor agentip command fails and no true security breach has occurred, remove the entry for that managed server from the known_hosts as described in To Update the ssh_known_hosts File. Then, retry the add command.
ALOM-based Managed Server Notifications are not Displayed
The ports of some models of manageable servers use the Advanced Lights Out Manager (ALOM) standard. These servers, detailed in Manageable Server Requirements in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide, use email instead of SNMP traps to send notifications about hardware events to the management server. For information about other events, see Managing Event Log Entries in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Discovery and Administration Guide and Setting Up Event Notifications in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Discovery and Administration Guide.
If there are no notifications about hardware events from ALOM architecture manageable servers, it could mean that all managed servers are all healthy. If you are using an external mail service instead of the internal secure N1 System Manager mail service, it is possible that the external mail service has not been configured correctly as an email server, or that email configuration has been invalidated due to other issues such as network error or domain name change.
To resolve, either:
-
Reconfigure the N1 System Manager by running n1smconfig, and choose the secure internal N1 System Manager mail service.
-
Check and reset your external email server configuration. See Resetting Email Accounts for ALOM-based Managed Servers
OS Updates
This section describes the most common OS update problems, their causes, and solutions.
The following topics are discussed:
OS Update Creation Fails
The name that is specified when you create a new OS update must be unique. The OS update to be created also needs to be unique. That is, in addition to the uniqueness of the file name for each OS update, the combination of the internal package name, version, release, and file name also needs to be unique.
For example, if test1.rpm is the source for an RPM named test1, another OS update called test2 cannot have the same file name as test1.rpm. To avoid additional naming issues, do not name an OS update with the same name as the internal package name for any other existing packages on the manageable server.
You can specify an adminfile value when you create an OS update. For the Solaris OS update packages, a default admin file is located at /opt/sun/n1gc/etc/admin.
mail= instance=unique partial=nocheck runlevel=nocheck idepend=nocheck rdepend=nocheck space=quit setuid=nocheck conflict=nocheck action=nocheck basedir=default authentication=nocheck |
If you use an adminfile to install an OS update, ensure that the package file name matches the name of the package. If the file name does not match that of the package, and an adminfile is used to install the OS update, uninstallation will fail. See OS Update Uninstallation Failures.
The default admin file setting used for Solaris package deployments in the N1 System Manager is instance=unique. If you want to report errors for duplicated packages, change the admin file setting to instance=quit. This change causes an error to appear in the Load Update job results if a duplicate package is detected.
See the admin(4) man page for detailed information about admin file parameter settings. Type man -s4 admin as root user on a Solaris system to view the man page.
For Solaris packages, a response file might also be needed. For instructions on how to specify an admin file and a response file when you create an OS update, see To Copy an OS Update in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Operating System Provisioning Guide.
Solaris OS Update Deployment Failures
This section describes troubleshooting scenarios and possible solutions for the following categories of failures during Solaris OS update deployment:
-
Failures that occur before the job is submitted
-
Load Update job failures
-
Unload Update job failures
-
Stop Job failures for Load Update
In the following unload command, the update could be either the update name in the list that appears when you type show update all list, or the update could be the actual package name on the target server.
N1-ok> load server server update update |
Always check the package is targeted to the correct architecture.
Note –
The N1 System Manager does not distinguish 32-bit from 64-bit for the Solaris (x86 or SPARC) OS, so the package or patch might not install successfully if it is installed on an incompatible OS.
If the package or patch does install successfully, but performance decreases, check that the architecture of the patch matches the architecture of the OS.
The following are common failures that can occur before the job is submitted:
Target server is not initialized
Solution:Check that the add server feature osmonitor command was issued and that it succeeded.
Another running job on the target server
Solution:Only one job is allowed at a time on a server. Try again after the job completes.
Update is incompatible with operating system on target server
Solution:Check that the OS type of the target server matches one of the update OS types. Type show update update-name at the N1–ok> prompt to view the OS type for the update.
Target server is not in a good state or is powered off
Solution:Check that the target server is up and running. Type show server server-name at the N1–ok> prompt to view the server status. Type reset server server-name force to force a reboot.
The following are possible causes for Load Update job failures:
Sometimes, Load Update jobs fail because either the same package already exists or because a higher version of the package exists. Ensure that the package does not already exist on the target server if the job fails.
error: Failed dependencies:
A prerequisite package and should be installed.
Solution:For a Solaris system, configure the idepend= parameter in the admin file.
Preinstall or postinstall scripts failure: Non-zero status
pkgadd: ERROR: ... script did not complete successfully
Solution:Check the pre-installation or post installation scripts for possible errors to resolve this error.
Interactive request script supplied by package
Solution:This message indicates that the response file is missing or that the setting in the admin file is incorrect. Add a response file to correct this error.
patch-name was installed without backing up the original files
Solution:This message indicates that the Solaris OS update was installed without backing up the original file. No action needs to be taken.
Insufficient diskspace
Solution:Load Update jobs might fail due to insufficient disk space. Check the available disk space by typing df -k. Also check the package size. If the package size is too large, create more available disk space on the target server.
The following are stop job failures for loading or unloading update operations:
If you stop a Load Update or Unload Update job and the job does not stop, manually ensure that the following process is killed on the management server:
# ps -ef |grep swi_pkg_pusher ps -ef |grep pkgadd, pkgrm, scp, ... |
Then, check any processes that are running on the manageable server:
# ps -ef |grep pkgadd, pkgrm, ... |
The following are common failures for Unload Server and Unload Group jobs:
The rest of this section provides errors and possible solutions for failures related to the following commands: unload server server-name update update-name and unload group group-name update update-name.
Removal of <SUNWssmu> was suspended (interaction required)
Solution:This message indicates a failed dependency for uninstalling a Solaris package. Check the admin file setting and provide an appropriate response file.
Job step failure without error details
Solution:This message might indicate that the job was not successfully started internally. Contact a Sun Service Representative for more information.
Job step failure with vague error details: Connection to 10.0.0.xx
Solution:This message might indicate that the uninstallation failed because some packages were not fully installed. In this case, manually install the package in question on the target server. For example:
To manually install a .pkg file, type the following command:
# pkgadd -d pkg-name -a admin-file |
To manually install a patch, type the following command:
# patchadd -d patch-name -a admin-file |
Then, run the unload command again.
Job hangs
Solution:If the job appears to hang, stop the job and manually kill the remaining processes. For example:
To manually kill the job, type the following command:
# n1sh stop job job-ID |
Then, find the PID of the PKG and kill the process, by typing the following commands:
# ps -ef |grep pkgadd # pkill pkgadd-PID |
Then run the unload command again.
Linux OS Update Deployment Failures
This section describes troubleshooting scenarios and possible solutions for the following categories of failures during Linux OS update deployment:
-
Failures that occur before the job is submitted
-
Load Update job failures
-
Unload Update job failures
-
Stop Job failures for Load Update
In the following unload command, the update could be either the update name in the list that appears when you type show update all list, or the update could be the actual package name on the target server.
N1-ok> load server server update update |
The following are common failures that can occur before the job is submitted:
Target server is not initialized
Solution:Check that the add server feature osmonitor command was issued and that it succeeded.
Another running job on the target server
Solution:Only one job is allowed at a time on a server. Try again after the job completes.
Update is incompatible with operating system on target server
Solution:Check that the OS type of the target server matches one of the update OS types. Type show update update-name at the N1–ok> prompt to view the OS type for the update.
Target server is not in a good state or is powered off
Solution:Check that the target server is up and running. Type show server server-name at the N1–ok> prompt to view the server status. Type reset server server-name force to force a reboot.
The following are possible causes for Load Update job failures:
Sometimes, Load Update jobs fail because either the same package already exists or because a higher version of the package exists. Ensure that the package does not already exist on the target server if the job fails.
error: Failed dependencies:
A prerequisite package should be installed
Solution:Use an RPM tool to address and resolve Linux RPM dependencies.
Preinstall or postinstall scripts failure: Non-zero status
ERROR: ... script did not complete successfully
Solution:Check the pre-installation or post installation scripts for possible errors to resolve this error.
Insufficient diskspace
Solution:Load Update jobs might fail due to insufficient disk space. Check the available disk space by typing df -k. Also check the package size. If the package size is too large, create more available disk space on the target server.
The following are stop job failures for loading or unloading update operations:
If you stop a Load Update or Unload Update job and the job does not stop, manually ensure that the following process is killed on the management server:
# ps -ef |grep swi_pkg_pusher ps -ef |grep rpm |
Then, check any processes that are running on the manageable server:
# ps -ef |grep rpm, ... |
The following are common failures for Unload Server and Unload Group jobs:
The rest of this section provides errors and possible solutions for failures related to the following commands: unload server server-name update update-name and unload group group-name update update-name.
Job step failure without error details
Solution:This message might indicate that the job was not successfully started internally. Contact a Sun Service Representative for more information.
Job step failure with vague error details: Connection to 10.0.0.xx
Solution:This message might indicate that the uninstallation failed because some RPMs were not fully installed. In this case, manually install the package in question on the target server. For example:
To manually install an RPM, type the following command:
# rpm -Uvh rpm-name |
Then, run the unload command again.
Job hangs
Solution:If the job appears to hang, stop the job and manually kill the remaining processes. For example:
To manually kill the job, type the following command:
# n1sh stop job job-ID |
Then, find the PID of the RPM and kill the process, by typing the following commands:
# ps -ef |grep rpm-name # pkill rpm-PID |
Then run the unload command again.
OS Update Uninstallation Failures
If you cannot uninstall an OS update that was installed with an adminfile, check that the package file name matches the name of the package. To check the package name:
bash-2.05# ls FOOi386pkg
FOOi386pkg
bash-2.05# pkginfo -d ./FOOi386pkg
application FOOi386pkg FOO Package for Testing
bash-2.05# pkginfo -d ./FOOi386pkg | /usr/bin/awk '{print $2}'
FOOi386pkg
---
bash-2.05# cp FOOi386pkg Foopackage
bash-2.05# pkginfo -d ./Foopackage
application FOOi386pkg FOO Package for Testing
bash-2.05# pkginfo -d ./Foopackage | /usr/bin/awk '{print $2}'
FOOi386pkg
bash-2.05#
|
If the name is not the same, rename the adminfile in the manageable server's /tmp directory to match the name of the package and try the unload command again. If the package still exists, remove it from the manageable server by using pkgrm.
Unable to Log On to a Managed ServerManagement Processor
- Cause:
-
The service processor account and password are not known.
- Solution:
-
Reset the service processor accounts to the factory defaults as described by the hardware documentation
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
