| RFID Software Developer's Guide
|
   
|
Sun Java System RFID Software Information Server
|
This chapter describes the Sun Java System RFID Software Information Server. The following topics are covered:
System RFID Software Information Server. The following topics are covered:
Architecture
The Sun Java System RFID Software Information Server (IS) is a J2EE application that runs on one of the supported application servers. RFID Information Server persists all data in a relational database. Any JDBC-compliant RDBMS can be used as the data store. In this release of Sun Java System RFID Software, RFID Information Server is supported on the following databases:
- Oracle Database 8.1.7
- Oracle Database 10g
- PostgreSQL 7.4.6
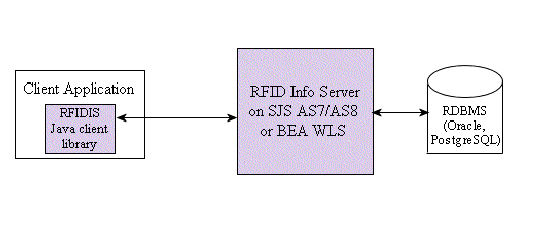
External applications interface with the RFID Information Server through XML message exchange. Requests and responses are expressed in XML and conform to an XML schema. The RFID Information Server supports HTTP and JMS message transports. The RFID Software provides a Java client library to access the RFID Information Server programatically. The API to query and manipulate data in the RFID Information Server is independent of the protocol used. FIGURE 1-1 shows the architecture. Chapter 2 describes the use of the client API.
FIGURE 1-1 RFID Information Server Architecture
Database Tables
This section describes the Sun Java System RFID Software database table names and descriptions.
TABLE 1-1 RFID Information Server Database Tables
|
Table Name
|
Definition
|
Database Table Keys
|
|
CONTAINER_TYPE
|
Each entry in this table represents a type of container.
Container types are specific to a deployment. Common container types include Pallets, Cases, Inner Packs and Items.
|
Primary Key: NAME
|
|
CONTAINMENT
|
Maintains a hierarchy of container relationships between EPCs.
Each container is identified by the 'parent' EPC. The parent may have zero or more 'child' EPCs. Since a child EPC can itself represent a container the hierarchy can be arbitrarily deep.
|
|
|
CURRENT_OBSERVATION
|
Maintains the list of tags that are reported as currently visible at a sensor.
This table can only be used in conjunction with the Delta filter in the Event Manager. To keep the table consistent the IS relies on the TagsIn and TagsOut attribute of the Delta event.
|
Foreign Key: SENSOR_EPC
|
|
OBSERVATION_LOG
|
Maintains the history of all tag observations.
Each entry in the table represents an observation which contains the EPC of the observer (sensor), the EPC of the observed value and the time at which it was observed.
|
Foreign Key: SENSOR_EPC
|
|
ORGANIZATION
|
A manufacturer or distributor of goods.
|
Primary Key: ORGANIZATION_ID
|
|
PRODUCT
|
A class of items, or Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) identified by a GTIN or UPC code.
|
Primary Key: PRODUCT_ID
Foreign Keys: MANUFACTURER_ID
|
|
SENSOR
|
An RFID reader or antenna uniquely identified by an EPC.
|
Primary Key: EPC
|
|
TAG_ALLOCATION
|
Assigns and de-assigns ranges of EPC number and keep track of them.
|
Primary Key: TAG_ALLOCATION_ID
|
|
TAG_ALLOCATION_LOG
|
Maintains the history of all tag allocated.
|
|
|
TX_LOG
|
Associates a set of EPCs with a business transaction ID.
Common transaction IDs include PO numbers and ASNs.
|
|
|
UNIT
|
A tagged entity identified by a unique EPC. An entry in the UNIT table can represent a pallet, case or any other entity that's tracked.
|
Primary Key: EPC
Foreign Keys: PRODUCT_ID, UNIT_TYPE
|
|
Note - Each sensor is identified by a unique EPC. The primary key in the SENSOR table is called EPC instead of SENSOR_EPC for brevity.
|
Entries in the OBSERVATION_LOG, CURRENT_OBSERVATION tables have an attribute called SENSOR_EPC to differentiate it from EPC which is the EPC that is observed. The SENSOR_EPC identifies the observer. It is a foreign key into the SENSOR table.
| RFID Software Developer's Guide
|
819-1698-10
|
   
|
Copyright © 2004, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 System RFID Software Information Server. The following topics are covered:
System RFID Software Information Server. The following topics are covered:
