| C H A P T E R 2 |
|
Accessing the System Controller |
This chapter explains step-by-step procedures with illustrations describing how to:
Topics covered in this chapter include:
By default, serial connections to the SC are enabled and remote connections are disabled. To enable remote connections, use the setupplatform command. For details on the setupplatform command, refer to the command description in the Sun Fire Midrange System Controller Command Reference Manual.
This section describes how to use the following types of connections to access the SC main menu:
 At the machine prompt, type tip and the serial port to be used for the system controller session.
At the machine prompt, type tip and the serial port to be used for the system controller session.
The SC main menu is displayed (see CODE EXAMPLE 2-1).
 Connect the system controller serial port to an ASCII terminal.
Connect the system controller serial port to an ASCII terminal.
The SC main menu is displayed (see CODE EXAMPLE 2-1).
Before you attempt to use SSH or TELNET, make sure that the SC has been configured to enable remote connections. For details on configuring the settings for remote connections, refer to the setupplatform command description in the Sun Fire Midrange System Controller Command Reference Manual.
|
Note - The SC provides SSH server functionality only. For security reasons, only connections requested by client software running the SSHv2 protocol are accepted by the SSH server on the SC. See Enabling SSH. |
 Type the following at the system prompt:
Type the following at the system prompt:
where schostname is the system controller host name.
The system controller main menu is displayed (see CODE EXAMPLE 2-1).
|
Note - When using SSH, you can open a maximum of five connections to the system controller at one time. |
If you receive the following message while attempting to open a remote connection with SSH
ssh_exchange_identification: Connection closed by remote host
run the connections command from the platform shell on the main SC to determine whether you have reached the connection limit.
 Type the following at the system prompt:
Type the following at the system prompt:
where schostname is the system controller host name.
The system controller main menu is displayed (see CODE EXAMPLE 2-1).
To bypass the SC main menu, use a port number as an additional argument to the telnet command (the port_number argument is not available for ssh). You can make a remote connection to the platform shell, a domain shell (if the specified domain is inactive), or a domain console (if the specified domain is active).
where schostname is the system controller host name and the port_number is one of the following:
This section describes the SC main menu.
1. Access the SC main menu by initiating a serial or remote connection to the SC.
The SC main menu is displayed. CODE EXAMPLE 2-1 shows the SC main menu, where schostname is the system controller host name. In this example, the selected destination is the platform shell.
The system controller prompt, schostname:SC>, is displayed for the platform shell of the main system controller. If you have a redundant SC configuration, the spare system controller prompt is schostname:sc>.
The system controller prompt for the domain you connected to is displayed. For example, the prompt for domain A is schostname:A>. If the domain is active, you get the domain console. If the domain is inactive, you get the domain shell.
For the definitions of platform shell, domain shell, and domain console, see Chapter 1.
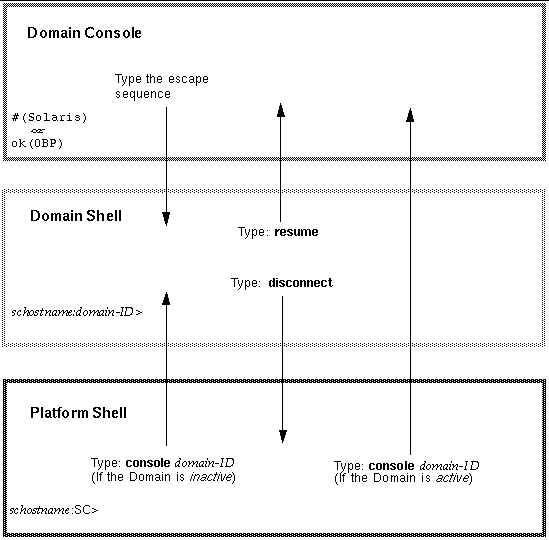
This section describes the navigation procedures summarized in FIGURE 2-1.
|
Note - This example shows entering an inactive domain from the platform shell. |
where domain_ID is the domain name.
For example, to go to the domain shell for domain a:
If you select a domain that is active (from the SC main menu), you get the domain console instead. An active domain is one in which the OpenBoot PROM is running or the domain keyswitch is set to on, diag, or secure.
 Type disconnect to return to the platform shell.
Type disconnect to return to the platform shell.
If you choose a domain and that domain is active (the domain keyswitch is set to on, diag, or secure which means you are running the Solaris operating environment, or are in the OpenBoot PROM), you will enter the domain console. To exit the domain console and enter the domain shell, perform the following steps
 Type the escape sequence to get to the domain shell prompt.
Type the escape sequence to get to the domain shell prompt.
By default, the escape sequence is #. (the pound sign, followed by a period).
1. If the domain is active, perform the following steps:
a. From the domain shell, type the following:
Note that because the domain is active, you will get a blank line.
b. Press the Return key to get a prompt.
|
Note - If the domain is not active, (the Solaris operating environment or the OpenBoot PROM is not running), the system controller stays in the domain shell and you will obtain an error. |
2. If the domain is inactive, activate and initialize the domain by typing the following in the domain shell:
The domain console is available only when the domain is active. To make the domain active, you must turn the keyswitch on. You will be automatically switched from the domain shell to the domain console.
The domain will go through POST and then the OpenBoot PROM. If the OpenBoot PROM auto-boot? parameter of the setupdomain command is set to true, the Solaris operating environment will boot. For details on the domain parameters, refer to the setupdomain command description in the Sun Fire Midrange System Controller Command Reference Manual.
This section describes how to terminate connections to the system controller.
If you are connected to the System Controller board with the serial port, use the disconnect command to terminate the system controller session then use a tip command to terminate your tip session.
1. At the domain shell or platform shell prompt, type disconnect.
|
Note - When you disconnect from a direct connection to a domain shell, you will see nothing. Press the Return key to obtain the prompt. |
2. If you are in a domain shell and are connected from the platform shell, type disconnect again to disconnect from the system controller session.
The SC main menu is displayed.
3. Type ~. to end your tip session (CODE EXAMPLE 2-3).
System Controller `schostname': Type 0 for Platform Shell Type 1 for domain A Type 2 for domain B Type 3 for domain C Type 4 for domain D Input: ~. machinename% |
The machinename% prompt is displayed.
 If you are connected directly to the domain and not from the platform shell, type the disconnect command at the domain shell prompt.
If you are connected directly to the domain and not from the platform shell, type the disconnect command at the domain shell prompt.
Your system controller session terminates.
|
Note - When you disconnect from a direct connection to a domain shell, you will see nothing. Press the Return key to obtain the prompt. |
If you have a connection to the domain initiated on the platform shell, you must type disconnect twice.
Typing disconnect the first time returns you to the platform shell connection and keeps your connection to the system controller. Typing disconnect again exits the platform shell and ends your connection to the system controller.
Copyright © 2004, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.