Chapter 11 Complex Jobs
This chapter explains how to manage hosts in the most consistent and efficient manner. Complex jobs are not difficult to create or use; they are complex because they combine several objects into one command from the user interface to the system dependency server. Complex jobs maintain consistency throughout the environment and to make sure that even the most complicated lifecycle management missions are orderly and error-free. Complex jobs allow you to include multiple tasks, each task combining a set of objects and operation options.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Terms
This chapter uses the following terms:
- Agent
-
Application of Sun Update Connection – Enterprise that is installed on every managed host and that runs the Dependency Resolver, finding solutions specific to its host.
- Cost-effective
-
Deployment solution that has the least requirements for number of dependency issues, time, and resources, to fulfill a job.
- dependency manager (DM)
-
Sub-system of the Sun Update Connection – Enterprise system dependency server, responsible for managing jobs on hosts and communications between the user interface and agents.
- dependency resolver (DR)
-
Set of patented algorithms to describe a solution for a job. Initiated by agent application when a job is received.
- Mode
-
Job option that determines whether the job changes hosts (Deploy) or tests the action list on hosts (Simulate).
- Job
-
Collection of actions and tests to be run on selected managed hosts by agents.
- Knowledge Base
-
Sub-system of the Sun Update Connection – Enterprise system dependency server, acts as a proxy server for the universal server, keeping dependency rules for CO deployment on managed hosts and the COs themselves.
A local knowledge base is a private, on-site only, collection of NCO listings and their deployment rules as generated by the Local Expansion technology.
- Policy
-
Set of confirmation rules for the implementation of the dependency resolver and level of automation of jobs.
- Profile
-
Definition of a component configuration for a type of machine; what is required and what is not allowed to be installed on this type of machine.
- system dependency server (SDS)
-
The complete management system for Sun Update Connection – Enterprise. Its sub-systems include the Server, the dependency manager, and the knowledge base.
- Task
-
Part of a job that contains a profile, a hostlist, a policy, an optional schedule, and performance options.
Complex Job Processes
You create a single job to be run on one or multiple hosts. Each agent that receives the job runs it individually, optimizing on the software configuration of the host.
To fulfill a job, an agent uses rules and components from the knowledge base. The agent runs the dependency resolver, which takes into account installed inventory, selected policy, and selected profile.
The dependency resolver is a set of algorithms that describes the best possible solution for an agent to complete a job. The best possible solution includes:
-
The most cost-effective package to deploy, matching component rules in the knowledge base to the existing configuration of the host
-
The most cost-effective way to fulfill dependency requirements, ensuring that the managed host will operate correctly after the job
When you create a job, the agent of each selected managed host picks up the job and runs the following processes. Each agent performs these actions only for the components of its distribution-architecture; irrelevant components are ignored. Therefore, you can safely create a multiple distribution job and send it to a mixed group of hosts.
The job process of each agent, for each task, is as follows:
-
Sends the software component inventory of the host to the dependency manager
-
Runs probes to test that host resources can fulfill the job, if you selected probes
-
Builds a tasklist (if a simulation job, job ends after this step)
-
Saves an inventory of each host to be changed
-
Gets confirmation for tasks, either from a policy or interactively
-
Runs local pre-actions, if you selected any
-
Installs local Configuration files, if you selected any
-
Customizes local Configuration files with macros, if any are called upon
-
Installs requested knowledge base components
-
Runs local post-actions, if you selected any
-
Runs post-fix actions, if applicable (see Post-Fix Actions)
-
Sends job status (success/failure) and new inventory to the DM
Post-Fix Actions
A post-fix action is a binary that performs an action on hosts when a specific package has been installed. Sun Update Connection – Enterprise runs post-fixes without user intervention. Post-fixes ensure machine functionality after changes.
Example 11–1 Using Post-Fix Actions
You create a job that upgrades the kernel. Before the job ends, a post-fix action is triggered, which updates the boot-loader file for the new kernel version.
Agent Queuing
While an agent is running a job, it cannot perform other Sun Update Connection – Enterprise actions:
-
It cannot upload its parameters to the Host Settings window.
-
It cannot upload an updated inventory to the console. The inventory of the managed host will be updated on the console after the job is done.
You may assign more jobs to this host, and the jobs will be queued.
Complex Job Objects
A complex job is made up of one or more tasks, a schedule, and a set of performance options. At the time that you create the job, you set the schedule (see To Set Job Schedules) and the options (see To Set Job Options). On the other hand, you may create the objects of the tasks either on the fly, as you create the tasks, or before you begin to create the job.
A task needs a profile:
-
You can create or copy a profile beforehand. See Chapter 9, Profiles
-
You can use Predefined Profiles. See Chapter 7, System Management Profiles
A task needs a policy:
-
You can create or copy a policy beforehand. See Chapter 10, Policies
-
You can use the default Always ask me policy.
A task needs a hostlist:
-
You can select groups to ensure hosts of similar functionality receive consist jobs. See Chapter 4, Hosts and Groups
-
You can select one or more hosts (using the Shift or Control keys) from the New Job window.
-
Users with restricted permissions over groups can select only groups and hosts of their authorized groups.
Creating Complex Jobs
In the following procedures, you will select the objects and options of a job and then run the job on selected hosts.
Before you begin a job on a Solaris machine, make sure the PKG deployment preferences are appropriate for your local needs. See Host Preferences – PKGs on Host Preferences – PKGs.
This procedure is broken up into the following parts:
 To Set Up the Objects of a Job
To Set Up the Objects of a Job
-
Make sure the Jobs panel is available in the main window by choosing Jobs from the View menu.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Give the job a name and a free-text description.
-
Select a mode for the job:
-
Do the following:
-
Create tasks for the job.
-
Set job options or leave the default settings.
See To Set Job Options.
-
Set a schedule or leave the default Now schedule.
See To Set Job Schedules.
-
 To Create the Tasks of a Job
To Create the Tasks of a Job
-
In the Tasks tab of the New Job window, click Add Task.
The Task Editor opens.
-
Type a name for a task.
-
Select a profile from the drop-down list, or click the profile editor button to open the Profile Editor and create a new profile.
If you select a user-defined profile and then click the button, you can edit an existing profile.
-
Select a policy from the drop-down list, or click the policy editor button to open the Policy Editor, to create or edit a policy as you would a profile.
-
Click the Hosts button to the right of the Hosts field.
The Select Hosts window opens.
-
Select hosts and groups and then click the Add button.
The hosts or groups are added to the Selected Hosts list.
-
When the Selected Hosts list contains the hosts or groups that you want to receive this job, click OK.
The Hosts window closes. The selected hosts and groups appear in the Hosts field of the Tasks tab.
-
Click OK.
The task is added to the Tasks list of the job. Add as many tasks as you want.
The order of the tasks in the list is the order that they will be executed. To change this order, select a task name and click the Up or Down buttons.
To edit a task, select the task and click the Edit button.
To remove a task from the job, select the task and click the Delete button.
-
Decide how to continue:
-
If you want to run the job with default settings, click OK now.
-
If you want to set a deployment schedule, go to To Set Job Schedules.
-
If you want to view and edit the job options, go to To Set Job Options.
-
If you want to save the tasks as a job template, click Save Template.
-
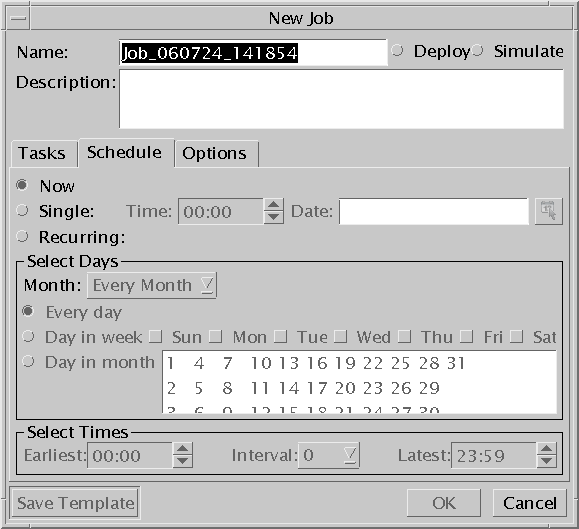
 To Set Job Schedules
To Set Job Schedules
 To Set a Single Schedule
To Set a Single Schedule
-
Select Single.
-
In the Time text box, select the hour and the minutes.
Type in the desired time, or use the arrows to change the selection.The time settings are by 24 hours: 13:00 = 1pm, 14:00 = 2pm, ... 00:00 = midnight.
-
Click the button to the right of the Date box.
The Calendar opens.
-
Select a date and then click OK.
The Calendar closes. The selected date appears in the Date field.
-
In the New Job window, click OK or set job options.
See To Set Job Options.
The job will begin on the selected time and date.
 To Set a Recurring Schedule
To Set a Recurring Schedule
-
Select Recurring.
-
In the Month drop-down list, select either Every Month (all year schedule) or a specific month (monthly schedule).
-
Select days of the month:
-
Select time of the day:
 To Set Job Options
To Set Job Options
-
Open the Options tab.
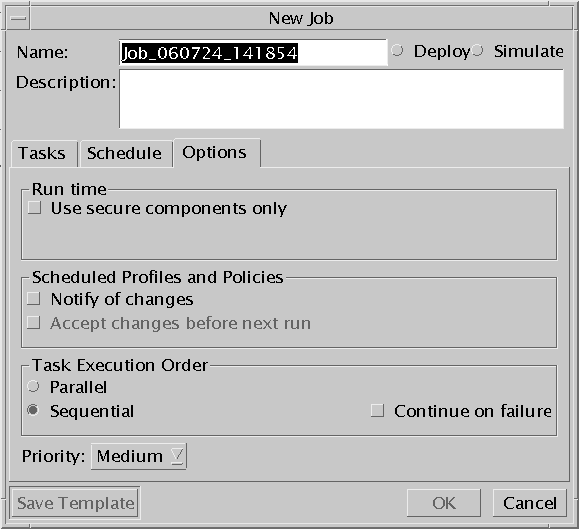
-
Select Use Secure Components only if you want to give priority to secure versions. Deselect it to give priority to cost-effective versions, which makes the job run faster.
-
If you set a recurring schedule for the job, decide how the job should be handled if selected profiles and policies are changed between now and the next run of the job.
Option
Selected Function
Deselected Function
Notify of changes
If the owner of the profiles or policies changes them, you will get an email notification. Select if using profiles/policies that other users created.
You are not notified of changes. Deselect if you own the selected profiles or policies and do not want the reminder emails.
Accept changes before next run
Use updated profiles or policies. Select for consistency and automation.
Use the profiles or policies as they were when you created the job. Deselect for predictability.
-
Specify how you want the task to run in relation to other tasks and how to handle failures.
Option
Selected Function
Deselected Function
Parallel
Run the job simultaneously with other jobs. Do not run jobs that depend on the results of other jobs in parallel. Run such jobs in sequential mode only.
Run the job after the previous job completed. By default, a job is run sequentially.
Sequential
Run the job after other jobs have completed.
Run the job in parallel mode.
Continue on failure
Continue to run a job even if one of the steps or tasks experienced a failure. This option is only available for jobs that run in sequential mode.
Terminate a job if a step or task experiences a failure.
Priority
Select or change a priority for ajob. Values are Low, Medium, and High.
By default, the priority is set to Medium.
Running a Job with the CLI
The CLI command to submit a job runs one task on a single selected host or group. See Submit Job (-sj) Command.
#! /bin/bash echo -n “Enter your user name:” read user echo -n “Enter your password:” read password echo -n “Type a name for this job:” read jobname echo -n “Do you want to run this job on a host or a group? (h|g):” read hostgroup if [ $hostgroup = “h” ];then echo “Hosts are:” uce_cli -lah -u “$user” -p “$password” else echo “Groups are:” uce_cli -lg -u “$user” -p “$password” fi echo -n “Copy host or group name to receive job:” read selected echo “Profiles are:” uce_cli -lp -u “$user” -p “$password” echo -n “Copy profile to use:” read profile echo “Policies are:” uce_cli -lc -u “$user” -p “$password” echo -n “Copy policy to use:” read policy echo “Simulating $jobname” uce_cli -sj -j “$jobname” -P “$profile” -C “$policy” -$hostgroup “$selected” -us -sm -u “$user” -p “$password” echo -n “Do you want to deploy $jobname? (y|n)” read yes if [ $yes = “y” ]; then uce_cli -sj -j “$jobname Deployed” -P “$profile” -C “$policy” -$hostgroup “$selected” -us -dp -u “$user” -p “$password” fi |
Saving Job Templates
 To Save a Job Template
To Save a Job Template
After you have set up the objects of a job, you can save it as a template. Using a job template, you can run the job, with or without edits, whenever you want. Use this procedure if you have the job requirements, but are unsure of when it should be run, or if the hosts are not yet online.
-
Open the New Job window and create tasks.
If you want, you can set a schedule and select options.
-
With any tab of the New Job window open, click Save Template.
Sun Update Connection – Enterprise saves the job without running it, and sends you a message when the save is complete.
The template name appears in the Jobs list, with an icon to indicate that it is not a running job.
To create a job from the template, select the template and then right-click and select Rerun. Select Deploy or Simulate and then click OK.
Copying Jobs
 To Copy a Job
To Copy a Job
You can use a job to be the base of another job. Use this procedure if you have a complex job that would fulfill new requirements with a few changes, rather than creating a new job.
-
In the Jobs list, select a job to use as the source and then right-click and select Copy.
The New Job window opens with the objects and settings of the selected job.
The profile is listed as Based on <source profile> from <date time>. This is to notify you that the job will be based on the profile as it was at the date and time that the source job was created. If the profile has been changed since then, this new job will not reflect those changes.
If the profile is listed as Task’s Profile, the job was not a complex job. It was created by applying job settings to inventory components. You can make a copy of this job, but you cannot view its ToDo basket.
-
Make any changes to the job that you want and then click OK.
The job is added to the Jobs list and begins according to its schedule settings.
Note –If you do make changes to the copied job, there is no indication in the Job list. See the Job Log for details of how the changes were translated into actions.
Creating Complex Jobs
 To Create a Simple Complex Job
To Create a Simple Complex Job
This procedure is a specific example of executing Complex Jobs. This example is of a very simple job. You could follow it even if you have not yet created profiles, policies, and groups.
-
Make sure the Jobs panel of the main window is open by choosing Jobs from the View menu.
-
From the tool bar, click the New Job button.
The New Job window opens.
-
Name the job CheckAllHosts. In the description, type This job checks all hosts for missing dependencies.
-
Select Simulate.
This job will find any missing dependencies on any of the hosts and give you an idea of how long the actual job would take.
-
In the Tasks tab, click Add Task and a task with:
-
Click OK in the Tasks tab.
The SingleCheck task is added to the job.
-
Click OK in the New Job window.
The job is sent to all managed hosts. Each host will be checked to see whether it has any missing or conflicting dependencies.
-
Check the progress of the hosts as they run the job, and the job log of each host when it is done.
If the results of the simulation are satisfactory, rerun the job in Deploy mode. See To Rerun a Job.
The DR finds a solution to fix any missing or conflicting dependencies. You will be asked to confirm the fixes before they are deployed. See To Confirm Tasks). On confirmation, the actions are carried out and all dependencies are fixed on all hosts.
 To Create a Feature-Rich Complex Job
To Create a Feature-Rich Complex Job
This procedure is a specific example of using the Complex Job feature. This example is of a more feature-rich job.
This example assumes the following:
-
You have a profile with your requirements of an NFS server (NfsServer) and a profile for an NFS client (NfsClient).
-
You have created a policy to automatically apply fixes (AutoFix).
-
You have created a group of machines destined to be NFS servers (nfs servers) and a group for NFS clients (nfs clients). The machines may be of differing distributions and architectures. You would have aligned the profile requirements for the different active distributions before creating this job. See To Align Component Settings for Multiple Distributions.
-
Make sure the Jobs panel of the main window is open by choosing Jobs from the View menu.
-
Click the New Job button.
The New Job window opens.
-
Name the job: NFS Environment.
In the description, type This job provisions NFS servers and NFS clients.
-
Select Deploy.
As the profiles are your own or the predefined profiles for system management, you have a good idea of what will be done on the hosts; you do not need to simulate the job before deploying it.
Before anything is changed on any host, Sun Update Connection – Enterprise saves its inventory. If you do not like the results of the job, you can easily restore it to its previous inventory. See Restoring Managed Hosts.
-
In the Tasks tab, click Add Task and a task with:
-
Click OK.
The IntegrityCheck task is added to the job.
-
Add another task:
-
Click OK.
The ProvisionNfsServer task is added to the job.
-
Add another task:
-
Click OK.
The ProvisionNfsClients task is added to the job.
Now you have a job with three tasks: check hosts for missing dependencies, provision the NFS server profile on the nfs servers group, and then provision the NFS client on the nfs clients group.
Let’s set a schedule for this job. If the job is run on a recurring basis, it will make sure that the hosts in the web servers group always comply with the web server profile. If they do comply, nothing is changed and the job finishes on success. If there has been an error in change management, the recurring run will find it.
-
Open the Schedule tab.
-
Select Recurring.
-
Select Every Month.
-
Select Day in week, and then select Monday.
-
Set Earliest to 7:00.
The job will now run every Monday, early in the morning. Let’s look at the job options now.
-
Open the Options tab.
-
Select Use secure components only.
-
If you are the owner of the profiles and of the AutoFix policy, you can leave the Notify of changes option deselected. They cannot be changed by any other user.
-
Select Accept changes before next run.
If the requirements of an NFS server change, you need only change the profile once. This option ensures that the job will automatically use any changes you make to the profile.
You now have a re-usable job, with multiple tasks to be run on multiple hosts in a specific order, according to what is relevant to the inventory, distribution, and hardware architecture of each managed host. The job has a schedule. You will be notified by email if there are any tasks to do or if a host goes down. The job options have been set to optimize this specific set of tasks. To execute the job, click OK in the New Job window.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates