Setting Permissions and Access Control Lists
The File Manager is the main tool for working with files and directories. It has been slightly modified for the Trusted Solaris environment to accommodate mandatory access control. This section focuses on the basic permissions and access control list (ACL) for files and folders in the Trusted Solaris environment. For other information on the File Manager, refer to the base Solaris documentation.
The File Manager provides the two methods for displaying the Properties dialog box. You can hold down the right mouse button over the specified file and select Properties... from the File Manager pop-up menu or you can select the file and choose Change Properties from the Selected menu. Both methods cause the Properties dialog box to be displayed. The Properties dialog box can display three types of properties:
-
Permissions - by selecting the permissions toggle and Hide Access List (see the permissions mode dialog box below)
Figure 5-1 File Properties: Permissions Mode -- Hide ACLs
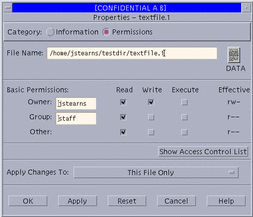
-
ACLs - by selecting the permissions toggle and Show Access Control List (see the ACLs mode dialog box below)
Figure 5-2 File Properties: Permissions Mode -- Show ACLs
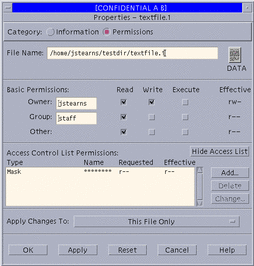
-
Basic information - by selecting the information toggle (see the information mode dialog box below)
Figure 5-3 File Properties: Information Mode

Basic Permissions
The term basic permissions refers to the traditional UNIX scheme for protecting files and folders (directories) regarding three types of access:
-
read permission - lets a user read the contents of a file or, if a folder, list the files in the folder
-
write permission - lets a user make changes to a file, or, if a folder, add or delete files
-
execute permission - lets a user run the file if it is executable or, if a folder, read or search its files
If access to a folder is limited, the File Manager displays special icons to show that a folder is inaccessible or read-only (see figure below).
Figure 5-4 Special File Manager Icons
Permissions are granted according to three classes of user:
-
owner - the user who created the file or folder (or received ownership through chown(1) ), usually with the greatest degree of access
-
group - the set of users to which the owner belongs, with common needs of access to the file or folder
-
other - all other users that are not the owner or in the owner's group
Access Control Lists
The access control list (ACL) lets you grant individual permissions (referred to as ACL entries) to specific users and groups. For example, if you want to grant write permission to your manager, you can create an ACL entry granting him or her write permission.
There are two general categories of ACL entries: access ACL entries and default ACL entries. Access ACL entries define who has access to a specific file or directory. Default access entries define the permissions to be applied to newly created files or folders with a specified folder.
By definition, every access control list has a special entry called a mask (which cannot be deleted). The mask sets the maximum permissions allowed on a file or folder for all groups and any non-owner users. (The mask does not apply to users who fall into the "other" category for basic permissions.) A good use of a mask is to turn off write permission for everyone but yourself when you need to have sole write access to a file.
The ACL entry types are described in the table below.
Table 5-1 ACL Types and Application|
Entry Type |
Applies to |
User Category |
|---|---|---|
|
Files or folders |
All users except owner and other. |
|
|
Files or folders |
Specified user |
|
|
Files or folders |
Specified group |
|
|
Files created in selected folder |
Specified user |
|
|
Files created in selected folder |
Specified group |
|
|
Files created in selected folder |
Folder's owner |
|
|
Files created in selected folder |
Owner's group |
|
|
Files created in selected folder |
Users other than the owner and users in the owner's group |
|
|
Files created in selected folder |
All users except owner and other |
Whenever you create any default ACL entry, the following entries are required:
-
default owning user
-
default owning group
-
default other
-
default mask
The File Manager creates these default entries automatically, taking its best guess at their permission settings. If you do not want these default permission settings, you are free to change them.
Viewing or Changing Permissions and ACL Entries
All changes to a file or folder's basic permissions and ACL entries are made using the File Manager's Properties dialog box.
To Display the Properties Dialog Box for a File or Folder
-
Display the File Manager.
-
Place the pointer over the file or folder whose properties you wish to access and press the right mouse button (see figure below).
Figure 5-5 Selecting Change Properties from the File Manager Popup Menu
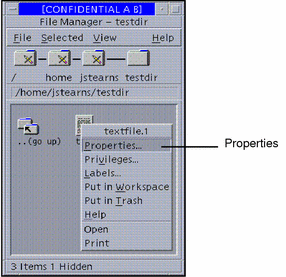
-
Select Properties...
This step displays the Properties dialog box for the selected file or folder. This dialog box lets you:
-
View the file or folder's basic information
-
View or change the file or folder's basic permissions
-
View or change the file or folder's ACL entries
-
Browse for other files or folders to be viewed or changed
-
To View the Basic Information of a File or Folder
A file or folder's basic information consists of: owner, group, size in bytes, the last access date, and the last modification date.
-
Display the File Manager Properties dialog box.
See "To Display the Properties Dialog Box for a File or Folder".
-
Click the Information button in the Category field.
This step sets the dialog box to basic information mode.
Figure 5-6 File Manager Basic Information Dialog Box
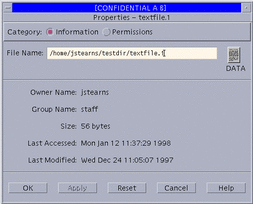
-
Examine the data in the basic file information area.
In addition to the data in the basic file information area, there is an icon at the right of the file identification area that indicates the file or folder's type.
To View or Change a File or Folder's Basic Permissions
-
Display the File Manager Properties dialog box.
See "To Display the Properties Dialog Box for a File or Folder".
-
Click the Permissions button in the Category field.
This step sets the dialog box to permissions mode (see below).
Figure 5-7 File Manager: Displaying ACL Entries
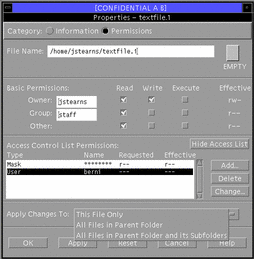
-
Examine the settings in the permissions area.
The owner, group, and other's read, write, and execute permissions are displayed here, along with buttons for making changes. The Effective column (at the right side of the permissions area) displays the permissions after the ACL mask has been applied as the permissions appear in the command line interface.
-
To make changes, click the appropriate read, write, or execute buttons for owner, group, or other.
You can check the result in the Effective column at the right of the area.
-
To specify the target item(s) for these changes, select the appropriate target in the Apply Changes To option menu at the bottom of the window.
You can select the current file, all files in the parent folder, or all files in the parent folder and its subfolders.
-
Click OK or Apply to save the permissions.
To View a File or Folder's ACL Entries
-
Display the File Manager Properties dialog box.
See "To Display the Properties Dialog Box for a File or Folder".
-
Click the Permissions button in the Category field.
This sets the dialog box to permissions mode (see Figure 5-7).
-
Click the Show Access Control List button if the access control list area is not currently displayed.
-
Examine the entries in the access control list area.
Any existing ACL entries for the item are displayed in the scroll list, including the type of entry, specified name, requested permissions, and effective permissions. The requested permissions are the default permissions before the ACL mask has been applied--the effective permissions reflect the permissions after the mask has been applied.
To Add an ACL Entry
-
Display the File Manager Properties dialog box as described in "To View a File or Folder's ACL Entries".
-
Click the Add button at the right of the ACL area (see Figure 5-7) to display the Add dialog box.
The File Manager Add Access List Entry dialog box with the Type menu displayed is shown below. Note that for folders all menu items are available. For files, only the User and Group menu items are active.
Figure 5-8 File Manager Add ACL Dialog Box
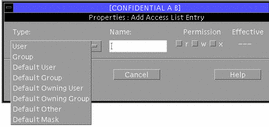
-
Specify the type of ACL entry.
The ACL types enabled in the options menu depend on whether you selected a file or folder. Only the User and Group items are available for files. All entries are enabled for folders. If you need to review the ACL types, see Table 5-1.
In addition, if you select one of the default entries, a message will be displayed at the bottom of the dialog box as a reminder that the default owning user, default owning group, default other, and default mask will be added with their permissions enabled accordingly.
-
Specify the name if enabled.
When you select User, Group, Default User, or Default Group, you must enter a name (or ID).
If you select Default Owning User, Default Owning Group, Default Other, or Default Mask, the name field is disabled, since it is not necessary.
-
Click the permissions you wish to enable (or disable).
A check mark means that the permission is enabled. If you select a permission that will be overridden by the mask, a warning will be displayed in the message display area at the bottom of the dialog box, along with a beep. The effective permissions column will indicate the difference. You are nonetheless allowed to make the entry and it will take effect if the mask is modified to permit it later.
-
Click Add in the dialog box.
This adds the entry, causing it (and any related default entries) to be displayed in the Access Control List area. If you do not like the setting in the default permission settings, you can change them (see "To Change an ACL Entry").
-
To specify the target item(s) for the permissions or ACL entries that you specified, select the appropriate target in the Apply Changes To option menu at the bottom of the window.
You can select the current file, all files in the parent folder, or all files in the parent folder and its subfolders.
-
Click OK or Apply to save the ACL entries (and any permissions you have changed).
To Change an ACL Entry
-
Display the File Manager Properties dialog box as described in "To View a File or Folder's ACL Entries".
-
Select an entry in the access control list area to be changed.
-
Click the Change button at the right of the ACL area to display the Change Access List Entry dialog box.
If you have selected an entry of type User, Group, Default User, or Default Group, the dialog box displays a Type menu and you can change the type. If you select Mask, Default Owning User, Default Owning Group, Default Other, or Default Mask, there is no ACL type menu button and the type is fixed. See the figure below, which is an example of changing a Default Mask entry.
Figure 5-9 File Manager Change ACL
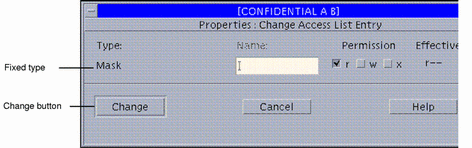
-
Specify the type of ACL entry.
The type will be limited as discussed in Step 3.
-
Specify the name (if enabled) and if you wish to change it.
-
Click the permissions you wish to enable (or disable).
A check mark means that the permission is enabled. If you select a permission that will be overridden by the mask, a warning will be displayed in the message display area at the bottom of the dialog box, along with a beep. The effective permissions column will indicate the difference. You are nonetheless allowed to make the entry and it will take effect if the mask is modified later.
-
Click Change in the dialog box.
This modifies the entry, causing the modification to be displayed in the Access Control List area. Remember that if you select Mask, your modifications may change the effectiveness of the entries for specified users and groups and for the owner's group.
-
To specify the target item(s) for the permissions or ACL entries that you specified, select the appropriate target in the Apply Changes To option menu at the bottom of the window (see Figure 5-7).
You can select the current file, all files in the parent folder, or all files in the parent folder and its subfolders.
-
Click OK or Apply to save the ACL entry changes (and any permissions you have changed).
To Delete an ACL Entry
-
Display the File Manager Properties dialog box as described in "To View a File or Folder's ACL Entries".
-
Select the entry to be deleted in the Access Control List area.
-
Click the Delete button at the right of the ACL area to display the Delete dialog box (see figure below).
Figure 5-10 File Manager Delete Access List Entry Dialog Box
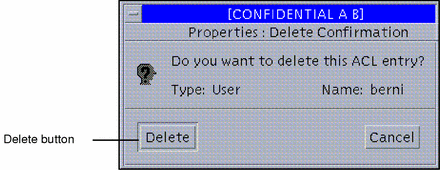
-
Confirm that the selected entry is correct and click Delete in the dialog box.
This removes the entry from the Access Control List area.
-
To specify the target item(s) for the permissions or ACL entries that you specified, select the appropriate target in the Apply Changes To option menu at the bottom of the window (see Figure 5-7).
You can select the current file, all files in the parent folder, or all files in the parent folder and its subfolders.
-
Click OK or Apply to save the current ACL entries (and any permissions you have changed).
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
