Chapter 9 Common Procedures
This chapter contains common administrative procedures that are useful to know when configuring a system. Each procedure, or part of it, is specific to the Trusted Solaris environment.
Logging In as a User
To Log In as a Regular User
-
Enter your password.
Note -Users must not disclose their passwords to another person, as that person may then have access to the data of the user and will not be uniquely identified or accountable. Note that disclosure can be direct, through the user deliberately disclosing his/her password to another person, or indirect, such as through writing it down, or choosing an insecure password. Trusted Solaris software provides protection against insecure passwords, but cannot prevent a user disclosing his/her password or writing it down.
The Enable Logins dialog box, shown in Figure 4-1, is displayed if you are authorized to enable logins.
If you see the error message:
Logins are currently disabled. Please ask your system administrator to enable logins.
then your user account was not assigned the Enable Login right. To fix, give the user the Enable Login right, or have someone else log in and enable logins.
-
Choose a login option and dismiss the dialog box.
The Message Of the Day dialog box is displayed. In a multilevel session, the default is to log in at the lowest label in your label range. You can also restrict your session to a single label.
-
Click OK to accept the default given to you by the security administrator.
Once the login process is complete, the Trusted Solaris screen appears briefly, and you are in a CDE session with four workspaces. If your user account is configured to display labels, the label of your session (a user account cannot be
ADMIN_LOW) is displayed in the trusted stripe.
Ending a Session
Users can lock their screen or log out at the end of a session. Users authorized to shut down the system can halt it and reboot.
Note -
Users must log off or utilize the lockscreen functionality before leaving a computer unattended. Otherwise a person may have access to the data of a user without having to pass identification and authentication, and that person would not be uniquely identified or accountable.
To Lock the Screen
To Log Out
-
Right-click the workspace background and select Log out... from the Workspace Menu, or left-click the EXIT icon on the Front Panel.
-
When prompted, confirm that you want to log out.
To Reboot the System
-
Right click the CDE front panel and select Shut Down from the TP (Trusted Path) menu.
The menu appears when the user or role is authorized to shut down the computer.
-
Confirm the shutdown.
-
Enter boot at the ok prompt or b at the > prompt:
Type help for more information <#2> ok boot
Type b (boot), c (continue), or n (new command mode) > b
Running Administrative Actions
The Application Manager contains a folder that holds administrative applications for the local machine, System_Admin and an action, Solaris Management Console,
for administering local and distributed databases. The Application Manager icon is shown below.![]()
How To Use System_Admin Actions
The System_Admin folder contains CDE actions for administering the local system. See the following table for a list of actions used during installation and configuration. For a full list of System_Admin actions, read the CDE online help. The System_Admin folder icon is shown
below.![]()
|
Action Name |
Action Behavior |
|---|---|
|
Add Allocatable Device |
Edit /etc/security/device_maps |
|
Add to NIS+ Administrative Group |
Run the nisgrpadm -a command |
|
Admin Editor |
Create or edit any file |
|
Audit Classes |
Edit /etc/security/audit_class |
|
Audit Control |
Edit /etc/security/audit_control |
|
Audit Events |
Edit /etc/security/audit_event |
|
Audit Startup |
Edit /etc/security/audit_startup |
|
Audit Users |
Edit /etc/security/audit_user |
|
Check Encodings |
Check syntax (and install) a label encodings file |
|
Check TN Files |
Check local tnrhdb and tnrhtp files |
|
Check TN NIS+ Tables |
Check NIS+ tnrhdb and tnrhtp databases |
|
Configure Selection Confirmation |
Edit /usr/dt/config/sel_config |
|
Create NIS Client |
Make this host a NIS client |
|
Create NIS Server |
Establish a NIS server with NIS maps |
|
Create NIS+ Administrative Group |
Run the nisgrpadm -c command |
|
Create NIS+ Client |
Make this host a NIS+ client |
|
Create NIS+ Server |
Establish a NIS+ domain |
|
Delete from NIS+ Administrative Group |
Run the nisgrpadm -r command |
|
Delete NIS+ Administrative Group |
Run the nisgrpadm -d command |
|
Edit Encodings |
Edit a label encodings file |
|
List Administrative Group |
Run the nisgrpadm -l command |
|
Name Service Switch |
Edit /etc/nsswitch.conf |
|
Populate NIS+ Tables |
Populate NIS+ tables from a files directory |
|
Printer Administrator |
Set up printers |
|
Set Default Routes |
Edit /etc/defaultrouter |
|
Set DNS Servers |
Edit /etc/resolv.conf |
|
Set Mail Options |
Edit the TSOL option in the sendmail.cf file |
|
Set Mount Attributes |
Edit /etc/security/tsol/vfstab_adjunct |
|
Set Mount Points |
Edit /etc/vfstab |
|
Set TSOL Gateways |
Edit /etc/tsolgateways |
|
Share Filesystems |
Edit /etc/dfs/dfstab |
|
View NIS Map |
View NIS map |
|
View Table Attributes |
View NIS+ table attributes |
|
View Table Contents |
View NIS+ table contents |
To Run a System_Admin Action
-
In an administrative role, open the Application Manager by right-clicking the background to bring up the Workspace menu. Choose Applications -> Application Manager from the top of the menu.
-
Double-click the appropriate action. For more details, see "To Create or Open a File from the Trusted Editor", "To Open a File that has a Defined Action" and "To Run a Script from the System_Admin Folder".
To Create or Open a File from the Trusted Editor
Actions that open files in an editor use the Admin Editor icon shown below.![]()
-
To create or open a file that does not have its own action, double-click the Admin Editor action.
A prompt appears for you to specify the file to be opened.
-
Enter the name of the file to be opened.
If the file exists, it is opened. If the file does not exist, it is created. You can create an empty file (touch) by exiting the editor.
Note -You cannot save a file to a different name from the trusted editor.
To Open a File that has a Defined Action
-
To open a file that has its own action, double-click its action in the System_Admin folder.
The file associated with the action appears in the trusted editor.
-
Enter the required information, write the file, and exit the editor.
To Run a Script from the System_Admin Folder
-
To run a script that has its own action, double-click the action in the System_Admin folder.
When the script requires input, the prompts are displayed.
-
Follow the instructions.
The script is finished when all prompt windows have been dismissed.
Using the Solaris Management Console
The Solaris Management Console action in the Application Manager folder invokes a Java-based administrative GUI for configuring and maintaining a Trusted Solaris environment. The GUI lists toolboxes in a Navigation pane, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 9-1 Solaris Management Console Tools in the Navigation Pane
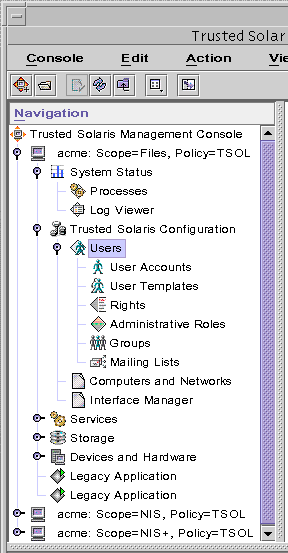
The following can be configured through the Solaris Management Console, using the Trusted Solaris Management Console > Trusted Solaris Configuration toolboxes in the Navigation pane:
User Accounts--Part of the Users tool, for administering users.
Administrative Roles--Part of the Users tool, for administering roles.
Rights--Part of the Users tool, for constructing rights profiles. A user account is not usable until the user's Rights have been assigned.
Mailing Lists--Part of the Users tool, for administering mail aliases.
Computers and Networks--For setting up networks.
Computers--Part of the Computers and Networks tool, for setting up hosts (the hosts database).
Security Families--Part of the Computers and Networks tool, for creating and assigning remote host templates (the tnrhtp(4) and tnrhdb(4) databases)
Interface Manager--For securing network interfaces (the tnidb(4) database). Accessible only when Scope=Files.
--
The following are configured through the Solaris Management Console, using Trusted Solaris Management Console toolboxes:
Mounts--Part of the Storage tool, for mounting file systems. Accessible only when Scope=Files.
Shares--Part of the Storage tool, for sharing file systems. Accessible only when Scope=Files.
To Locate a Solaris Management Console Tool
Scope=Files and Scope=name-service contain different tools. Read the online help for what the tool does and how to use it.
-
To find and use a tool in this-host: Scope=Files, Policy=TSOL in the Navigation pane:
-
Click the System Status key to view the Processes and Log Viewer tools.
-
Click the Trusted Solaris Configuration key to view the Users, Computers and Networks, and Interface Manager tools.
-
Click the Services key to view the SMC Server and the Scheduled Jobs tools.
-
Click the Storage key to view the Mounts and Shares and Disks tools.
-
Click the Devices and Hardware key to view the Serial Ports tool.
-
-
To find and use a tool in the name-server: Scope=name-service, Policy=TSOL toolbox in the Navigation pane, click the Trusted Solaris Configuration key.
The Users and the Computers and Networks tools are available in the name-server: Scope=name-service, Policy=TSOL scope.
-
In the Navigation pane, click a toolset icon, such as Users.
-
When prompted, enter the role password in the Role Login prompt.
-
Double-click the tool, such as User Accounts.
-
Read and follow the online help for assistance with each tool.
Copying to and from a Portable Medium
When copying to a portable medium, label the medium with the sensitivity label of the information.
Note -
During installation, the root role copies administrative files to and from portable media. Most files are copied at label ADMIN_LOW.
To Copy Files to a Diskette
-
First, in a workspace at the target label, allocate the floppy device at the correct label using the Device Allocation action, and insert a clean diskette.
For a fuller task description, see "Allocate the Appropriate Device".
-
Open a second File Manager from the Front Panel and navigate to the folder that contains the files to be copied, such as /export/clientfiles.
-
Highlight the icon for the file and drag the file to the floppy disk folder.
-
Deallocate the device.
-
On the floppy disk folder, choose Eject from the File menu.
Note -Remember to physically affix a label to the medium with the sensitivity label of the copied files.
To Copy Files From a Diskette
It is safe practice to rename the original Trusted Solaris file before copying in a file to replace it. When configuring a system, the root role renames and copies administrative files at ADMIN_LOW
-
Allocate the floppy device using the Device Allocation action and insert the diskette.
-
If the system has a file of the same name, copy the original to a new name.
For example,
# cp /etc/security/tsol/tnrhtp /etc/security/tsol/tnrhtp.orig
-
Open a second File Manager from the Front Panel and navigate to the desired destination directory, such as /etc/security/tsol.
-
Highlight the icon for the file and drag the file from the floppy disk folder to the destination directory.
-
Deallocate the device as described in "Deallocate the Device".
-
Click OK on the dialog box when prompted to manually eject the floppy, and remove it.
Modifying a Role's Rights
When setting up a network or custom JumpStart install, some required commands may not be available to the role because they are in a path that is not assigned to the role. To add commands, programs, or scripts to the role's rights, the security administrator must modify the role's rights.
To Add a Command to a Role's Rights
-
Log in as a user who can assume the role secadmin and assume it.
-
In the secadmin role at
ADMIN_LOW, invoke the Solaris Management Console from the Application Manager. -
Click the appropriate toolbox under Trusted Solaris Management Console.
Choose this-host: Scope=Files, Policy=TSOL if you are adding a command for a locally-defined role, or are not using a name service.
Choose name-server: Scope=name-service, Policy=TSOL if you are adding a command for a role defined on the network, such as for the admin role when setting up network install.
-
In the Navigation pane, click Trusted Solaris Configuration, then click Users.
Note -If toolbox icons display as red stop signs, the toolboxes will not load. To load them, see Step 2 in "Initialize the SMC Server".
-
Supply a role password if prompted, then double-click Rights.
-
In the View pane, scroll to the Custom Rolename Role and double-click.
-
Follow the online help for assistance in setting up the Custom Rolename Role right.
For a network installation example, use the Commands tab to add the add_install_client command from a non-standard directory, such as /export/ultra_install_tsol/Trusted_Solaris_8/Tools to the Custom Admin Role right. The command should have all privileges.
-
Make sure that the Custom Rolename Role right is assigned to Rolename. If it is not, assign it to Rolename.
-
Navigate to Administrative Roles.
-
Double-click the Rolename role.
-
Click the Rights tab.
-
Open the rights displayed in the Granted Rights column.
If it has already been granted, click the Cancel button. If the Custom Rolename Role right is not granted, continue.
-
Add Custom Rolename Role to the role's Granted Rights.
-
Click OK to save your work.
-
To Verify That a Command is Available to a Role
-
Log in as a user who can assume the role whose profile has been updated.
-
Assume the role and launch a terminal from the role's workspace.
-
Verify that the new profile is in effect in the new terminal by using the profiles(1) command.
For example, to verify that the setup_install_server command is included in the admin role's rights profile with all privileges, in the admin role enter the following:
$ profiles -l | grep setup_install_server /export/ultra_install_tsol//Trusted_Solaris_8/Tools/setup_install_server: all
To Remove a Command from a Role's Rights
-
In the secadmin role at
ADMIN_LOW, in the Solaris Management Console use the same toolbox that you used to add the command to the rights profile, and navigate to Rights. -
In the View pane, select the Custom Rolename Profile.
-
Follow the online help for how to remove the command from the profile.
Saving and Restoring Trusted Solaris Databases
The Trusted Solaris 8 and Trusted Solaris 8 4/01 user and profile databases are in new formats with new names. To retain the usable data from their previous versions requires an administrator, before installing the Trusted Solaris 8 4/01 operating environment, to run the tsolconvert utility on a Trusted Solaris 7 or Trusted Solaris 2.5.1 system, to save the output directory to a safe storage area, and then to restore the files and run a shell script on the Trusted Solaris 8 4/01 system.
The following table shows the name or content difference between earlier releases and the Trusted Solaris 8 4/01 release.
|
Trusted Solaris Databases |
Trusted Solaris 8 4/01 Database Description |
|---|---|
|
/etc/security/tsol/tsoluser |
user_attr(4) |
|
/etc/security/tsol/tsolprof |
exec_attr(4) and prof_attr(4) |
|
/etc/security/tsol/tnidb |
Format is extended for IPv6. No conversion required. |
|
/etc/security/tsol/tnrhtp |
Format is extended for IPv6. New templates with doi and ip_label changes. See the tnrhtp(4) man page. |
|
/etc/security/tsol/tnrhdb |
Format is extended for IPv6. No conversion required. |
To Save Profile and User Attribute Information
-
See the README file and tsolconvert man page that you download from the Trusted Solaris web site for instructions.
http://www.sun.com/software/solaris/trustedsolaris
-
On the web site, click Technical FAQs, then click Transitions Between Environments.
Backup and conversion must be completed on the Trusted Solaris 2.5.1 or Trusted Solaris 7 NIS+ master before the Trusted Solaris 8 4/01 software is installed.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
