Chapter 4 Monitoring and Messaging
This chapter provides an overview of the monitoring and messaging system. The chapter describes the events being monitored within an Infrastructure Fabric (I-Fabric). Topics covered in this chapter include:
Monitoring System Overview
N1 Provisioning Server monitoring software performs the following tasks:
-
Monitoring of availability, health, and performance of the following I-Fabric components:
-
The control plane server on which N1 Provisioning Server software runs
-
Resource pool servers
-
-
Providing a message routing framework for events, including the ability to forward messages to a third-party application.
The primary software package for monitoring consists of the following components:
-
Monitoring manager processes on the control plane database (CPDB) that collect all messages
-
The message repository in the CPDB to which the monitoring manager forwards all messages
-
N1 Provisioning Server agents on resource pool servers to monitor their state and health
The N1 Provisioning Server manages all monitoring processes within an I-Fabric. The N1 Provisioning Server actively monitors the state and health of devices within an I-Fabric.
Failing Over or Restarting Failed Processes
Monitoring provides the information needed by the farm manager to make decisions about device failover and recovery or the restarting of failed processes in the control plane, the resource pool, and the fabric layer.
For details on how to define monitoring from the Control Center, see theN1 Provisioning Server 3.1, Blades Edition, Control Center Management Guide.
Monitoring Within the Control Plane
Monitoring the control plane has three purposes:
-
Monitoring I-Fabric devices for network accessibility
-
Acting as a single point of contact for all critical events that can occur within an I-Fabric
-
Monitoring the control plane server for availability
The monitoring manager on the CPDB monitors the health and performance of the control plane server. Messages are logged to appropriate log files as specified in the postinstall scripts for the TSPRmon and TSPRmlg packages. The log file locations are set using the command slconfig, which is not supported for use outside of the packages postinstall and preremove scripts.
See the slconfig man page for details on configuring these log files. The default locations for monitoring log files are /var/opt/terraspring/log/snmp.log and /var/opt/terraspring/log/mon.log.
 To Start and Stop the Monitoring Manager
To Start and Stop the Monitoring Manager
Steps
-
To start the monitoring manager, type:
/opt/terraspring/sbin/mmd start
-
To stop the monitoring manager, type:
/opt/terraspring/sbin/mmd stop
Monitoring Within the Resource Pool
The N1 Provisioning Server is responsible for monitoring its assigned farms as directed by the configuration stored in the CPDB. The N1 Provisioning Server is also the control gateway for some system configuration and control commands, such as configuring additional network interfaces. The monitoring software running on the N1 Provisioning Server forwards monitoring messages to the CPDB.
Monitoring Resource Pool Servers
N1 Provisioning Server agents are deployed on resource pool servers during installation and configuration. The agent software collects various monitoring data from the resource pool server and sends it to the N1 Provisioning Server.
The N1 Provisioning Server processes monitoring data and stores it in the message repository in the CPDB. The CPDB has a local database for messages processed by the servers. You also can route messages to an external application, such as a Network Monitoring System (NMS).
The monitoring system includes the TSPRagsol agent package for the Solaris 8 operating environment and the TSPRaglinx agent for the RedHat AS2.1 operating environment.
For resource pool servers assigned to farms, the system can monitor the following events:
-
Availability of the primary Ethernet interface (ICMP ECHO or ping)
-
CPU utilization
-
Disk utilization
-
RAM utilization
-
Swap memory allocation
Refer to Chapter 4, Building, Updating, and Monitoring Server Farms, of the N1 Provisioning Server 3.1, Blades Edition, Control Center Management Guide for additional monitoring configuration information.
Stopping the Resource Pool Server Monitoring Process
If you need to reboot a resource pool server that is active in a farm, stop the monitoring process. Rebooting is often required after adding applications or other software packages to a server. To stop the monitoring process use the /opt/terraspring/sbin/tsprmonitor command to stop the monitoring process. Doing so prevents replaceFailedDevice requests from occurring. The time during which the resource pool server should not be available is configurable. See the tsprmonitor man page for details.
Monitoring Within the Fabric Layer
The monitoring manager on the CPDB monitors the health and performance of devices in the fabric layer, such as Ethernet switches. The monitoring manager logs the information according to the logging configuration.
Registering I-Fabric Devices for Monitoring
The equipment that makes up the I-Fabric, such as the control plane server, routers, and switches, must be registered for monitoring with the CPDB. When the system is installed, this registration is done as part of the original deployment. However, you can modify registration if you add, remove, or replace devices.
The detailed process of registering devices with the CPDB is described in the installation procedure in the N1 Provisioning Server 3.1, Blades Edition, Installation Guide. After registering the devices, you can view messages about these devices in the CPDB message repository or on the Control Center monitoring screen.
Removing I-Fabric Devices from Monitoring
I-Fabric devices registered for monitoring must be removed when they are no longer needed, or when they are permanently removed (because of hardware failure, for example).
 To Remove a Control Plane Device from the CPDB
To Remove a Control Plane Device from the CPDB
Step
-
Type the following command:
/opt/terraspring/sbin/cereg -deleteCPDevice -ipaddr IP Address
This command removes the device with IP address 10.10.10.21.
Example 4–1 Removing a Control Plane Device from the CPDB
/opt/terraspring/sbin/cereg -deleteCPDevice ipaddr 10.10.10.21 |
Automating the Monitoring Process
Monitoring system health requires little manual intervention. The primary activities relevant to monitoring system health that you need to perform include:
-
Using the Control Center Monitoring screen to view or configure specific monitoring events for an individual server of a farm.
-
Adding and removing resource pool servers from monitoring. This activity is normally handled during initial installation. The addition of new equipment requires some manual intervention.
-
Registering or unregistering I-Fabric devices for monitoring if they have been added or removed manually.
Day-to-Day Monitoring Activities
The CPDB provides a single location from where you can observe all critical events and messages.
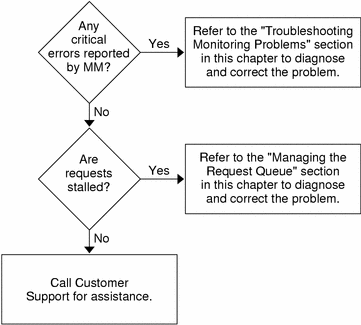
When a device fails, you must determine the corrective action. Many of the required actions are described in Chapter 6, Error Messages. The section Troubleshooting Monitoring Problems in Chapter 7, Troubleshooting also describes troubleshooting scenarios.
Monitoring and Messaging Log Files
The monitoring log file holds messages from the registration and deregistration of nodes by the Farm Manager. This file also holds all messages that the monitoring daemon generates. Check this log file as part of your day-to-day activities and take the appropriate action to correct any errors as necessary. See Chapter 7, Troubleshootingfor details.
Log file rotation is configured automatically by the slconfig command used in the postinstall package at installation time. The default log file size in the /etc/opt/terraspring/logfile_rotation is 5 MBytes.
The monitoring debug level governs the verbosity of the monitoring system's messages logged in the /var/opt/terraspring/log/mon.log file.
By default the debug level is set to 9. To change the debug level edit the /etc/opt/terraspring/tspr.properties file on the N1 Provisioning Server:
com.terraspring.mon.MonLog.debugLevel=debug level value |
Logs of all messages forwarded to an NMS are located in the /var/opt/terraspring/log/snmp.log file.
The default Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) verbosity level is set to 9. The SNMP messages are logged into the /var/opt/terraspring/log/snmp.log file.
To change the SNMP verbosity level, edit the /etc/opt/terraspring/tspr.properties file on the N1 Provisioning Server:
com.terraspring.mon.snmpLog.debugLevel=debug level value |
Messaging
The N1 Provisioning Server software provides a message routing framework directing messages related to farms and monitoring activities to a central repository on the CPDB or to an external NMS.
N1 Provisioning Server software generates three types of messages:
-
Informational messages
-
Farm messages
-
Billing messages
All messages are forwarded to the N1 Provisioning Server. The N1 Provisioning Server then sends the messages to the message repository in the CPDB. You can view monitoring data for farm servers through the Control Center Monitor screen.
Optionally, you can configure the CPDB to forward messages to an external NMS. See Management Information Base Definitions for details.
Message Flow to the CPDB
Message flow from the I-Fabric components to the CPDB is automatic. Message flow from the CPDB to an optional third-party NMS is configurable. The following graphic illustrates the flow of messages from I-Fabric elements to the CPDB message repository of an I-Fabric.
Figure 4–1 Message Flow from I-Fabric Elements to the CPDB
Forwarding Messages to an NMS
If you are forwarding messages to an NMS, you need to set up an SNMP connection because all N1 Provisioning Server monitoring messages sent to an NMS are in the form of an SNMP trap. SNMP requires the implementation of a management information base (MIB) for implementing trap versions. The N1 Provisioning Server monitoring mechanism sends only version 2 traps. However the CPDB can convert the trap versions. You can configure the monitoring mechanism to forward messages to an NMS in the tspr.properties file on the /etc/opt/terraspring directory as follows:
com.terraspring.mlg.SnmpConf.forwardingIP=IP address of NMS
After configuring this property, restart the SnmpTrap daemon as follows:
/opt/terraspring/sbin/snmpd stop /opt/terraspring/sbin/snmpd start |
See Chapter 2, I-Fabric Operation for more details on monitoring properties.
Configuring Message Routing
You can configure which type of message (farm, billing, or informational) to send to either CPDB or NMS in the tspr.properties file in the /etc/opt/terraspring directory as follows:
Table 4–1 Configuring Message Routing Properties
Monitoring Commands
You can use monitoring commands on a command-line interface (CLI) to perform monitoring activities, such as viewing the status of devices, manually registering devices, or troubleshooting. N1 Provisioning Server monitoring software provides the following commands:
-
cereg
-
cecmd
-
mls
Using the cereg Monitoring Command
Use the /opt/terraspring/sbin/cereg command to manually register and unregister resource pool servers for monitoring. In normal operation, registration of resource pool servers for monitoring is done automatically at I-Fabric installation time, so you would use this command only in an error or troubleshooting situation. See Chapter 7, Troubleshooting for details and examples on how to use this command.
|
Command Usage |
Description |
|---|---|
|
-addAllCPDevices |
Registers all devices on the control plane. |
|
-deleteCPDevice -ipaddr IP address |
Deregisters the control plane server from monitoring. |
|
-deletenode -ipaddr IP address -netmask netmask -nodetype node type |
Deregisters the resource pool server from monitoring. |
|
-addnode -ipaddr IP address -netmask netmask -nodetype node type |
Adds a resource pool server for monitoring. |
Using the cecmd Monitoring Command
Use the /opt/terraspring/sbin/cecmd command to do one of the following:
-
Configure an interface
-
Shut down a resource pool server
-
Back up a resource pool server
This command is typically used in an error or troubleshooting situation. See Chapter 7, Troubleshooting for details and examples on how to use this command.
Using the mls Monitoring Command
You can execute the /opt/terraspring/sbin/mls monitoring command to view the state of an I-Fabric component, the status of all N1 Provisioning Server agents, or the status of a particular N1 Provisioning Server agent. The mls command is useful for troubleshooting as well as day-to-day monitoring of the health of the system.
Table 4–2 Using the mls Command|
Command Usage |
Description |
|---|---|
|
mls -l |
Lists all nodes on the current control plane server. |
|
mls -all |
Modifies the query scope to the control plane server. |
|
mls -c |
Lists customer monitoring values for nodes registered on the current control plane server. |
|
mls -a |
Lists agent status for all registered nodes on the current control plane server. |
|
mls -x |
Lists the agent version information for the resources controlled by the control plane server. |
|
mls -f |
Modifies the query scope to a particular farm. |
|
mls -i |
Modifies the query scope to a particular resource pool server. |
|
mls -v |
Verbose output. |
|
mls -d |
Suppresses header information. |
|
mls -h |
Displays the command's usage information. |
Management Information Base Definitions
MIB definitions are described in the following standard SNMP configuration file. The file describes messages supported by the SNMP N1 Provisioning Server agent.
-- N1 Provisioning Server Monitoring MIB.
N1PS-MIB DEFINITIONS ::= BEGIN
IMPORTS
MODULE-IDENTITY, OBJECT-TYPE, NOTIFICATION-TYPE,
enterprises, IpAddress
FROM SNMPv2-SMI
OBJECT-GROUP, NOTIFICATION-GROUP
FROM SNMPv2-CONF;
smiModuleIdentity MODULE-IDENTITY
LAST-UPDATED "200303172342Z"
ORGANIZATION
"Sun Microsystems, Inc.
4150 Network Circle,
Santa Clara, CA 95054 USA"
CONTACT-INFO
"http://www.sun.com/service/contacting/index.html"
DESCRIPTION
"N1 Provisioning Server MIB."
::= { enterprises 12816 }
-- The root of N1 Provisioning Server MIB Tree.
SMI OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { enterprises 12815 }
-- The version 1 branch.
version1 OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { SMI 1 }
-- A tspr.log message.
tsprlogmessage NOTIFICATION-TYPE
OBJECTS { severity,
type,
farmid,
message,
originatingIPAddress }
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"A message with type debug."
::= { ifabricLog 11 }
-- A message sent on change of state of a node monitored by the N1 Provisioning Server.
nodeEvents NOTIFICATION-TYPE
OBJECTS { severity,
message,
originatingIPAddress }
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"A message sent on change of state of a node monitored by the N1 Provisioning Server."
::= { monLog 11 }
-- A message sent on change of Customer Monitoring Values detected by the N1 Provisioning Server.
cmEvents NOTIFICATION-TYPE
OBJECTS { severity,
message,
originatingIPAddress }
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"A message sent on change of Customer Monitoring Values detected by the N1 Provisioning Server."
::= { monLog 21 }
-- A message sent on change of the state of the Agent on a Resource Pool Server detected by the N1
PS.
agentEvents NOTIFICATION-TYPE
OBJECTS { severity,
message,
originatingTimeStamp }
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"A message sent on change of the state of the Agent on a Resource Pool Server
detected by the N1 Provisioning Server."
::= { monLog 31 }
-- A message received from a Control Plane Node that is to be forwarded.
controPoolTraps NOTIFICATION-TYPE
OBJECTS { message,
originatingIPAddress,
originatingTimeStamp }
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"A message received from a Control Plane Node that is to be forwarded."
::= { deviceTraps 11 }
-- A message received from a Resource Pool Node that is to be forwarded.
resoursePoolTraps NOTIFICATION-TYPE
OBJECTS { message,
originatingIPAddress,
originatingTimeStamp }
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"A message received from a Resource Pool Node that is to be forwarded."
::= { deviceTraps 21 }
-- The type of message.
type OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX OCTET STRING
MAX-ACCESS accessible-for-notify
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"The type of message."
::= { trapVariables 1 }
-- The severity of the message.
severity OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX OCTET STRING
MAX-ACCESS accessible-for-notify
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"The severity of the message."
::= { trapVariables 2 }
-- The Farmid for which the message is sent.
farmid OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX OCTET STRING
MAX-ACCESS accessible-for-notify
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"The Farmid for which the message is sent."
::= { trapVariables 3 }
-- The actual body of the message.
message OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX OCTET STRING
MAX-ACCESS accessible-for-notify
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"The actual body of the message."
::= { trapVariables 4 }
originatingIPAddress OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX IpAddress
MAX-ACCESS accessible-for-notify
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
""
::= { trapVariables 5 }
-- The TimeStamp of the original Trap.
originatingTimeStamp OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX OCTET STRING
MAX-ACCESS accessible-for-notify
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"The TimeStamp of the original Trap."
::= { trapVariables 6 }
-- All notifications send for tsprlog messages.
ifabricLog NOTIFICATION-GROUP
NOTIFICATIONS { tsprlogmessage }
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"All notifications send for tsprlog messages."
::= { version1 100 }
-- All monitoring log messages.
monLog NOTIFICATION-GROUP
NOTIFICATIONS { agentEvents,
cmEvents,
nodeEvents }
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"All monitoring log messages."
::= { version1 200 }
-- All traps received from nodes that need to be forwarded onwards.
deviceTraps NOTIFICATION-GROUP
NOTIFICATIONS { controPoolTraps,
resoursePoolTraps }
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"All traps received from nodes that need to be forwarded onwards."
::= { version1 300 }
trapVariables OBJECT-GROUP
OBJECTS { severity,
type,
farmid,
message,
originatingIPAddress,
originatingTimeStamp }
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
""
::= { version1 400 }
END
|
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
