Troubleshooting Monitoring Problems
This section describes some common monitoring problems. It shows how to diagnose these problems and suggests possible corrective actions. See Chapter 4, Monitoring and Messaging for an introduction to monitoring concepts.
The most common problems are as follows:
-
An UP message is not received from one or more resource pool servers.
-
Monitors do not show colors on the Element Monitor window of the Control Center.
-
A farm does not activate even though an UP message was sent.
-
Frequent UP and DOWN messages are received.
Many of these problems have interconnected root causes. The most common causes are:
-
Network, DNS, or DHCP issues.
-
Monitoring processes are not running on the control plane server.
-
Agent processes are not running on the resource pool servers.
This section describes how to diagnose these symptoms. Corrective Actions for Monitoring describes the corrective action to take to resolve these problems.
An UP Message Not Received From One or More Servers
You can confirm an UP message problem on the control plane server by checking whether the following conditions exist:
-
In the /var/adm/tspr.debug file, a message is listed similar to the following:
"Still waiting for 1 device(s) in 2879974 ms"
-
The farm activation shows ERROR 50, as shown in the following example:
FARM_ID FARM_NAME CUSTOMER STATE ISTATE ERROR 123 Farm_Name Customer NEW DISPATCHED 50
The following figure shows the steps needed to diagnose and resolve this problem.
Figure 7–2 Resolving Monitoring Problems
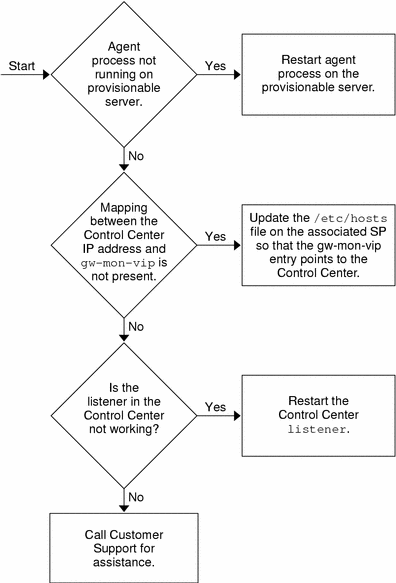
The preceding illustration shows the following troubleshooting sequence:
-
Check for a network, DNS, or DHCP problem. See Network, DNS, or DHCP Problems for details on how to do this.
-
Check that the monitoring processes are running on the control plane server. See Monitoring Processes Are Not Running on the Control Plane for details. Follow the instructions in this section to restart the processes.
-
Check that the agent processes are running on the resource pool server. See Agent Processes Are Not Running on a Resource Pool Server for details. If the agent processes are not running, follow the instructions in this section to restart them.
Monitors Do Not Show Colors in the Element Monitor Window of the Control Center
Farm-specific monitors might not appear on the Control Center. This condition could be caused by one of the following problems:
-
Agent processes are not running on the servers.
-
The mapping between the gw-mon-vip and the IP address of the Control Center server software is not set in the /etc/hosts file on the control plane server.
-
The listener on the Control Center is not running. See Control Plane Server-to-Control Center Messages Not Working for information on how to verify this condition.
Figure 7–2 shows the sequence of steps for you to follow to diagnose and resolve the above error condition. See Control Plane Server-to-Control Center Messages Not Working for details on how to resolve these problems.
Farm Does Not Activate
Even though the UP message was sent by the monitoring system, the segment manager might not be running. In this case, restart the segment manager. See Check for Blocked Requests for details on this procedure.
Frequent UP and Down Messages Received
A number of UP and DOWN messages received for a server might be received as a result of incorrect configuration of the interfaces on the N1 Provisioning Server.
Clear the duplicate Ethernet interfaces on the control plane server by running the clearNicInterface command. See the man pages for details on using this command.
Diagnosing Common Monitoring Symptoms
A number of symptoms are common to a number of problems. This section describes how to diagnose the following symptoms.
Network, DNS, or DHCP Problems
Perform the checks in the following table for network, DNS, or DHCP problems:
Table 7–4 Checking for Errors|
Error Check |
Error Confirmation |
|---|---|
|
Verify that all the resource pool servers can receive pingsignals by running the following command on the control plane server: /opt/terraspring/sbin/mls -lf farm-ID. Note – This command lists all the servers in the farm that can receive ping signals. |
Any of the servers are listed as ADDED |
|
Verify that all the resource pool servers are reachable by performing a telnet to each of the servers. |
Any of the servers are not reachable with telnet |
Note –
Sometimes a server can receive ping signals but is not reachable with telnet when in a single-user mode. To resolve this problem, connect to the console port and boot into multiuser mode.
Monitoring Processes Are Not Running on the Control Plane
After you determine a diagnosis for a monitoring process run the command:
/usr/ucb/ps -auxww | grep MM |
If the monitoring process is running, you will see an output similar to this example:
USER PID %CPU %MEM SZ RSS TT S START TIME COMMAND root 14540 0.2 1.14 485 620 608? S Mar 05 18:32 /bin/../java/bin/.. /bin/sparc/native_threads/java -Dsun.net.inetaddr.ttl=0 com. terraspring.mon.MM root 9529 0.1 0.1 976 672 pts/2 S 11:49:40 0:00 grep MM |
If the monitoring process is not running, you will see an output similar to this example:
USER PID %CPU %MEM SZ RSS TT S START TIME COMMAND root 9565 0.1 0.1 976 672 pts/2 S 11:50:28 0:00 grep MM |
See Restart the Monitoring Processes on the Control Plane Server for details on how to restart the process.
Agent Processes Are Not Running on a Resource Pool Server
Agent processes might not be running on a resource pool server. You can verify this condition by one of two methods:
-
On the control plane server run the following command:
/opt/terraspring/sbin/mls -a IP address of host
To be able to use this command, you must know the IP address of the server.
-
On the server on which the agent you want to verify is running, run the following command:
/usr/ucb/ps -auxww | grep tspragt
If the agent processes are running, you will see output similar to the following example:
root 7652 0.1 0.1 976 656 pts/1 S 11:37:30 0:00 grep tspragt
root 321 0.1 0.73167213816 ? S 16:26:37 0:10 /usr/bin/../java/bin/.. /bin/sparc/native_threads/java -Dsun.net.inetaddr.ttl=0 com.terraspring.mon.client.tspragt start 10.42.14.2
If the agent processes are not running, you will see output similar to the following example:
root 7709 0.1 0.1 976 656 pts/1 S 11:39:54 0:00 grep tspragt
See Restart the Agent Processes on a Resource Pool Server for details on how to restart the process.
Control Plane Server-to-Control Center Messages Not Working
For a number of reasons messages between the control plane server and Control Center might not work. The most common reasons include:
-
The mapping between the gw-mon-vip to the IP address of the Control Center server software is not set in the /etc/hosts file on the control plane server. Verify that a suitable entry is present to check this condition.
For example:
10.5.131.19 gw-mon-vip
-
The listener on the Control Center server software is not running. You can verify this condition by running finger test@gw-mon-vip on the control plane server. The expected sample output is similar to the following examples:
[gw-mon-vip]
or
[hostname]
Corrective Actions for Monitoring
This section describes a number of corrective actions that you can take to resolve a monitoring problem.
Restart the Monitoring Processes on the Control Plane Server
To restart the monitoring process run the following commands on the control plane server:
/opt/terraspring/sbin/mmd stop |
This command ensures that all relevant processes are stopped. Restart the monitoring processes with the following command:
/opt/terraspring/sbin/mmd start |
Restart the Agent Processes on a Resource Pool Server
If the control agent process terminated on the server, start the process on the server with the following command:
/etc/init.d/N1PSagt start |
To verify that the processes have restarted, run the following command from the control plane server:
/opt/terraspring/sbin/mls -a server IP address |
If the agent is running you will see output similar to the following:
FARM_ID IP_ADDRESS TYPE STATE DB_STATE SINCE 134 10.9.0.35 Server UP UP Feb 05 14:15:32 |
If the agent is down in real-time (STATE) it might still be marked as being UP in the database (DB_STATE because the database state is updated every five minutes. Therefore it will be up in real time, but still down in the database state. You will see output similar to the following:
FARM_ID IP_ADDRESS TYPE STATE DB_STATE SINCE 134 10.9.0.35 Server DOWN UP Feb 10 14:20:33 |
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
