Setting Up Solstice AutoClient Name Service Policy
A name service policy is used to specify the location of system and network information managed by the Solstice AutoClient software. This information can be located in the /etc directory for a local system, or in the NIS+ or NIS name service.
The Solstice AutoClient software supports a mixed-mode name service policy. A mixed-mode name service policy enables you to specify different name services for configuration information.
You can use the admtblloc(1M) command to choose a mixture of name services for the Solstice AutoClient tools to populate. For example, you can set up Host Manager to populate local /etc files for bootparams information and to populate the NIS+ tables for the other host configuration information, as shown in Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-1 Example Mixed-Mode Name Service Policy
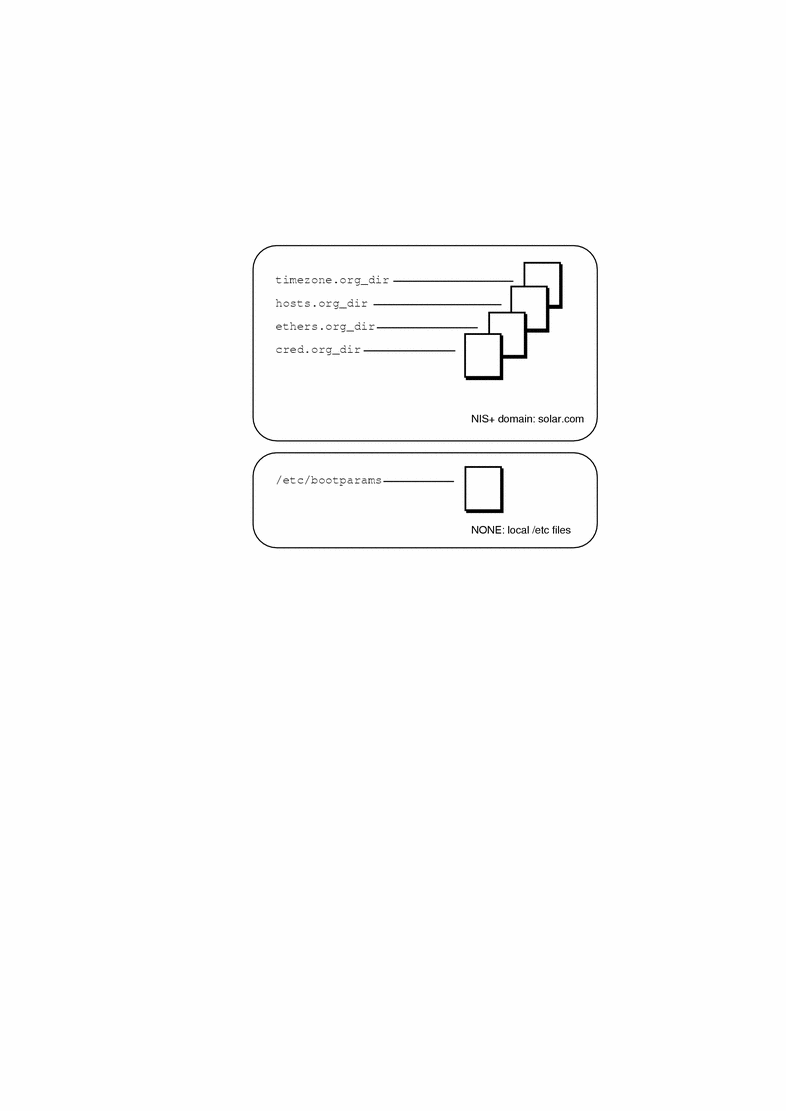
If you choose to implement a mixed-mode name service policy, you must run the Solstice AutoClient software from the system containing information in the /etc directory.
The admtblloc Command
The admtblloc command is used to implement a mixed-mode name service policy in the Solstice AutoClient software. To use this command, you must have permission to use the software for each name service as described in "Setting Up User Permissions to Use the Solstice AutoClient Software".
Note -
The admtblloc command has no relation to the /etc/nsswitch.conf file used to set the system-wide name service selection policy in the Solaris 2.x operating environment. The admtblloc command is used to set the policy for all users of the Solstice AutoClient software graphical user interface tools or command line interfaces.
Specifying the Name Service Policy Using admtblloc
This example shows how to specify the name service policy specified in Figure 3-1 using the admtblloc command:
$ admtblloc -c NIS+ -d solar.com bootparams NONE |
In this example,
|
- c NIS+ -d solar.com |
The NIS+ domain solar.com is the name service context (the name service and domain name specified in the Load window). |
|
bootparams |
bootparams is the configuration file to set the name service policy for. |
|
NONE |
NONE specifies that the host running the Solstice AutoClient tool or command line interface must use the bootparams file found in the local /etc directory. |
After setting the mixed-mode name service policy specified in Figure 3-1, the Solstice AutoClient software will use the bootparams information stored in the /etc directory on the current host running the Solstice AutoClient tool whenever the name service (specified in the Load window) is NIS+. The name service policy for the other configuration files (hosts, ethers, timezone and credential) is NIS+, unless you specify otherwise using admtblloc again. The mixed-mode name service policy remains in effect for all users of the Solstice AutoClient software in the name service until you change it using the admtblloc command once again.
Note -
If you specify that the name service location of a configuration file is NONE using the admtblloc command, the /etc file on the current host running the Solstice AutoClient application or command-line interface is modified. You should log in to the host where you want to use the local /etc file and perform operations using the Solstice AutoClient on that system.
Viewing the Name Service Policy Using admtblloc
This example shows how to display the name service policy using the admtblloc command:
$ admtblloc Name Name Service Path Aliases NIS+ Hosts NIS+ Group NIS+ Netgroup NIS+ Protocols NIS+ Bootparams NONE Auto.home NIS+ RPC NIS+ Timezone NIS+ Netmasks NIS+ Ethers NIS+ Passwd NIS+ Services NIS+ Networks NIS+ Locale NIS+ |
In this example output,
|
Name |
Is the name of the configuration file. |
|
Name Service |
Specifies the name service used to access the configuration file. |
|
Path |
(Optional) Specifies the path to the ASCII source file on NIS servers in the NIS name service. The default is the /etc directory. |
By default, the admtblloc command displays the policy for the name service to which the current host belongs. To display the name service policy for a different name service, specify the name service context.
This example shows how to display the name service policy for the NONE or local /etc files name service context domain using the admtblloc command:
$ admtblloc -c NONE Name Name Service Path Aliases NONE Hosts NONE Group NONE Auto_home NONE Netgroup NONE Protocols NONE Bootparams NONE RPC NONE Timezone NONE Netmasks NONE Ethers NONE Passwd NONE Services NONE Networks NONE Locale NONE |
In this example,
|
-c |
Specifies the name service context. |
|
NONE |
Is the local /etc files name service. |
You can also use the admtblloc command to display the name service policy for a specified configuration file. This example shows how to display the name service policy for the hosts file in the default name service:
$ admtblloc Hosts Hosts NIS+ |
Note -
The configuration file names are case-sensitive.
Configuration Supported by the admtblloc Command
Following is a list of the configuration files the Solstice AutoClient software can use in a mixed-mode name service environment.
-
Aliases
-
Hosts
-
Group
-
Auto_home
-
Credentials
-
Netgroup
-
Protocols
-
Bootparams
-
Rpc
-
Timezone
-
Netmasks
-
Ethers
-
Passwd
-
Services
-
Networks
-
Locale
Note -
The admtblloc command can be used to set the name service policy for only the configuration files present in this list.
Refer to the admtblloc(1M) man page for more information about how to use this command.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
