Creating and Managing Zone Hosts
The SAP plug-in version 1.3 enables you to create and manage Solaris non-global zones as zone hosts in your SAP environment. When you create a Solaris zone host, you essentially create a physical host onto which you can deploy SAP services.
This section explains the following topics.
Creating Zone Hosts
To create a zone host, perform the following tasks.
-
Create a physical host record for the global zone host in N1 Service Provisioning System.
For more information, see How to Create a Global Zone Host Record.
-
(Optional) Create an SAP Logical Host component or Storage component for the global zone host.
Based on your business needs, you can create a Logical Host or High Availability Storage component for the global zone. For more information, see Sun N1 Service Provisioning System User’s Guide for SAP Plug-In 1.0.
Note –When you create the Logical Host or Storage component for the global zone host, you must change the value for the globalZoneHostName variable to an empty string, or the component creation fails. For a non-global zone, you must not change the default value of the globalZoneHostName.
-
Create the Container component variables for the zone host.
For more information see How to Create Container Component Variables for a Zone Host.
-
Create the zone host.
You can create a zone host in the N1 SPS browser user interface or the N1 AA web console. For more information, see the appropriate procedure.
 How to Create a Global Zone Host Record
How to Create a Global Zone Host Record
This procedure describes how to create a new global zone host record. You can also edit an existing host and assign the host the com.sun.sap#global_zone host type.
-
In the N1 SPS browser user interface, go to the Hosts page.
-
In the Host text box, type a name for the new host.
-
In the Host Type drop down menu, select the com.sun.sap#global_zone host type.
-
In the Description text box, type a brief description of the new host.
-
Click Create.
The Edit page for the new host is displayed.
-
Ensure that the host name, description, and host type display properly.
-
Indicate that you are creating a physical host by selecting Physical Host.
-
If necessary, change the host type attribute values for the target host.
Verify that the local_zone_connection_type, local_zone_port, and local_zone_advanced_params attributes match the settings for the remote agent on the target host. If you need to change these values, select the check box next to the attribute value, then type in the new value in the text field.
-
Select the check box next to Include Remote Agent on This Physical Host.
-
Configure the connection type, network address, and parent information for this host.
Note –For information on configuring SSL and SSH network connections, see Sun N1 Service Provisioning System 5.2 Installation Guide.
-
(Optional) To add this host to a host set, click Add to Host Sets in the Host Relationships area of the page.
In the window that appears, select the host set to which you want to add the host. For more information on host sets, see About Host Sets in Sun N1 Service Provisioning System 5.2 System Administration Guide.
-
To hide the host, select Hidden at the bottom of the page.
-
Verify that the check box beside the Update or Prepare Host With Most Recent System Updates or Services option is checked.
-
Click Save.
-
Repeat the previous procedure for each zone host you want to create.
Next Steps
After you create the global zone host records, you must create container component variables to install and configure the zone host on your target host. For more information, see How to Create Container Component Variables for a Zone Host.
Based on your business needs, you can create a Logical Host or High Availability Storage component for the global zone. If you create the Logical Host or Storage component for the global zone host, you must change the value for the globalZoneHostName variable to an empty string, or the component creation fails. For more information, see Sun N1 Service Provisioning System User’s Guide for SAP Plug-In 1.0.
If you want to provision SAP resources in this global zone, you must change the host type of this global zone from com.sun.sap#global_zone to com.sun.sap#SAPHT. For more information about how to modify host types in N1 Service Provisioning System, see About Hosts in Sun N1 Service Provisioning System 5.2 System Administration Guide.
 How to Create Container Component Variables
for a Zone Host
How to Create Container Component Variables
for a Zone Host
After you create a Zone Host record, you must create the container component variables to install and configure the zone host on your target host. Follow these steps.
-
From the N1 SPS Common Tasks page, click Create New Component.
The Components page is displayed.
-
If necessary, change to the /com/sun/sap/components folder.
-
In the Component table, click the Details link in the Actions column for the Container component.
The Components > Details page is displayed.
-
Scroll to the bottom of the page and click the Variable Settings button.
The Components > Details > Variable Settings page is displayed.
-
Click the Create Set link at the bottom of the Create and Edit Variable Settings table.
A new variable set column is displayed in the Create and Edit Variable Settings table.
-
Type the name of the container component variable set in the Set Name text field.
Note the name of this variable set. The variable set name is required to create the zone host.
-
Edit the variable settings by selecting the check box for each variable that you want to modify, then typing the value in the text field.
Note –Do not specify values for the local_zone_pool or the installPath variables. You specify these values when you create the zone host, as described in How to Create Non-Global Zone as a Physical Host in the N1 Service Provisioning System.
- local_zone_base_path
-
Required. Specifies the boot path to the non-global zone file system.
- local_zone_autoboot
-
Required. Setting this variable value to TRUE specifies that the non-global zone should be booted during system boot. Setting this variable to FALSE specifies that the non-global zone should not be booted at system boot. Default is FALSE.
- local_zone_pool
-
Specifies the resource pool to which this non-global zone is assigned.
- installPath
-
Do not specify a value for this variable. If necessary, manually delete any value for this variable.
- local_zone_filesystem
-
Required. Specifies the type of file system for the non-global zone.
- local_zone_connection_type
-
Specifies the type of connection for the non-global zone. Valid values are raw, ssh, and ssl. Ensure that this value matches the value for the remote agent on the non-global zone.
- local_zone_port
-
Specifies the port on which the non-global zone will listen. Ensure that this value matches the value for the remote agent on the non-global zone.
- local_zone_advanced_params
-
Specifies any advanced parameters for the non-global zone. Ensure that this value matches the value for the remote agent on the non-global zone.
- n1sps_cli_host
-
Specifies the name of the host on which the N1 SPS command line interface (CLI) is installed.
- n1sps_cli_path
-
Specifies the path to the N1 SPS CLI on the target host.
- globalZoneHostName
-
Do not specify a value for this variable. If necessary, manually delete any value for this variable.
- zoneIfaceDetails
-
Specifies the network interface information for the non-global zone. Use the pound sign (#) as a delimiter between multiple entries.
Example: hme0,192.168.2.5/6#eri0,192.167.2.4/5
- zoneFsLayout
-
Specifies the file systems in the global zone to mount in the non-global zone. Use the pound sign (#) as a delimiter between multiple entries.
Example: dir=/usr/local special=/opt/local raw=/dev/rdsk/c0t0d0s7 type=lofs [ro,nodevices]#dir=/opt/mydir special=empty type=lofs ro
- inheritPkgDir
-
Specifies the global zone directories to inherit on the non-global zone. Use the pound sign (#) as a delimiter between multiple entries.
Note –You must set the local_zone_filesystem variable to SPARSE to use this variable.
Example: /opt/sfw#/var/tmp
- device
-
Specifies the device file systems for the non-global zone. Use the pound sign (#) as a delimiter between multiple entries.
Example: /dev/sound#/dev/cdrom
- rctl
-
Specifies the name value pairs for the resource controls to use with this non-global zone. Use the pound sign (#) as a delimiter between multiple entries.
Example: zone.cpu-shares:priv=priveleged,limit=20,action=none#zone.max-lwps:priv=priveleged,limit=500,action=deny
- attributes
-
Specifies the attributes for the non-global zone. Use the pound sign (#) as a delimiter between multiple entries.
Example: audio:boolean:true#group:string:zoneUser
For information about the zone information to include for each variable, see the zoneadm(1M) and zonecfg(1M) man pages.
-
Click the Save button.
The Components > Details > Variable Settings page is displayed, with your new variable set included in the table.
Next Steps
After you create the container component variables, you can create the zone host on a target host. For more information, see the appropriate procedure.
-
How to Create Non-Global Zone as a Physical Host in the N1 Service Provisioning System
-
How to Import a Non-Global Zone as a Physical Host in the N1 Service Provisioning System
-
How to Create Non-Global Zone as a Physical Host in the N1 Advanced Architecture
 How to Create Non-Global Zone as a Physical
Host in the N1 Service Provisioning System
How to Create Non-Global Zone as a Physical
Host in the N1 Service Provisioning System
Before You Begin
Before you can create a non-global zone host, you must first create a global zone host record and a container component variable set for the com/sun/sap/components/Container component. For more information, see the following procedures.
-
In the Common Tasks section in the N1 SPS browser interface, click SAP.
-
Click the Solaris Non-Global Zone as a Physical Host: Create link.
The Plan Details page is displayed.
-
Click Run.
The Plan Details Run page is displayed.
-
In the Plan Parameters section of the page, specify the target host that you want to set up as the non-global zone host.
You can select an individual host, or all the members of a host set.
-
Specify the plan variables for your zone host creation.
-
In the Name of the Container component variable setting field, specify the container component variable set you created in How to Create Container Component Variables for a Zone Host.
-
In the Name of the local Zone field, specify a name for the non-global zone that you want to create.
-
In the Name of the pool field, specify the resource pool that you want to associate with the zone host.
-
-
Click Run Plan (Includes Preflight).
The plan performs the following tasks on the physical host.
-
Creates a non-global zone on the host of the host type com.sun.sap#SAPHT.
-
Installs the N1 SPS Remote Agent software in the non-global zone.
-
Starts the non-global zone.
-
Checks the status of the non-global zone.
-
Stops the non-global zone.
-
Next Steps
After you create the non-global zone, you must start the non-global zone to bring the non-global zone online. For more information, see How to Start a Non-Global Zone on a Physical Host.
Based on your business needs, you can create a Logical Host or High Availability Storage component for the non-global zone. When you create the Logical Host or High Availability Storage component, you must not change the default value of the globalZoneHostName. For more information, see Sun N1 Service Provisioning System User’s Guide for SAP Plug-In 1.0.
After you create the Logical Host or Storage component for this non-global zone, you can provision SAP resources into this non-global zone. For more information, see Sun N1 Service Provisioning System User’s Guide for SAP Plug-In 1.0.
Troubleshooting
If the N1 Service Provisioning System reports that the zone host creation plan failed, check the operating system to verify that the non-global zone was not indeed created. If the non-global zone is installed and configured on the target host, delete the non-global zone with the zonecfg delete command, then recreate the zone host in SPS. For more information, see the zonecfg(1M) man page.
 How to Import a Non-Global Zone as a Physical
Host in the N1 Service Provisioning System
How to Import a Non-Global Zone as a Physical
Host in the N1 Service Provisioning System
-
In the Common Tasks section in the N1 SPS browser interface, click SAP.
-
Click the Solaris Non-Global Zone as a Physical Host: Attach link.
The Plan Details page is displayed.
-
Click Run.
The Plan Details Run page is displayed.
-
In the Plan Parameters section of the page, click the Select From List link in the Variable Settings column.
The Select Variable Settings From List window is displayed.
-
Click the Create Set link at the bottom of the Select a Variable Setting table.
A new variable set column is displayed in the Select a Variable Setting table.
-
Type the name of the container component variable set in the Set Name text field.
-
Edit the variable settings by selecting the check box for each variable that you want to modify, then typing the value in the text field.
Note –Be sure to specify the name of the non-global zone that you want to import for the installPath variable.
- local_zone_base_path
-
Required. Specifies the boot path to the non-global zone file system.
- local_zone_autoboot
-
Required. Setting this variable value to TRUE specifies that the non-global zone should be booted during system boot. Setting this variable to FALSE specifies that the non-global zone should not be booted at system boot. Default is FALSE.
- local_zone_pool
-
Specifies the resource pool to which this non-global zone is assigned.
- installPath
-
Required. Specifies the name of the non-global zone that you want to import.
- local_zone_filesystem
-
Required. Specifies the type of file system for the non-global zone.
- globalZoneHostName
-
Required. Specifies the name of the global host on which the non-global zone is installed.
- zoneIfaceDetails
-
Specifies the network interface information for the non-global zone. Use the pound sign (#) as a delimiter between multiple entries.
Example: hme0,192.168.2.5/6#eri0,192.167.2.4/5
- zoneFsLayout
-
Specifies the file systems in the global zone to mount in the non-global zone. Use the pound sign (#) as a delimiter between multiple entries.
Example: dir=/usr/local special=/opt/local raw=/dev/rdsk/c0t0d0s7 type=lofs [ro,nodevices]#dir=/opt/mydir special=empty type=lofs ro
- inheritPkgDir
-
Specifies the global zone directories to inherit on the non-global zone. Use the pound sign (#) as a delimiter between multiple entries.
Note –You must set the local_zone_filesystem variable to SPARSE to use this variable.
Example: /opt/sfw#/var/tmp
- device
-
Specifies the device file systems for the non-global zone. Use the pound sign (#) as a delimiter between multiple entries.
Example: /dev/sound#/dev/cdrom
- rctl
-
Specifies the name value pairs for the resource controls to use with this non-global zone. Use the pound sign (#) as a delimiter between multiple entries.
Example: zone.cpu-shares:priv=priveleged,limit=20,action=none#zone.max-lwps:priv=priveleged,limit=500,action=deny
- attributes
-
Specifies the attributes for the non-global zone. Use the pound sign (#) as a delimiter between multiple entries.
Example: audio:boolean:true#group:string:zoneUser
For information about the zone information to include for each variable, see the zoneadm(1M) and zonecfg(1M) man pages.
-
Click the Save button.
The Select Variable Settings From List window is displayed, with your new variable set included in the table.
-
Click the Select button at the bottom of the column for the variable set you created.
The Plan > Details > Run page is displayed.
-
Specify the target host from which you want to import the non-global zone.
-
In the Plan Variables section, specify the install path of the non-global zone that you want to import.
-
If necessary, modify the values in the Limits section.
-
Click Run Plan (Includes Preflight).
The non-global zone is imported into your N1 SPS environment from the target host. You can now manage the non-global zone as a zone host with the SAP plug-in.
Next Steps
Based on your business needs, you can create a Logical Host or High Availability Storage component for the non-global zone. When you create the Logical Host or High Availability Storage component, you must not change the default value of the globalZoneHostName. For more information, see Sun N1 Service Provisioning System User’s Guide for SAP Plug-In 1.0.
After you create the Logical Host or Storage component for this non-global zone, you can provision SAP resources into this non-global zone. For more information, see Sun N1 Service Provisioning System User’s Guide for SAP Plug-In 1.0.
 How to Create Non-Global Zone as a Physical
Host in the N1 Advanced Architecture
How to Create Non-Global Zone as a Physical
Host in the N1 Advanced Architecture
This procedure describes how to create a zone host in the N1 AA web console.
Before You Begin
Before you can create a non-global zone host, you must perform the following tasks.
-
Create a zone host record in N1 Service Provisioning System.
For more information, see How to Create a Global Zone Host Record.
-
Create the container component variables for you non-global zones.
For more information, see How to Create Container Component Variables for a Zone Host.
-
Create the server group and physical host entries in the N1 Advanced Architecture for the systems on which you want to install zone hosts.
For more information, see Sun N1 Advanced Architecture for SAP Solutions 5.2.1 User’s Guide.
-
In the N1 AA web console, click the SunTM N1 Advanced Architecture for SAP Solutions link in the Systems section.
The Sun N1 Advanced Architecture for SAP Solutions page is displayed.
-
In the left pane, click the arrow for the appropriate server group.
-
Click the arrow for the Builder entry for the server group.
-
Click the Zone Provisioning link.
The N1AA Builder - Zone Provisioning page is displayed.
Figure 3–1 N1 AA Builder — Zone Provisioning Page

-
In the Zone name field, type the name of the non-global zone host that you want to create.
-
From the Global Zone Host drop-down menu, select the global zone on which you want to create a non-global zone host.
-
From the Zone Parameters drop-down menu, select the name of the container component variable set that you created in How to Create Container Component Variables for a Zone Host.
-
In the Zone Pool field, type the name of the resource pool that you want to associate with the non-global zone host.
To include multiple resource pools, type the pool names, separated by the pound sign (#). For more information about using resource pools with non-global zones, see the zonecfg(1M) man page.
-
Click the Create Zone button.
The plan performs the following tasks on the global zone host.
-
Creates a non-global zone on the host of the host type com.sun.sap#SAPHT.
-
Installs the N1 SPS Remote Agent software in the non-global zone.
-
Starts the non-global zone.
-
Adds the newly created non-global zone host record to the list of N1AA Physical Hosts.
Note –This new physical host is defined as a non-global zone host and as a non OS Provisionable host.
-
Checks the status of the non-global zone.
-
Stops the non-global zone.
-
Next Steps
After you create the non-global zone host, perform the following tasks.
-
Start the non-global zone to bring the non-global zone online. For more information, see How to Start a Non-Global Zone on a Physical Host.
-
Based on your business needs, you can create a Logical Host or High Availability Storage component for the non-global zone. When you create the Logical Host or High Availability Storage component, you must not change the default value of the globalZoneHostName. For more information, see Sun N1 Service Provisioning System User’s Guide for SAP Plug-In 1.0.
-
After you create the Logical Host or Storage component for this non-global zone, you can provision SAP resources into this non-global zone. For more information, see Sun N1 Service Provisioning System User’s Guide for SAP Plug-In 1.0.
Troubleshooting
If the N1 AA web console reports that the zone host creation plan failed, check the operating system to verify that the non-global zone was not indeed created. If the non-global zone is installed and configured on the target host, delete the non-global zone with the zonecfg delete command, then recreate the zone host in SPS. For more information, see the zonecfg(1M) man page.
 How to Create Non-Global Zone as a Physical
Host With the N1 AA Command Line Interface
How to Create Non-Global Zone as a Physical
Host With the N1 AA Command Line Interface
This procedure describes how to create a zone host with the N1 AA command line interface (CLI). The N1 Advanced Architecture 5.2 Update 2 release includes two new commands for creating non-global zone hosts.
-
n1aa_exec deployment.ListSPSHosts
This command lists all the N1 SPS hosts of a specified host type. This command requires the following syntax.
# n1aa_exec deployment.ListSPSHosts host-type
where host-type specifies an N1 SPS host type, for example, com.sun.sap#global_zone.
-
n1aa_exec deployment.CreateZoneHost
This command creates a new non-global zone host. This command requires the following syntax.
# n1aa_exec deployment.CreateZoneHost servergroup=server-group-ID globalzonename=global-zone-name localzonename=local-zone-name zonepool=zone-pool zoneparamsetname=zone-param-set-name
For more information about the arguments and syntax for the n1aa_exec deployment.CreateZoneHost command, see the following procedure.
Before You Begin
Before you can create a non-global zone host, you must perform the following tasks.
-
Create a zone host record in the N1 Service Provisioning System.
For more information, see How to Create a Global Zone Host Record.
-
Create the container component variables for you non-global zones.
For more information, see How to Create Container Component Variables for a Zone Host.
-
Create the server group and physical host entries in the N1 Advanced Architecture for the systems on which you want to install zone hosts.
For more information, see Sun N1 Advanced Architecture for SAP Solutions 5.2.1 User’s Guide.
-
Check the identifier of the server group on which you want to create a zone host.
# ./n1aa_exec GetServerGroups
The output of the previous command lists the unique IDs and names of the server groups in your N1 AA environment.
-
Check the names of the global zone hosts in your N1 SPS environment.
# ./n1aa_exec deployment.ListSPSHosts com.sun.sap#global_zone
The output of the previous command lists the names of all the global zone hosts in your N1 SPS environment.
-
Create the non-global zone host.
# ./n1aa_exec deployment.CreateZoneHost servergroup=server-group-ID globalzonename=global-zone-name localzonename=local-zone-name zonepool=zone-pool zoneparamsetname=zone-param-set-name
- server-group-ID
-
Specifies the server group ID that you identified in Step 1.
- global-zone-name
-
Specifies the name of the global zone that you identified in Step 2.
- local-zone-name
-
Specifies the name of the non-global zone host that you want to create.
- zone-pool
-
Specifies the name of the resource pool that you want to associate with the non-global zone host.
- zone-param-set-name
-
Specifies the name of the container component variable set that you created in How to Create Container Component Variables for a Zone Host.
The plan performs the following tasks on the global zone host.
-
Creates a non-global zone on the host of the host type com.sun.sap#SAPHT.
-
Installs the N1 SPS Remote Agent software in the non-global zone.
-
Starts the non-global zone.
-
Adds the newly created non-global zone host record to the list of N1AA Physical Hosts.
Note –This new physical host is defined as a non-global zone host and as a non OS Provisionable host.
-
Checks the status of the non-global zone.
-
Stops the non-global zone.
Next Steps
After you create the non-global zone host, perform the following tasks.
-
Start the non-global zone to bring the non-global zone online. For more information, see How to Start a Non-Global Zone on a Physical Host.
-
Based on your business needs, you can create a Logical Host or High Availability Storage component for the non-global zone. When you create the Logical Host or High Availability Storage component, you must not change the default value of the globalZoneHostName. For more information, see Sun N1 Service Provisioning System User’s Guide for SAP Plug-In 1.0.
-
After you create the Logical Host or Storage component for this non-global zone, you can provision SAP resources into this non-global zone. For more information, see Sun N1 Service Provisioning System User’s Guide for SAP Plug-In 1.0.
Troubleshooting
If the N1 AA CLI reports that the zone host creation plan failed, check the operating system to verify that the non-global zone was not indeed created. If the non-global zone is installed and configured on the target host, delete the non-global zone with the zonecfg delete command, then recreate the zone host in SPS. For more information, see the zonecfg(1M) man page.
Managing Zone Hosts
After you create zone hosts, you can perform the following management tasks through the N1 Service Provisioning System.
-
View information about the zone hosts in your environment.
For more information, see Viewing Zone Host Information in the N1 Advanced Architecture.
-
Start a non-global zone.
For more information, see How to Start a Non-Global Zone on a Physical Host.
-
Stop a non-global zone.
For more information, see How to Stop a Non-Global Zone on a Physical Host.
-
Delete a non-global zone from a physical host.
For more information, see How to Delete a Non-Global Zone From a Physical Host in the N1 Service Provisioning System or How to Delete a Non-Global Zone in the N1 Advanced Architecture.
-
Delete a non-global zone from your N1 SPS environment without deleting the non-global zone from the physical host.
For more information, see How to Delete a Non-Global Zone From the N1 SPS Environment.
Viewing Zone Host Information in the N1 Advanced Architecture
The Physical Hosts table in the N1 AA – Customizing page now includes information about the presence of non-global zones on the physical hosts in your environment. The table now includes a Local Zone column that indicates if a non-global zone is installed on the physical host.
Figure 3–2 Physical Hosts Table of N1 AA – Customizing Page
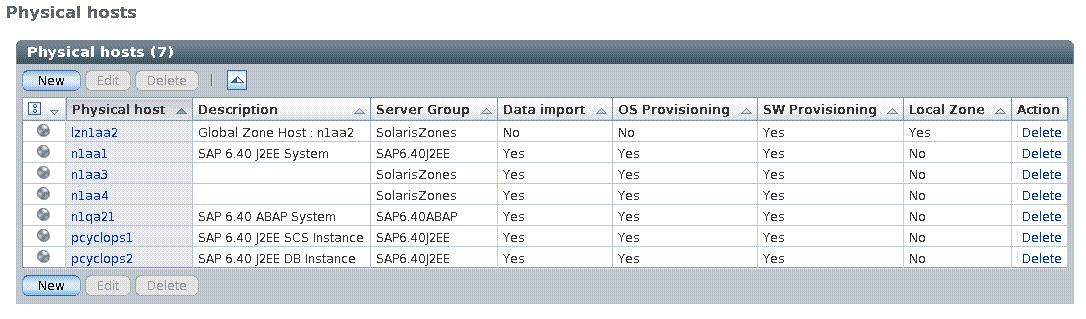
You can access the Physical Hosts table by clicking on the Administration arrow in the left panel of the N1 AA web console, then clicking on the Customizing link.
For more information, see Physical Hosts in Sun N1 Advanced Architecture for SAP Solutions 5.2.1 User’s Guide.
 How to Start a Non-Global Zone on a Physical
Host
How to Start a Non-Global Zone on a Physical
Host
Before You Begin
To start a zone host, you need to know the install path of the non-global zone host that you want to start. You can view the install path by clicking the View All link in the Solaris Non-Global Zone as a Physical Host section of the SAP plug-in page.
-
In the Common Tasks section in the N1 SPS browser interface, click SAP.
-
Click the Solaris Non-Global Zone as a Physical Host: Start link.
The Plan Details page is displayed.
-
Click Run.
The Plan Details Run page is displayed.
-
In the Plan Parameters section of the page, specify the target host on which you want to start the non-global zone.
You can select an individual host, or all the members of a host set.
-
In the Plan Variables section, specify the install path of the non-global zone that you want to start.
-
If necessary, modify the values in the Limits section.
-
Click Run Plan (Includes Preflight).
The non-global zone is started on the target host.
 How to Stop a Non-Global Zone on a Physical
Host
How to Stop a Non-Global Zone on a Physical
Host
Before You Begin
To stop a zone host, you need to know the install path of the non-global zone host that you want to stop. You can view the install path by clicking the View All link in the Solaris Non-Global Zone as a Physical Host section of the SAP plug-in page.
-
In the Common Tasks section in the N1 SPS browser interface, click SAP.
-
Click the Solaris Non-Global Zone as a Physical Host: Stop link.
The Plan Details page is displayed.
-
Click Run.
The Plan Details Run page is displayed.
-
In the Plan Parameters section of the page, specify the target host on which you want to stop the non-global zone.
You can select an individual host, or all the members of a host set.
-
In the Plan Variables section, specify the install path of the non-global zone that you want to stop.
-
If necessary, modify the values in the Limits section.
-
Click Run Plan (Includes Preflight).
The non-global zone is halted on the target host.
 How to Delete a Non-Global Zone From a Physical
Host in the N1 Service Provisioning System
How to Delete a Non-Global Zone From a Physical
Host in the N1 Service Provisioning System
Before You Begin
To delete a zone host, you need to know the install path of the non-global zone host that you want to delete. You can view the install path by clicking the View All link in the Solaris Non-Global Zone as a Physical Host section of the SAP plug-in page.
-
In the Common Tasks section in the browser interface, click SAP.
-
Click the Solaris Non-Global Zone as a Physical Host: Delete link.
The Plan Details page is displayed.
-
Click Run.
The Plan Details Run page is displayed.
-
In the Plan Parameters section of the page, specify the target host on which you want to delete the non-global zone.
You can select an individual host, or all the members of a host set.
-
In the Plan Variables section, specify the install path of the non-global zone that you want to delete.
-
If necessary, modify the values in the Limits section.
-
Click Run Plan (Includes Preflight).
Next Steps
To completely delete the non-global zone from the operating system, you must delete the non-global zone with the zonecfg delete command. For more information, see the zonecfg(1M) man page.
If you are using the N1 Advanced Architecture to manage your zone hosts, you must manually delete the zone host from your N1 AA environment after you delete the zone host in N1 SPS. For more information, see How to Delete a Non-Global Zone in the N1 Advanced Architecture.
 How to Delete a Non-Global Zone in the N1 Advanced Architecture
How to Delete a Non-Global Zone in the N1 Advanced Architecture
This procedure explains how to delete a non-global zone host from your N1 AA environment.
Note –
This procedure does not delete a non-global zone from the N1 Service Provisioning System or the operating system.
-
In the N1 AA web console, click the Sun N1 Advanced Architecture for SAP Solutions link in the Systems section.
The Sun N1 Advanced Architecture for SAP Solutions page is displayed.
-
In the left navigation pane, click the arrow next to the Administration section.
The Administration section is expanded.
-
Click the Customizing link.
The N1AA - Customizing page is displayed.
-
Click the Physical Hosts link the top of the N1AA - Customizing page.
-
Click the radio button for the physical host entry on which you want to delete the non-global zone.
-
Click the Delete button.
-
If prompted, confirm the deletion by clicking the OK button in the confirmation pop-up window.
The non-global zone host is removed from the Physical Hosts table. The non-global zone host is not deleted from the N1 Service Provisioning System, and it is not deleted from the operating system.
Next Steps
If you want to delete the non-global zone host from the N1 Service Provisioning System, but leave the non-global zone intact on the operating system, see How to Delete a Non-Global Zone From the N1 SPS Environment.
If you want to delete the non-global zone host from both the N1 Service Provisioning System and the operating system, see How to Delete a Non-Global Zone From a Physical Host in the N1 Service Provisioning System.
 How to Delete a Non-Global Zone From the N1
SPS Environment
How to Delete a Non-Global Zone From the N1
SPS Environment
You can use the SAP plug-in to remove a non-global zone from your N1 SPS environment, without affecting the status of the non-global zone on the physical host. Follow these steps.
-
In the Common Tasks section in the browser interface, click SAP.
-
Click the Solaris Non-Global Zone as a Physical Host: Detach link.
The Plan Details page is displayed.
-
Click Run.
The Plan Details Run page is displayed.
-
Specify the target host that includes the non-global zone that you want to delete from your N1 SPS environment.
-
If necessary, modify the values in the Limits section.
-
Click Run Plan (Includes Preflight).
The non-global zone is deleted from your N1 SPS environment. The status on the non-global zone on the physical host is not affected.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
