Chapter 7 Nautilus File Manager
This chapter describes how to use the Nautilus file manager.
Introduction to Nautilus File Manager
The Nautilus file manager provides
an integrated access point to your files and applications. The file manager
enables you to do the following:
-
Display your files and folders.
-
Manage your files and folders.
-
Run scripts.
-
Customize your files and folders.
-
Open special URI locations.
-
Write data to a CD.
Nautilus also manages the desktop. The desktop
lies behind all of the other components on your visible desktop. The desktop
is an active component of the user interface.
File manager windows enable you to display and manage your files and folders. To open a file manager window, double-click on the Documents object on the desktop. The file manager window displays the contents of your default documents location in the view pane.
File Manager Windows
File manager windows enable you to display and manage your files and folders. Figure 7–1 shows a file manager window that displays the contents of a folder.
Figure 7–1 Contents of a Folder in a File Manager Window
Table 7–1 describes the components of file manager windows.
Table 7–1 File Manager Window Components
You can also open a popup menu from file manager windows. To open this popup menu right-click in a file manager window. The items in this menu depend on where you right-click. For example, when you right-click on a file or folder, you can choose items related to the file or folder. When you right-click on the background of a view pane, you can choose items related to the display of items in the view pane.
Note –
In other distributions of the GNOME Desktop, the Home toolbar button might have another designation, for example, Documents.
View Pane
The view pane can display the contents of the following:
-
Particular types of files
-
Folders
-
FTP sites
-
Locations that correspond to special URIs
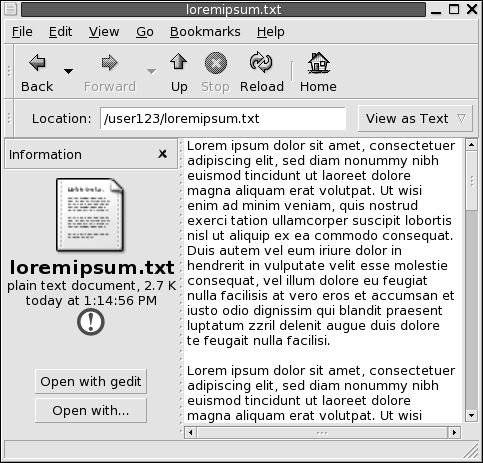
The file manager contains viewer components that enable you to display particular types of file in the view pane. For example, you can use a text viewer to display text files in the view pane. Figure 7–2 shows a text file displayed in the view pane.
Figure 7–2 Text File in a File Manager Window
Displaying a file in the view pane provides the following benefits:
-
Uses less system resources than when you launch an application.
-
Takes less time than when you launch an application.
However, you cannot edit a file in the view pane.
The file manager also includes views that enable you to display the contents of your folders in different ways. For example, you can display the contents of a folder in the following types of view:
-
Icon view: Shows the items in the folder as icons.
-
List view: Shows the items in the folder as a list.
-
Audio view: Shows only the audio items in the folder.
Use the View menu to choose how to display a folder. For more information on views, see Using Views to Display Your Files and Folders.
Side Pane
To display the side pane, choose View -> Side Pane. You can choose what information you want to view in the side pane. You can choose to display one of the following:
-
Information
Displays an icon that represents the current file or current folder. Also displays information about the current file or current folder. If a file is displayed in the view pane, buttons appear in the side pane. The buttons enable you to perform actions on a file, other than the default action.
-
Emblems
Contains emblems that you can add to a file or folder. For more information on emblems, see the next section.
-
History
Contains a history list of files, folders, FTP sites, and URIs that you have recently visited.
-
Notes
Enables you to add notes to your files and folders.
-
Tree
Displays a hierarchical representation of your file system. You can use the Tree to navigate through your files.
To close the side pane, click on the X button at the top right of the side pane.
Icons and Emblems
In icon view, the file manager displays your files and folders as icons. You can add emblems to your file icons and folder icons. An emblem is a small icon that you can add to an item to visually mark the item. For example, to mark a file as important, you can add an Important emblem to the file icon to create the following visual effect:
For more information on how to add an emblem to an icon, see To Add an Emblem to a File or Folder.
The following table describes the structure of the file icon:
|
Component |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Emblem. This emblem is the Important emblem. |
|
|
Icon that represents the file. This icon might contain a preview of the contents of the file. |
|
|
Icon caption. You can modify what items of information are displayed in the icon caption. |
The file manager includes default emblems for the following types of item:
-
Symbolic links
-
Items for which you have the following permissions:
-
Read permission only
-
No read permission and no write permission
-
The following table shows the default emblems:
|
Default Emblem |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Read permission only |
|
|
No read permission and no write permission |
Navigating Your Computer
Each file manager window displays the contents of a single file, folder, FTP site, or special URI location. This section describes the following:
-
How to display items in file manager windows.
-
How to open files from file manager windows.
-
How to navigate the files and folders in your file system.
-
How to navigate to FTP sites.
-
How to access special URI locations.
To Display a Folder
You can display the contents of a folder in any of the following ways:
-
Double-click on the folder in the view pane.
-
In the Location field, type the path of the folder that you want to display, then press Return. The Location field includes an autocomplete feature. As you type a path, the file manager reads your file system. When you type enough characters to uniquely identify a directory, the file manager completes the name of the directory in the Location field.
-
Use the Tree in the side pane. For more information, see Using the Tree From the Side Pane.
-
Use the Back toolbar button and the Forward toolbar button to browse through your navigation history.
To change to the folder that is one level above the current folder, choose Go -> Up. Alternatively, click on the Up toolbar button.
To reload the display, click on the Reload button.
If you cannot find the folder that you want to display, you can use Search Tool. To
start Search Tool, choose Find Files from the Main Menu.
Using the Tree From the Side Pane
The Tree displays a hierarchical representation of your file system. The Tree provides a convenient way to navigate your file system. To display the Tree in the side pane, choose Tree from the drop-down list at the top of the side pane.
In the Tree, folders are represented as follows:
|
Folder State |
Graphic Representation |
|---|---|
|
Closed folder |
Right arrow |
|
Open folder |
Down arrow |
Table 7–2 describes the tasks that you can perform with the Tree, and how to perform the tasks.
Table 7–2 Tree Tasks|
Task |
Action |
|---|---|
|
Open the Tree. |
Choose Tree from the drop-down list at the top of the side pane. |
|
Close the Tree. |
Choose another item from the drop-down list at the top of the side pane. |
|
Open a folder in the Tree. |
Click on the arrow next to the folder in the Tree. |
|
Close a folder in the Tree. |
Click on the arrow next to the folder in the Tree. |
|
Display the contents of a folder in the view pane. |
Select the folder in the Tree. |
|
Display the contents of a file in the view pane. |
Select the file in the Tree. |
You can set your preferences so that the Tree does not display files. For more information, see To Set Views Preferences.
Opening Files
When you open a file, the file manager performs the default action for that file type. The default action can be one of the following:
-
Use a viewer component to display the file in the view pane.
-
Launch an application that opens the file.
The file manager checks the contents of a file to determine the type of a file. If the first lines do not determine the type of the file, then the file manager checks the file extension.
If you cannot find the file that you want to open, you can use Search Tool. To
start Search Tool, choose Find Files from the Main Menu.
Viewing Files in the View Pane
The file manager contains viewer components that enable you to display particular types of file in the view pane. For example, you can display the following types of files in the view pane:
-
Plain text files
-
PNG files
-
Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG) files
To reload the contents of the view pane, choose View -> Reload. To stop loading an item in the view pane, choose View -> Stop.
When you display a file in the view pane, the viewer component might add menu items to the file manager menus. The menu items relate to the file type that is displayed. For example, when you display a PNG file, the Edit menu contains flip and rotate menu items.
Also, when you display some types of file in the view pane, you can use the file manager zoom buttons to change the size of the item.
To Execute the Default Action
To execute the default action for a file, double-click on the file. For example, if the default action for plain text documents is to display the file in a text viewer. In this case, you can double-click on the file to display the file in a text viewer.
You can set your file manager preferences so that you click once on a file to execute the default action. For more information, see To Set Behavior Preferences.
To Execute Non-Default Actions Using the Open With Submenu
To execute actions other than the default action for a file, perform the following steps:
-
In the view pane, select the file that you want to perform an action on. Choose File -> Open With. The Open With submenu opens. The items in this submenu correspond to the contents of the following parts of the
File Associationspreference tool:-
Default action drop-down list in the Edit file type dialog
-
Viewer component drop-down list in the Edit file type dialog
-
-
Choose an action from the Open With submenu.
To Execute Other Actions When Displaying a File
When you display a file in the view pane, the side pane might contain buttons. Figure 7–2 shows the buttons in the side pane when a text file is displayed in the view pane.
The buttons represent any actions that are defined in the File
Associations preference tool. The actions are defined in
the Default action drop-down list in the Edit
file type dialog in the File
Associations preference tool. Click on a button to execute
an action. For example, if an action defined for plain text documents is to
open the file in the gedit text editor. If this
action is defined, an Open with gedit button is displayed
in the side pane. To open the file in the gedit
application, click on the Open with gedit button.
Note –
A button that represents the action does not appear in the side pane if the actions are excluded in either of the following dialogs:
-
Open with Other Application
-
Open with Other Viewer
To Access FTP Sites
You can use the file manager to access FTP sites. To access an FTP site, enter the URL for the site in the field on the location bar, then press Return. The contents of the site are displayed in the view pane. To copy a file from the FTP site, drag the file to the new location.
To access an FTP site that requires a username and password, you can enter the URL in the following form:
ftp://username:password@hostname.domain
To reload the FTP site in the view pane, choose View -> Reload. To stop loading the FTP site, choose View -> Stop.
To Access Network Places
If your system is configured to access places on a network, you can use the file manager to access the network places.
To access network places, open the file manager and choose Go -> Network Places. A file manager window is displayed. The window displays the network places that you can access. Double-click on the network place that you want to access.
To access UNIX shares, double-click on the Unix Network (NFS) object. A list of the UNIX shares available to you is displayed in the file manager window.
To access Windows shares, double-click on the Windows Network (SMB) object. A list of the Windows shares available to you is displayed in the file manager window.
To Add a Network Place
To add a network place, perform the following steps:
-
Open the file manager and choose Go -> Network Places. A file manager window is displayed.
-
Double-click on the Add Network Place object. The Add Network Place dialog is displayed. Enter the details of the server in the dialog, as follows:
-
Click OK to add your network place.
Accessing Special URI Locations
The GNOME Desktop contains special URI locations that enable you to access particular functions from the file manager. For example, to access the preference tools, you can access the preferences:/// URI in a file manager window. Table 7–3 lists the special URI locations that you can use with the file manager.
Table 7–3 Special URI Locations|
URI Location |
Description |
|---|---|
|
applications:/// |
Displays a list of the applications in the GNOME Desktop. The applications are the same as the applications in the Applications menu. To open an application, double-click on the application. |
|
burn:/// |
Copy files and folders that you want to write to a CD to this location. You can write the contents of this location to a CD. |
|
fonts:/// |
Displays all the fonts that are available in your system. To preview a font, double-click on the font. You can also use this location to add fonts to the GNOME Desktop. |
|
network:/// |
Displays the Network Places location. Network Places displays network locations to which you can connect, if your system is configured to access locations on a network. To access a network location, double-click on the network location. You can also use this URI to add network locations to your system. |
|
nfs:/// |
Displays UNIX NFS network locations, if your system is configured to access UNIX NFS locations. To access a NFS location, double-click on the NFS location. |
|
preferences:/// |
Displays a list of the preference tools in the GNOME Desktop. The preference tools are the same as the preference tools in the Preferences menu. To open a preference tool, double-click on the preference tool. |
|
printers:/// |
Displays printers, if your system is configured to access printers. To access a printer, double-click on the printer. You can also use this URI to add printers to your system. |
|
smb:/// |
Displays Windows servers, if your system is configured to access Windows servers. To open a Windows server, double-click on the Windows server. |
|
system-settings:/// |
Displays a list of applications that you can use to modify your system settings. |
Using Your Navigation History
The file manager maintains a history list of files, folders, FTP sites, and URI locations. You can use the history list to navigate to files, folders, FTP sites, and URI locations that you have recently visited. Your history list contains the last ten items that you viewed. The following sections describe how to navigate your history list.
To clear your history list choose Go -> Clear History.
To Navigate Your History List Using the Go Menu
To display a list of previously-viewed items, choose the Go menu. Your history list is displayed in the lower part of the Go menu. To open an item in your history list, choose the item from the Go menu.
To Navigate Your History List Using the Toolbar
To use the toolbar to navigate your history list, perform one of the following actions:
-
To open the previous file, folder, or URI in your history list, click on the Back toolbar button.
-
To open the next file, folder, or URI in your history list, click on the Forward toolbar button.
-
To display a list of previously-viewed items, click on the down arrow to the right of the Back toolbar button. To open an item from this list, click on the item.
-
To display a list of items that you viewed after you viewed the current item, click on the down arrow to the right of the Forward toolbar button. To open an item from this list, click on the item.
To Navigate Your History List Using History in the Side Pane
To display the History list in the side pane, choose History from the drop-down list at the top of the side pane. The History list in the side pane displays a list of your previously-viewed items.
To display an item from your history list in the view pane, click on the item in the History list.
To Bookmark Your Favorite Locations
To access an item in your bookmarks, choose the item from the Bookmarks menu. You can add your favorite locations to your Bookmarks menu. You can add bookmarks to files and folders in your file system, to FTP sites, or to URI locations.
To Add a Bookmark
To add a bookmark, display the item that you want to bookmark in the view pane. Choose Bookmarks -> Add Bookmark.
To Edit a Bookmark
To edit your bookmarks perform the following steps:
-
Choose Bookmarks -> Edit Bookmarks. An Edit Bookmarks dialog is displayed.
-
To edit a bookmark, select the bookmark on the left side of the Edit Bookmarks dialog. Edit the details for the bookmark on the right side of the Edit Bookmarks dialog, as follows:
Dialog Element
Description
Name
Use this text box to specify the name that identifies the bookmark in the Bookmarks menu.
Location
Use this field to specify the location of the bookmark.
-
To delete a bookmark, select the bookmark on the left side of the dialog. Click Delete.
Managing Your Files and Folders
This section describes how to work with your files and folders.
Drag-and-Drop in the File Manager
You can use drag-and-drop to perform several tasks in the file manager. When you drag-and-drop, the mouse pointer provides feedback about the task that you perform. Table 7–4 describes the tasks that you can perform with drag-and-drop. The table also shows the mouse pointers that appear when you drag-and-drop.
Table 7–4 Drag-and-Drop in the File Manager
To Select Files and Folders
You can select files and folders in several ways in the file manager. Table 7–5 describes how to select items in file manager windows and on the desktop.
Table 7–5 Selecting Items in the File Manager|
Task |
Action |
|---|---|
|
Select an item |
Click on the item. |
|
Select a group of contiguous items |
In icon view, drag around the files that you want to select. In list view, click on the first item in the group. Press-and-hold Shift, then click on the last item in the group. |
|
Select multiple items |
Press-and-hold Ctrl. Click on the items that you want to select. Alternatively, press-and-hold Ctrl, then drag around the files that you want to select. |
|
Select all items in a folder |
Choose Edit -> Select All Files. |
To perform the default action on an item, double-click on the item. You can set your file manager preferences so that you click once on a file to execute the default action. For more information, see To Set Behavior Preferences.
To Move a File or Folder
The following sections describe the ways that you can move a file or folder.
Drag to the New Location in a View Pane
To drag a file or folder to a new location in a view pane, perform the following steps:
-
Open a file manager window. Choose File -> New Window to open a second file manager window.
-
In one window, select the folder from which you want to move the file or folder. In the other window, select the folder to which you want to move the file or folder.
-
Drag the file or folder that you want to move to the new location in the other window.
To move the file or folder to a folder that is one level below the current location, do not open a new window. Instead, drag the file or folder to the new location in the same window.
Cut and Paste to the New Location
You can cut a file or folder and paste the file or folder into another folder, as follows:
-
Select the file or folder that you want to move, then choose Edit -> Cut File.
-
Open the folder to which you want to move the file or folder, then choose Edit -> Paste Files.
To Copy a File or Folder
The following sections describe the ways you can copy a file or folder.
Drag to the New Location in a View Pane
To copy a file or folder perform the following steps:
-
Open a file manager window. Choose File -> New Window to open a second file manager window.
-
In one window, select the folder from which you want to copy the file or folder. In the other window, select the folder to which you want to copy the file or folder.
-
Grab the file or folder, then press-and-hold Ctrl. Drag the file or folder to the new location in the other window.
To copy the file or folder to a folder that is one level below the current location, do not open a new window. Instead, grab the file or folder, then press-and-hold Ctrl. Drag the file or folder to the new location in the same window.
Copy and Paste to the New Location
You can copy a file or folder and paste the file or folder into another folder, as follows:
-
Select the file or folder that you want to copy, then choose Edit -> Copy File.
-
Open the folder to which you want to copy the file or folder, then choose Edit -> Paste Files.
To Duplicate a File or Folder
To create a copy of a file or folder in the current folder perform the following steps:
-
Select the file or folder that you want to duplicate in the view pane.
-
Choose Edit -> Duplicate. Alternatively, right-click on the file or folder in the view pane, then choose Duplicate.
A copy of the file or folder appears in the current folder.
To Create a Folder
To create a folder perform the following steps:
-
Select the folder where you want to create the new folder.
-
Choose File -> New Folder. Alternatively, right-click on the background of the view pane, then choose New Folder.
An untitled folder is added to the view pane. The name of the folder is selected.
-
Type a name for the folder, then press Return.
To Rename a File or Folder
To rename a file or folder perform the following steps:
-
Select the file or folder that you want to rename in the view pane.
-
Choose Edit -> Rename. Alternatively, right-click on the file or folder in the view pane, then choose Rename.
The name of the file or folder is selected.
-
Type a new name for the file or folder, then press Return.
To Move a File or Folder to Trash
To move a file or folder to Trash perform the following steps:
-
Select the file or folder that you want to move to Trash in the view pane.
-
Choose Edit -> Move to Trash. Alternatively, right-click on the file or folder in the view pane, then choose Move to Trash.
Alternatively, you can drag the file or folder from the view pane to the Trash object on the desktop.
Note –
When you move a file or folder from a removable media to Trash, the file or folder is stored in a Trash location on the removable media. To remove the file or folder permanently from the removable media, you must empty Trash.
To Delete a File or Folder
When you delete a file or folder, the file or folder is not moved to Trash, but is deleted from your file system immediately. The Delete menu item is only available if you select the Include a Delete command that bypasses Trash option in the Folder Options dialog.
To delete a file or folder perform the following steps:
-
Select the file or folder that you want to delete in the view pane.
-
Choose Edit -> Delete. Alternatively, right-click on the file or folder in the view pane, then choose Delete.
To Create a Symbolic Link to a File or Folder
A symbolic link is a special type of file that points to another file or folder. When you perform an action on a symbolic link, the action is performed on the file or folder to which the symbolic link points. However, when you delete a symbolic link, you delete the link file, not the file to which the symbolic link points.
To create a symbolic link to a file or folder, select the file or folder to which you want to create a link. Choose Edit -> Make Link. A link to the file or folder is added to the current folder.
Alternatively, grab the item to which you want to create a link, then press-and-hold Ctrl + Shift. Drag the item to the location where you want to place the link.
By default, the file manager adds an emblem to symbolic links.
Note –
The permissions of a symbolic link are determined by the file or folder to which a symbolic link points.
To View the Properties of a File or Folder
To view the properties of a file or folder, perform the following steps:
-
Select the file or folder whose properties you want to view.
-
Choose File -> Properties. A properties dialog is displayed.
-
Use the properties dialog to view the properties of the file or folder.
-
Click Close to close the properties dialog.
To Change Permissions
Permissions are settings assigned to each file and folder that determine what type of access users can have to the file or folder. The following table lists the permissions that you can set for files and folders, and the effect of the permission on files and folders:
|
Permission |
File |
Folder |
|---|---|---|
|
Read |
Permission to read the file. |
Permission to list the contents of the folder. |
|
Write |
Permission to make changes to the file. |
Permission to create and delete files in the folder. |
|
Execute |
Permission to run the file as a program. This is only relevant if the file is a program or script. |
Permission to access files in the directory. |
You can set permissions for different types of user. The following table lists the types of user that you can set for which you can set permissions:
|
User Category |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Owner |
The user that created the file or folder. |
|
Group |
The group to which the owner belongs. |
|
Others |
All other users who are not in the group to which the owner belongs. |
To change the permissions on a file or folder perform the following steps:
-
Select the file or folder that you want to change.
-
Choose File -> Properties. A properties dialog is displayed.
-
Click on the Permissions tab. In the Permissions tabbed section, use the drop-down lists and check boxes to change the permissions for the file or folder. The following table describes the dialog elements on the Permissions tabbed section:
Element
Description
File owner
To change the owner of the file or folder, select the owner from the drop-down list.
File group
To change the group to which a file or folder belongs, select the group from the drop-down list.
Owner
Select the permissions that you want to apply to the owner of the file or folder.
Group
Select the permissions that you want to apply to the group to which the owner of the file or folder belongs.
Others
Select the permissions that you want to apply to all other users who are not in the group to which the owner belongs.
Text view
Displays the permissions that you select from the Read, Write, and Execute options, in text format.
Number view
Displays the permissions that you select from the Read, Write, and Execute options, in text format.
Last changed
Displays the date and time that the file or folder was last modified.
-
Click Close to close the properties dialog.
Adding Notes to Files and Folders
You can add notes to files or folders. You can add notes to files or folders in the following ways:
-
From the properties dialog
-
From Notes in the side pane
To Add a Note Using the Properties Dialog
To add a note to a file or folder, perform the following steps:
-
Select the file or folder to which you want to add a note.
-
Choose File -> Properties. A properties dialog is displayed.
-
Click on the Notes tab. In the Notes tabbed section, type the note.
-
Click Close to close the properties dialog. A note emblem is added to the file or folder.
To delete a note, delete the note text from the Notes tabbed section.
To Add a Note Using Notes in the Side Pane
To add a note to a file or folder, perform the following steps:
-
Open the file or folder to which you want to add a note in the view pane.
-
Choose Notes from the drop-down list at the top of the side pane. To display the side pane, choose View -> Side Pane.
-
Type the note in the side pane. A note emblem is added to the file or folder in the view pane, and a note icon is added to the side pane. You can click on this icon to display the note.
To delete a note, delete the note text from Notes in the side pane.
Using Trash
You can move the following items to Trash:
-
Files
-
Folders
-
Desktop objects
If you need to retrieve a file from Trash, you can display Trash and move the file out of Trash. When you empty Trash, you delete the contents of Trash permanently.
To Display Trash
You can display the contents of Trash in the following ways:
-
From a file manager window
Choose Go -> Trash. The contents of Trash are displayed in the window.
-
From the desktop
Double-click on the Trash object on the desktop.
To Empty Trash
You can empty the contents of Trash in the following ways:
-
From a file manager window
Choose File -> Empty Trash.
-
From the desktop
Right-click on the Trash object, then choose Empty Trash.
Modifying the Appearance of Files and Folders
The file manager enables you to modify the appearance of your files and folders in several ways, as described in the following sections.
To Add an Emblem to a File or Folder
To add an emblem to an item perform the following steps:
-
Select the item to which you want to add an emblem.
-
Right-click on the item, then choose Properties. A properties dialog is displayed.
-
Click on the Emblems tab to display the Emblems tabbed section.
-
Select the emblem to add to the item.
-
Click Close to close the properties dialog.
To Add a New Emblem
To add a new emblem, perform the following steps:
-
Choose Edit -> Backgrounds and Emblems.
-
Click on the Emblem button, then click on the Add a New Emblem button. A Create a New Emblem dialog is displayed.
-
Type a name for the emblem in the Keyword text box.
-
Click on the Image button. A dialog is displayed. , click Browse. When you choose an emblem, click OK.
-
Click OK on the Create a New Emblem dialog.
To Change the Icon for a File or Folder
To change the icon that represents an individual file or folder, perform the following steps:
-
Select the file or folder that you want to change.
-
Choose File -> Properties. A properties dialog is displayed.
-
On the Basic tabbed section, click on the Select Custom Icon button. A Select an icon dialog is displayed.
-
Use the Select an icon dialog to choose the icon to represent the file or folder.
-
Click Close to close the properties dialog.
To restore an icon from a custom icon to the default icon specified
in the File Associations preference tool, right-click on the icon
then choose Remove Custom Icon. Alternatively,
click on the Remove Custom Icon button on the Properties dialog.
To change the icon that represents a file type, use the File
Associations preference tool.
To Change the Size of Items in a View
You can change the size of items in a view. You can change the size if the view displays a file or a folder. You can change the size of items in a view in the following ways:
-
To enlarge the size of items in a view, choose View -> Zoom In.
-
To reduce the size of items in a view, choose View -> Zoom Out.
-
To return items in a view to the normal size, choose View -> Normal Size.
You can also use the zoom buttons on the location bar to change the size of items in a view. Table 7–6 describes how to use the zoom buttons.
Table 7–6 Zoom Buttons|
Button |
Button Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Zoom Out button |
Click on this button to reduce the size of items in a view. |
|
|
Normal Size button |
Click on this button to return items in a view to normal size. |
|
|
Zoom In button |
Click on this button to enlarge the size of items in a view. |
The file manager remembers the size of items in a particular folder. The next time that you display the folder, the items are displayed in the size that you selected. In other words, when you change the size of items in a folder, you customize the folder to display the items at that size. To return the size of the items to the default size specified in your preferences, choose View -> Reset View to Defaults.
Using Views to Display Your Files and Folders
The file manager provides several ways to display the contents of your files. The file manager includes viewer components that enable you to display particular types of file in the view pane. For example, you can use a web page viewer to display HTML files in the view pane. You can use a text viewer to view plain text files in the view pane.
You can also use the file manager to open a file in an appropriate application. For more information, see Opening Files.
The file manager includes views that enable you to show the contents of your folders in different ways. For example, you can show the contents of a folder in the following types of view:
-
Icon view
Shows the items in the folder as icons. Figure 7–1 shows a folder in icon view.
-
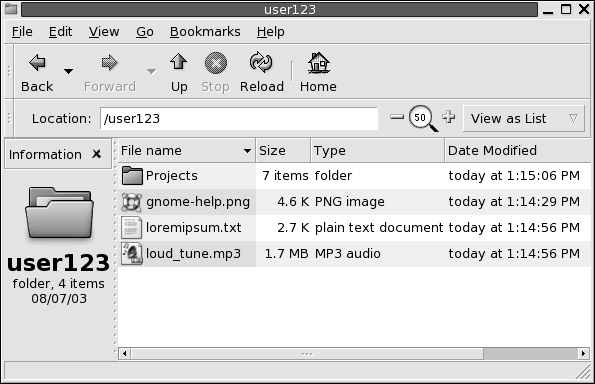
List view
Shows the items in the folder as a list. Figure 7–3 shows a folder in list view.
Figure 7–3 File Manager Window in List View
-
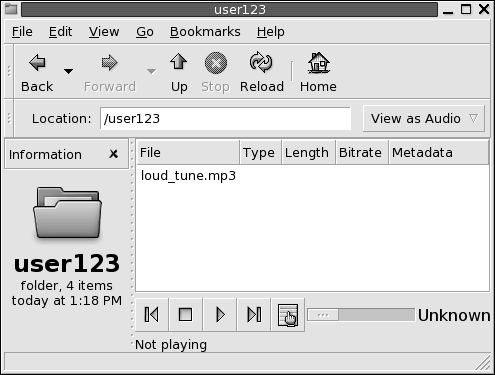
Audio view
Shows the audio items in the folder only, and displays controls that enable you to play the audio files. Figure 7–4 shows a folder in audio view.
Figure 7–4 File Manager Window in Audio View
Use the View menu to choose how to display a file or folder. You can also use the View as drop-down list to choose how to display a file or folder. When you display a folder, you can specify how you want to arrange or sort items in the folder. You can modify the size of the items in the view pane. The following sections describe how to work with icon view, list view, and views of files.
To Choose a View in Which to Display a File or Folder
Choose the type of view in which to display the contents of a file or folder from the View menu.
Alternatively, to choose a view, choose View -> View as. Select the view that you want to use from the Open with Other Viewer dialog, then click on the Choose button.
You can also choose the type of view from the View as drop-down list. The View as drop-down list is located at the right side of the location bar.
You can display different folders in different views. The file manager remembers the view that you choose for a particular folder. The next time that you display the folder, the file manager displays the folder in that view. To return the view for the folder to the default view specified in your preferences, choose View -> Reset View to Defaults.
To Arrange Your Files in Icon View
When you display the contents of a folder in icon view, you can specify how to arrange the items in the folder. To specify how to arrange items in icon view, choose View -> Arrange Items. The Arrange Items submenu contains the following sections:
-
The top section contains an option that enables you to arrange your files manually.
-
The middle section contains options that enable you to sort your files automatically.
-
The bottom section contains options that enable you to modify how your files are arranged.
Choose the appropriate options from the submenu, as described in the following table:
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Manually |
Select this option to arrange the items manually. To arrange the items manually, drag the items to the location you require within the view pane. |
|
By Name |
Select this option to sort the items alphabetically by name. The order of the items is not case sensitive. If the file manager is set to display hidden files, the hidden files are shown last. |
|
By Size |
Select this option to sort the items by size, with the largest item first. When you sort items by size, the folders are sorted by the number of items in the folder. The folders are not sorted by the total size of the items in the folder. |
|
By Type |
Select this option to sort the
items alphabetically by object type. The items are sorted alphabetically by
the description of their MIME type in the |
|
By Modification Date |
Select this option to sort the items by the date the items were last modified. The most recently modified item is first. |
|
By Emblems |
Select this option to sort the items by any emblems that are added to the items. The items are sorted alphabetically by emblem name. Items that do not have emblems are last. |
|
Compact Layout |
Select this option to arrange the items so that the items are closer to each other. |
|
Reversed Order |
Select this option to reverse the order of the option by which you sort the items. For example, if you sort the items by name, select the Reversed Order option to sort the items in reverse alphabetical order. |
The file manager remembers how you arrange the items in a particular folder. The next time that you display the folder, the items are arranged in the way that you selected. In other words, when you specify how to arrange the items in a folder, you customize the folder to display the items in that way. To return the arrangement settings of the folder to the default arrangement settings specified in your preferences, choose View -> Reset View to Defaults.
To Resize an Icon in Icon View
In icon view, you can change the size of the icon that represents an item that is displayed. To change the size of an item in icon view, perform the following steps:
-
Right-click on the item that you want to resize, then choose Stretch Icon. A rectangle appears around the item, with a handle at each corner.
-
Grab one of the handles, then drag the icon to the size that you want.
To return the icon to the original size, right-click on the icon, then choose Restore Icon's Original Size.
You can also resize objects on the desktop.
To Modify the Behavior of a View
You can modify the behavior of a view in the following ways:
-
Specify that the view is the default view for a particular file or folder.
-
Specify that the view is the default view for a file type or all folders.
-
Specify that the view is an item in the View as submenu for a particular file or folder.
-
Specify that the view is an item in the View as submenu for all of a particular file type or for all folders.
-
Specify that the view is not an item in the View as submenu for a particular file or folder.
To modify the behavior of a view perform the following steps:
-
Choose View -> View as. An Open with Other Viewer dialog is displayed.
-
Select the view that you want to modify from the table in the dialog.
-
Click on the Modify button. A Modify dialog is displayed. The following table describes the options on the Modify dialog:
Option
Description
Include in the menu for item-name items
Select this option to include the view in the View as submenu for this type of item.
Use as default for item-name items
Select this option to use the view as the default for this type of item.
Include in the menu for item-name only
Select this option to include the view in the View as submenu for this item only.
Use as default for item-name only
Select this option to use the view as the default for this item only.
Don't include in the menu for item-name items
Select this option to exclude the view from the View as submenu for this type of item.
-
Click OK, then click Cancel to close the Open with Other Viewer dialog.
Note –
You can also modify the actions that are associated with a file
type in the Edit file type dialog in the File
Associations preference tool. To open the Edit
file type dialog, click on the Go There
button.
Assigning Actions to Files
When you open a file, the file manager
performs the default action for that file type. The File
Associations preference tool contains a table of file types,
their associated file extensions, and their default actions. This table specifies
what happens when you double-click on a file in the file manager.
You can also use the file manager to modify the actions that are associated with a particular file or file type.
You can use the File Associations
preference tool to perform the following tasks:
-
Specify the default action for a file type. You can also change the default action for a file type in the file manager.
-
Associate a file type with one or more applications. The default action might specify to open the file in an application that is associated with the file type.
-
Associate a file type with one or more viewers. The default action might specify to open the file in a viewer that is associated with the file type.
-
Associate a file extension with a MIME type. The MIME type specifies the format of the file so that Internet browsers and email applications can read the file.
To Modify Actions
You can modify the actions associated with a file or file type. You can do the following:
-
Specify that the action is the default action for a particular file.
-
Specify that the action is the default action for a particular file type.
-
Specify that the action is an item in the Open With submenu for a particular file.
-
Specify that the action is an item in the Open With submenu for a particular file type.
-
Specify that the action is not an item in the Open With submenu for a particular file type.
To modify the actions associated with a file or file type, perform the following steps:
-
In the view pane, select the file for which you want to modify an action. If you want to modify an action associated with a file type, select a file of that type.
-
Choose File -> Open With. Perform either of the following steps:
-
Choose Other Application. An Open with Other Application dialog is displayed.
-
Choose Other Viewer. An Open with Other Viewer dialog is displayed.
-
-
From the table in the dialog, select the application or viewer for which you want to modify the behavior.
-
Click on the Modify button. A Modify dialog is displayed. The following table describes the options on the Modify dialog:
Option
Description
Include in the menu for filetype items
Select this option to include the application or viewer in the Open With submenu for this file type.
Use as default for filetype items
Select this option to use the application or viewer as the default action for this file type.
Include in the menu for filename only
Select this option to include the application or viewer in the Open With submenu for this file, and not for other files of this type.
Use as default for filename only
Select this option to use the application or viewer as the default action for this file, and not for other files of this type.
Don't include in the menu for filetype items
Select this option to exclude the application or viewer from the Open With submenu for this file type.
-
Click OK, then click Cancel to close the dialog.
Note –
You can also modify the actions that are associated with a file
type in the Edit file type dialog in the File
Associations preference tool. To open the Edit
file type dialog, click on the Go There
button.
Customizing the File Manager
You can customize the file manager to suit your requirements and preferences. This section describes how to customize the file manager.
Setting Your Preferences
Use the Folder Options dialog to set preferences for the file manager. To display the Folder Options dialog, choose Edit -> Preferences.
You can set preferences in the following categories:
-
The default settings for views.
-
The behavior of files and folders, executable text files, and Trash.
-
The information that is displayed in icon captions.
-
Preview options to improve the performance of the file manager.
To Set Views Preferences
You can specify a default view, and select sort options and display options. You can also specify default settings for icon views and list views. To specify your default view settings, choose Edit -> Preferences. Click on the Views tab to display the Views tabbed section.
Table 7–7 lists the views preferences that you can modify.
Table 7–7 Views Preferences|
Dialog Element |
Description |
|---|---|
|
View new folders using |
Select the default view for folders. When you open a folder, the folder is displayed in the view that you select. |
|
Arrange items |
Select the characteristic by which you want to sort the items in folders that are displayed in this view. |
|
Sort folders before files |
Select this option to list folders before files when you sort a folder. |
|
Sort in reverse |
Select this option if you want to reverse the order by which items are sorted in this view. If you select this option, the order of the characteristic you select in the Arrange Items drop-down list is reversed. For example, if you select By Name, the items are sorted in reverse alphabetical order. |
|
Show hidden and backup files |
Select this option to display hidden files and backup files in the view pane. The first character in a hidden filename is a period (.). The last character in a backup filename is a tilde (~). |
|
Default zoom level |
Icon view and list view. Select the default zoom level for folders that are displayed in this view. The zoom level specifies the size of items in a view. |
|
Use compact layout |
Select this option to arrange the items in icon view so that the items in the folder are closer to each other. |
|
Text beside icons |
Select this option to place the icon captions for items beside the icon rather than under the icon. |
|
Use manual layout |
Select this option if you want to arrange the items in icon view manually. |
|
Show only folders |
Select this option to display only folders in the Tree in the side pane. |
To Set Behavior Preferences
To set your preferences for files and folders, choose Edit -> Preferences. Click on the Behavior tab to display the Behavior tabbed section.
Table 7–8 lists the preferences that you can modify for files and folders.
Table 7–8 File and Folder Behavior Preferences
To Set Icon Captions Preferences
An icon caption displays the name of a file or folder in an icon view. The icon caption also includes three additional items of information on the file or folder. The additional information is displayed after the file name. Normally only one item of information is visible, but when you zoom in on an icon, more of the information is displayed. You can modify what additional information is displayed in icon captions.
To set your preferences for icon captions, choose Edit -> Preferences. Click on the Icon Caption tab to display the Icon Caption tabbed section.
Select the items of information that you want to display in the icon caption from the three drop-down lists. Select the first item from the first drop-down list, select the second item from the second drop-down list, and so on. The following table describes the items of information that you can select:
To Set Preview Preferences
The file manager include some file preview features. The preview features can affect the speed with which the file manager responds to your requests. You can modify the behavior of some of these features to improve the speed of the file manager. For each preview preference, you can select one of the options described in the following table:
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Always |
Performs the action for both local files, and files on other file systems. |
|
Local Files Only |
Performs the action for local files only. |
|
Never |
Never performs the action. |
To set your preview preferences, choose Edit -> Preferences. Click on the Preview tab dialog to display the Preview tabbed section.
Table 7–9 lists the preview preferences that you can modify.
Table 7–9 Preview Preferences|
Dialog Element |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Show text in icons |
Select an option to specify when to preview the content of text files in the icon that represents the file. |
|
Show thumbnails |
Select an option to specify when to show thumbnails of image files. The file manager stores the thumbnail files for each folder in a .thumbnails directory that is one level below the folder. |
|
Only for files smaller than |
Specify the maximum file size for files for which the file manager creates a thumbnail. |
|
Preview sound files |
Select an option to specify when to preview sound files. |
|
Count number of items |
Select an option to specify when to show the number of items in folders. If you have set your View to Icon View, you might need to increase your default zoom level in the Views tabbed section to see the number of items in each folder. |
Changing Backgrounds
The file manager includes backgrounds that you can use to change the look-and-feel of the following screen components:
-
Desktop
-
Side pane
-
View pane
-
Panels
To change the background of a screen component perform the following steps:
-
Choose Edit -> Backgrounds and Emblems. The Backgrounds and Emblems dialog is displayed.
-
To display a list of patterns that you can use on the background, click on the Patterns button. To display a list of the colors that you can use on the background, click on the Colors button.
-
To change the background to a pattern, drag the pattern to the screen component. To change the background to a color, drag the color to the screen component.
-
Click Close to close the dialog.
To reset the background of the view pane or side pane to the default background, right-click on the background of the pane, then choose Use Default Background.
When you change the background of the side pane or the view pane of a particular folder, the file manager remembers the background that you chose. The next time that you display the folder, the background that you selected is displayed. In other words, when you change the background of a folder, you customize the folder to display the background.
To Add a Pattern
To add a pattern to the patterns that you can use on your screen components, choose Edit -> Backgrounds and Emblems. Click on the Patterns button, then click on the Add a New Pattern button. A dialog is displayed. Use the dialog to find the new pattern. Click OK to add the new pattern to the Backgrounds and Emblems dialog.
To Add a Color
To add a color to the colors that you can use on your screen components, choose Edit -> Backgrounds and Emblems. Click on the Colors button, then click on the Add a New Color button. A color selector dialog is displayed. Use the color wheel or the sliders to choose the color. Click OK to add the new color to the Backgrounds and Emblems dialog.
To Show and Hide Window Components
You can show and hide file manager window components as follows:
-
To hide the side pane, choose View -> Side Pane. To display the side pane again, choose View -> Side Pane again.
-
To hide the toolbar, choose View -> Toolbar. To display the toolbar again, choose View -> Toolbar again.
-
To hide the location bar, choose View -> Location Bar. To display the location bar again, choose View -> Location Bar again.
-
To hide the statusbar, choose View -> Statusbar. To display the statusbar again, choose View -> Statusbar again.
-
To remove a tab from the side pane, right-click in the side pane. Choose the tab that you want to remove from the popup menu. To add the tab to the side pane again, choose the tab from the popup menu again.
Using Removable Media
The file manager supports all removable media that have the following characteristics:
-
The removable media has an entry in the /etc/fstab file. The /etc/fstab file describes the file systems that the computer uses.
-
The user option is specified in the entry for the removable media in the /etc/fstab file.
To Mount Media
To mount media is to make the file system of the media available for access. When you mount media, the file system of the media is attached as a subdirectory to your file system.
To mount media, insert the media in the appropriate device. An object that represents the media is added to the desktop. The object is added only if your system is configured to mount the device automatically when media is detected.
If your system is not configured to mount the device automatically, you must mount the device manually. Right-click on the desktop, then choose Disks -> device-name. For example, to mount a floppy diskette, choose Disks -> Floppy. An object that represents the media is added to the desktop.
Note –
You cannot change the name of a removable media object.
To Display Media Contents
You can display media contents in any of the following ways:
-
Double-click on the object that represents the media on the desktop.
-
Right-click on the object that represents the media on the desktop, then choose Open.
A file manager window displays the contents of the media. To reload the display, click on the Reload button.
To Display Media Properties
To display the properties of removable media, right-click on the object that represents the media on the desktop, then choose Properties. A dialog displays the properties of the media.
To close the properties dialog, click Close.
To Format a Floppy Diskette
To format media is to prepare the media for use with a particular file system. You can use the file manager to format floppy diskettes.
When you format media, you overwrite any existing information on the media.
To format a floppy diskette, perform the following steps:
-
Insert the diskette in the diskette drive. Mount the diskette. For information on how to mount media, see To Mount Media.
-
Right-click on the object that represents the diskette on the desktop, then choose Format. A Floppy formatter dialog is displayed.
-
Select your format options in the Floppy formatter dialog. The following table describes the elements on the dialog:
-
Click Format to format the diskette.
To Eject Media
To eject media, right-click on the media object on the desktop, then choose Eject. If the drive for the media is a motorized drive, the media is ejected from the drive. If the drive for the media is not motorized, wait until the desktop object for the media disappears, then eject the media manually.
You cannot eject media from a motorized drive when the media is mounted. To eject media, first unmount the media. To remove a floppy diskette from the drive, perform the following steps:
-
Close all file manager windows,
Terminalwindows, and any other windows that access the diskette. -
Right-click on the object that represents the diskette on the desktop, then choose Eject. The desktop object for the diskette disappears.
-
Eject the diskette from the drive.
 Caution –
Caution – If you eject the diskette from the drive before you unmount the diskette, you might lose the data on the diskette.
Writing CDs
The file manager provides a special location where you can copy files and folders that you want to write to a CD. You can write the contents of the location to a CD easily.
To write a CD, perform the following steps:
-
Choose Go -> CD Creator. The file manager opens a special location, burn:///, from which you can write CDs.
-
Copy the files and folders that you want to write to CD into the burn:/// location.
-
Insert a writable CD into the CD writer device on your system.
-
Choose File -> Write to CD. A Write files to a CD recorder dialog is displayed.
-
Use the Write files to a CD recorder dialog to specify how you want to write the CD, as follows:
Dialog Element
Description
Target to write to
Select the device to which you want to write the CD from the drop-down list. To create an CD image file for the files and folders, select the File image option.
Write speed
Select the speed at which you want to write the CD from the drop-down list.
CD name
Type a name for the CD in the text box.
Erase CD
Select this option to erase the current contents of the CD.
Eject CD when done
Select this option to eject the CD from the drive when the CD is written.
Reuse these files for another CD
Select this option if you do not want to write the files and folders to another CD. If you select this option, the files and folders are not removed from the burn:/// location after the CD is written.
-
Click on the Write files to CD button.
If you selected the File image option from the Target to write to drop-down list, a Choose a filename for the cdrom image dialog is displayed. Use the dialog to specify the location where you want to save the CD image file. By default, CD image files have a .iso file extension.
A Writing CD dialog is displayed. When the CD is written or when the CD image file is created, a message to indicate that the process is complete is displayed in the dialog.
If you created a CD image file, you can write this file to a CD. To write a CD image file to CD, right-click on the CD image file, then choose Write to CD from the popup menu.
If you did not select the Reuse these files for another CD option, the files and folders are removed from the burn:/// location.
Running Scripts From the File Manager
The file manager includes a special folder where you can store your scripts. When you add an executable file to this folder, the file is added to the Scripts submenu. To run a script choose File -> Scripts, then choose the script that you want to run from the submenu.
To run a script on a particular file, select the file in the view pane. Choose File -> Scripts, then choose the script that you want to run on the file from the submenu. You can also select multiple files to run your scripts on.
To view the contents of your scripts folder, choose File -> Scripts -> Open Scripts Folder.
Mounting and Unmounting a File System
To mount a file system is to make the file system available for access. When you mount a file system, the file system is attached as a subdirectory to your file system.
You can mount a directory on a remote system, or a file system on a device attached to a system that you can access. You must have root access permissions to mount or unmount a file system.
When you do not need to access the file system, you can unmount the file system.
To Mount a File System
To mount a file system, perform the following steps:
-
Right click on a folder in the file manager and choose Sharing -> Mount. A Mounting/Unmounting dialog is displayed.
Note –If the Unmount menu item is in the popup menu, the directory that you selected already has a file system mounted.
-
Enter the information for the file system that you want to mount in the Mounting/Unmounting dialog. The following table describes the elements on the dialog:
Dialog Element
Description
mount local Directory
Displays the name of the currently selected folder.
as directory
Enter the path of the file system that you want to mount on the folder.
on remote machine
If the on remote machine is selected, this means that the file system to mount is on another system. You must enter the IP address or DNS name of the system.
-
To select advanced options for the file system that you want to mount, click on the Advanced button. A Mount Options dialog is displayed. The following table describes the elements on the dialog:
Dialog Element
Description
Read Write
Select this option to assign read and write access permissions to the mounted file system.
Read Only
Select this option to assign read only access permissions to the mounted file system.
Specify mount type
Select this option to specify the type of file system to mount. Enter the file system type in the field.
Specify additional options: (comma separated)
Select this option to specify further options for the file system that you want to mount. Enter the options in the field. Use a comma to separate each option.
-
Click on the Mount button. A dialog displays a success or failure message.
To Unmount a File System
To unmount a file system, perform the following steps:
-
Right click on a folder in the file manager and choose Sharing -> Unmount. A Mounting/Unmounting dialog is displayed with details of the mounted file.
Note –If the Mount menu item is in the popup menu, the directory that you selected does not have a file system mounted.
-
Click on the Unmount button. A dialog displays a success or failure message.
Using NFS Shares
You can use Network File System (NFS) shares to make folders available to other systems. You must have root access permissions to add or remove NFS shares.
To Add an NFS Share
To add an NFS share to a folder, perform the following steps:
-
Right click on a folder in the file manager and choose Sharing -> Add/Remove NFS Share. A Share dialog is displayed.
-
Enter the information for the folder that you want to share in the Share dialog. The following table describes the elements on the dialog:
Dialog Element
Description
Share to client(s)
Enter the name of the system or group of systems with which you want to share the folder.
Read Only
Select this option to assign read only access permissions to the folder.
Read Write
Select this option to assign read and write access permissions to the folder.
-
To configure advanced options for the share, click on Advanced. The Advanced Sharing Properties dialog is displayed. The following table describes the elements on the dialog:
Dialog Element
Description
Allow connections from port 1024 and higher
NFS shares that start on port numbers less than 1024 must start with root permissions. Select this option to enable users, other than root, to start NFS shares.
Allow asynchronous server reply
Select this option to enable the NFS server to reply to a request before any changes made by that request are saved.
This option can cause data to be lost or corrupted if you start the NFS server after a system crash.
Allow synchronous write
Select this option if you do not want any delay when data is saved. This option has no effect if the Allow asynchronous server reply option is selected.
If an NFS server receives small unrelated requests, deselect this option to increase performance.
Allow transparent recursive mapping
If a server exports two file systems, one of which is mounted on the other, then the client must mount both file systems.
If the client mounts only the parent file system, the other file system is not displayed and contains an empty directory.
Select this option if you want to display the file system. This allows an authorized client to transparently move from the parent file system to another file system.
Enable subtree consistency checking
Select this option to enable subtree checking. If a subdirectory of a file system is exported to another system, but the entire file system is not exported, the server checks if the requested file is contained in the exported subdirectory. This check is called subtree checking.
If you want to export an entire file system, deselect this option to increase the transfer rate.
Treat client root as server root
Do not select this option unless it is absolutely necessary.
By default, the user ID and group ID of the root user are both 0. Root permissions on the client are not mapped to root permissions on the NFS server.
If this option is selected, root permissions are not mapped to an anonymous user, and root on a client has root permissions to export your directories.
Note –If you select this option, you decrease the security of your system.
Treat all clients' users as anonymous users
Select this option to map all user IDs and group IDs to an anonymous user.
Specify local ID for anonymous users:
If the Treat all clients' users as anonymous users option is selected, this option enables you specify a user ID for an anonymous user.
Specify local group ID for anonymous users:
If the Treat all clients' users as anonymous users option is selected, this option enables you specify a group ID for an anonymous user.
-
Click on the Add button. A dialog displays a success or failure message.
To Remove an NFS Share
To remove an NFS share from a folder, perform the following steps:
-
Right click on the folder in the file manager and choose Sharing -> Add/Remove NFS Share. A Share dialog is displayed.
-
Click on the Remove button. A dialog displays a success or failure message.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
