| C H A P T E R 7 |
|
Diagnostics Overview |
This chapter describes some diagnostic tools. This chapter contains the following topics:
The Sun Ultra 45 and Ultra 25 Workstations Service and Diagnostics Manual uses displayed messages, system sounds, flowcharts, and firmware and software diagnostic tools to help you locate and identify workstation malfunctions.
|
For information on system power and Ethernet LEDs, see LED Diagnostics. |
|||
|
Single beep indicates keyboard connection when the system boots. Continuous beeping indicates a stuck key on the keyboard. |
If continuous beeping, disconnect and reconnect keyboard. Inspect for stuck keys, or replace. |
||
|
Runtime diagnostics program that monitors system errors and reports any hardware needing replacement. |
Use Predictive Self-Healing first to diagnose the workstation. |
||
|
Commands iostat, prtdiag, prtconf, netstat, ping, ps, and prstat are run with superuser privileges. See Traditional Solaris Troubleshooting Commands. |
|||
|
Contains properties and flags to configure system and diagnostic tests. |
The setenv command typed at the ok prompt or the eeprom command in a terminal window can configure the OpenBoot PROM for diagnostics and automatic execution of scripts. See NVRAM. |
||
|
Checks low-level interaction between CPU, caches, memory, JBus, and PCI bridge. Output displayed through serial port. See Power-On Self-Test. |
|||
|
Component tests are selected from menu. If component is PCI card with IEEE 1275-compliant Fcode, internal self-test is executed. See OpenBoot Diagnostics. |
|||
|
Invoked from the Solaris Operating System. Command-line or GUI user interface. SunVTS must be installed on the system under test. See SunVTS. |
The Predictive Self-Healing (predictive self-healing tools) is often your first and best tool for diagnostics. Use TABLE 7-2 to determine which diagnostic program to use to troubleshoot a component.
|
Max diag level performs tests including block memory and quick memory tests |
||||
|
Yes. See OpenBoot Diagnostics. |
||||
|
Some tests available. See OpenBoot Diagnostics. |
||||
One approach to diagnostics is shown in FIGURE 7-1 and FIGURE 7-2.
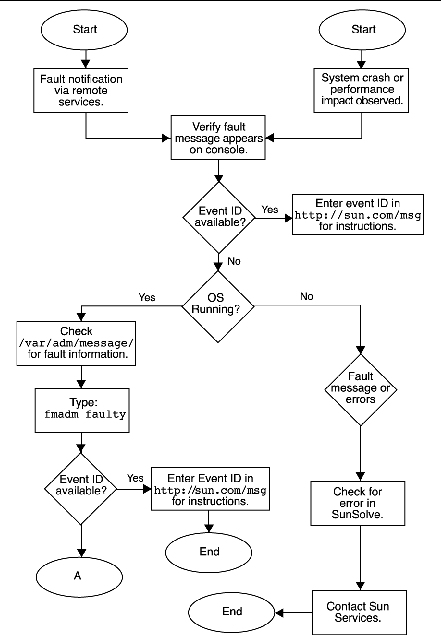
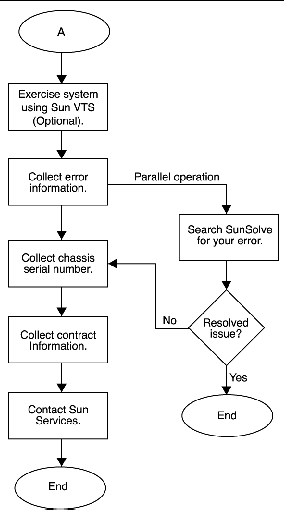
When you power on the Sun Ultra 45 or Ultra 25 workstation, a series of processes brings the workstation to a user-ready state.
The sequence of power-on events is shown below:
1. User presses the Power button.
2. OpenBoot PROM initiates system power-on reset (SPOR).
3. OpenBoot PROM initiates power-on self-test (POST) (if enabled).
4. OpenBoot PROM loads device drivers.
5. OpenBoot PROM loads workstation configuration from NVRAM.
6. OpenBoot PROM probes PCI bus.
7. OpenBoot PROM loads OpenBoot Diagnostics.
8. OpenBoot PROM loads and executes boot block.
9. Boot block loads and executes bootstrap program.
|
Note - If the Solaris kernel does not load, you can run diagnostics from the ok prompt |
10. Bootstrap loads Solaris kernel.
11. Bus connections and hardware components are probed.
12. init program is loaded and executed.
13. init program reads /etc/inittab.
14. init program starts rc scripts, that read, check, and mount file systems.
15. /etc/vfstab file system is checked and mounted.
16. Additional rc script files are executed.
Copyright © 2006, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.