Using Application Variables
Application variables allow you to define a list of variable names and values along with their type. The application variable name can then be used as a token for a WSDL extensibility element attribute for the REST BC. For example, you could define a string variable named ServerName with a value of MyHost.com. To reference this in the WSDL document, you would enter ${ServerName}. When you deploy an application that uses application variables, any variable that is referenced in the application's WSDL document is loaded automatically.
Note –
If you start an application and a value is not defined for an application variable, an exception is thrown.
You can define the following four variable types:
-
String – A string value, such as a path or directory.
-
Number – A numeric value.
-
Boolean – A Boolean true or false. When you define a Boolean variable, a check box appears in the value field. Select the check box if the variable value should be true; otherwise, deselect the check box.
-
Password – A login password. The password is masked and appears as asterisks.
Variables allow greater flexibility in WSDL documents. For example, you can use the same WSDL document for multiple runtime environments by using application variables to specify system-specific information. The variable values can be changed from the binding component runtime properties for each specific environment.
To change a property when the application is running, change your Application Variable property value, then right-click your application in the Services window under Servers -> GlassFish -> JBI -> Service Assemblies, and click Stop in the popup menu. When you restart your project, your new settings will take effect.
 To Create an Application Variable
To Create an Application Variable
-
On the NetBeans IDE Services window, expand Servers > GlassFish v2.1 > JBI > Binding Components.
-
Right-click sun-rest-binding, and then select Properties.
The Properties window appears.
-
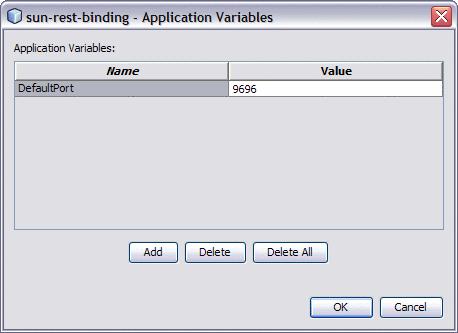
Click the ellipsis next to Application Variables.
The Application Variables Editor appears.
-
Click Add.
A list of possible variable types appears.
-
Select String, Number, Boolean, or Password, and then click OK.
A new row appears in the application list.
-
In the new row, enter a variable name and then do one of the following:
-
For a Boolean variable, select the check box if the variable value should be true; otherwise leave it deselected.
-
For all other variables types, enter the variable value.
Note –If you created a password variable, the value you enter appears as asterisks.
The variable can now be reference from WSDL documents using a dollar sign and curly brackets to indicate the variable; for example, ${MyVariable}.
-
 To Use an Application Variable for Password
Protection
To Use an Application Variable for Password
Protection
To protect passwords that would otherwise appear as clear text in your WSDL document, you can enter a Password application variable as a token. In the following example, a password application variable is created that uses the name SECRET and the password PROTECT.
-
On the NetBeans IDE Services window, expand Servers > GlassFish v2.1 > JBI > Binding Components.
-
Right-click sun-rest-binding, and then select Properties.
The Properties window appears.
-
Click the ellipsis next to Application Variables.
The Application Variables Editor appears.
-
Click Add, select Password, and then click OK.
A new row appears in the variable list.
-
Enter SECRET as the name, and enter PROTECT as the value.
Because this is a password type, the characters appear as asterisks.
-
Use the application variable name ${SECRET} as the WSDL password attribute, using the dollar sign and curly braces as shown.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
