The Architecture of the SPOT Software
The major tools that spot uses to generate the results are shown in Figure 3–1.
Figure 3–1 SPOT Software Architecture
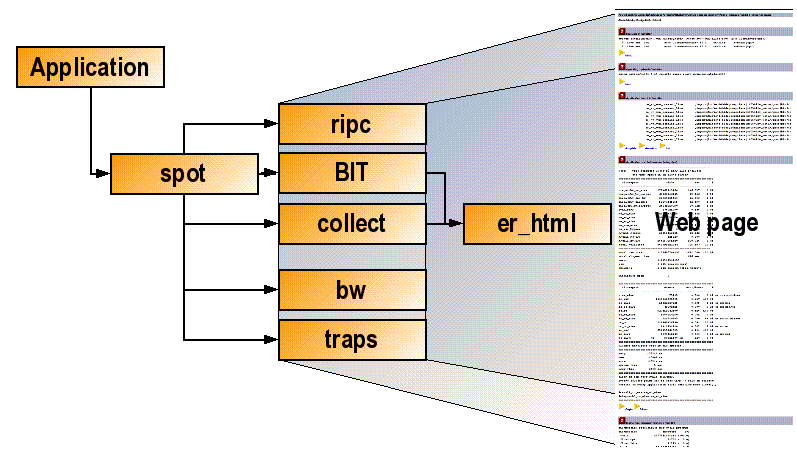
The tools have the following purposes:
-
The ripc tool collects performance counter information over the run of a program and outputs a text summary of the stall time that each processor event contributed to the runtime of the program.
-
The Binary Improvement Tool (BIT) instruments any application compiled with the compiler flag -xbinopt=prepare and generates information on the number of times each routine is called, the number of times each individual instruction is executed, and the instruction frequency for each assembly language instruction.
-
The collect tool is part of Sun Studio 12 software, and it is used by the SPOT software to profile the application over time and, when extended information is requested, profile where the processor events occur.
-
The bw tool collects system-wide bandwidth utilization data, if it is possible for the target platform, and under the current privileges.
-
The tool traps is a wrapper for trapstat (which is shipped as part of Solaris) which will also only be able to collect data with sufficient privileges.
-
The tool er_html is a wrapper for the Sun Studio 12 tool er_print. er_html takes Sun Studio Performance Analyzer experiments and generates a set of hyperlinked web pages from them.
-
The tool spot_diff produces a report comparing multiple SPOT reports.
As mentioned previously, each of the tools invoked by SPOT can be invoked stand-alone. With the exception of er_html amd spot_diff, the tools will not produce data in HTML format when invoked stand-alone.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
