System-Wide Bandwidth
It is not possible to measure the bandwidth consumption of a single process, since one process can read memory that is attached to processors running other processes. Hence the bandwidth reported here is system wide. A consequence of this is that it is not possible to attribute the memory activity to a single process if there are multiple processes running on the system. Bandwidth data will be collected by SPOT if the -X flag is specified, and if SPOT has root privileges.
The tool bw can be also be invoked stand-alone, outside of spot. Type bw -h to get a list of the options, and consult the bw man page for more details.
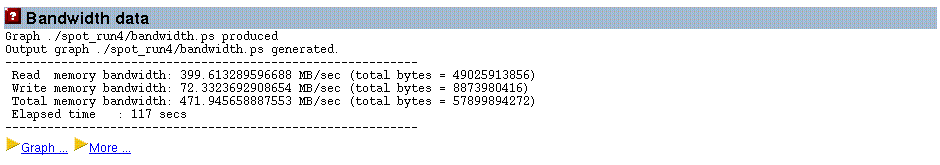
The average bandwidth consumption over the entire run of the test program is reported as shown in the figure below:
Figure 3–6 Average System-Wide Bandwidth Consumption
If the gnuplot software is installed, then this data will also plotted as a graph, as shown in Figure 3–7.
Figure 3–7 Graphic Showing the Read Memory Bandwidth Consumed Over an Application Run
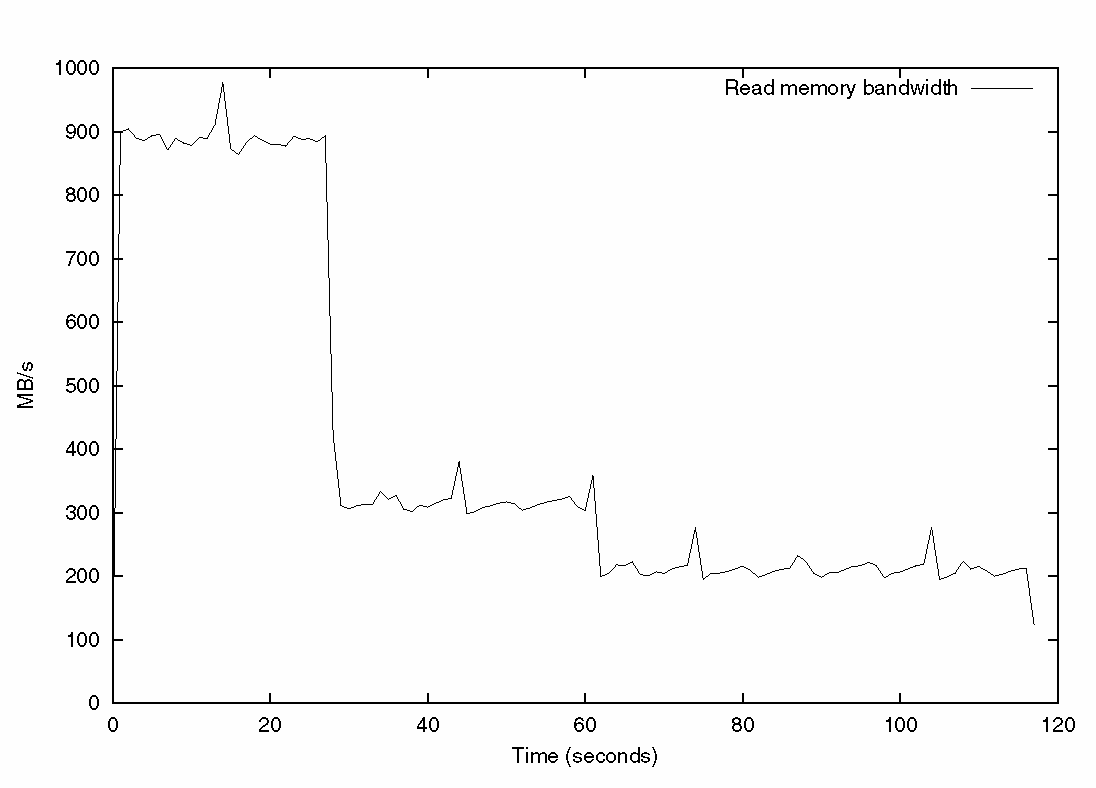
Figure 3–7 shows the read memory bandwidth consumed over the entire run of the application. The routine fp_routine consumes the most bandwidth because it is three streams of data being used by the processor. The other two routines use less bandwidth because they are pointer chasing, and, therefore, more tests of memory latency.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
